Exam 1 NURS357
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/191
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Med/Surg (357) - Inflammation, Infection, COVID, UTI, HIV, Cardiac pt 1/2
Last updated 11:55 PM on 2/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
1
New cards
Inflammation
* second line of defense
* non-specific response to any tissue injury
* non-specific response to any tissue injury
2
New cards
inflammation purpose
Neutralize and dilute the inflammatory agent, remove necrotic material, establish environment suitable for healing and repair
3
New cards
Local clinical manifestations of inflammation
redness (vasodilation), swelling (fluid shift to interstitial spaces), heat (increase metabolism), pain(change in pH, nerve stimulation, pressure), loss of function (swelling and pain)
4
New cards
Systemic clinical manifestations of inflammation
increase WBC (shift to left, increase release from bone marrow), fever (cytokines), increase pulse and respiratory rate, malaise, nausea, anorexia
5
New cards
local inflammation (lab/sub/odj data)
observation - 5 signs (redness, swelling, heat, pain, loss of function
6
New cards
systemic inflammation (lab, subj/obj data)
* diagnostic - lab
* assessment - vital signs and observations
* assessment - vital signs and observations
7
New cards
Nursing care and inflammation
prevent infection, trauma, surgery
promote healing
* nutrition
* early recognition
* access to health care
promote healing
* nutrition
* early recognition
* access to health care
8
New cards
medical treatment for inflammation and risks if untreated
* physical - clinical manifestations and vital signs
* RICE
* Fever management - drug therapy, environmental controls
* Pain management - pharmacologic and non-therapies
* RICE
* Fever management - drug therapy, environmental controls
* Pain management - pharmacologic and non-therapies
9
New cards
Clinical manifestations of SIRS to septic shock
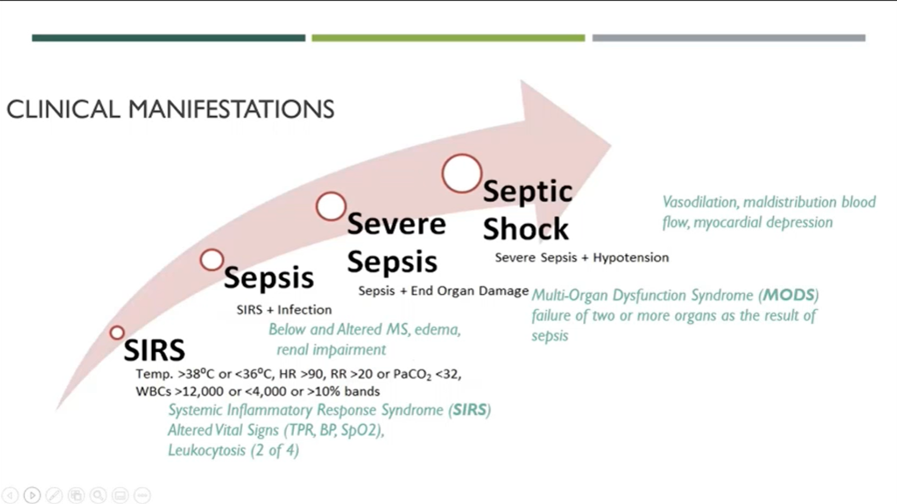
10
New cards
Septic shock s/s
Persistent hypotension, despite fluid resuscitation, vasopressor support, results in profound circulatory and cellular dysfunction associated with an increased risk of death (40% mortality)
11
New cards
Systemic s/s
Fever, decrease LOC, tachycardia, tachypnea, hypotension, hypoxemia, malaise, anorexia
12
New cards
Stop the cascade
Cultures and sensitivity before admin antibiotics, administer broad spectrum first --> narrow spectrum, O2 support, push fluids to keep BP up vasopressors
13
New cards
Infection
* invasion of host body by disease causing pathogens
* multistep process
* invade
* multiply
* produce disease
* cause harm to host
* multistep process
* invade
* multiply
* produce disease
* cause harm to host
14
New cards
Local (contained) infection manifestations
* limited to specific body part
* pain, redness, swelling, temp, motion
* change in vital sign
* pain, redness, swelling, temp, motion
* change in vital sign
15
New cards
Disseminated infection
spread of microorganisms beyond initial site
16
New cards
Systemic (diffused) infection
* Spread extensively throughout the body
* malaise, anorexia, altered MS
* lymph node enlargement
* change in renal function and/or cardiac output
* malaise, anorexia, altered MS
* lymph node enlargement
* change in renal function and/or cardiac output
17
New cards
Infection diagnostics
* CBC
* Leukocytosis – increase WBC (normal: 4,500-11,000)
