Scalars and Vectors
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Two types of quantities:
Scalars and vectors
Quantities that have magnitude but not direction
Scalars
The extent, size, or amount of something
Magnitude
Mass is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Why is mass a scalar quantity?
It has magnitude but no direction
Quantities that have both magnitude and direction
Vectors
Weight is a scalar/vector quantity
Vector
Why is weight a vector quantity?
It is a force and has both magnitude and direction
A measure of how far an object has travelled, regardless of direction
Distance
The total length of the path taken
Distance
Does distance have magnitude?
Yes
Does distance have direction?
No
Distance is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
A measure of how far it is between two points in space, including the direction
Displacement
The length and direction of a straight line drawn from the starting point to the finishing point
Displacement
Does displacement have magnitude?
Yes
Does displacement have direction?
Yes
Displacement is a scalar/vector quantity
Vector
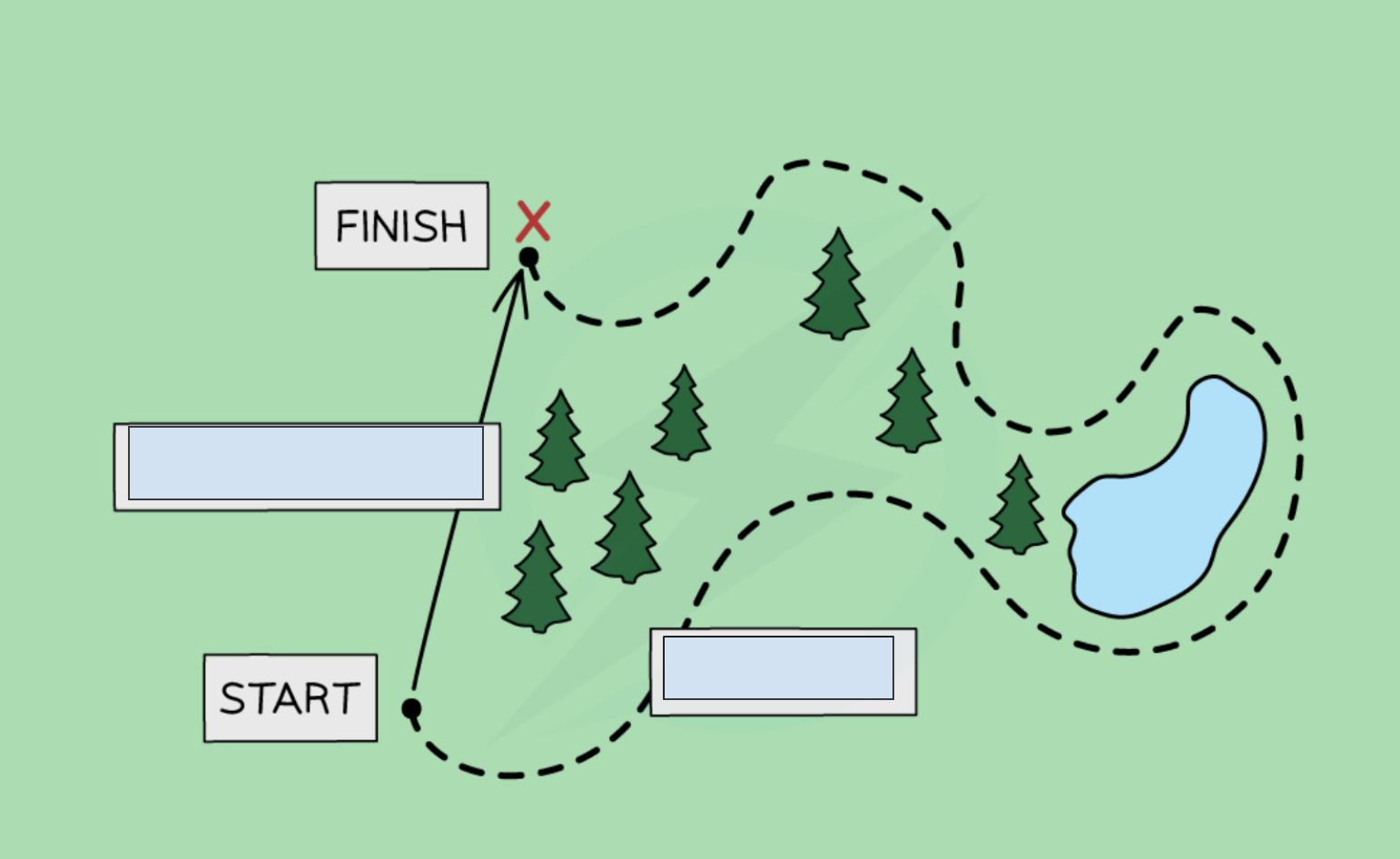
Which one is displacement and which is distance?
