Ramp Function (Part-II)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Discrete-Time Ramp Function
A signal that increases linearly with the discrete-time index for nonnegative values and is zero otherwise.
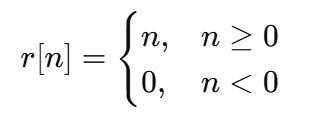
r[n] = n u[n]
Ramp Function Relation to Unit Step (Discrete-Time)
The discrete-time ramp function can be expressed as the product of the index and the unit-step function.
i(t) = I0u(t)
Unit-Step Representation of a Switching Event
A sudden change in a circuit (such as opening a switch at t=0t = 0t=0) can be modeled using the unit-step function.
Capacitor Voltage–Current Relationship
The voltage across a capacitor equals the time integral of its current scaled by the reciprocal of capacitance.
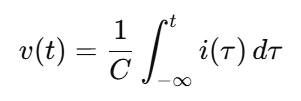
Ramp Response of a Capacitor to a Step Current
If a step current I0u(t) is applied to a capacitor, the resulting voltage is a ramp function.
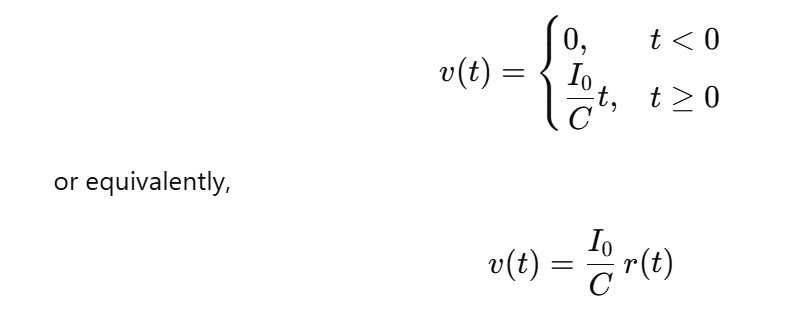
y(t) = H{x(t)}
Continuous-Time System (Operator View)
A system can be viewed as an operator H that maps an input signal to an output signal.
y[n] = H{x[n]}
Discrete-Time System (Operator View)
In discrete time, a system transforms an input sequence into an output sequence through an operator.
y[n] = (1/3)(x[n] + x[n - 1] + x[n - 2])
Moving-Average System (3-Point)
A discrete-time system whose output is the average of the three most recent input samples.
(S^k)x[n] = x[n - k]
Time-Shift Operator
An operator that delays a discrete-time signal by a fixed number of samples.
H = (1/3)(1 + S + S^2)
Operator Representation of a Moving-Average System
The moving-average system can be represented compactly using time-shift operators.
Cascade Implementation of a System
A system implementation where signals pass sequentially through multiple subsystems.
Example: cascading two unit-delay blocks S to obtain S²
Parallel Implementation of a System
A system implementation where multiple signal paths operate simultaneously and are summed.
Used to implement: H = (1/3)(1 + S + S²)
Feedback Connection
A system configuration where part of the output is fed back to the input, forming a closed loop.
Used to improve performance but may introduce stability concerns.
Linear Growth Signal
A signal whose amplitude increases proportionally with time or index.
Continuous-time: r(t) = t u(t)
Discrete-time: r[n] = n u[n]
Physical Interpretation of a Ramp Signal
Represents constant-rate accumulation, such as:
Capacitor voltage under constant current
Angular displacement under constant rotational speed