* Differential – left shift
* Blood cultures
* This must be done before the antibiotics are given to the patient
* Urinary culture
* Leukocytosis – increase WBC (normal: 4,500-11,000)
* Differential – left shift
* Blood cultures
* This must be done before the antibiotics are given to the patient
* Urinary culture
18
New cards
Nursing diagnosis (infection)
1. risk for shock
2. impaired tissue integrity
19
New cards
nursing management (w/ infection)
1. assessment
2. administer antibiotics/antifungals (after culture)
3. address fever and discomfort
4. encourage fluid intake
1. IV line
5. ongoing monitoring
1. urine output very important
6. Emotional support
20
New cards
Healthcare associated infections (HAI’s)
CLABSI, CAUTI, surgical site infection, ventilator associated events
common pathogens: MRSA, C. diff
common pathogens: MRSA, C. diff
21
New cards
endogenous
from patient themselves
22
New cards
exogenous
from hospital
23
New cards
Iatrogenic
from intervention procedure
24
New cards
Risk factors for HAI’s
i. Hospital environment
ii. Immune deficiencies
iii. Age
iv. Stress
v. Nutrition
vi. Medications
ii. Immune deficiencies
iii. Age
iv. Stress
v. Nutrition
vi. Medications
25
New cards
Tier one (standard)
applies to all patients, contact with blood or bodily fluids
26
New cards
Tier two (transmission-based precautions)
i. Contact – direct contact (MRSA, VRE)
ii. Droplet – greater than 5 microns (Pneumonia)
iii. Airborne – less than 5 microns (TB, Varicella)
ii. Droplet – greater than 5 microns (Pneumonia)
iii. Airborne – less than 5 microns (TB, Varicella)
27
New cards
Compromised defenses of susceptible host
i. Neutropenic/reverse
ii. Chemo, steroid, compromised skin integrity
iii. Hygiene, immunization, nutrition, stress, hydration, rest and sleep
ii. Chemo, steroid, compromised skin integrity
iii. Hygiene, immunization, nutrition, stress, hydration, rest and sleep
28
New cards
Hour 1 Bundle
ii. Measure lactic acid – greater than 2, recheck within 3 hours
iii. Blood culture before antibiotics
iv. Administer broad spectrum antibiotics
v. Rapid fluid infusion – isotonic IV
iii. Blood culture before antibiotics
iv. Administer broad spectrum antibiotics
v. Rapid fluid infusion – isotonic IV
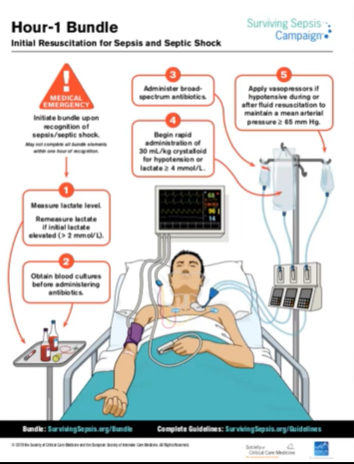
29
New cards
Sepsis prevention
aseptic care, prophylaxis, patient teaching
30
New cards
Sepsis treatment
A – support oxygenation
B – may require ventilation
C – optimize fluid status – IVT
B – may require ventilation
C – optimize fluid status – IVT
31
New cards
Sepsis IV treatments
* large bore catheters
* crystalloids
* Colloids (blood, albumin)
* crystalloids
* Colloids (blood, albumin)
32
New cards
Crystalloids
a. Stay in the vascular system
b. Electrolytes flow across the membrane to it into cells and body tissues
c. Increase fluid volume in both interstitial and intravascular spaces
d. Types: hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic
b. Electrolytes flow across the membrane to it into cells and body tissues
c. Increase fluid volume in both interstitial and intravascular spaces
d. Types: hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic
33
New cards
Colloids (blood, albumin)
a. Contains large molecules do not pass membrane
b. When infused, remain in vascular system expand the intravascular volume
c. “Volume expanders”
d. Increase flow of fluids
b. When infused, remain in vascular system expand the intravascular volume