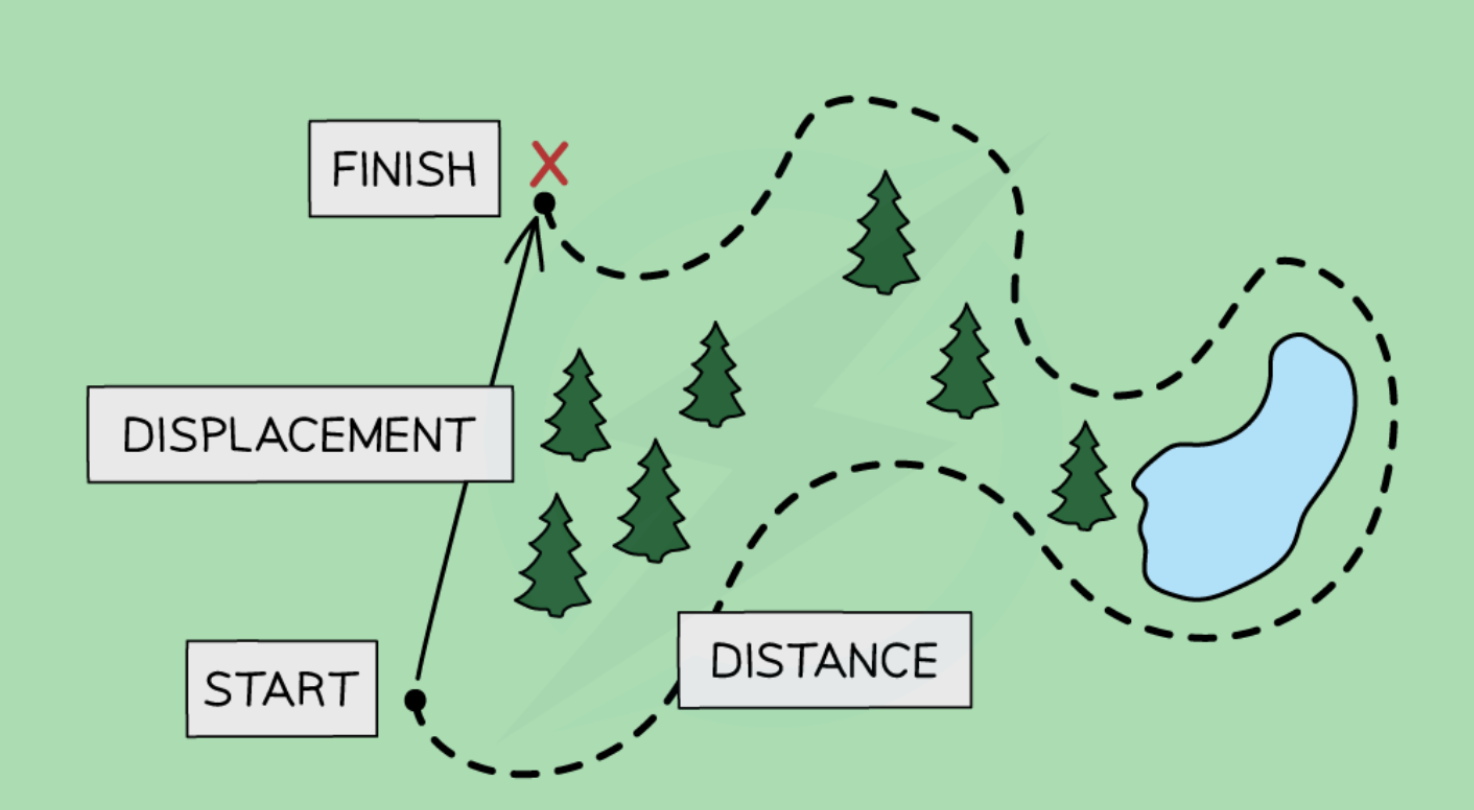
When a student travels to school, will there probably be a difference in the distance they travel and their displacement?
Yes
When a student travels to school, the overall distance they travel includes the:
Total lengths of all the roads, including any twists and turns
When a student travels to school, the overall displacement of the student would be a:
Straight line between their home and school
When a student travels to school, does the overall displacement take into account obstacles like buildings, lakes or motorways?
