Psych Unit 2
1/190
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
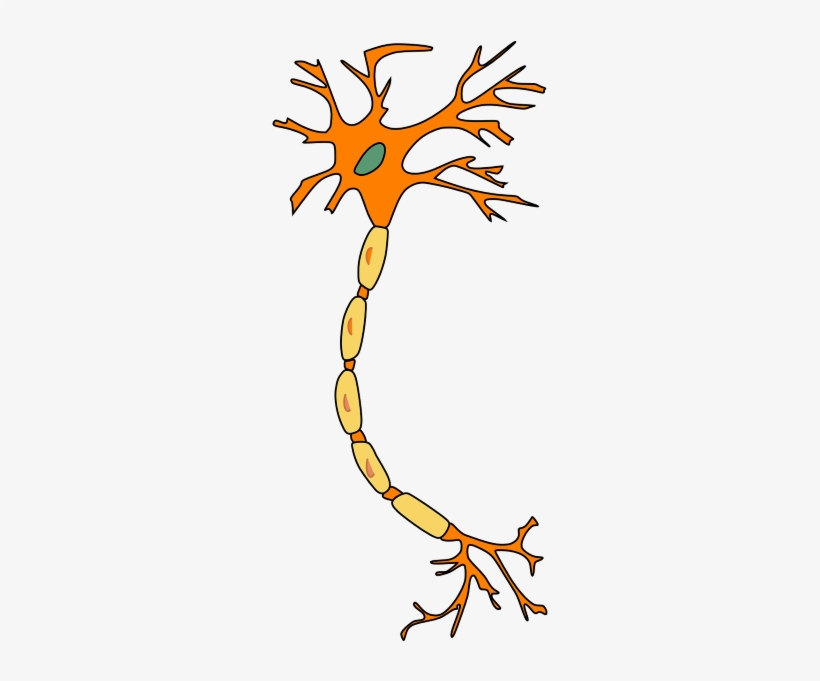
* skeletal system
* provides nourishment
* creates myelin for the myelin sheath
* repairs damage
* removes waste
* helps to create the blood-brain barrier
* having too much is associated with Schizophrenia
* having too little is associated with Parkinson’s
* a malfunction is associated with depression or anxiety
* SSRI is an agonist for it and is a common antidepressant
* tells your neurons when to stop and not send info
* when there is too little it is associated with epilepsy
* Anxiety meds are usually antagonists of this as depression meds are agonists of this
* important for memory and learning
* a dysfunction with tis is associated with memory disorders
law of forward condition
information will start at the dendrites and end at the terminal buttons but never go the other way around
all or none principle
if a soma decides to send the info along it will fully go to the terminal buttons, if it decides to not send info along, it will stop at the soma.
excitatory
if this wins, the info will be sent along
inhibitory
if this wins, the info will not be sent along
clean-up
happens after the neuron has released the neurotransmitters into the synapse
enzymatic degradation
where some of the glial cells that are in our brain are going to clean up the neurotransmitters and break them down
reuptake
terminal buttons take back neurotransmitters that they released
synaptic pruning
eliminates synapses that are no longer useful
center of the nervous system
the most important component of the neuro system, info comes to it and directions come from it
intelligence correlation
the more surface area/bumps and ridges a brain has, the smarter it is
contralateral control
your brain controls the opposite sides of your body,
association area
there are different parts of your brain that are important/related to different tasks
hindbrain
brainstem, main job is to keep you alive, oldest part of the brain
medulla
in the hindbrain, largely in charge of heart rate, circulation, respiration, and reflexes
pons
sit on top of the medulla, which helps with sleep, mood, arousal, and focus but also important for creating and reading facial expressions
cerebellum
the densest level of neurons, critical for balance and fine motor skills. one of the first places you can see the effects of alcohol.
midbrain
the smallest most specialized part of the brain
orientation is the main focus
tectum
midbrain, responsible for receiving sense info and doing base-level processing
tegmentum
responsible for movement, arousal, or focus
forebrain
newest part of the brain developmentally and evolutionarily
cerebral cortex
forebrain, wrinkly parts of the brain
corpus callosum
a band of fibers in the middle that allows the left side of your brain to talk to the right. a lobotomy separates this
Frontal lobe
higher order processing
prefrontal cortex
motor cortex
prefrontal cortex
executive control functions, coordinates convos with the brain, doesn’t finish developing until around age 25, highly affected by alcohol, 28% of the frontal lobe
parietal lobe
somatosensory cortex, deals with sensory information
visual integration
orientation
optical lobe
primarily responsible for vision. starts with color, shape, and direction, then begins to process the info more.
temporal lobe
mostly used for hearing and language
broca’s area
only on the left hemisphere of the brain, shared between the frontal + temporal lobe. responsible for speech.
broca’s aphasia
commonly associated with strokes. means you can’t produce speech but you are aware of that.
wernicke’s area
only on the left hemisphere, responsible for speech comprehension.
wernicke’s aphasia
words can be understood but there is no real meaning to what is being said. they don’t realize how they are speaking. associated with strokes.
thalamus
where most senses (not smell) info goes first before being sent to other parts of the brain for deeper processing
pituitary gland
executive control of hormones
limbic system
really important for memory and emotions
hypothalamus
known for the 4 f’s (feeding, fleeing, fighting, fornicating). also gives hunger skills when it thinks you should eat and stationary signals when it thinks you should stop eating.
amygdala
important for emotional memory (specifically fear, anger, and disgust
hippocampus
closest tie to memory, close to the amygala
cingulate gyrus
a belt of tissue around the brain, critical for focusing on information. people with schizophrenia often experience and issue with this
basal ganglia
a system of structures, important for voluntary movement. an important source of dopamine for the brain, this area is less active with Parkinsons.
MRI
uses magnets to get a static image of the brain (structural technique)
DTI
specifically looks for myelination, looks for where there is myelin (structural technique)
NIRS
uses a light pulse to get a different pic of the brain (structural technique)
EEG
uses electrodes to track electrical activity in the brain, measuring differences in charges and can tell the general area but not much specificity (active technique)
ERP
tells us when activity is happening (active technique)
fMRI
tracking the metal in our blood and seeing how much blood is going to different parts of the brain. this is more specific than an EEG but more expensive, (active technique)
PET
measures where the glucose is going in the brain, if one part is getting more that means its more active, (active technique)
TMS
uses magnetic plue to disrupt or encourage, (active technique)
gate control theory
sometimes pain signals get sent to the spinal cord and stop there so you can move out of the situation without handling the pain
cerebrospinal fluid
protects the central nervous system and provides nourishment to it
somatic
controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles (conscious)
sympathetic nervous
fight or flight system, unconscious behaviors
parasympathetic
rest or digest system, brings you out of fight or flight
enteric
focuses solely on digestion, nerve cells in your gastro intestine, 95% of serotonin which is why depression and eating issues can go hand in hand
sensation
interaction of your sense organs with external stimuli, happens first, more externally, and is OBJECTIVE
perception
processing of sensations, happens second, internally, and is SUBJECTIVE
transduction
turning sensations into perceptions
weber’s law
the just noticeable difference is a constant proportion to the size of the initial stimulus
absolute threshold
the minimal level of stimuli for you to detect the existence
signal detection theory
hits- correctly identified stimulus
false alarms- saying the stimulus exists when it doesn’t
correct rejection- where the stimulus doesn’t exists and you correctly say that
misses- where there is a stimulus but you do not identify it
liberal response criteria
doesn’t need much evidence to say yes, more likely to have a false alarm
conservative response criteria
you have to be very sure in order to say yes, more likely to miss instances
button-up processing
starting at the sensation, based on your sense organs responding, builds up your perception from that sensation (more likely to be accurate but takes more effort)
top-down processing
where we let our expectations and beliefs to guide or processing (easier but can lead you wrong)
light
something that is dealt with by sensations
color
perception, how your brain processes lights
wavelengths
shorter ones are objectively cooler colors, longer ones are objectively warmer colors
amplitude
the larger the wave, the more intense the sensation and the darker the color
cornea
a thin membrane that protects the inner eye
pupil
a hole in your eye that allows for the light to be let in
iris
a muscle that controls the size of the pupil
lens
behind the pupil, changes shape depending on what you are looking at
fovea
where you can see the best, directly behind the iris, has all the cones