c. “Volume expanders”
d. Increase flow of fluids
34
New cards
Complicated sepsis treatments
* vasopressor
* norepinephrine, dopamine
* MAP >65 mmHg
* norepinephrine, dopamine
* MAP >65 mmHg
35
New cards
Nursing diagnosis (sepsis)
* risk for infection/shock
* ineffective tissue perfusion
* anxiety
* ineffective tissue perfusion
* anxiety
36
New cards
Sepsis (ongoing monitoring)
i. v/s, LOC, urinary output, and organ function
37
New cards
Population more at risk for sepsis
* 2-3 times higher than younger people
* UTI more common in adults residing in long-term facilities, with indwelling catheters
* Atypical manifestations
* cognitive and behavioral change appear as symptoms before fever, pain or alterations in lab values
* do not rely on rely on fever to indicate infections in older adults
* UTI more common in adults residing in long-term facilities, with indwelling catheters
* Atypical manifestations
* cognitive and behavioral change appear as symptoms before fever, pain or alterations in lab values
* do not rely on rely on fever to indicate infections in older adults
38
New cards
COVID risk, prevention and care considersations
* ssRNA found in humans and other mammals
* cause common cold symptoms
* target respiratory system
* transmission
* via respiratory droplets from face-to-face
* prevention
* i. keep 6 ft apart from other people
ii. wear mask
iii. indoor ventilation
iv. wear medical masks
v. hand hygiene
* cause common cold symptoms
* target respiratory system
* transmission
* via respiratory droplets from face-to-face
* prevention
* i. keep 6 ft apart from other people
ii. wear mask
iii. indoor ventilation
iv. wear medical masks
v. hand hygiene
39
New cards
Cystitis
Infection of the bladder
40
New cards
Symptoms of cystitis
Dark, blood urine, pain in lower stomach, pain and burning during urination, strong selling, sick and tired
41
New cards
Urethritis
* Infection of urethra, often related to STI
* colonization of the vaginal introitus or urethra, ascends by urethra into bladder
* colonization of the vaginal introitus or urethra, ascends by urethra into bladder
42
New cards
UTIs causes
i. Gram negative bacterium – e coli (most common)
ii. Sometimes simultaneous infection with multiple pathogen
ii. Sometimes simultaneous infection with multiple pathogen
43
New cards
UTIs Risk Factors
i. Inadequate fluid consumption
ii. Urinary catheter use
iii. UT obstruction
iv. Vesicoureteral reflux
v. Urinary stasis
vi. Bowel incontinence
vii. Immobility
viii. Poor personal hygiene
ix. Immunosuppression
x. Sexual activity
ii. Urinary catheter use
iii. UT obstruction
iv. Vesicoureteral reflux
v. Urinary stasis
vi. Bowel incontinence
vii. Immobility
viii. Poor personal hygiene
ix. Immunosuppression
x. Sexual activity
44
New cards
Medical and Nursing management of UTI’s
* Antibiotic therapy based on culture and sensitivity of the bacteria
* Warm compresses and sitz bath
* Increase fluid intake (avoid citrus or caffeine)
* I/O, VS, voiding patterns and pain
* Warm compresses and sitz bath
* Increase fluid intake (avoid citrus or caffeine)
* I/O, VS, voiding patterns and pain
45
New cards
Crucial education w/ UTI patient
a. Encourage increase oral fluid
b. Personal hygiene
c. Take antibiotics as prescribed
d. Emptying the bladder at least every 4 hours
b. Personal hygiene
c. Take antibiotics as prescribed
d. Emptying the bladder at least every 4 hours
46
New cards