No
A measure of the distance travelled by an object per unit time, regardless of the direction
Speed
Speed of an object describes how:
Fast it is moving
Does speed of an object describe the direction it is traveling in?
No
Does speed have magnitude?
Yes
Does speed have direction?
No
Speed is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
A measure of the displacement of an object per unit time, including the direction
Velocity
The velocity of an object describes how:
Fast it is moving and which direction it is traveling in
Can an object have a constant speed but changing velocity?
Yes
When can an object have a constant speed but changing velocity?
If it is changing direction
Does velocity have a magnitude?
Yes
Does velocity have a direction?
Yes
Velocity is a vector/scalar quantity
Vector
Distance is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Speed is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Mass is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Time is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Energy is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Volume is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Density is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Pressure is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Electric charge is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Temperature is a scalar/vector quantity
Scalar
Displacement is a scalar/vector quantity
Vector
Velocity is a scalar/vector quantity
Vector
Acceleration is a scalar/vector quantity
Vector
Force is a scalar/vector quantity
Vector
Momentum is a scalar/vector quantity
Vector
Vectors are represented by an:
Arrow
The arrowhead indicates the _______ of the vector
Direction
The length of the arrow represents the ______ of the vector
Magnitude
Vectors can be combined by:
Adding or subtracting them from each other
Two methods to combine vectors:
Triangle and parallelogram method
How to combine vectors with the triangle method?
Link the vectors head-to-tail
When using the triangle method, the resultant vector is formed by:
Connecting the tail of the first vector to the head of the second vector
How to subtract vectors using the triangle method?
Change the direction of the vector from positive to negative and add them in the same way as when adding vectors
The triangle method links vectors ___ to ___ to find the resultant vector
Tip, tail
How to combine vectors using the parallelogram method?
Link the vectors tail-to-tail and complete the resulting parallelogram
When using the parallelogram method, the resultant vector is the:
Diagonal of the parallelogram
The parallelogram method links vectors ___ to ___ to find the resultant vector
Tail, tail
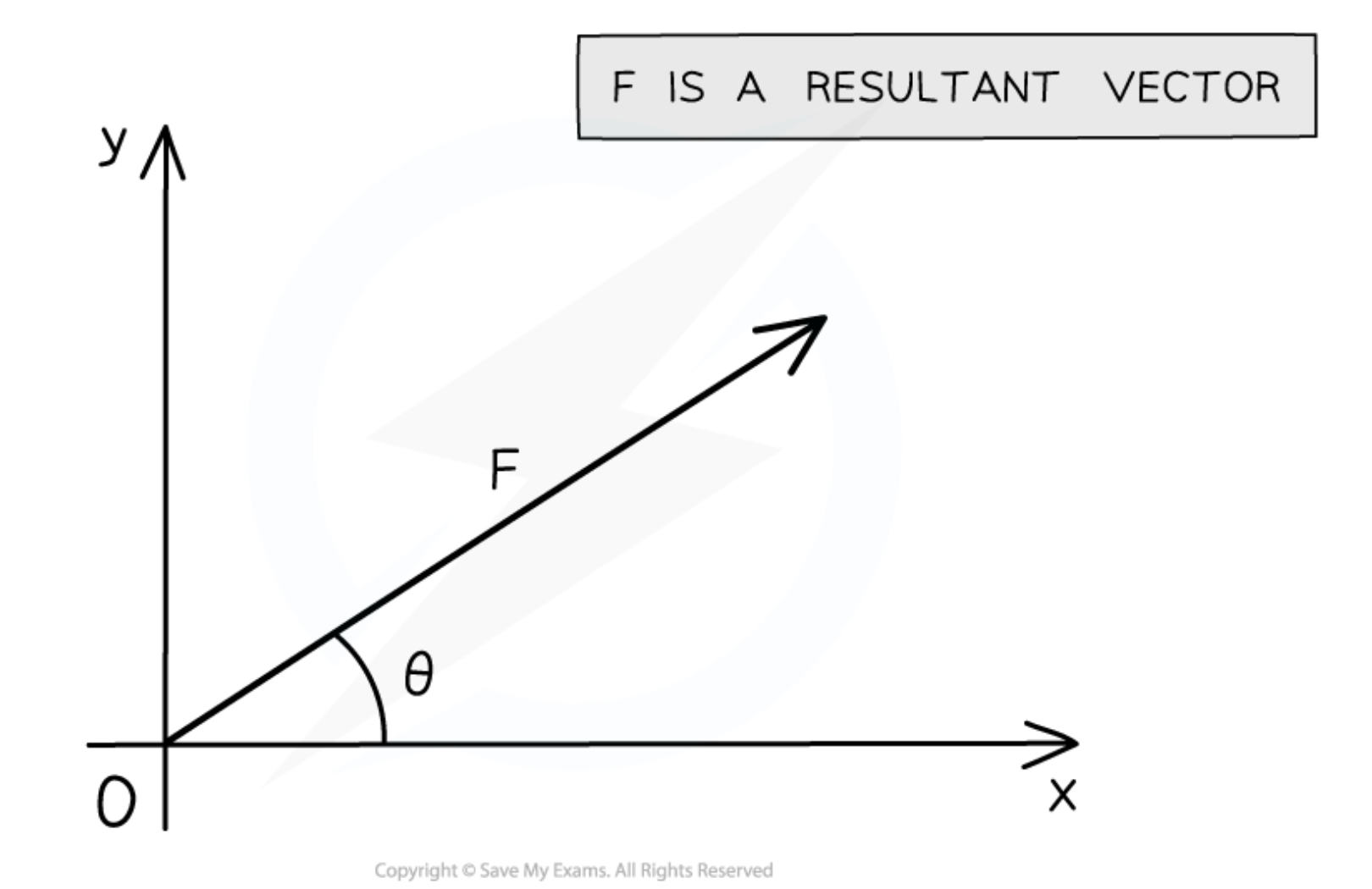
When two or more vectors are added together (or one is subtracted from the other) using the parallelogram method, a single vector is formed, known as the:
Resultant vector
When using the parallelogram method, the magnitude of the resultant vector can be found using:
Pythagoras' theorem or trigonometry
Forces which act in the same plane
Coplanar forces