Lab and diagnostic data (UTI)
Urine analysis (WBC, hematuria), blood culture
47
New cards
Special considerations and teaching points (UTI)
* Older adults present with confusion rather than fever
* Risk increases with catheter use
* Perineal care
* Empty bladder before and after intercourse
* Risk increases with catheter use
* Perineal care
* Empty bladder before and after intercourse
48
New cards
Pathophysiology and transmission of HIV
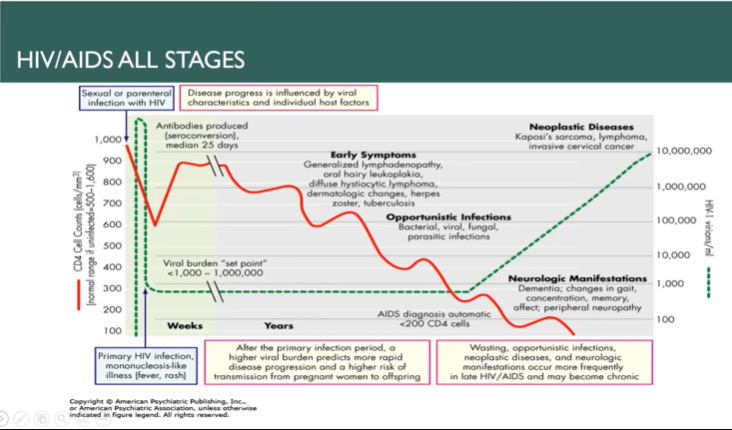
49
New cards
Clinical manifestations of HIV
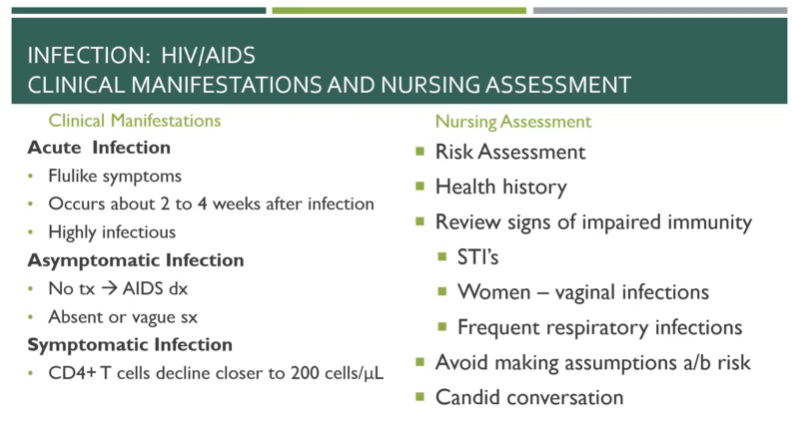
50
New cards
How HIV is diagnosed
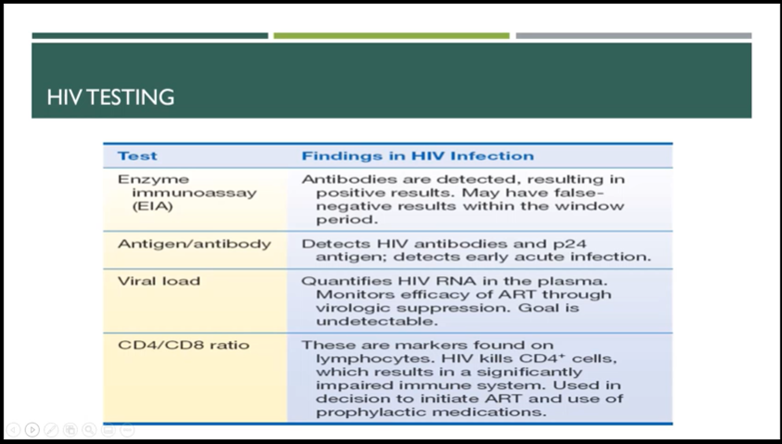
51
New cards
main goal of antiretroviral therapy and goals of care for HIV patients

52
New cards
HIV/AIDS patient teaching
* gerontologic consideration
* increasing rates of HIV disease among older adults
* Death rate from opportunistic infections reduced
* people 60 and older are increasingly being infected
* increasing rates of HIV disease among older adults
* Death rate from opportunistic infections reduced
* people 60 and older are increasingly being infected

53
New cards
Assessment of HIV
History, risk factors, physical, depends on stage of disease
54
New cards
Asymptomatic infection (HIV)
Vague or no symptoms, if not diagnosed, HIV can develop into AIDS
55
New cards
Acute infection (HIV)
2-4 weeks after infection and manifest as flu-like symptoms, patient highly contagious
56
New cards
Symptomatic infection (HIV)
CD4T cell count drops below 200 and patient is incredibly susceptible to infection
57
New cards
Lab and diagnostic data (HIV)
Rapid HIV, antigen/antibody immunoassay, WBC, CD4/CD8 ratio, CD4 sub 200 = AIDS, viral load
58
New cards
Nonmodifiable risk factors of CAD
age, gender, ethnicity, family history and genetic predispositions
59
New cards
Modifiable risk factors of CAD
stress, substance abuse, elevated serum lipids, hypertension, tobacco use
60
New cards
Asymptomatic (CAD)
silent ischemia
61
New cards
Symptomatic (CAD)
angina
62
New cards
S/S (CAD)
acute onset of chest pain, SOB, Diaphoresis, difficulty breathing, jaw/back/arm pain, nausea/vomiting, extreme fatigue
63
New cards
Women and Older Adults (atypical chest pain)
unexplained anxiety, shoulder pain, throat or toothache, pain under breastbone or stomach
64
New cards
Precipitating factors for angina
overstressing the heart, temperature extremes, strong emotions, consumption of heavy meal, sexual activity, tobacco use, stimulants, circadian rhythm (early morning)
65
New cards
Stable angina
predictable and consistent pain that occurs on exertion and is relieved by rest
66
New cards
Unstable angina symptoms
occur more freq and last longer than in stable angina, pain threshold is lower, pain may occur at rest
67
New cards
Intractable (refractory)
severe incapacitating chest pain
68
New cards
Variant
pain at rest with reversible ST-segment elevation; thought to be caused by coronary artery vasospasm
69
New cards
Silent ischemia
no sub data (patient is asymptomatic), objective evidence of ischemia (ECG changes with a stress test
70
New cards
Diagnoses of angina
thorough history related to s/s of ischemia, chest x-ray, ECG, biomarkers, exercise stress test, nuclear scan or invasive procedure (cardiac cath)
71
New cards
Treatment of angina
goal: decrease O2 demand, increase O2 supply, pharmacologic therapy, reperfusion procedures (PCI, PTCA, CABG)
72
New cards
What is ACS?