Coplanar forces can be represented by:
Vector triangles
In equilibrium, vector triangles are:
Closed
When vectors are joined together, they form a:
Closed path
If three forces acting on an object are in equilibrium; they form a:
Closed triangle
Two vectors can be represented by a:
Single resultant vector
Does the single resultant vector that represents two vectors have the same effect as the original vectors?
Yes
How can a single resultant vector be resolved?
By being represented by 2 vectors
When a single resultant vector is represented by 2 vectors, the vectors in combination have the same ______ as the original one
Effect
When a single resultant vector is broken down into its parts, those parts are called:
Components
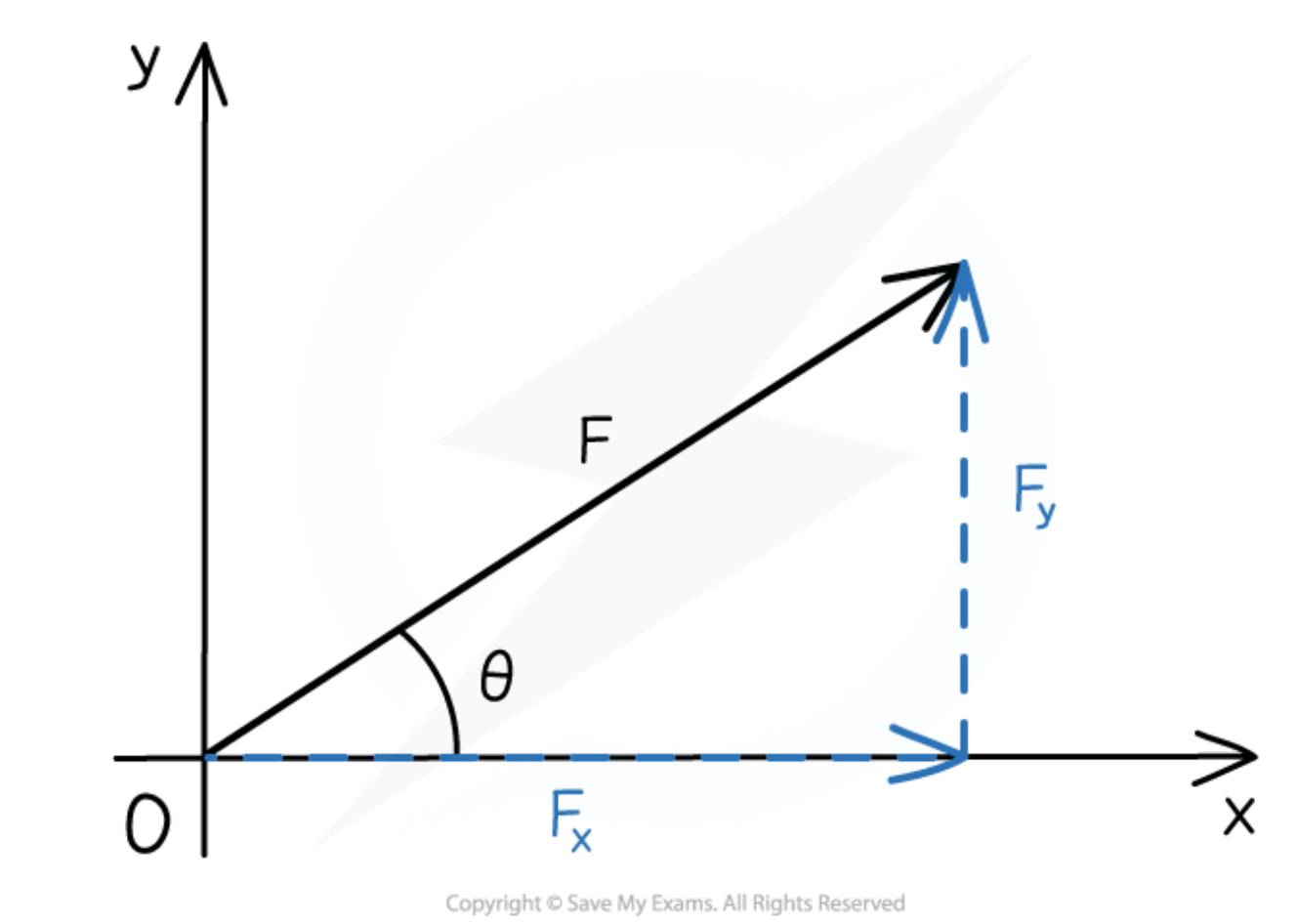
Is it possible to resolve this vector into its horizontal and vertical components?
Yes
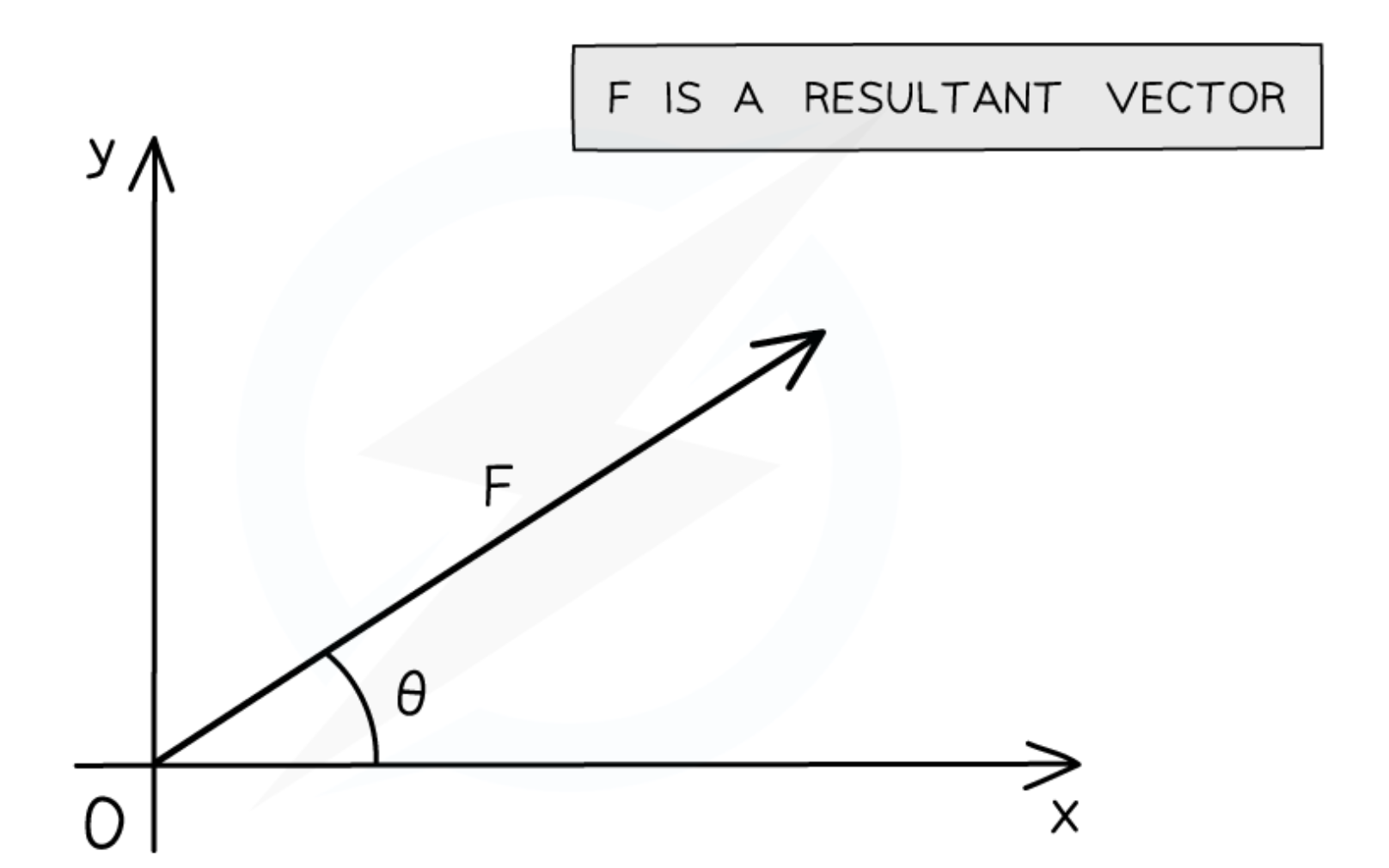
How to resolve this vector into its horizontal and vertical components?
By using trigonometry
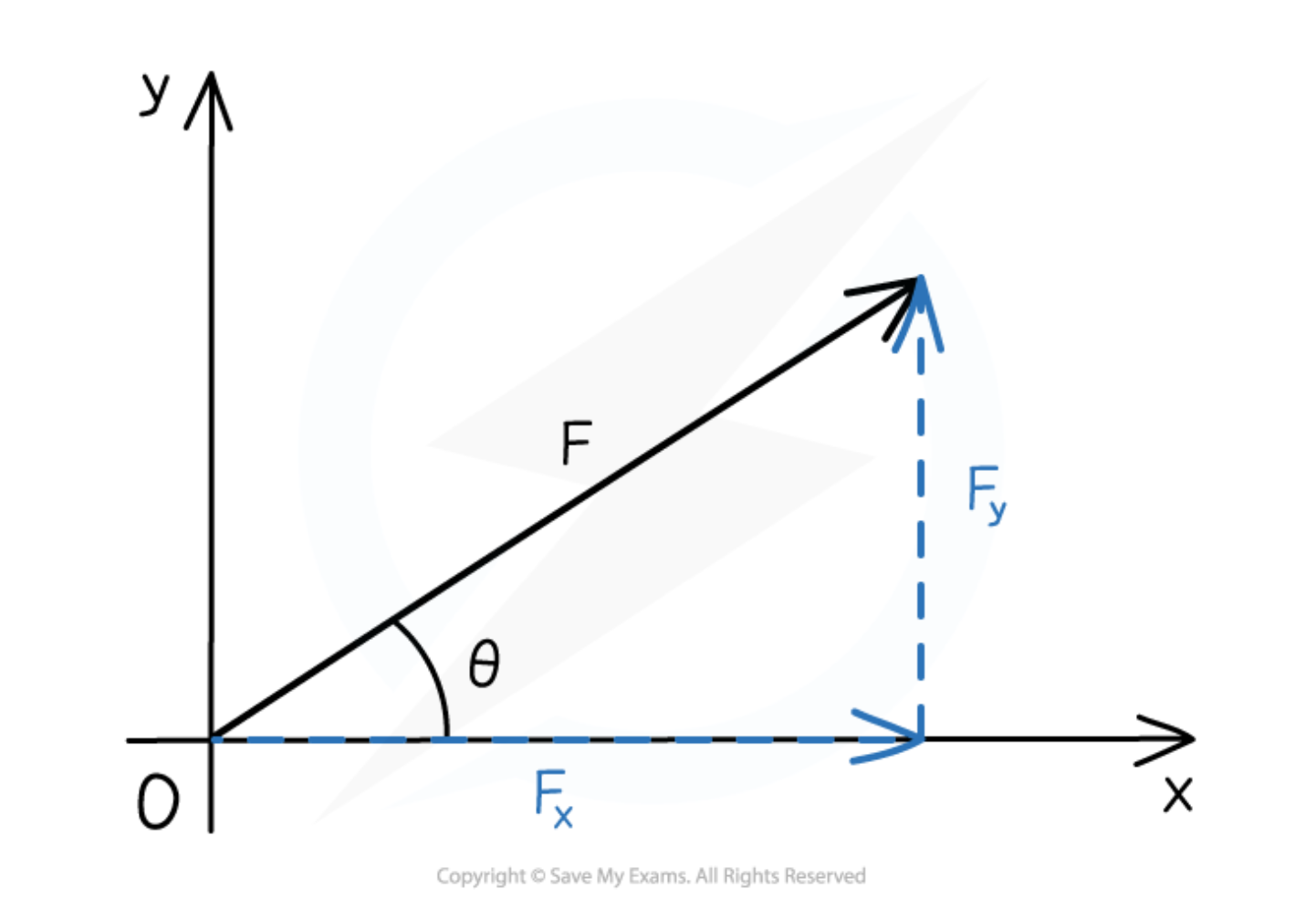
How to calculate Fx?
Fx = Fcosθ
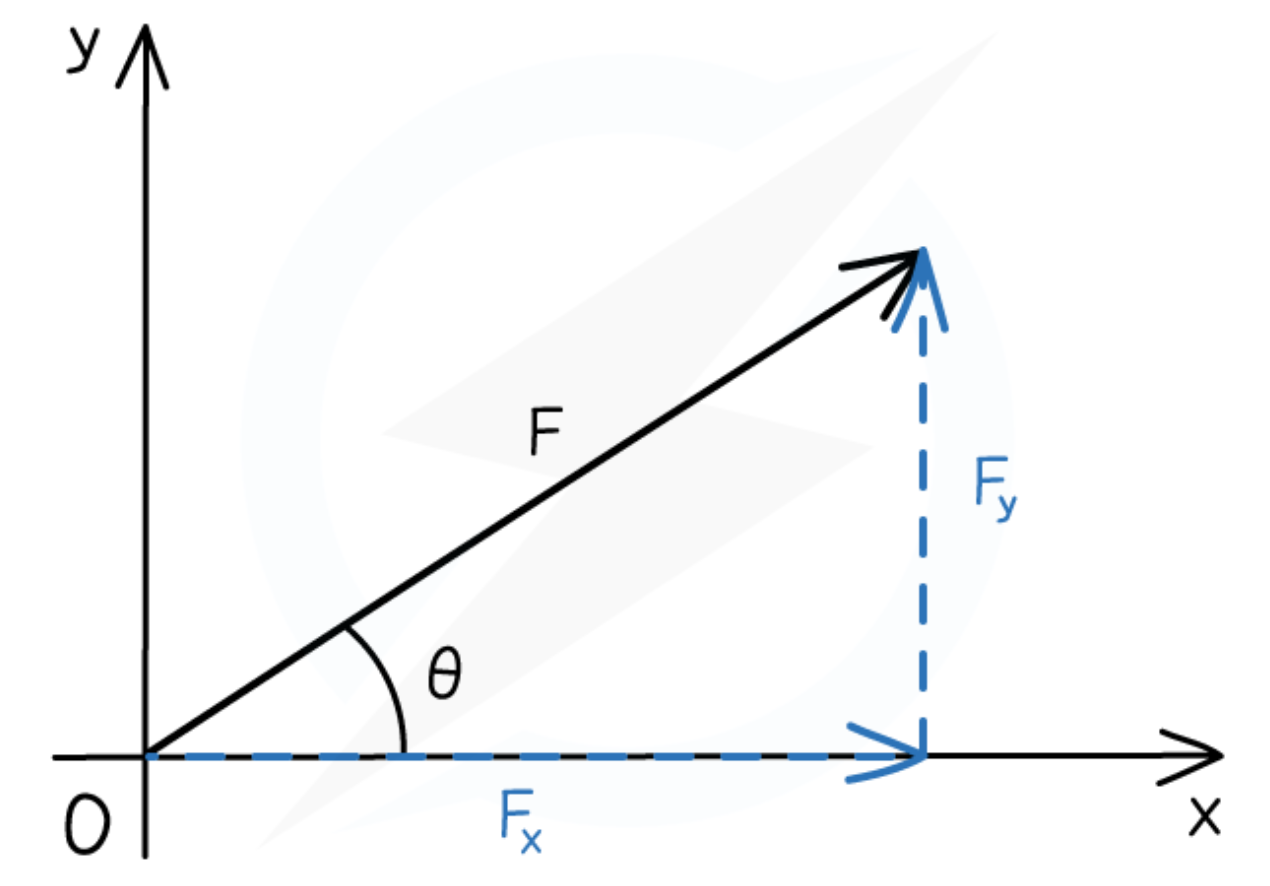
How to calculate Fy?