unstable angina, MI: sudden blockage of blood flow, duration: 15 mins or more
73
New cards
What is an MI?
coronary occlusion or heart attack, area of the myocardium is permanently destroyed, infraction over mins/hrs
74
New cards
Classic S/S (ACS)
early signs, prior to more serious ACS events, onset of ACS (4 or more)
75
New cards
Atypical S/S (elderly, diabetics)
unusual fatigue or SOB
76
New cards
Asymptomatic (ACS)
silent ischemia
77
New cards
CK-MB
*earliest increase 4-8hrs, peak 12-24 hrs, return to normal 3-4 days
78
New cards
Myoglobin
*earliest increase 1-3hrs, peak 4-12 hrs, return to normal 12 hours
79
New cards
Troponin T or I
*earliest increase 3-4 hours, peak 4-24 hrs, return to normal 1-3 weeks
80
New cards
Caring for a patient with ACS
Goal \= relieve pain, prevent, or minimize myocardial tissue death and to prevent complications
81
New cards
Thrombolytic therapy
within 4 hours of symptom onset
82
New cards
Percutaneous coronary intervention
w/ or w/o stent placement
83
New cards
Immediate MONA
morphine, oxygen, nitroglycerin, ASA (Plavix)
84
New cards
Initial Interventions
12 lead ECG, upright position, oxygen (> 93%), IV access, nitroglycerin, ASA, Morphine
85
New cards
Ongoing monitoring and care
Treat dysrhythmias, vital sign (daily weight), bed rest/limit activity for 12-24 hours, IM injections
86
New cards
Unstable Angina or NSTEMI
Duel antiplatelet therapy and heparin, Cardiac catheterization with PCI once stable (Balloon, stent)
87
New cards
Emergent PCI (cardiac cath)
Treatment of choice for confirmed STEMI, Goal:
88
New cards
Thrombolytic therapy (no cath lab)
For patients with NSTEMI or STEMI, Given IV within 30 min of arrival to ED, Patient selection critical (any bleeding disorders), Draw blood and start 2 IV sites (given blood supplement is common), Return of ST segment to baseline best sign
89
New cards
IV heparin
prevent re-occlusion
90
New cards
Coronary Artery Bypass (CABG)
Using another artery to replace the artery with the blockage to bypass the blockage, Recover in ICU \> Med/Surg \> Rehab
91
New cards
Nutritional Therapy
Initially NPO, Progress to low salt, sat fat, cholesterol
92
New cards
Cardiac Rehab
Medically supervised program designed to improve cardiovascular health (Exercise, Education for heart-healthy living, Counseling to reduce stress – id and tackle everyday source of stress)
93
New cards
Nursing diagnoses
Decreased cardiac output, anxiety acute pain, activity intolerance, ineffective management
94
New cards
Stenosis
not opening correctly
95
New cards
Regurgitation
not closing correctly
96
New cards
Valve prolapse
valve bulging into the chamber
97
New cards
Mitral valve stenosis
dyspnea on exertion, hemoptysis fatigue, A-fib, palpitation, load, accentuated S1, low-pitched, diastolic murmur
98
New cards
Mitral valve regurgitation
acute: poorly tolerated, new systolic murmur with pulmonary edema and cardiogenic shock develop rapidly, chronic: weak, fatigue, exertional dyspnea, palpitations, S3 gallop, systolic murmur
99
New cards
Mitral Valve Prolapse
palpitations, dyspnea, chest pain, activity intolerance, syncope, systolic murmur
100
New cards
Aortic valve stenosis
angina, syncope, dyspnea on exertion, heart failure, normal or soft S1, diminished or absent S2, systolic murmur, prominent S4