Fy = Fsinθ
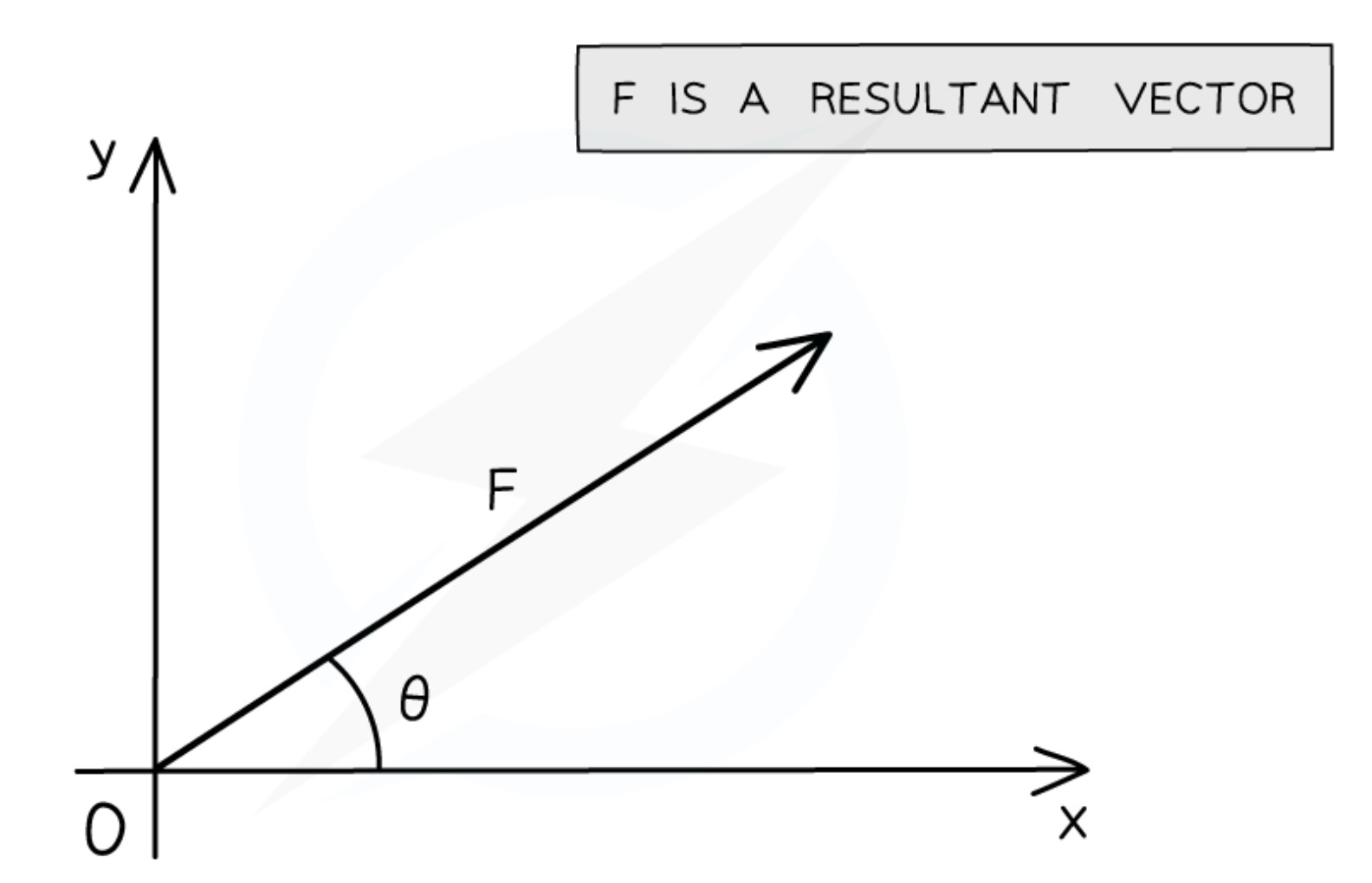
Draw the horizontal and vertical components of F: