L20 The Eye (Imported from Quizlet)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Detect prey, detect predators, detect mates, communicate
What does having vision allow us to do?
Third, visual
More than a ________ of the human neocortex is involved in analysing the ________ world
Electromagnetic, visible
Light is ___________________ radiation that is ________
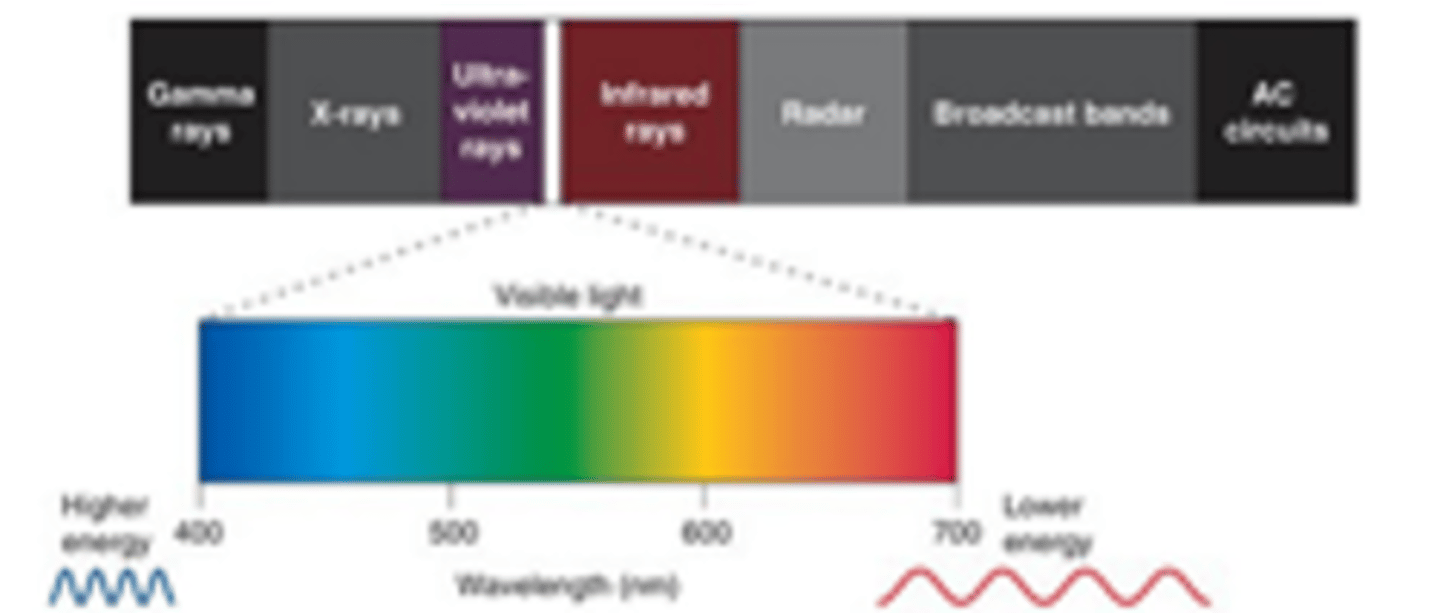
Wavelength, frequency, amplitude
What 3 things does light have?
Distance between peaks or troughs
What is wavelength?
Number of waves per second
What is frequency?
Difference between wave peak and trough
What is amplitude?
Straight, rays, atoms, molecules
Electromagnetic light travels in ____________ lines, known as ______, until it interacts with ________ and ______________
Light rays interact in 3 ways
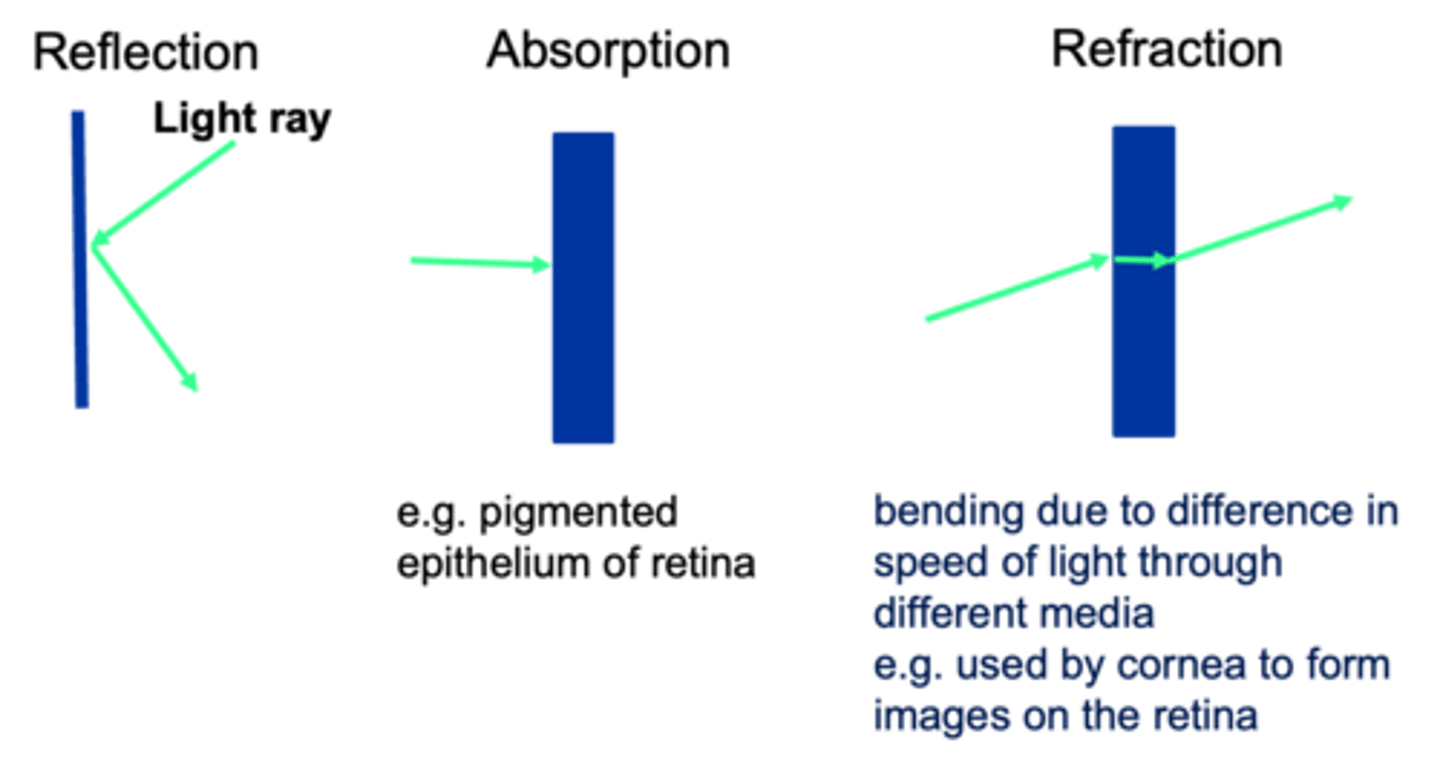
The speed of light differs between medium (e.g. slower through water than air, the greater the difference in speed in the two media the greater the angle of refraction)
Refraction occurs because ...?
Perpendicular
Refraction occurs towards a line that is ________________ to the border
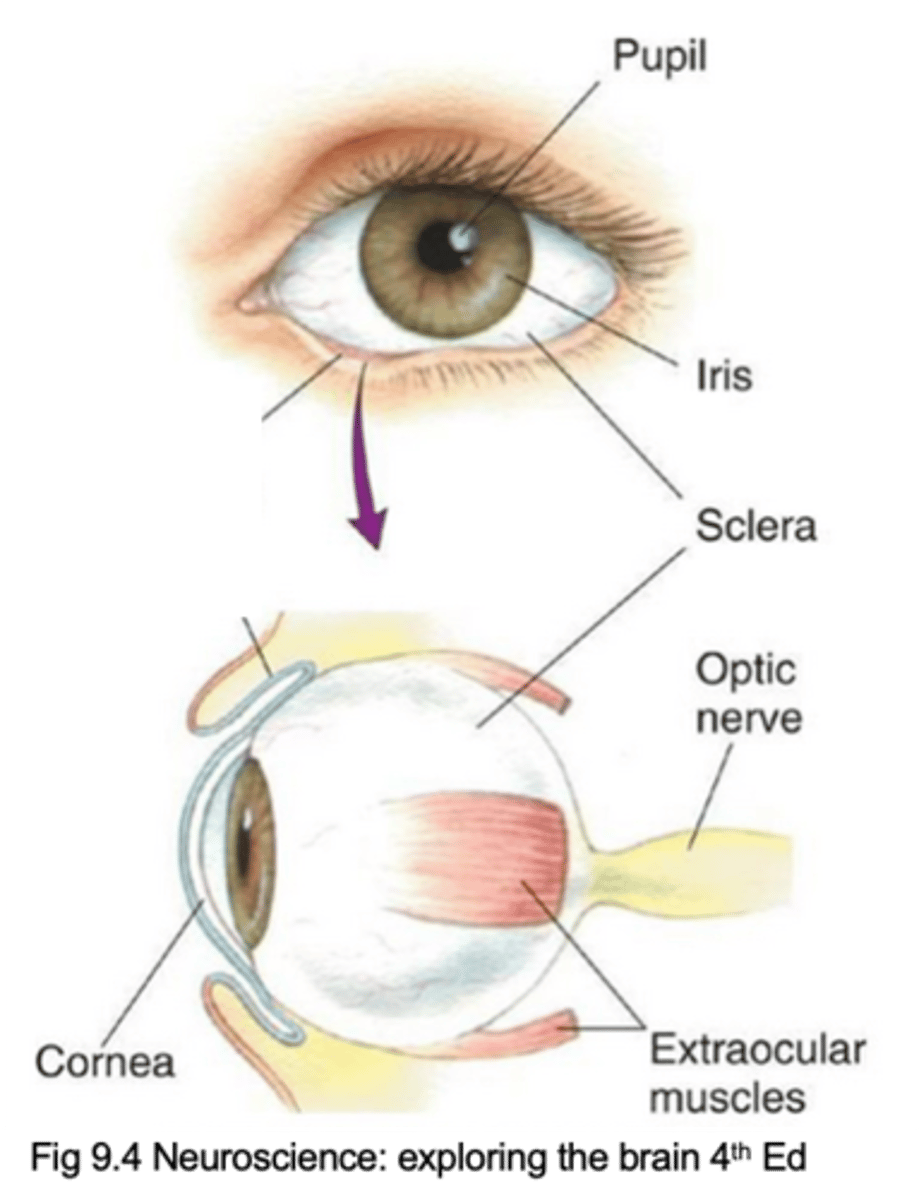
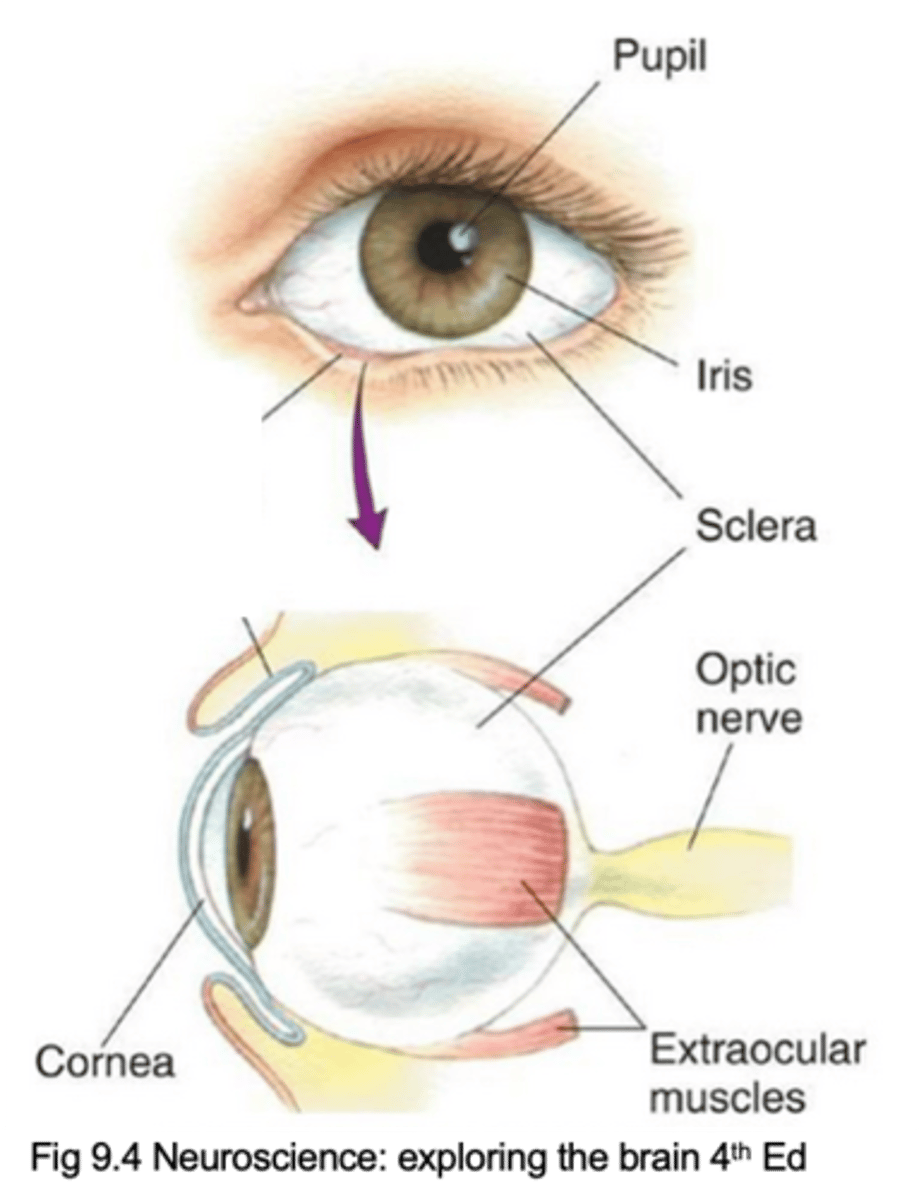
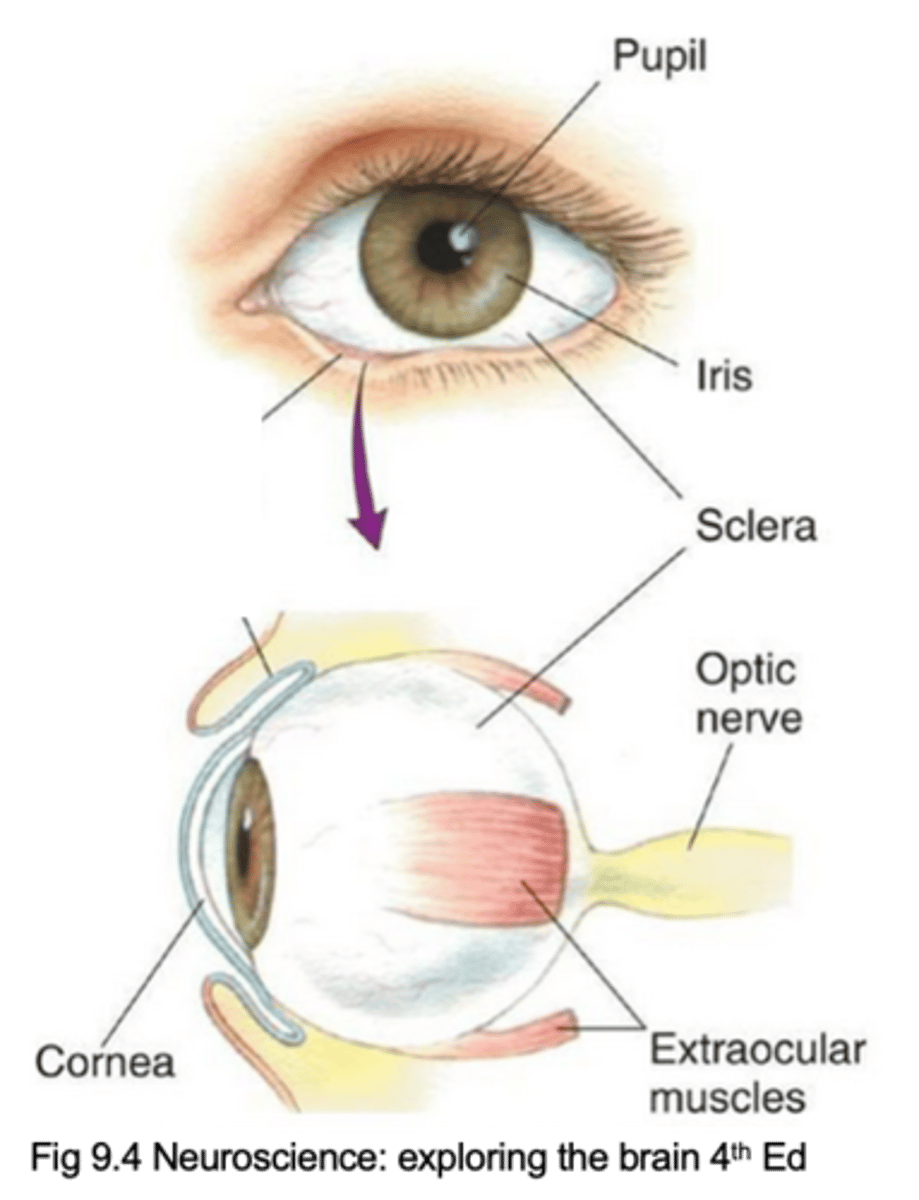
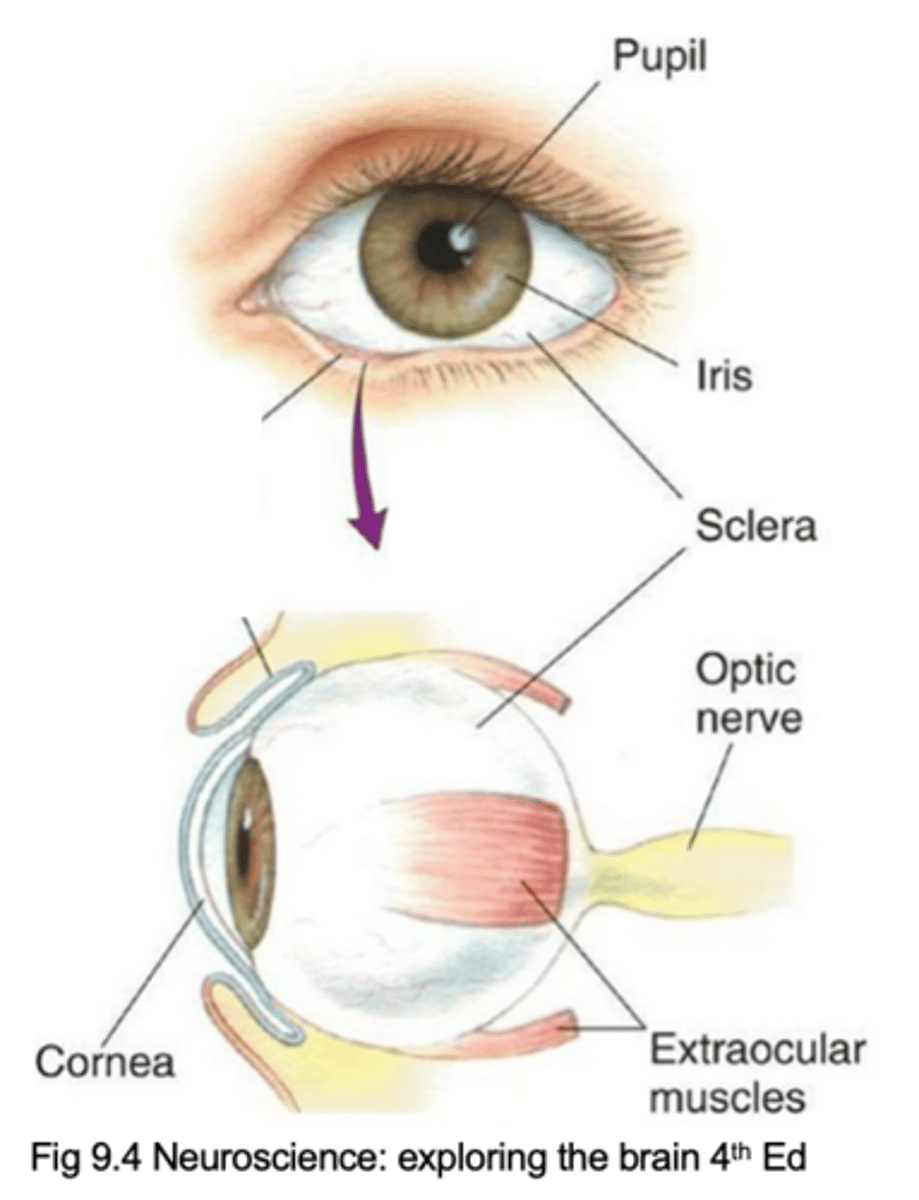
Pupil, iris, cornea, sclera, extraocular muscles, optic nerve (cranial nerve II)
Name the 6 key components of the eye
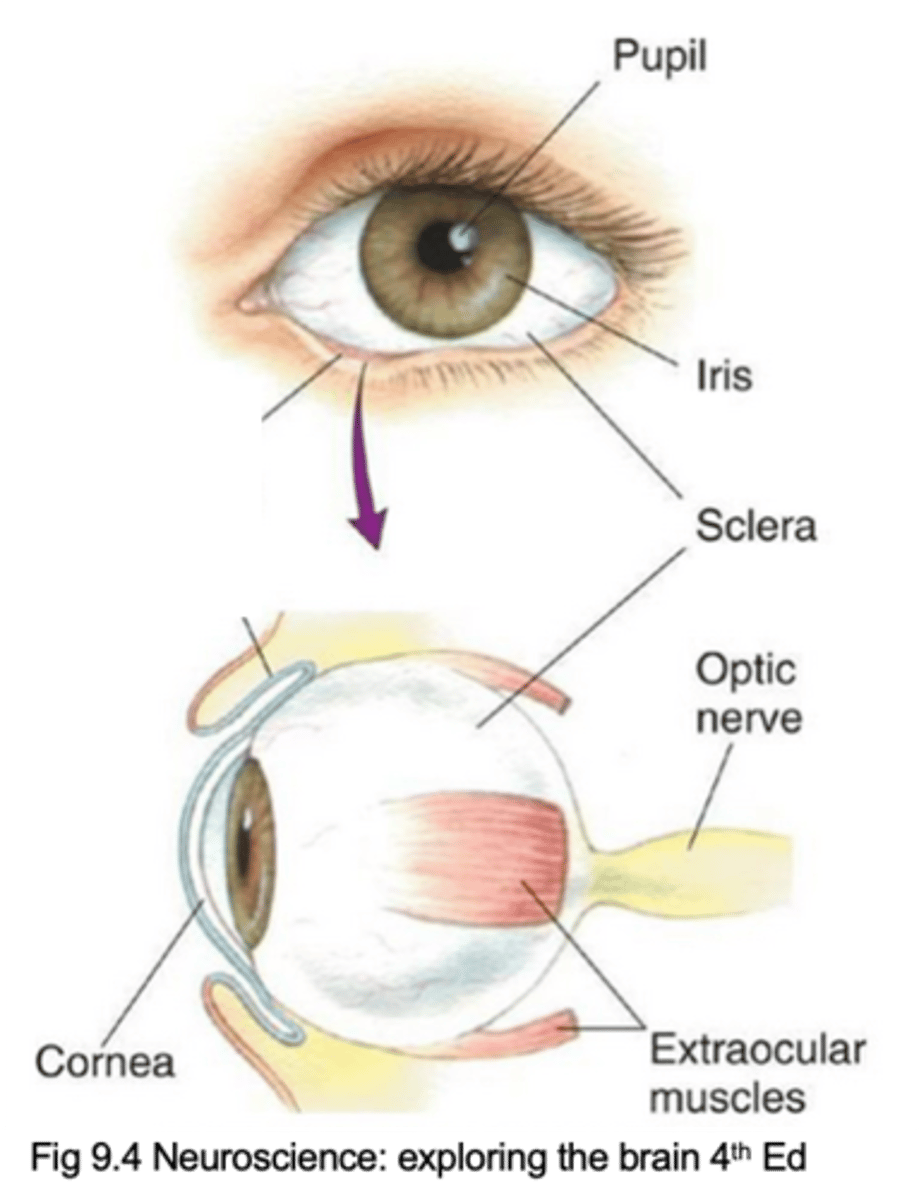
Lets light inside the eye
What does the pupil do?
Contains muscles which control the amount of light entering the eye
What does the iris do?
Glassy, transparent covering of the pupil and iris that refracts light
Describe the cornea and its purpose
Continuous with cornea, forms the tough, protective wall of the eyeball to give it its shape
Describe the sclera and its purpose
Move the eyeball, controlled by oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve III)
What do extraocular muscles do and what are they controlled by?
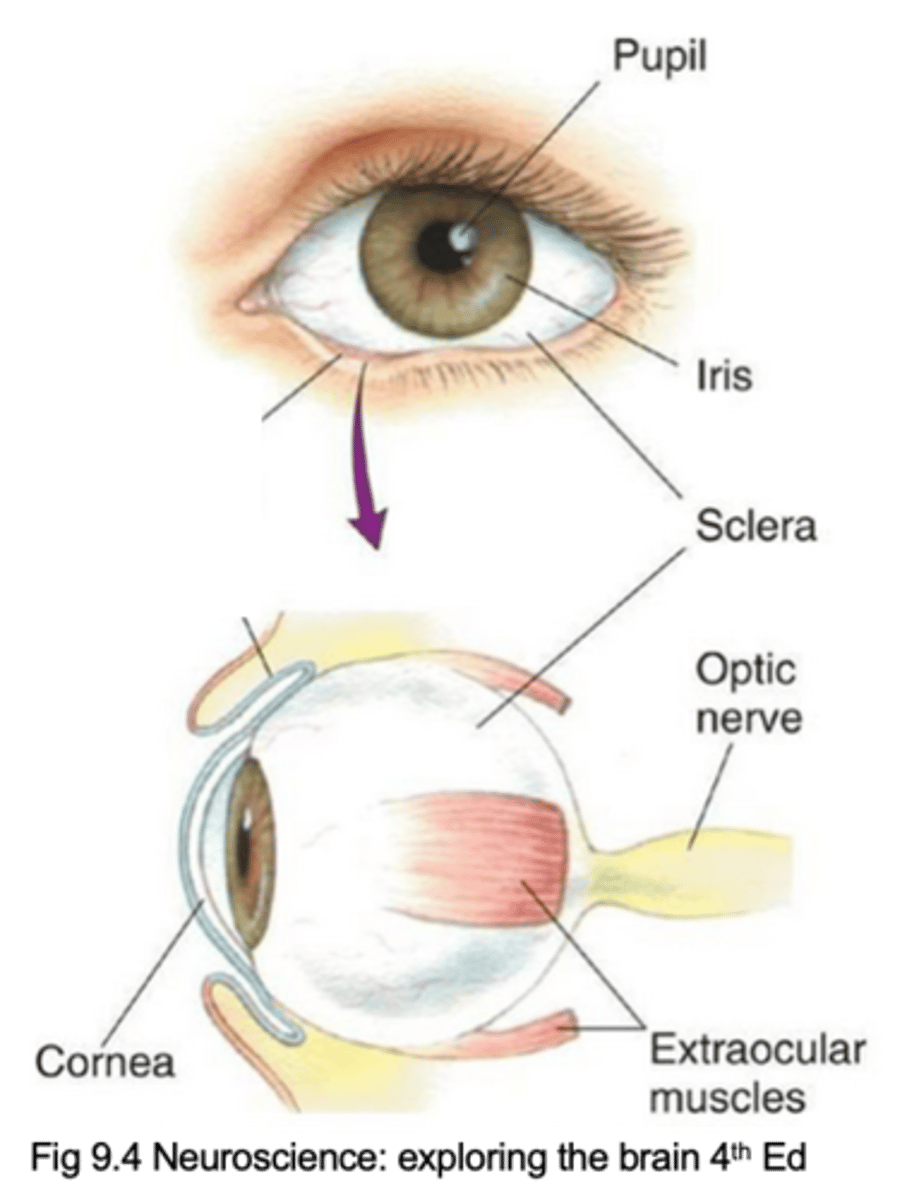
Carries axons from retina to brain
What does the optic nerve (cranial nerve II) do?
Due to heavy pigment at back of the eye
Why does the pupil appear black?
Due to blood vessels on the surface of the retina
Reflected light appears bright red when light is shined, why?
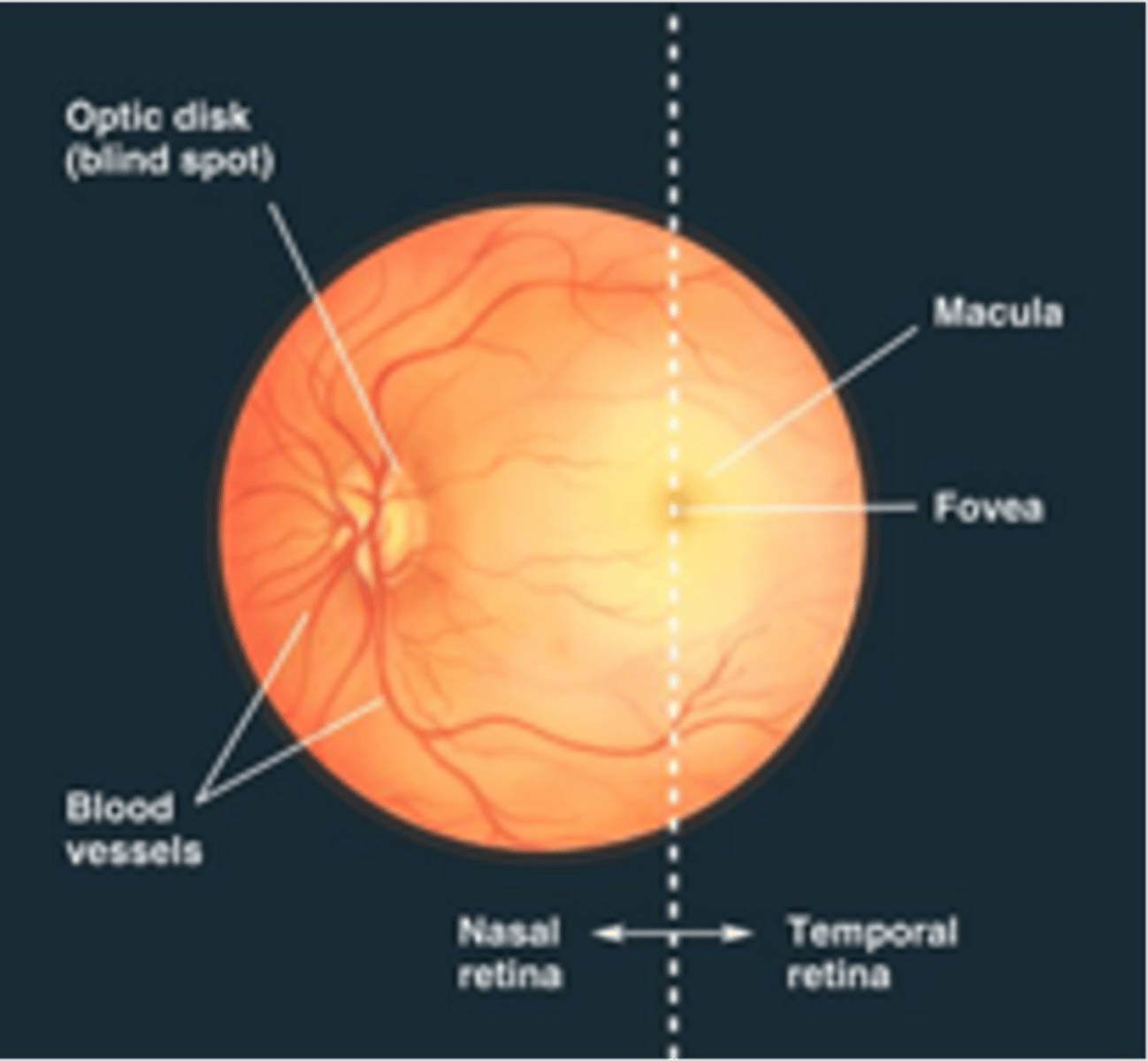
This image shows the eye using an ophthalmoscope
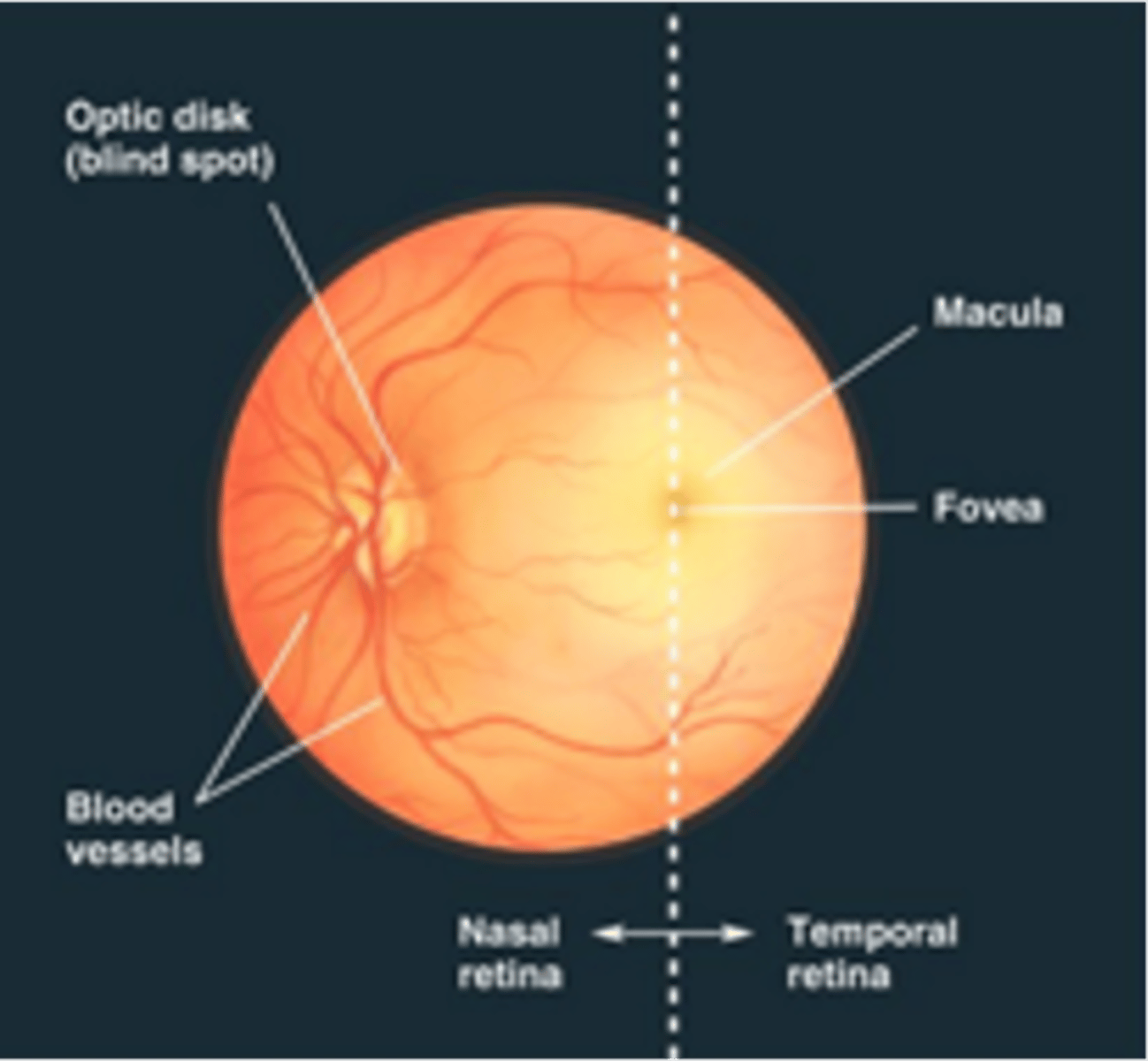
Blood vessels and optic nerve, cannot sense light
What originates in the optic disk and what can't it sense?
Region of retina for central vision, devoid of large blood vessels to improve vision quality
Describe the macula, what is it devoid of and what does this entail?
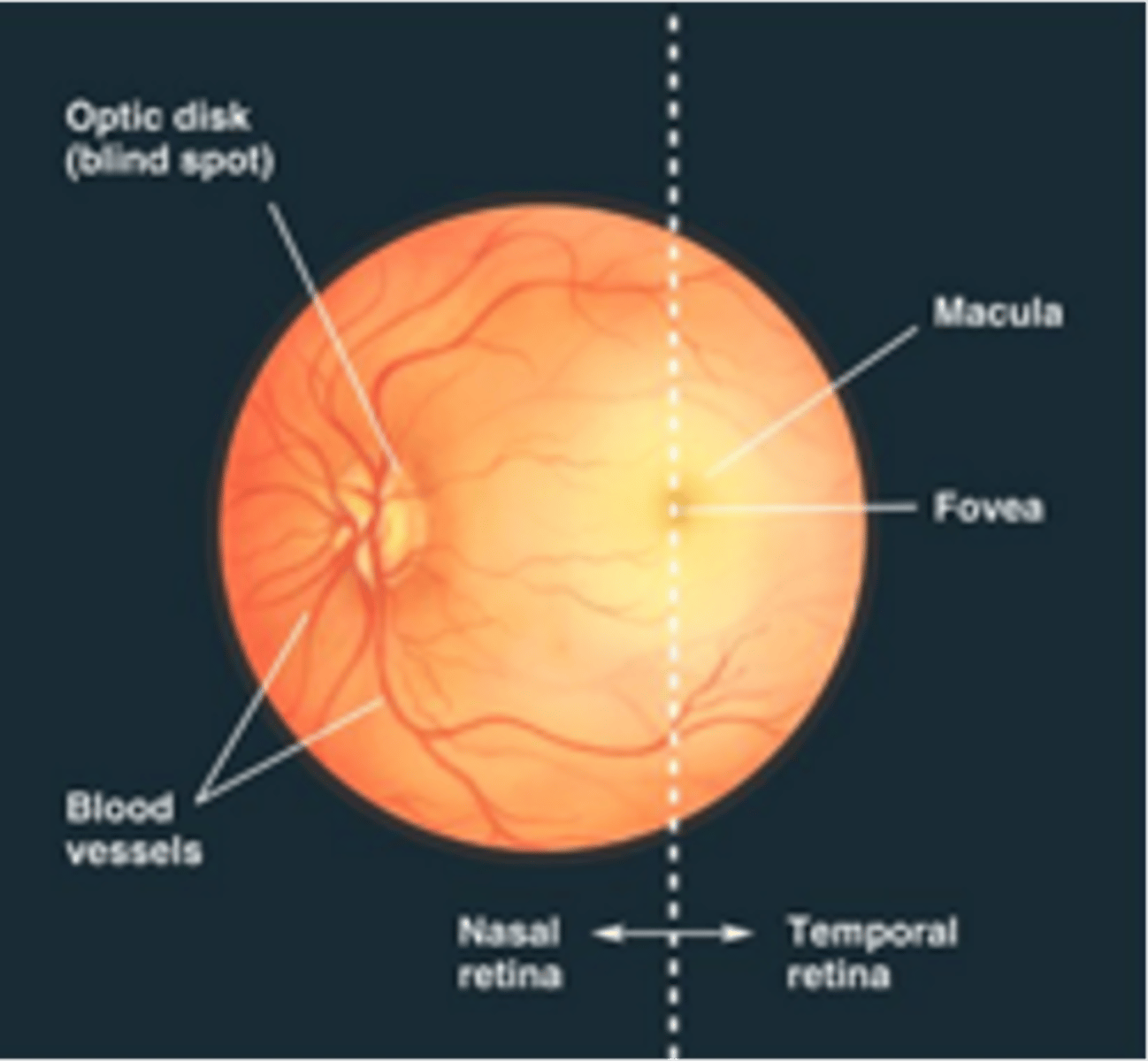
Retina is thinnest here and is the area of higher visual acuity
Describe the fovea
To ensure that the area of interest in our visual field is focused on the fovea to give us the highest resolution image possible
Why do we move our eyes?
Sensory receptor cells and afferent neurons
What does the retina contain?
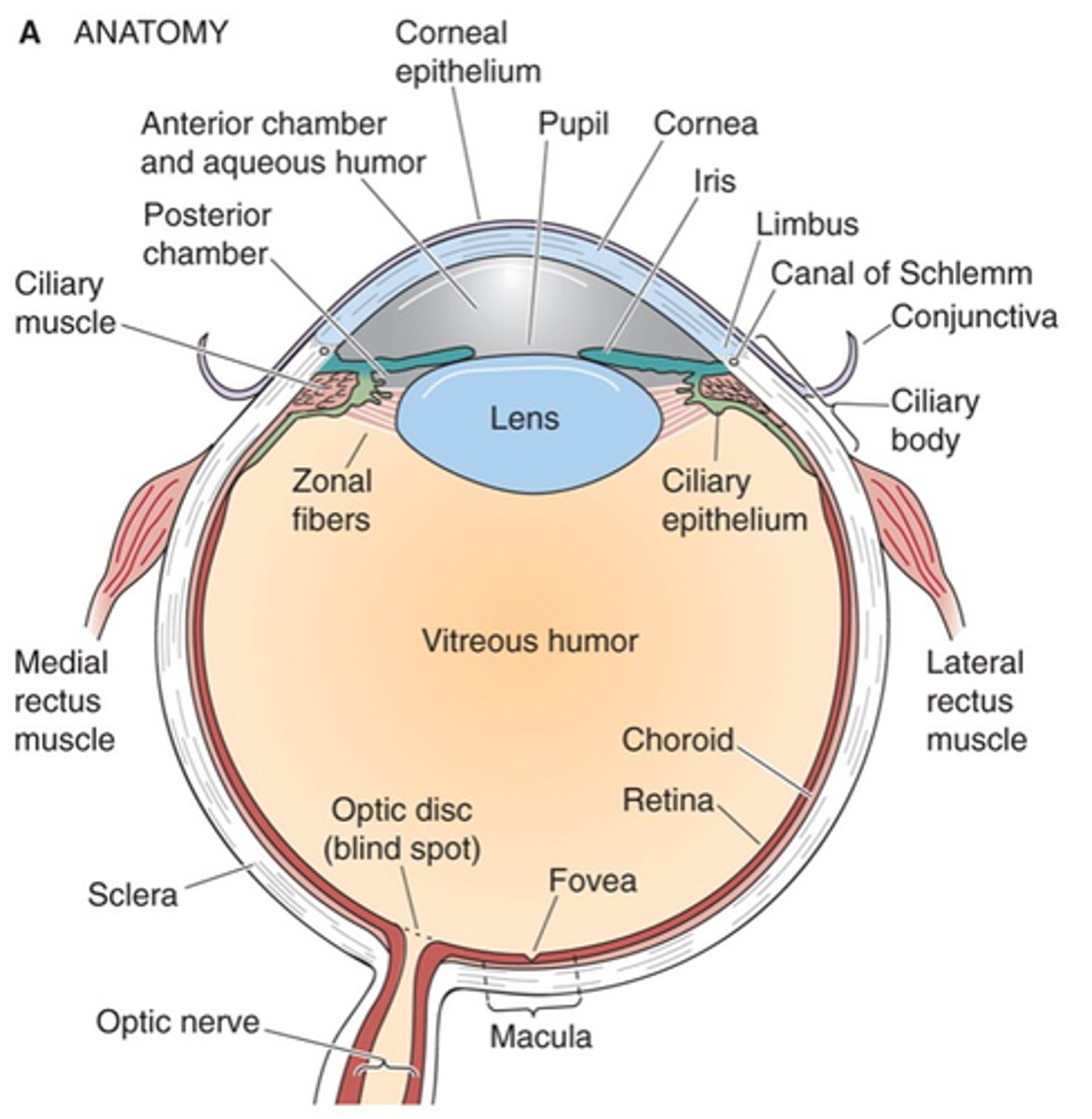
Zonal fibres, ciliary muscle
The lens is suspended by _______ ________ (ligaments) which are attached to the ___________ ___________, enabling stretching of the lens
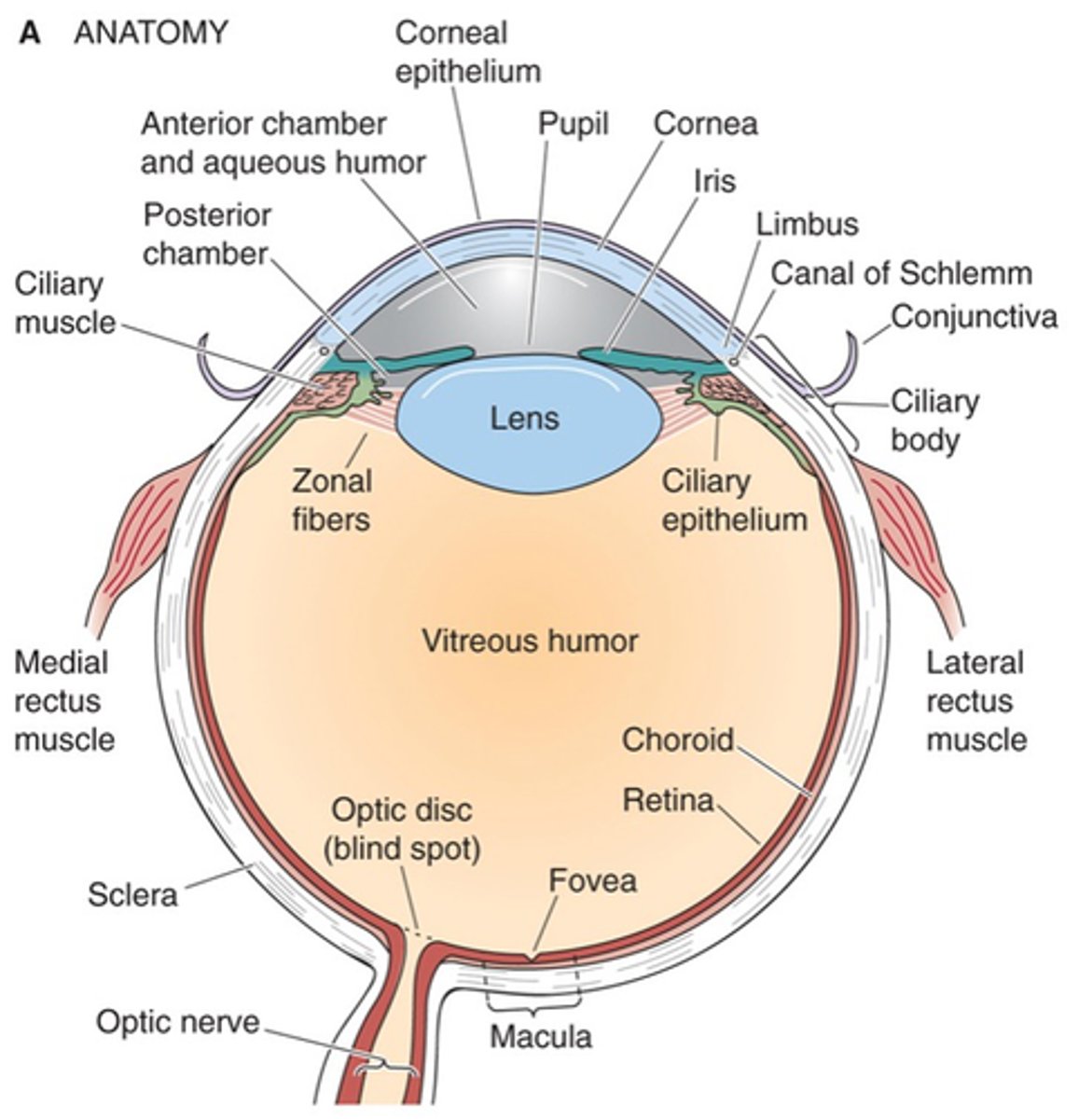
Retina, fovea
Light rays must be focussed onto the ___________ (ideally the _______)
80, 20
Refraction occurs at the:
Cornea ~__%
Lens, remaining __%
Difference in refractive indices between the two media
The angle at which light hits the interface between these two media
The degree of refraction is determined by 2 things, what are they?
Speed, light, quicker, increased density
Refractive index is essentially a measure of ________ of ________ within it - so light moves ___________ through air (1.003) than the cornea (1.376) due to the ______________ ________ of the cornea
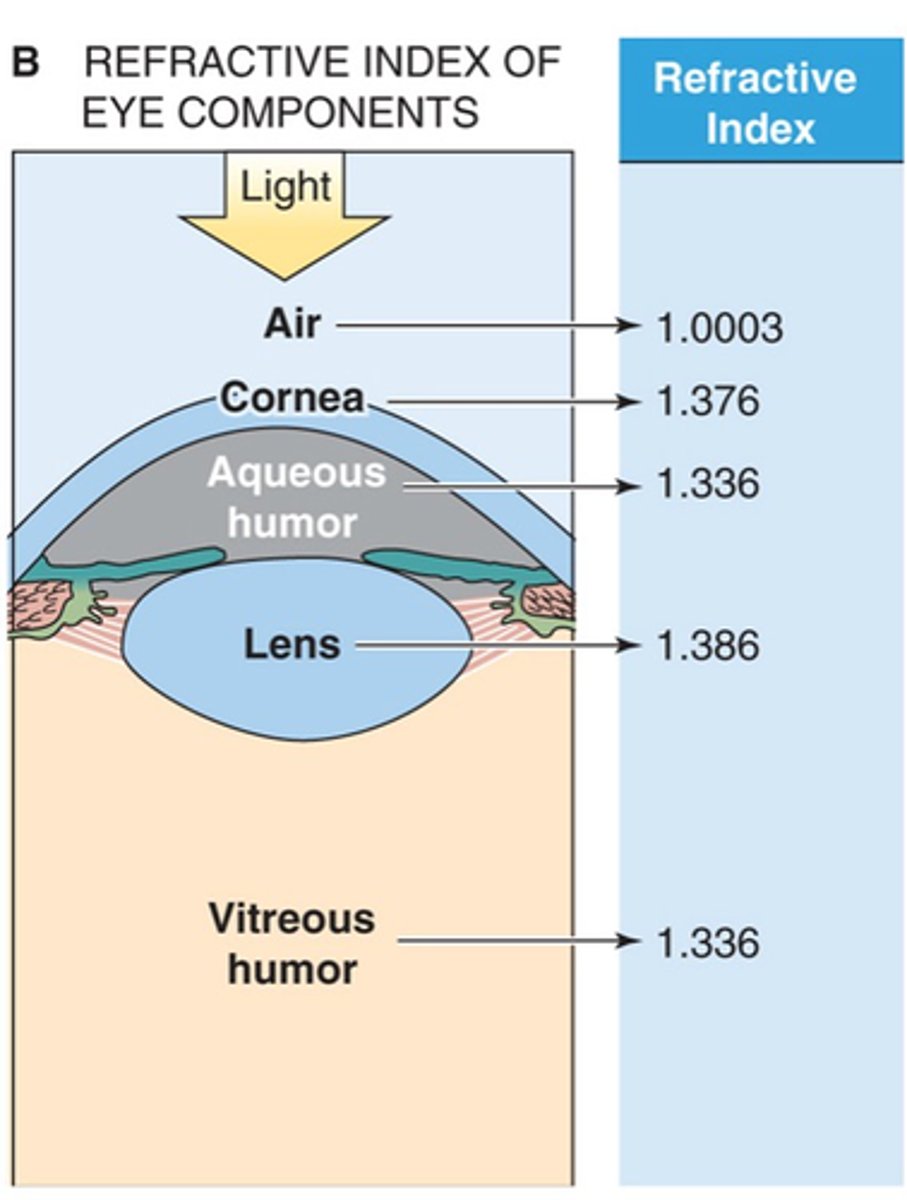
Air, water
Light arrives at the cornea through _____ but the cornea is mainly _________
Slowly, higher density
Light travels more _________ through water than air due to __________ __________ = refraction occurs
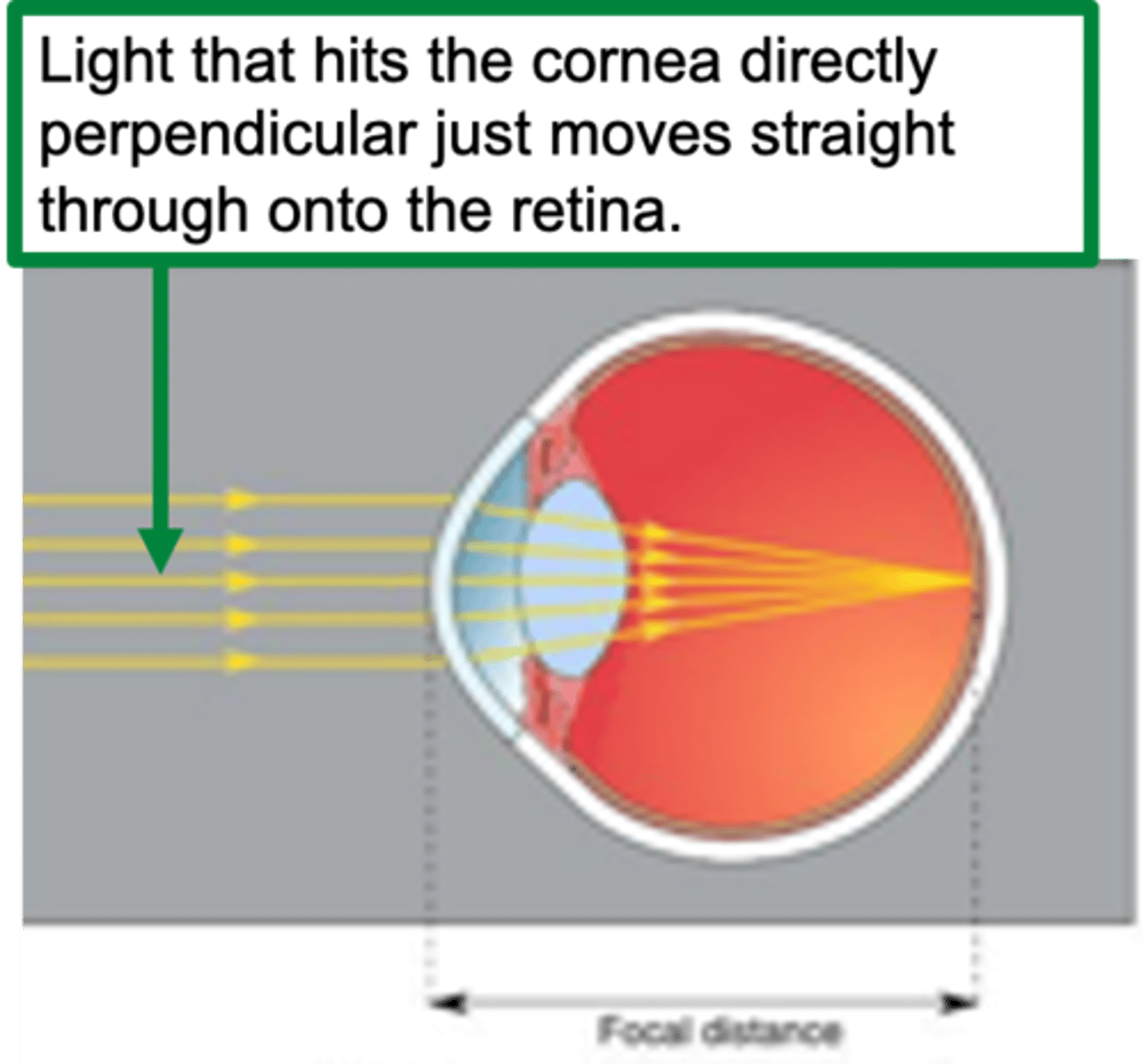
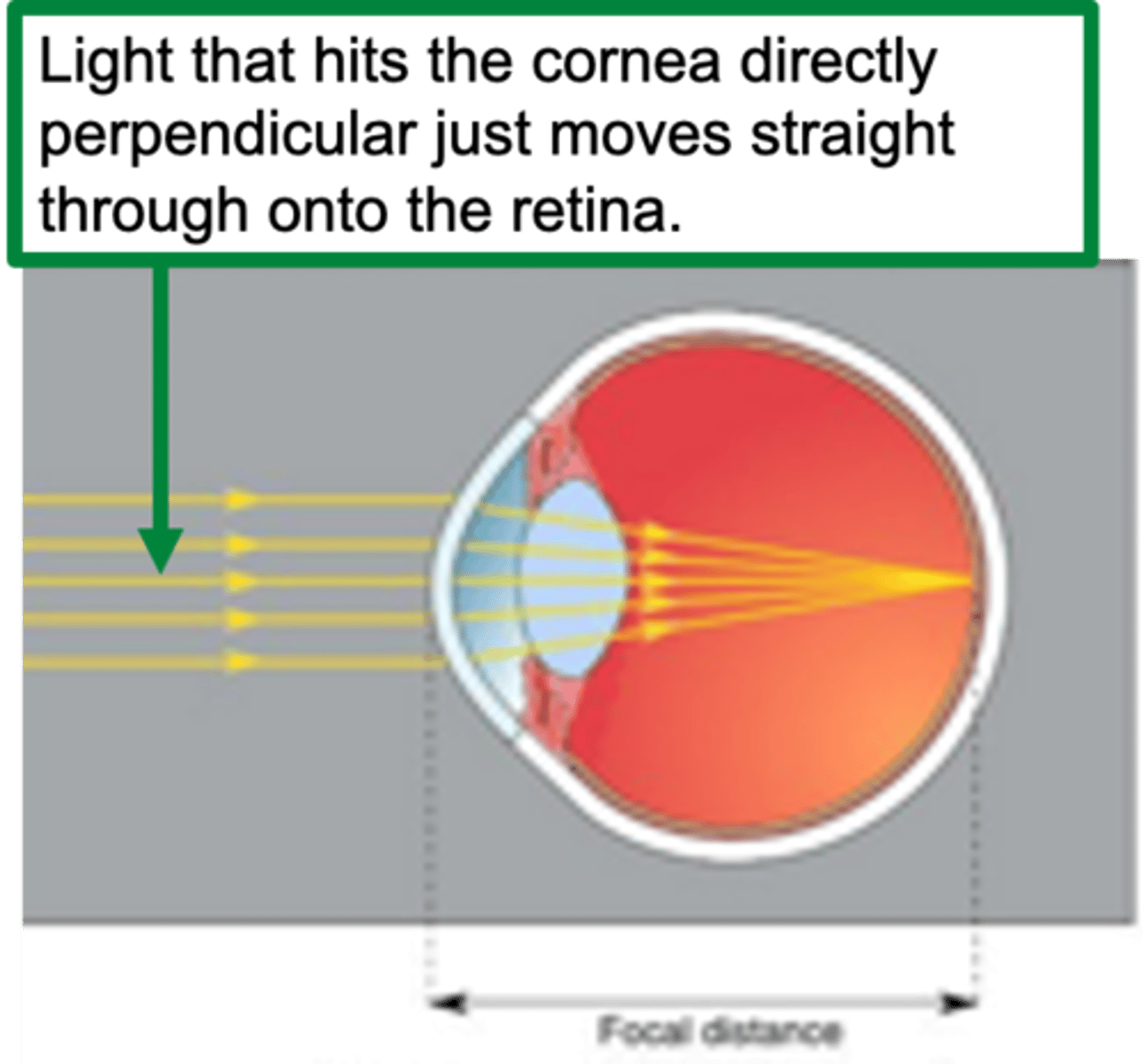
Focal distance
Distance from refractive surface to convergence of parallel light rays = ?
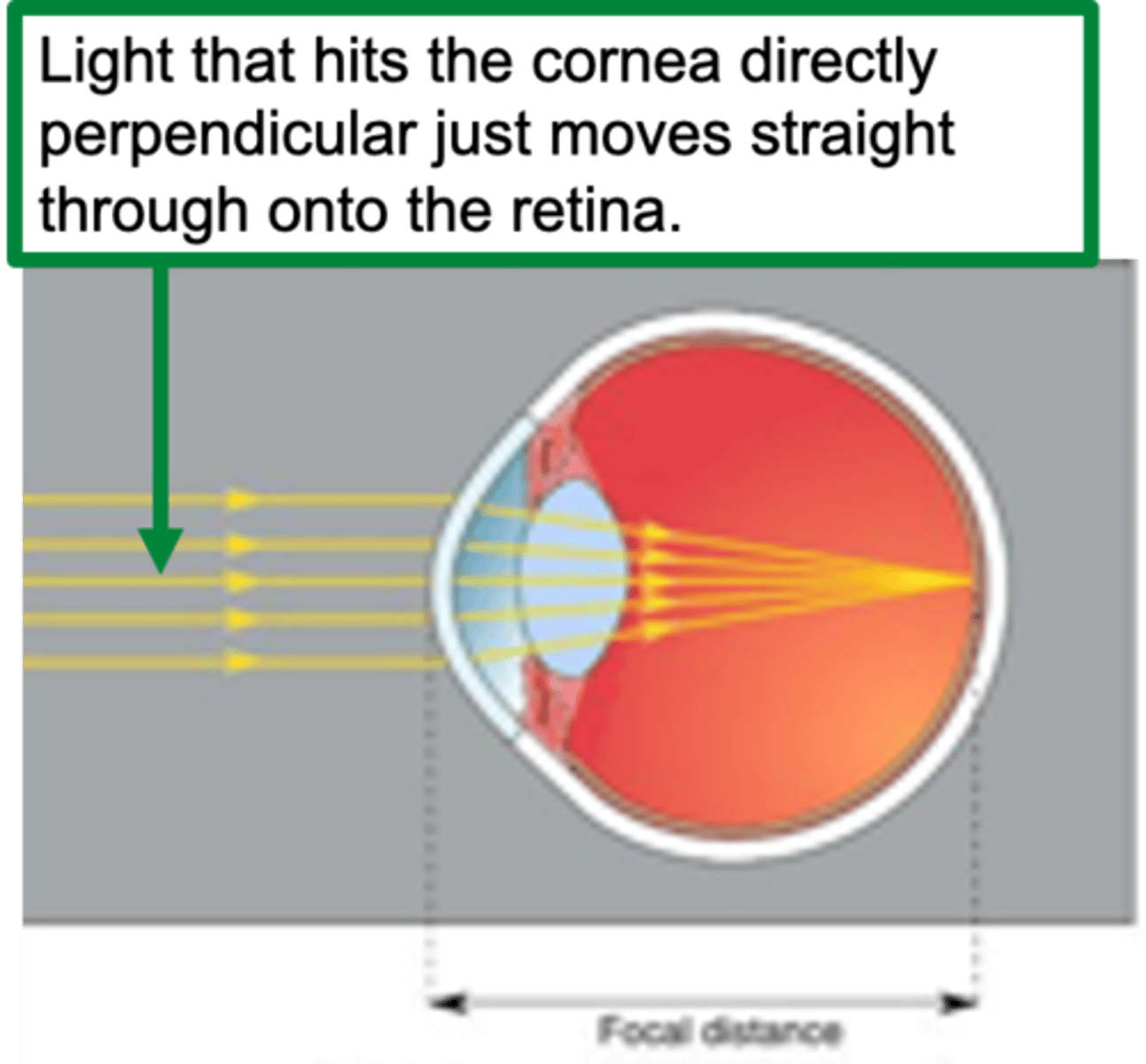
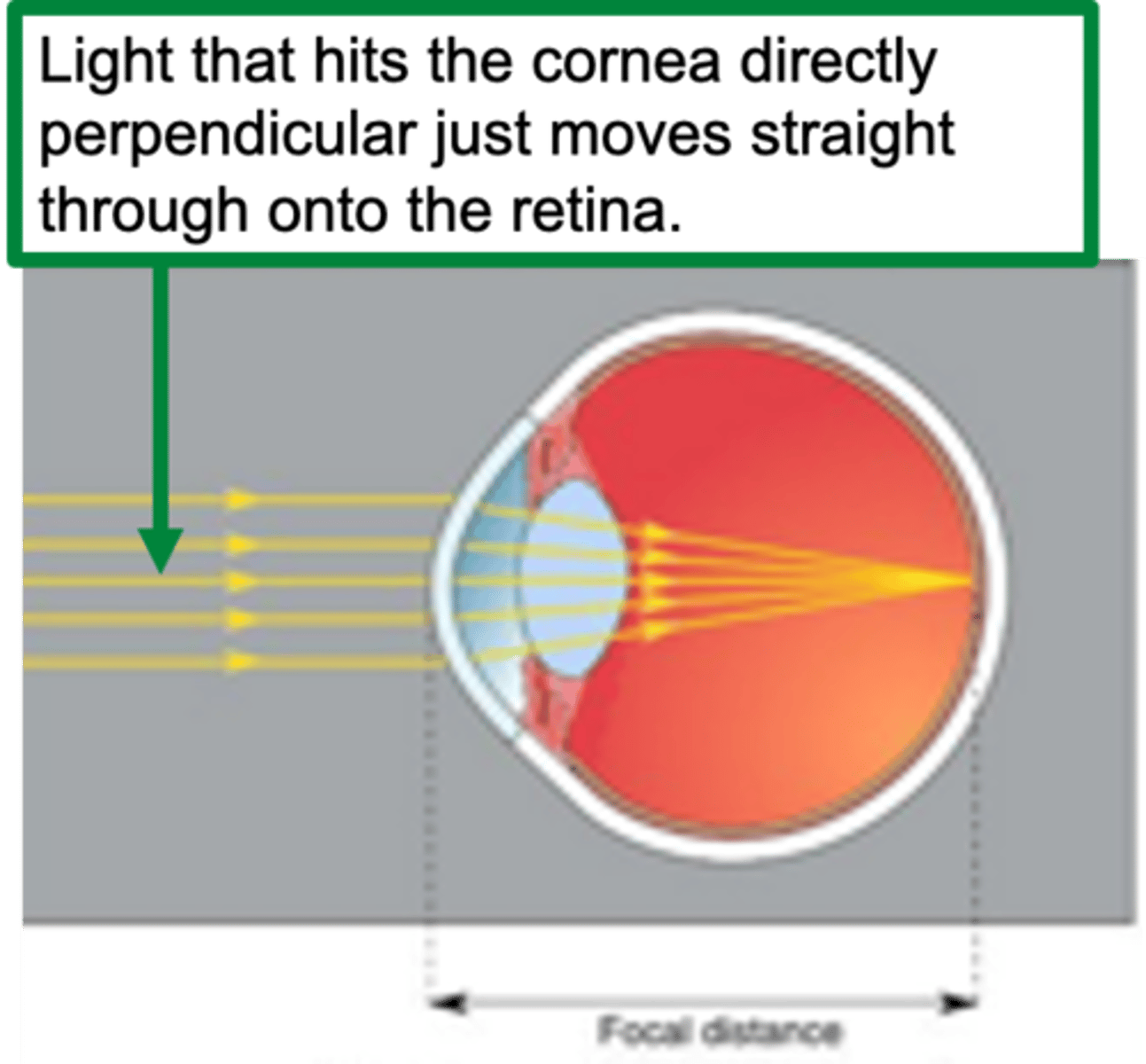
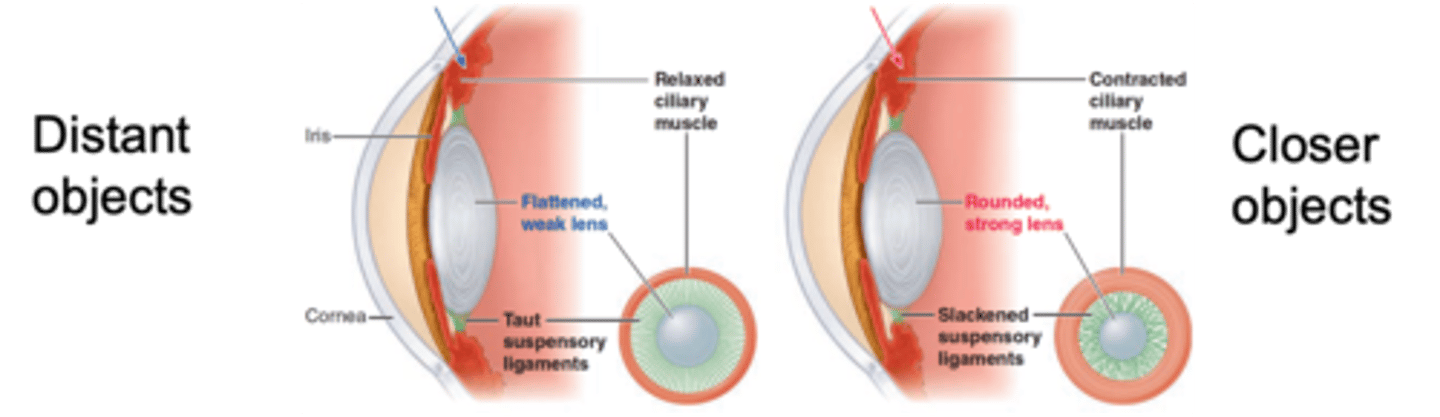
Almost parallel light rays
Cornea provides sufficient refraction to focus them on the retina
How does the lens accommodate distant objects?
Light rays are not parallel
Requires additional refraction to focus them on the retina
Provided by the flattening of the lens
How does the lens accommodate closer objects (<7m away)?
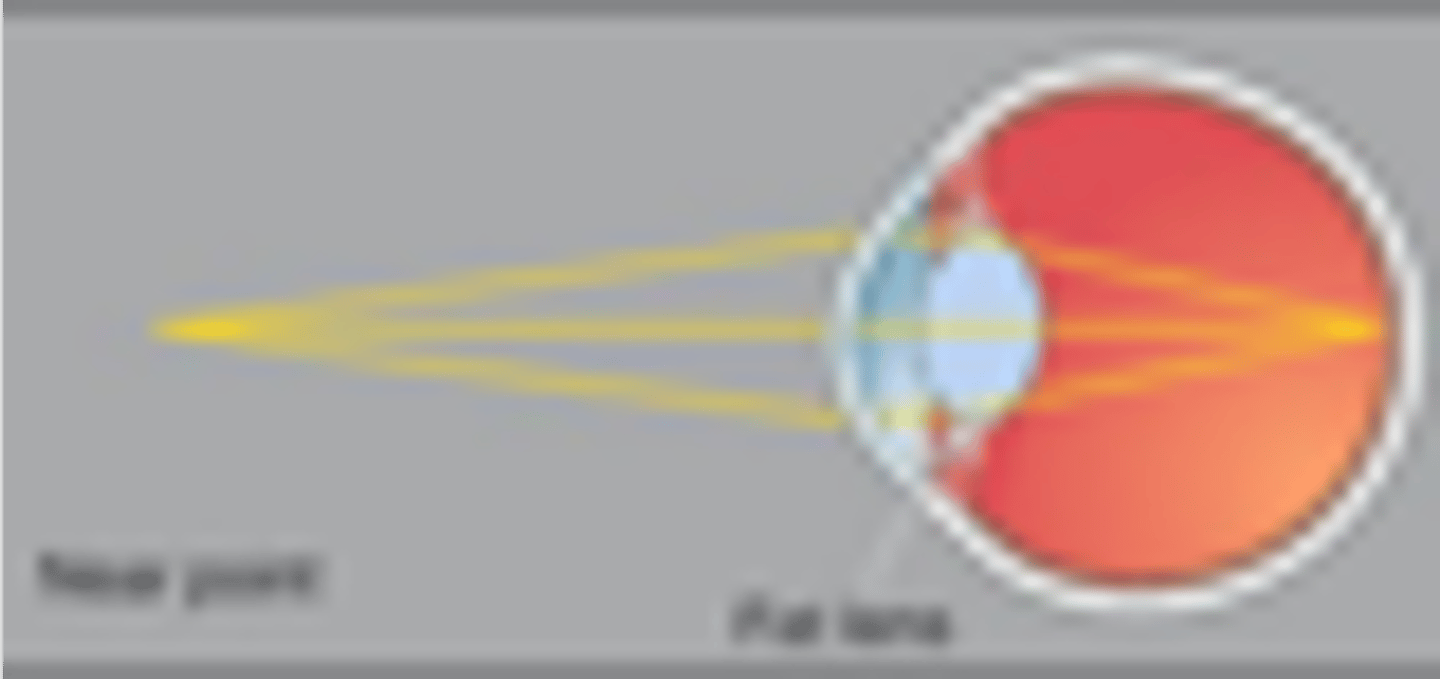
The refractive power to focus closer objects on the fovea
What does rounding of the lens increase and why is this done?
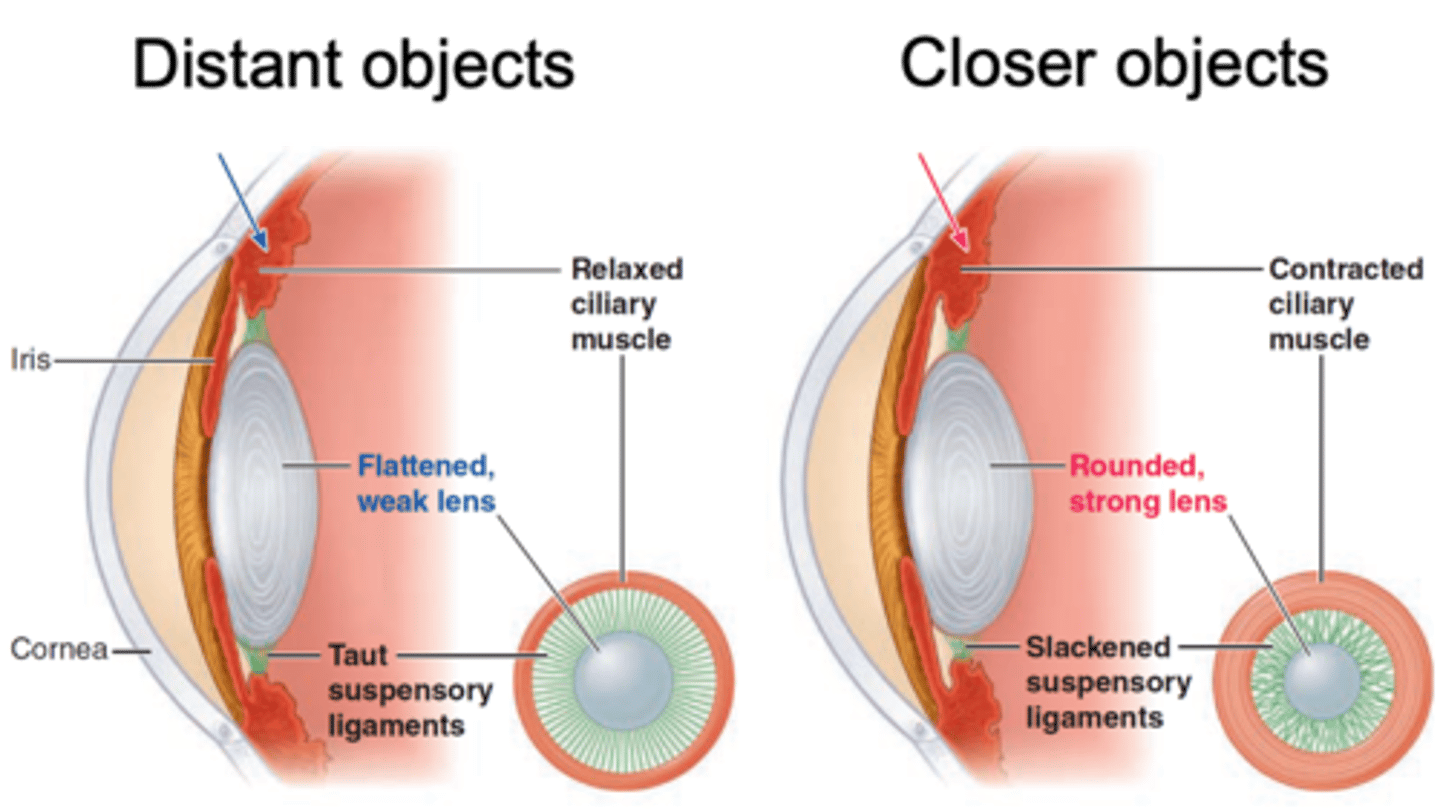
Elasticity, spherical
The lens has natural ____________ so if not stretched it will become more ___________
Emmetropic
Eye is ______________ when lens is flat and we are focussing a distant object
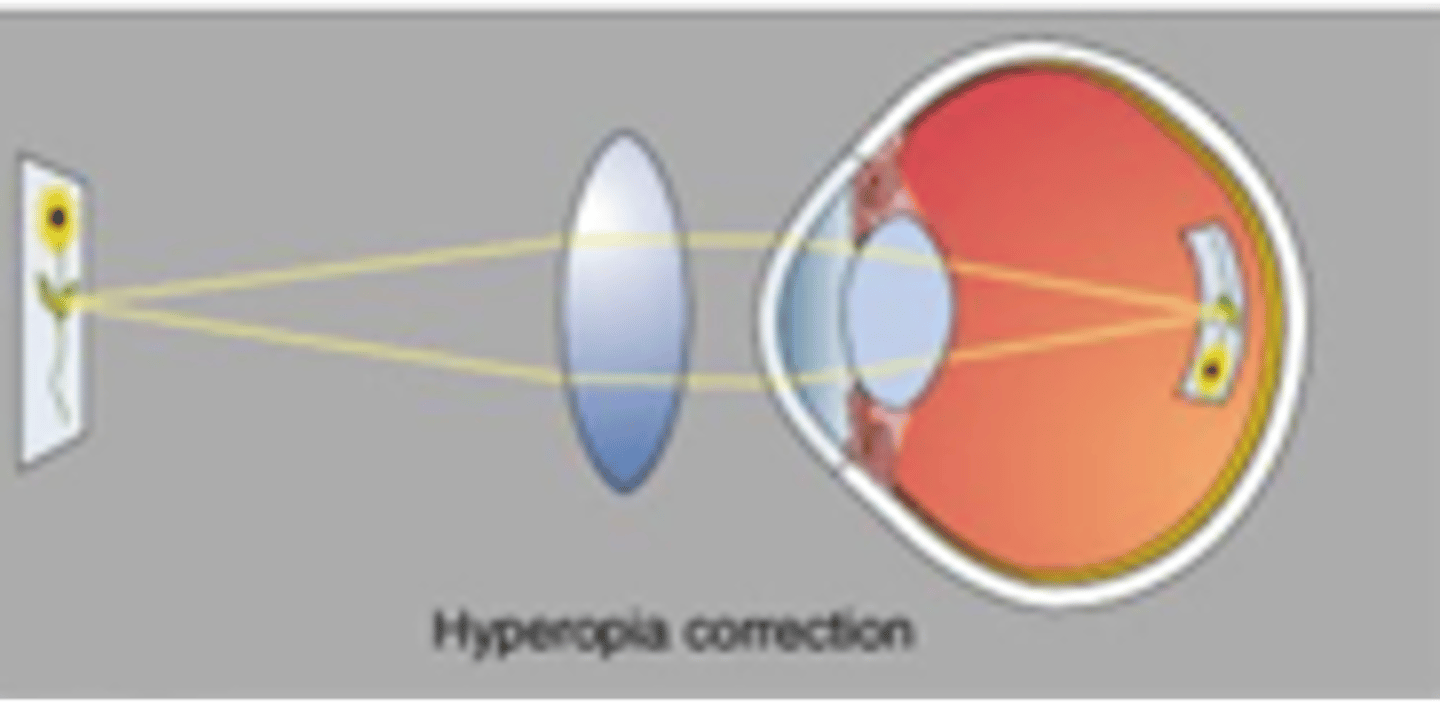
Eye is too short
Near objects are focussed behind the retina
Hyperopia is also referred to as farsightedness, describe this
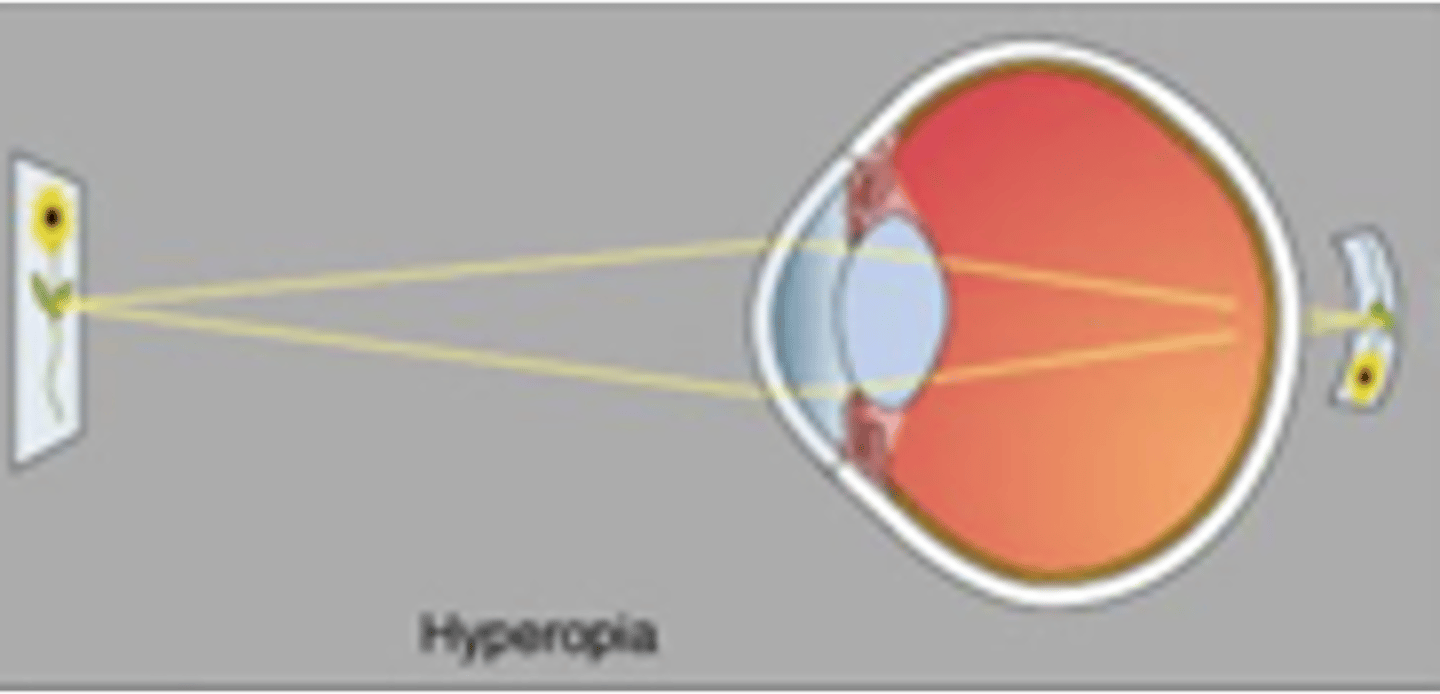
Farsightedness
What kind of sight problem would this lens fix?
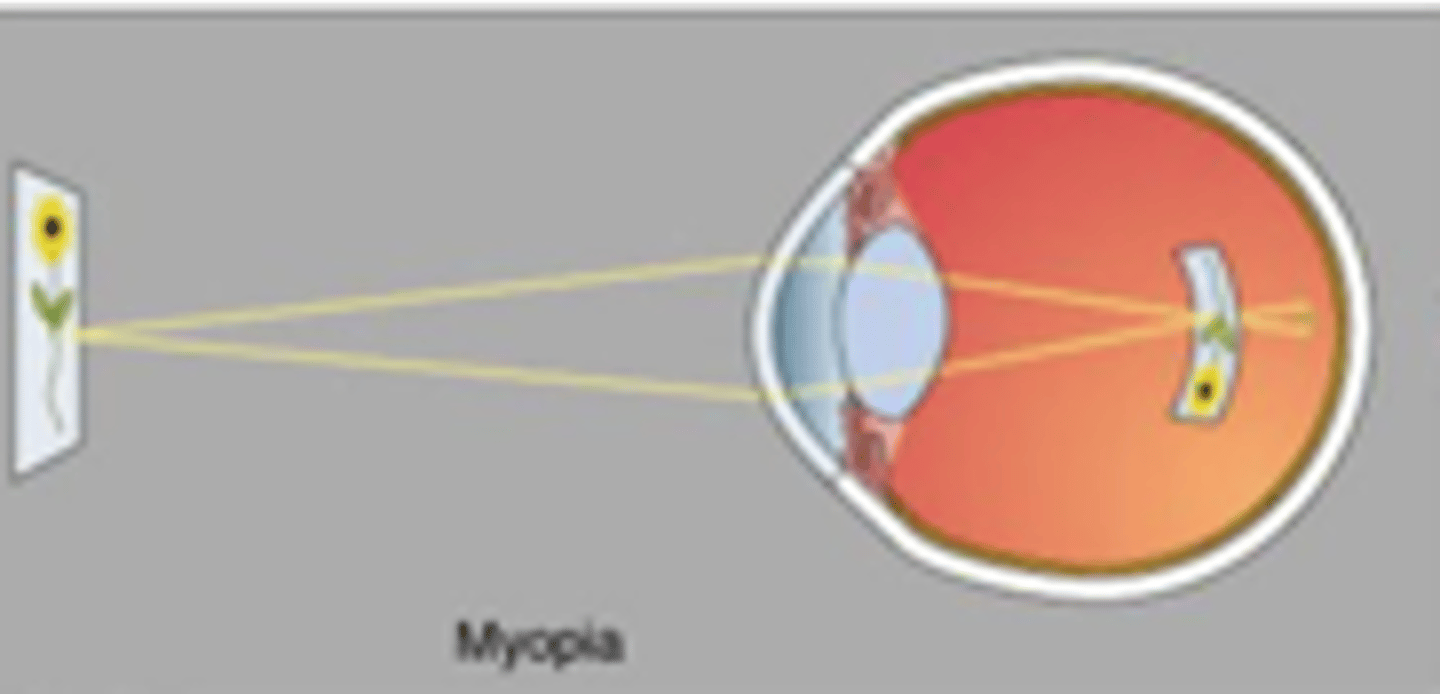
Eye is too long
Distant objects are focussed before retina
Too much refraction
Myopia is also known as near-sightedness, describe this
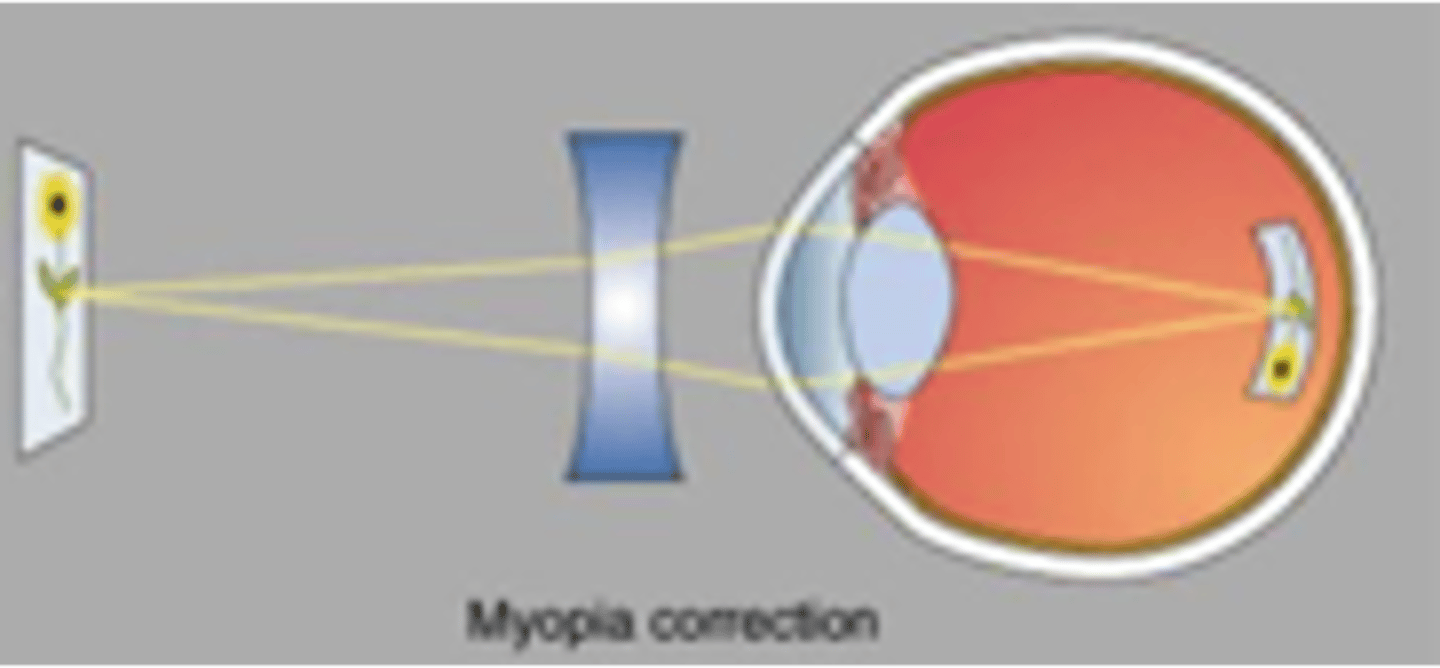
Near-sightedness
What kind of sight problem would this lens fix?
Cornea, fovea, retina, refraction
The _________ focuses most of the light on the _______ of the _______ due to the power of ______________
Accommodation of the lens, ciliary muscles
Closer objects require additional refraction, achieved by _________________ __ ____ _____ which is regulated by contraction and relaxation of the ____________ __________
Neural activity
What must the light focused on the retina be converted into?
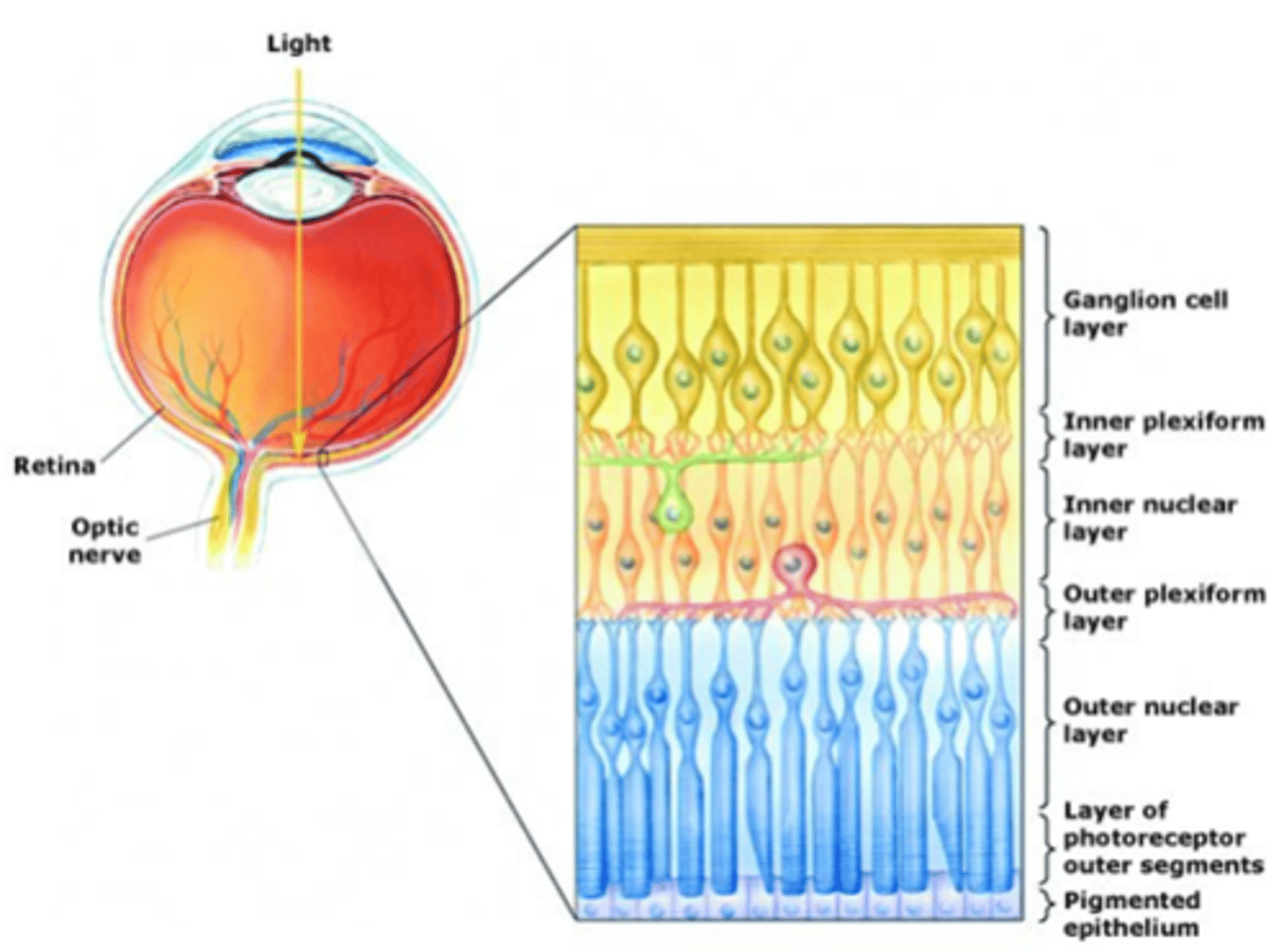
Ganglion cells, bipolar cells
Light must pass through ____________ _____ and ___________ ______ before it reaches the photoreceptors
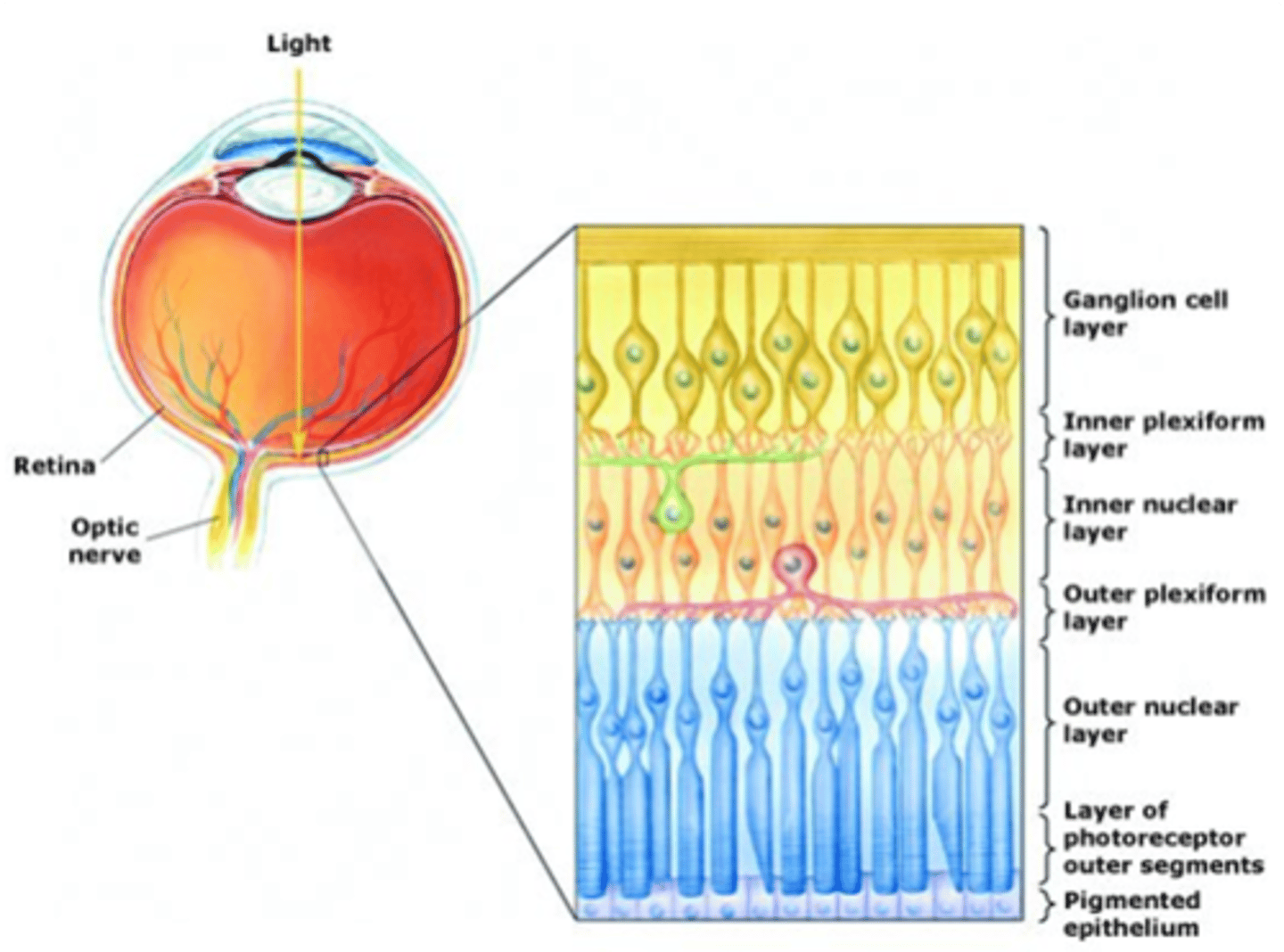
The pigmented epithelium
Light that passes all the way through the retina is absorbed by ...?
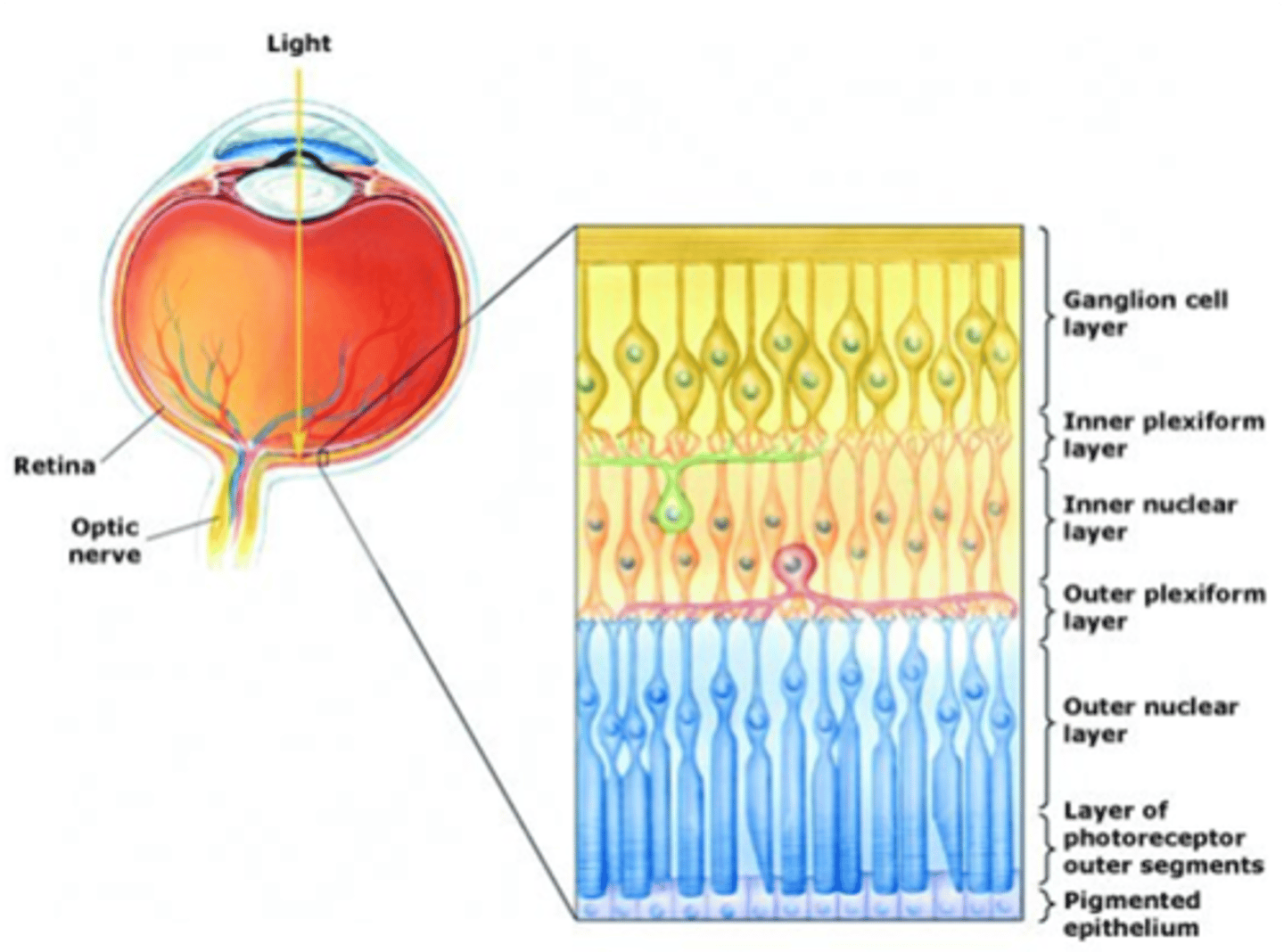
Layers are organised in reference to centre of the eye (i.e. photoreceptors are in the outer layer)
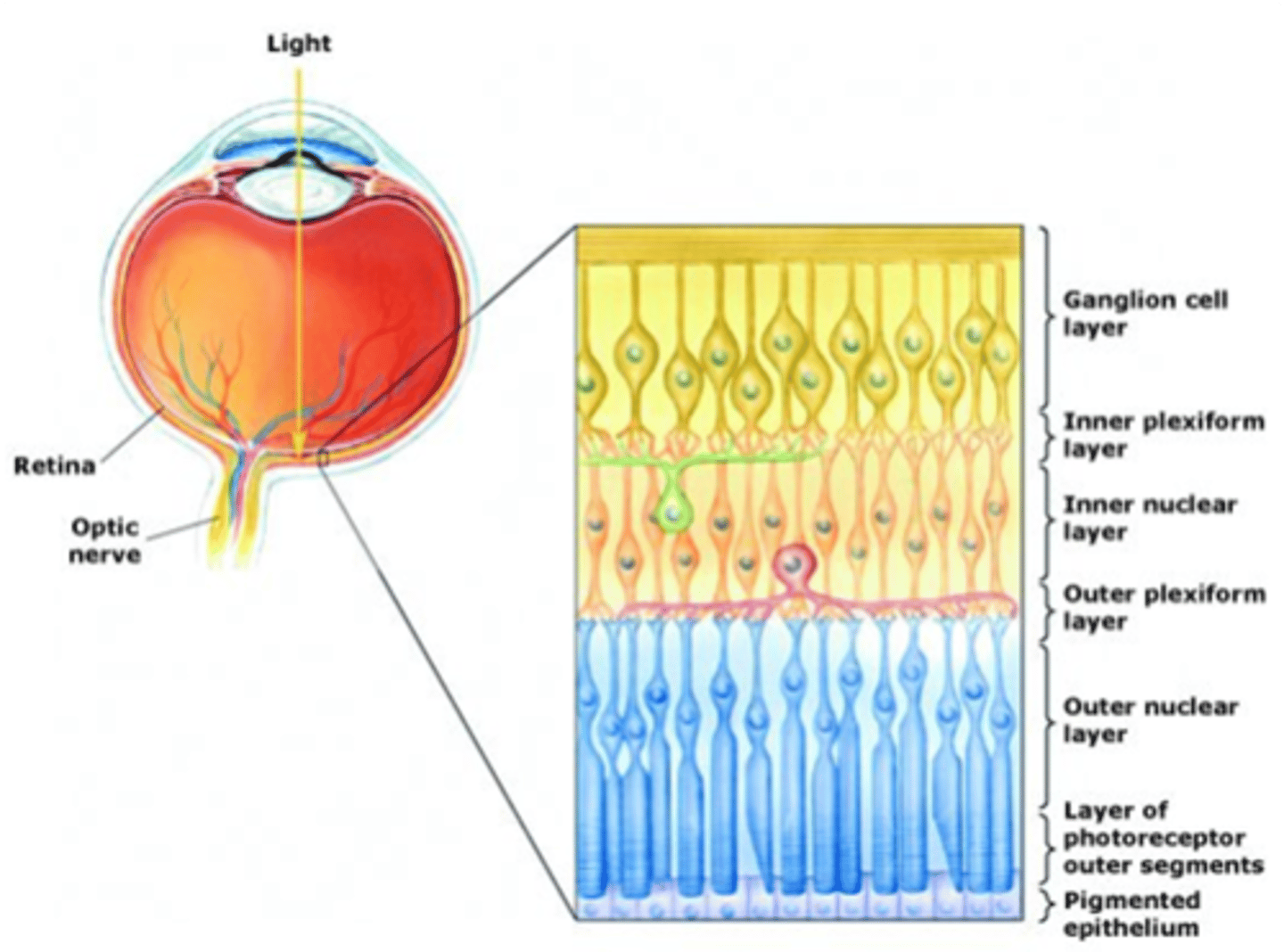
Cell bodies
What does the nuclear layer contain?
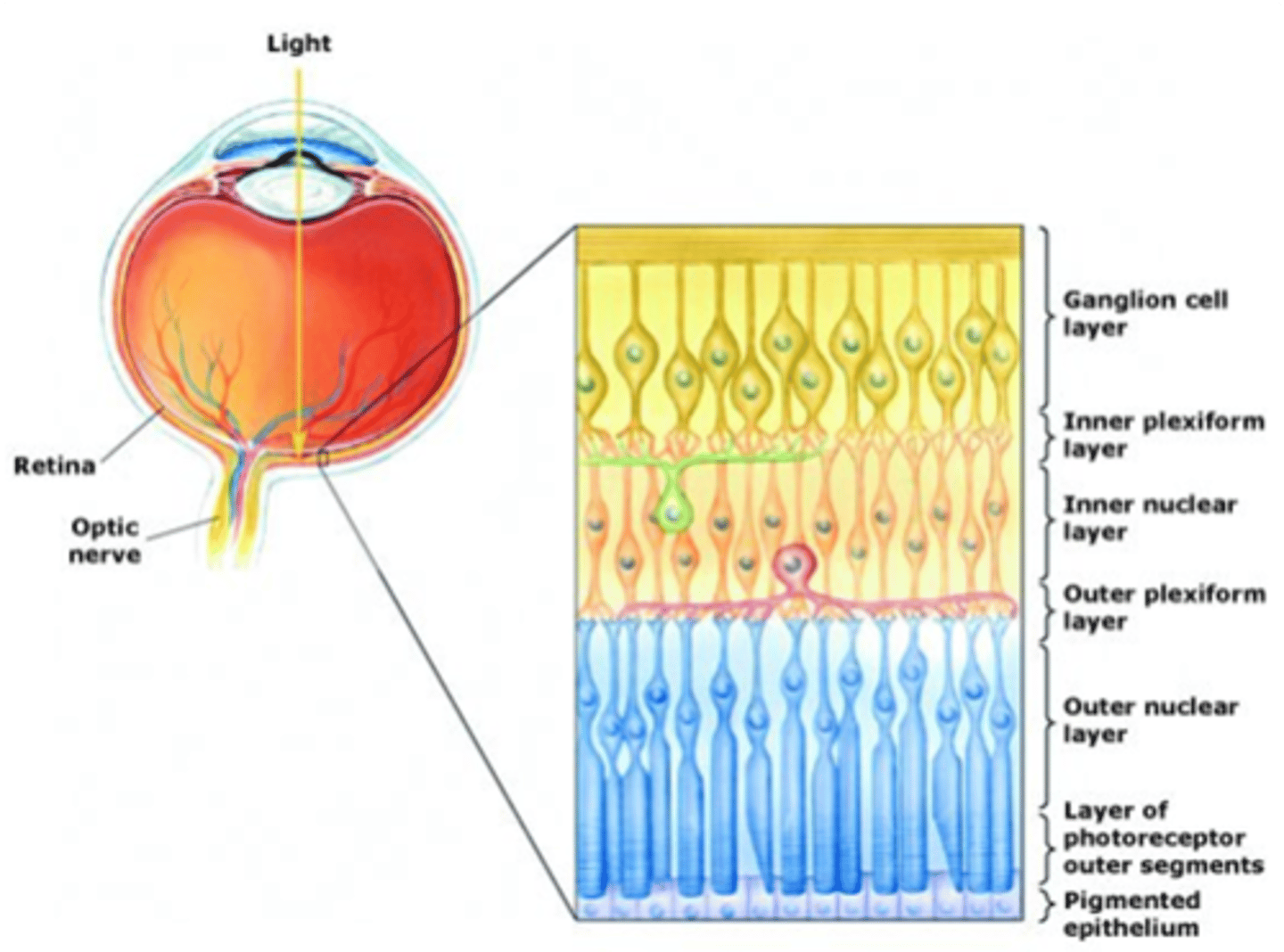
Synaptic connections
What occurs in plexiform layers?
Ganglion cells, amacrine cells, bipolar cells, horizontal cells, photoreceptors
What are the 5 cells of the retina?
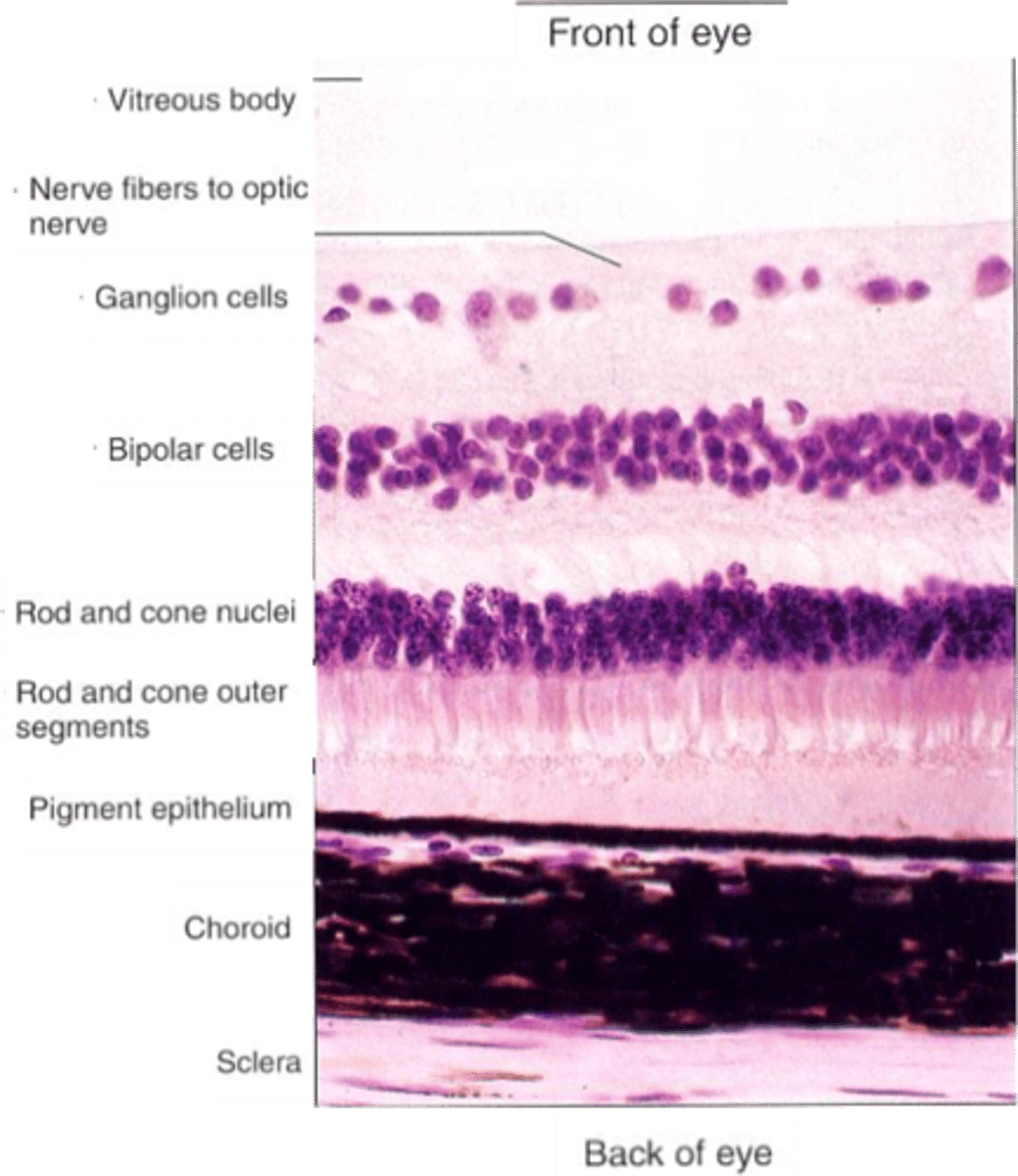
Output from retina
What do ganglion cells do?
Modulate information transfer between GCs and BCs
What do amacrine cells do?
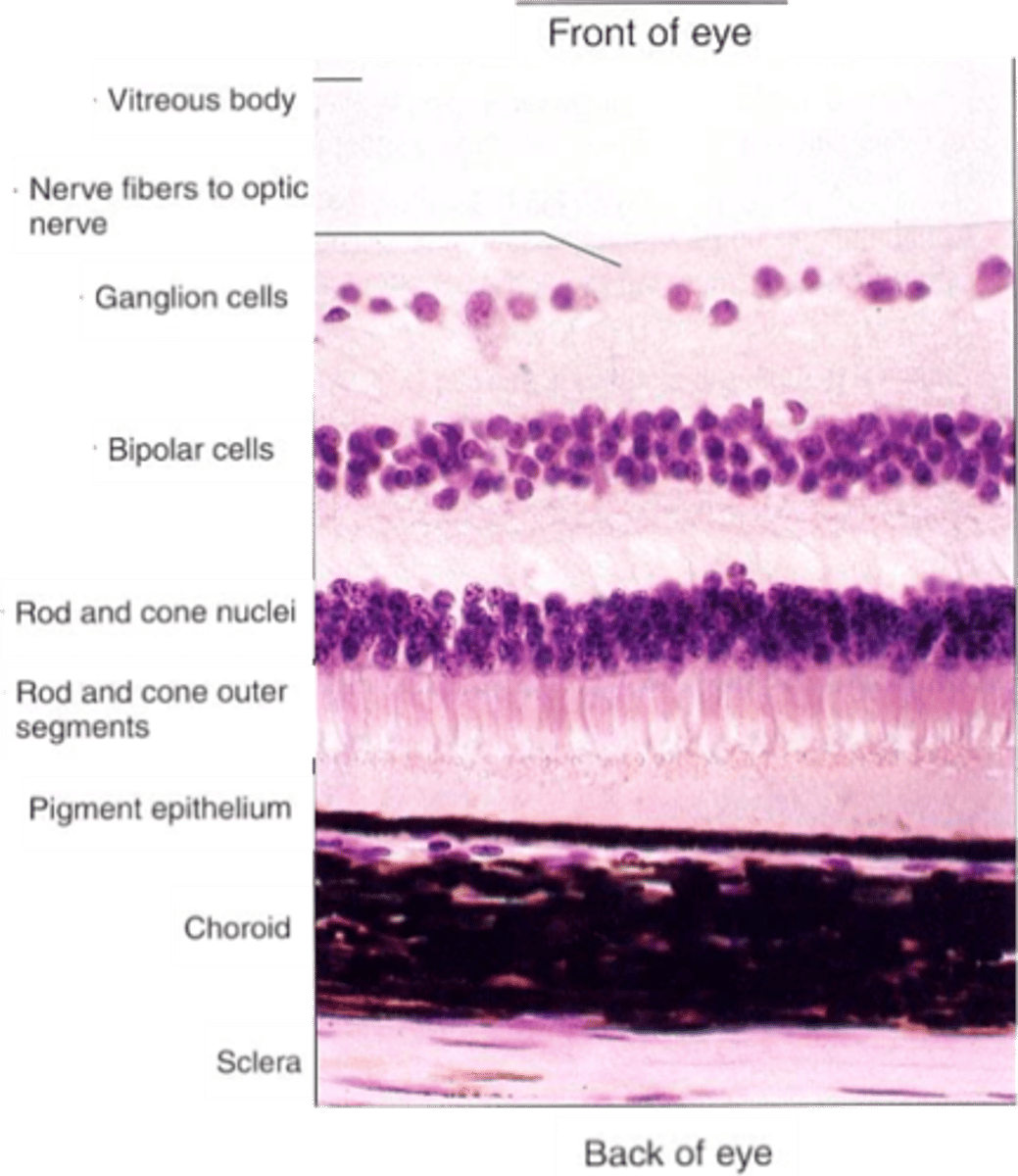
Connect photoreceptors to ganglion cells
What do bipolar cells do?
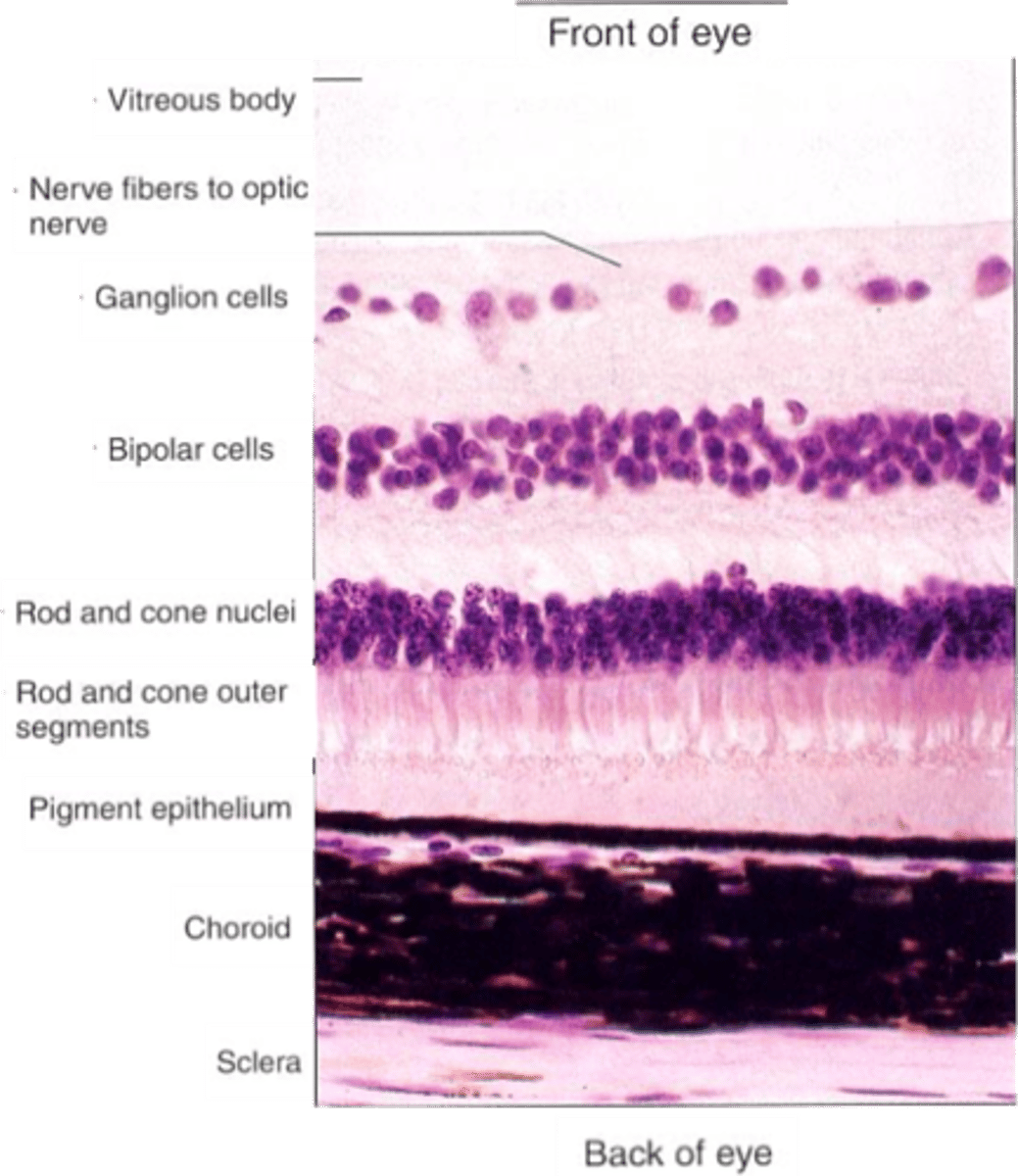
Modulate information transfer between photoreceptor and BCs
What do horizontal cells do?
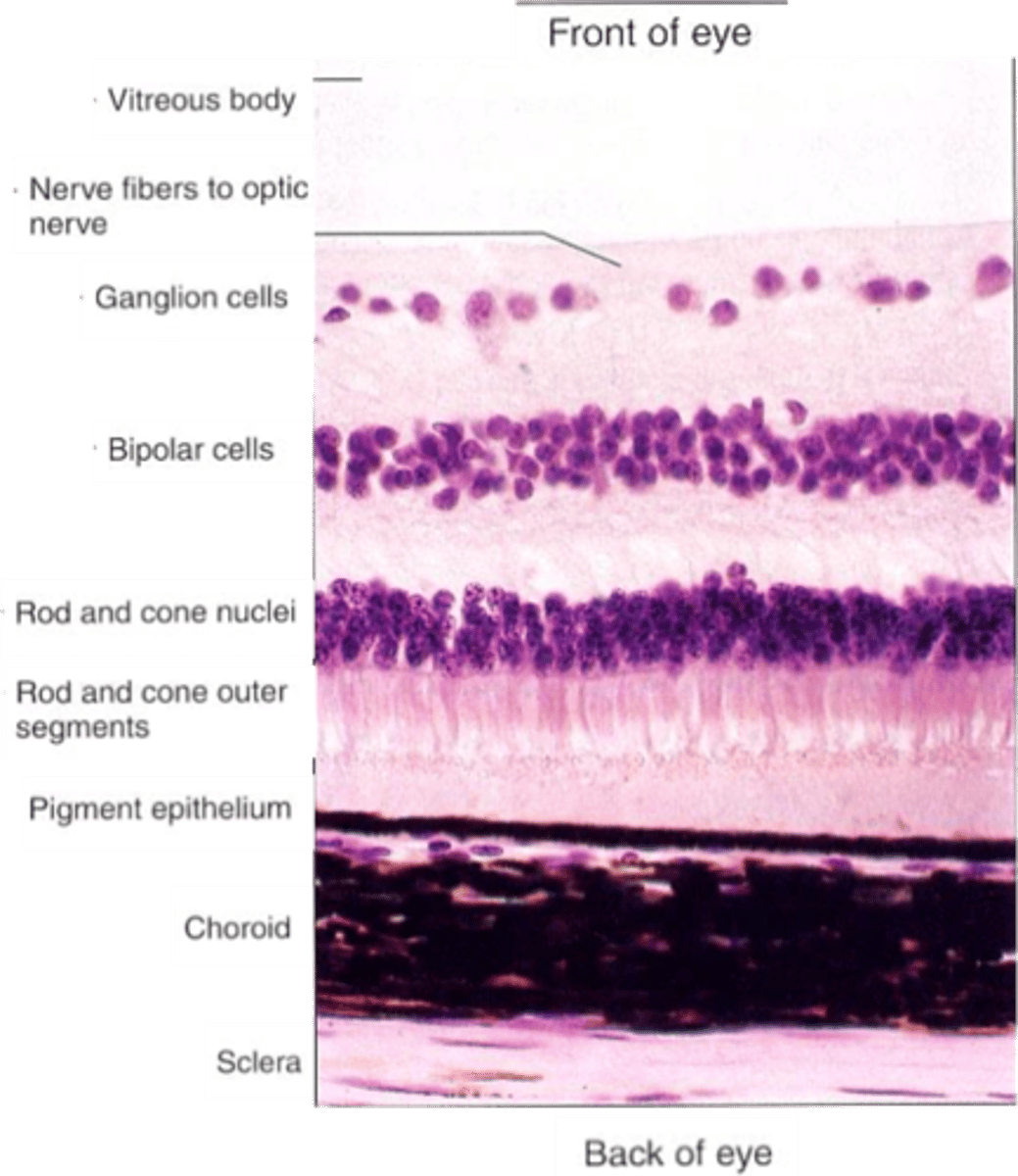
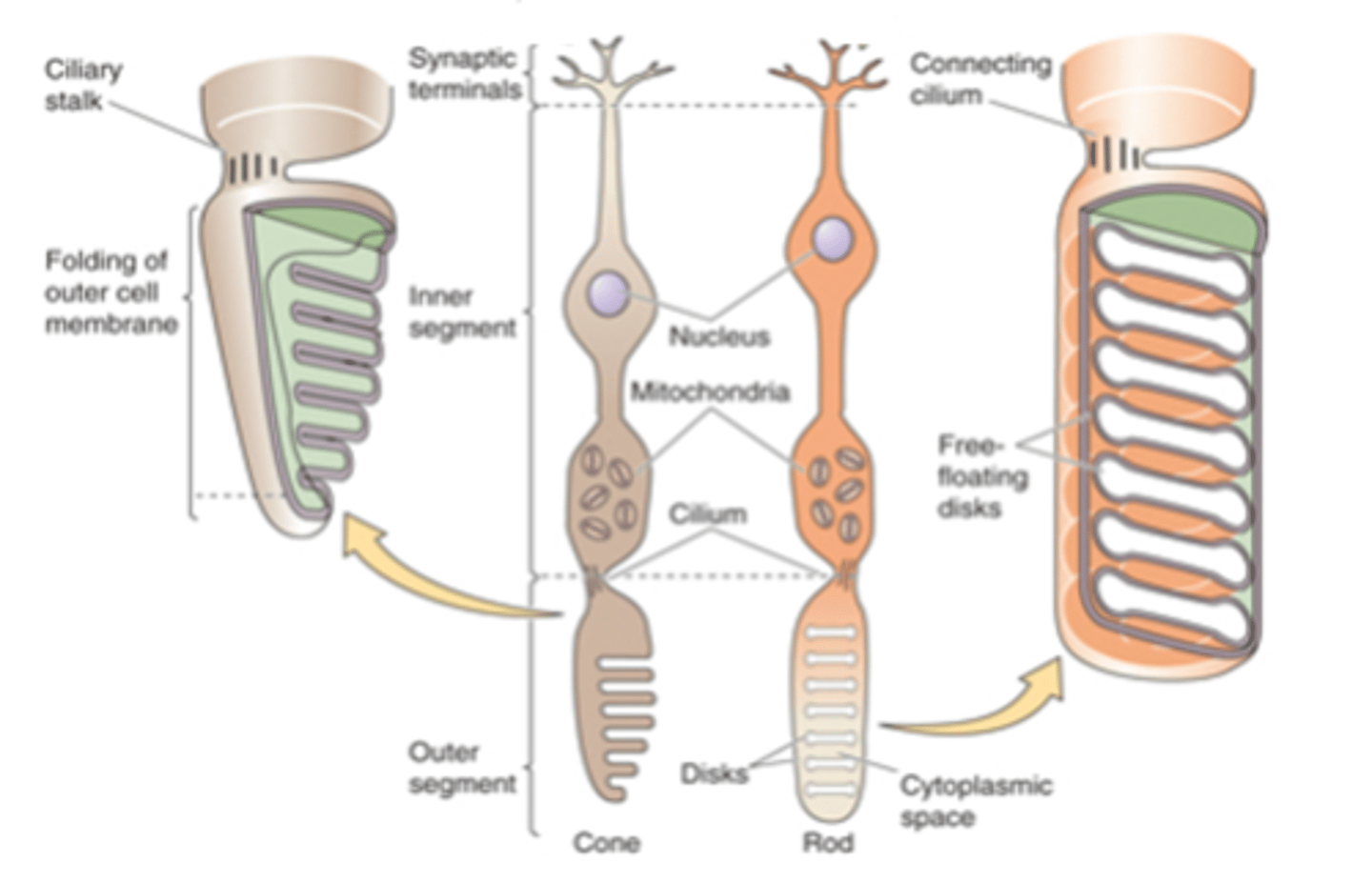
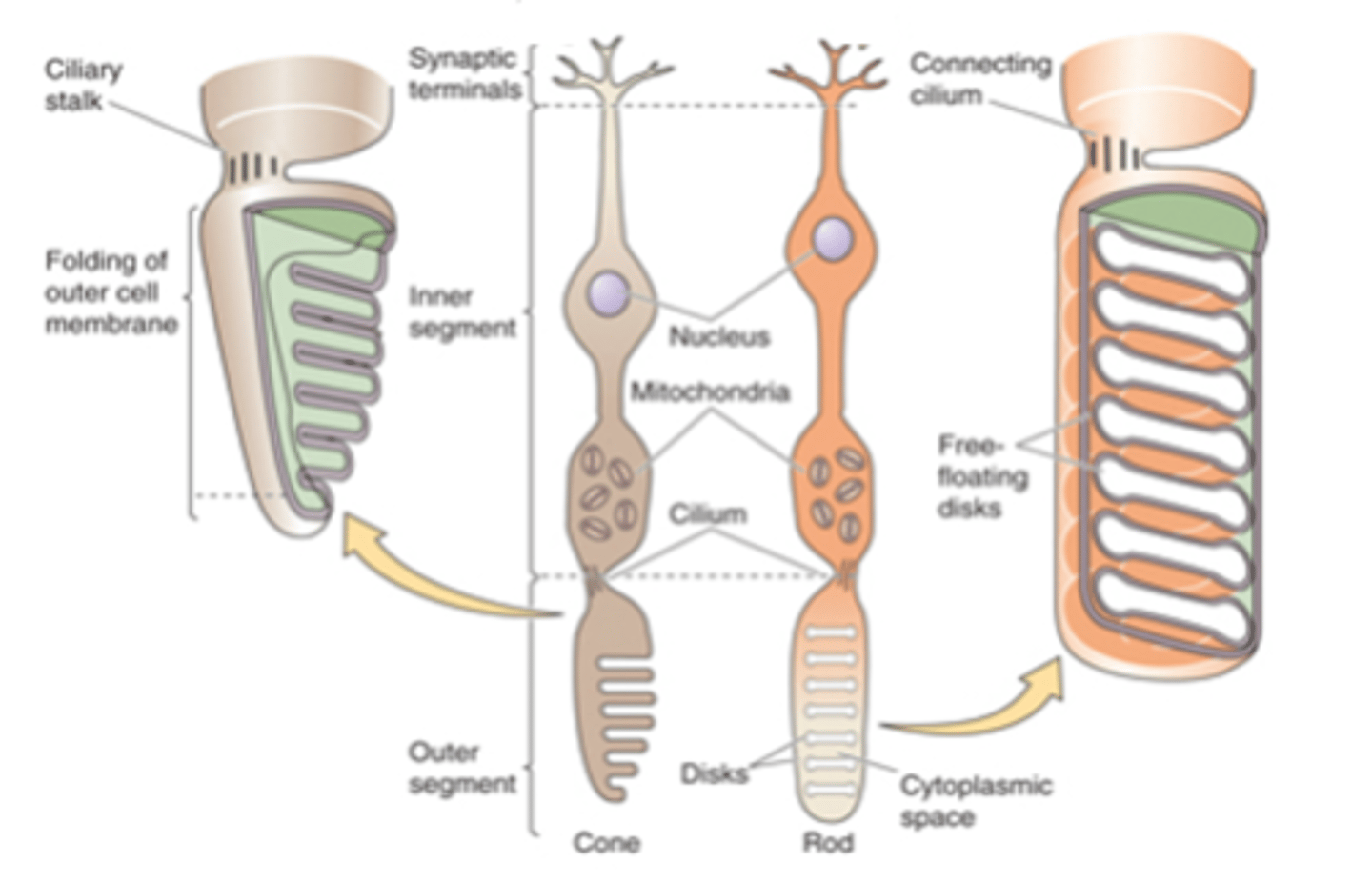
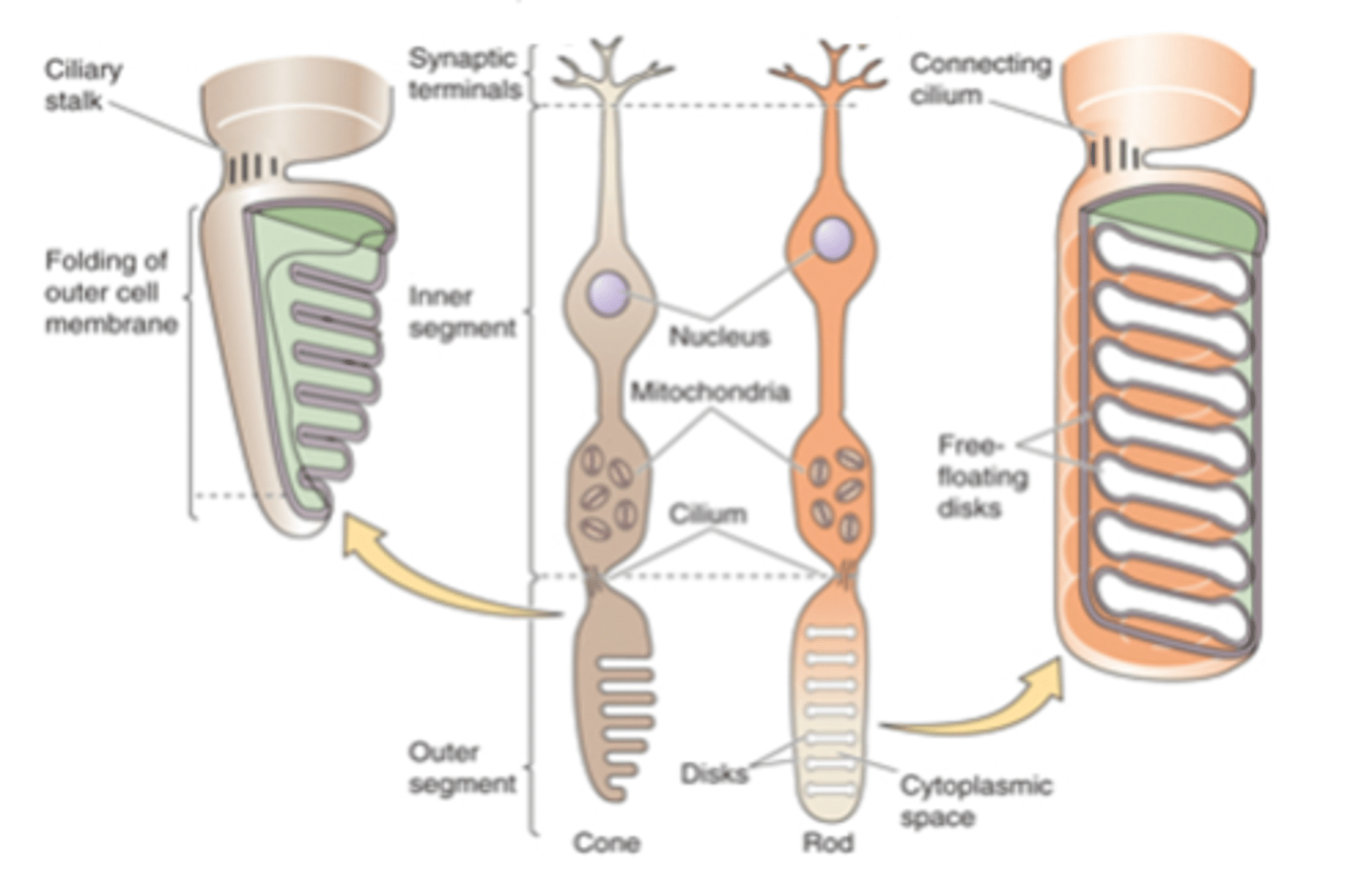
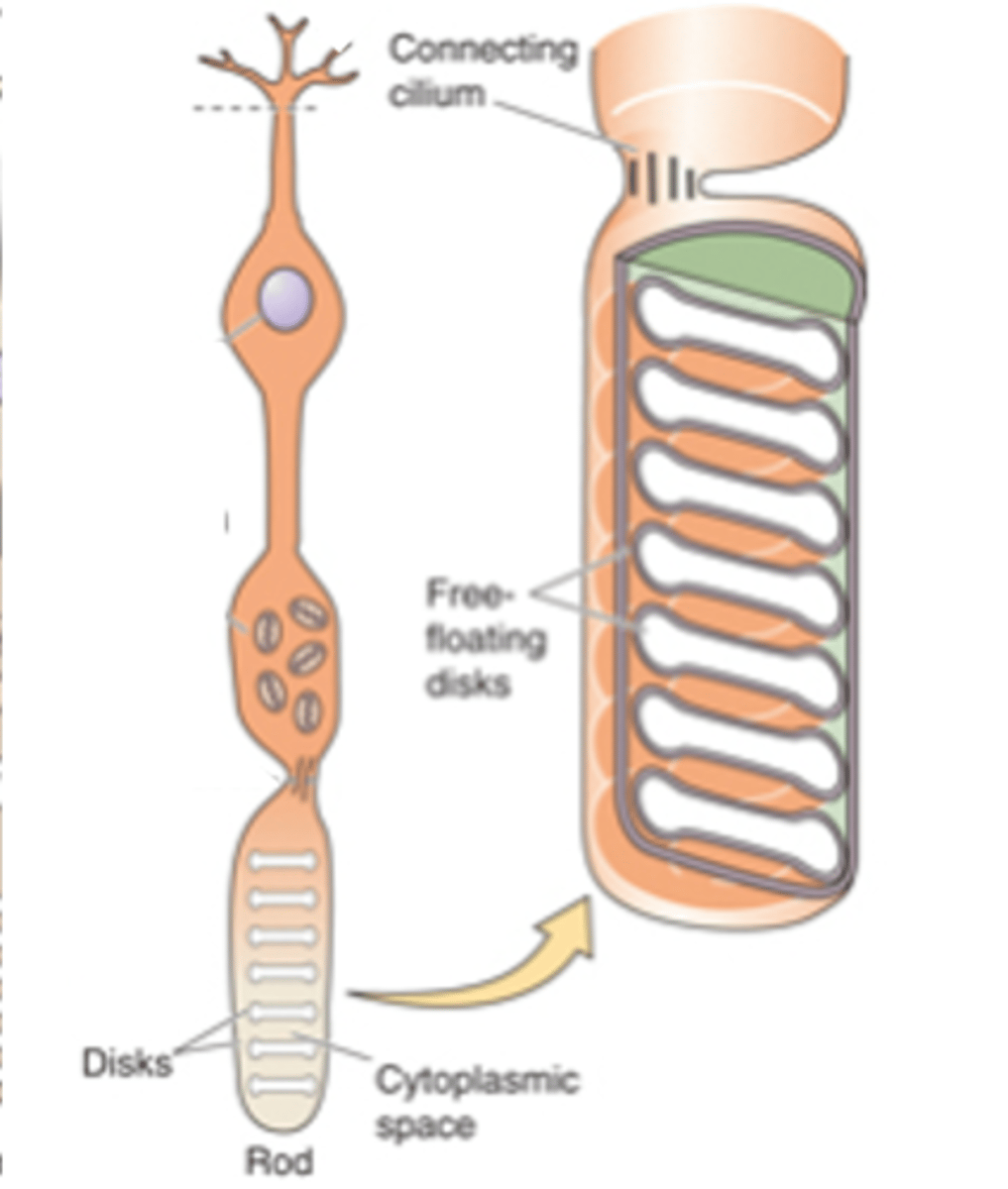
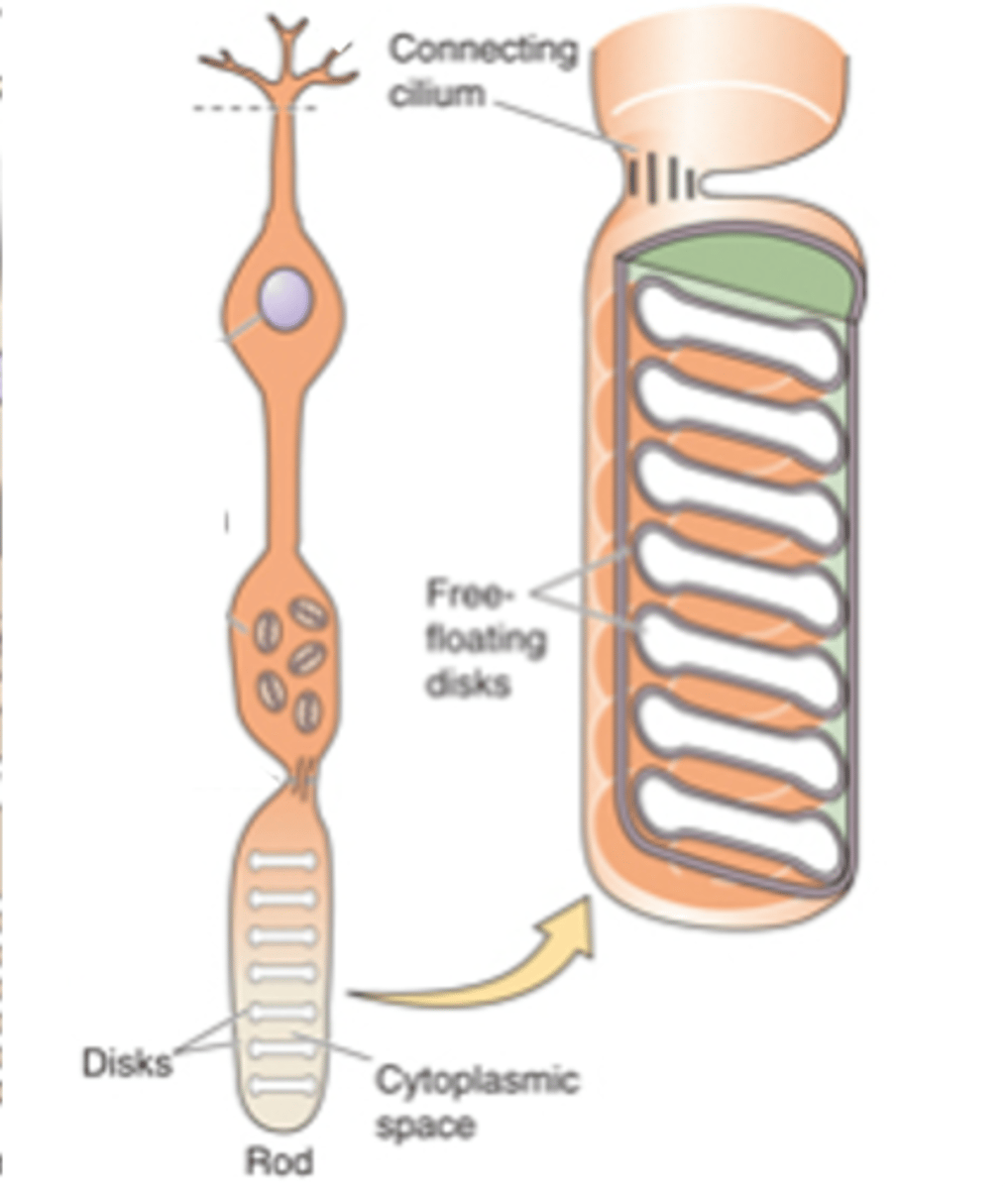
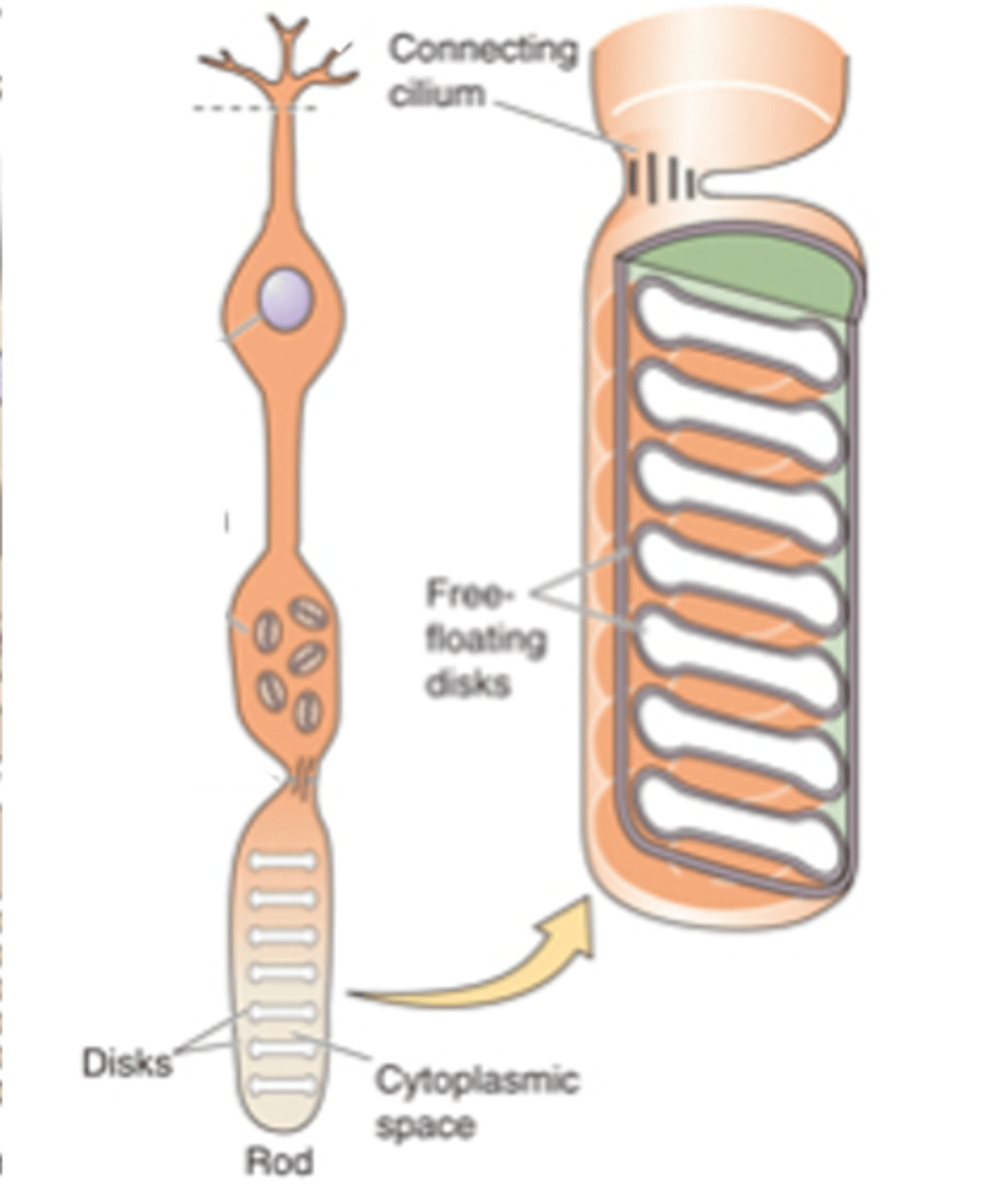
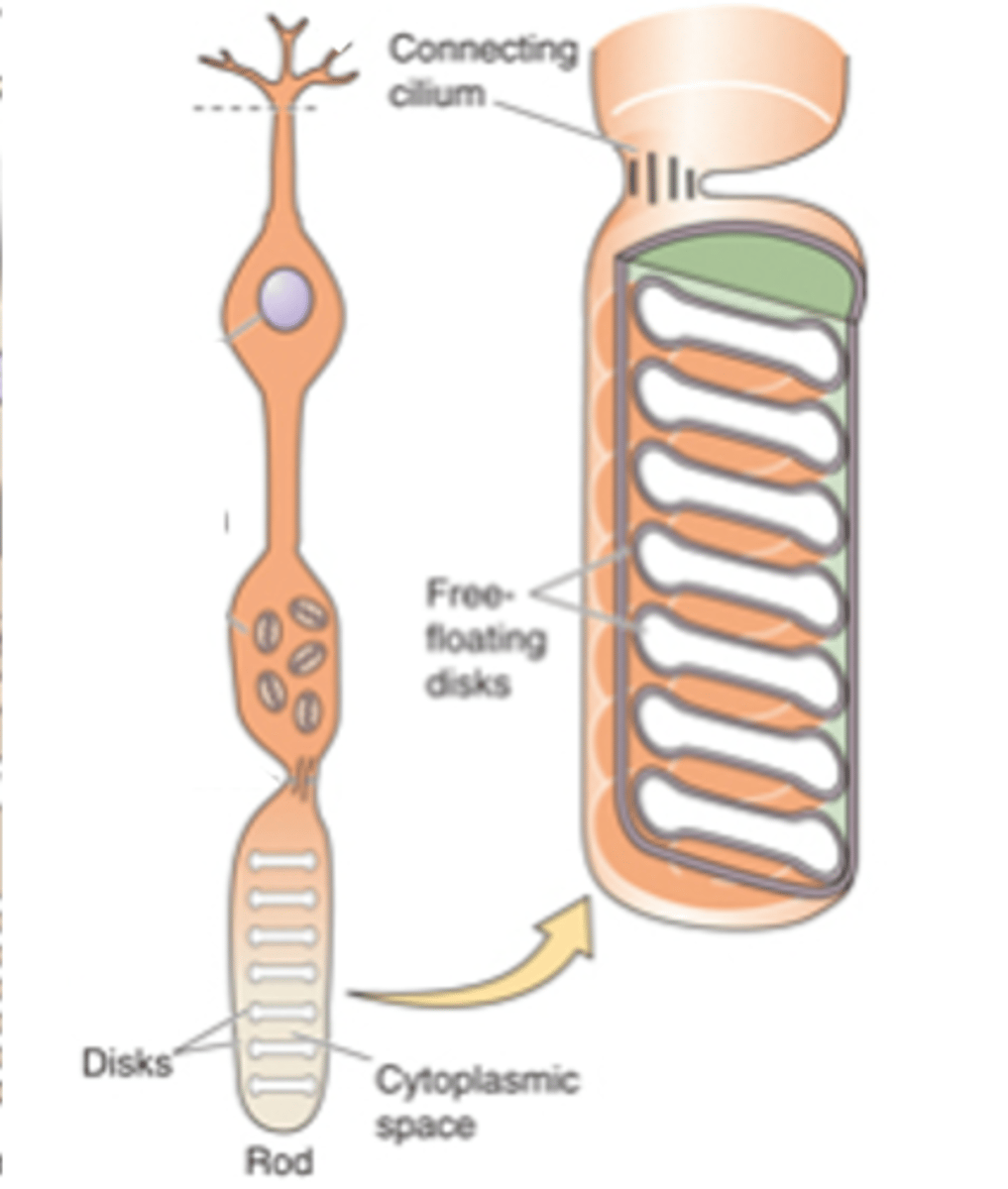
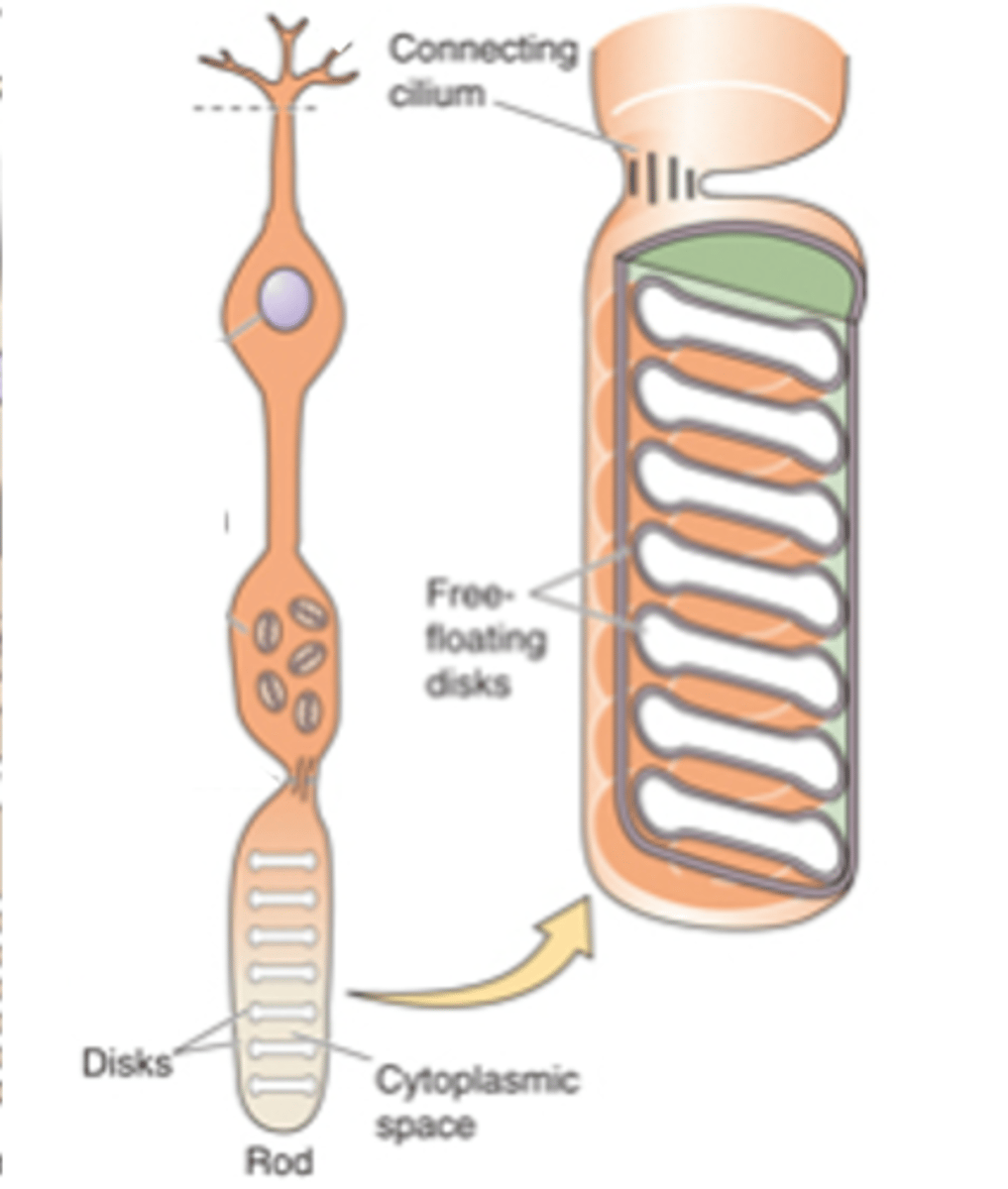
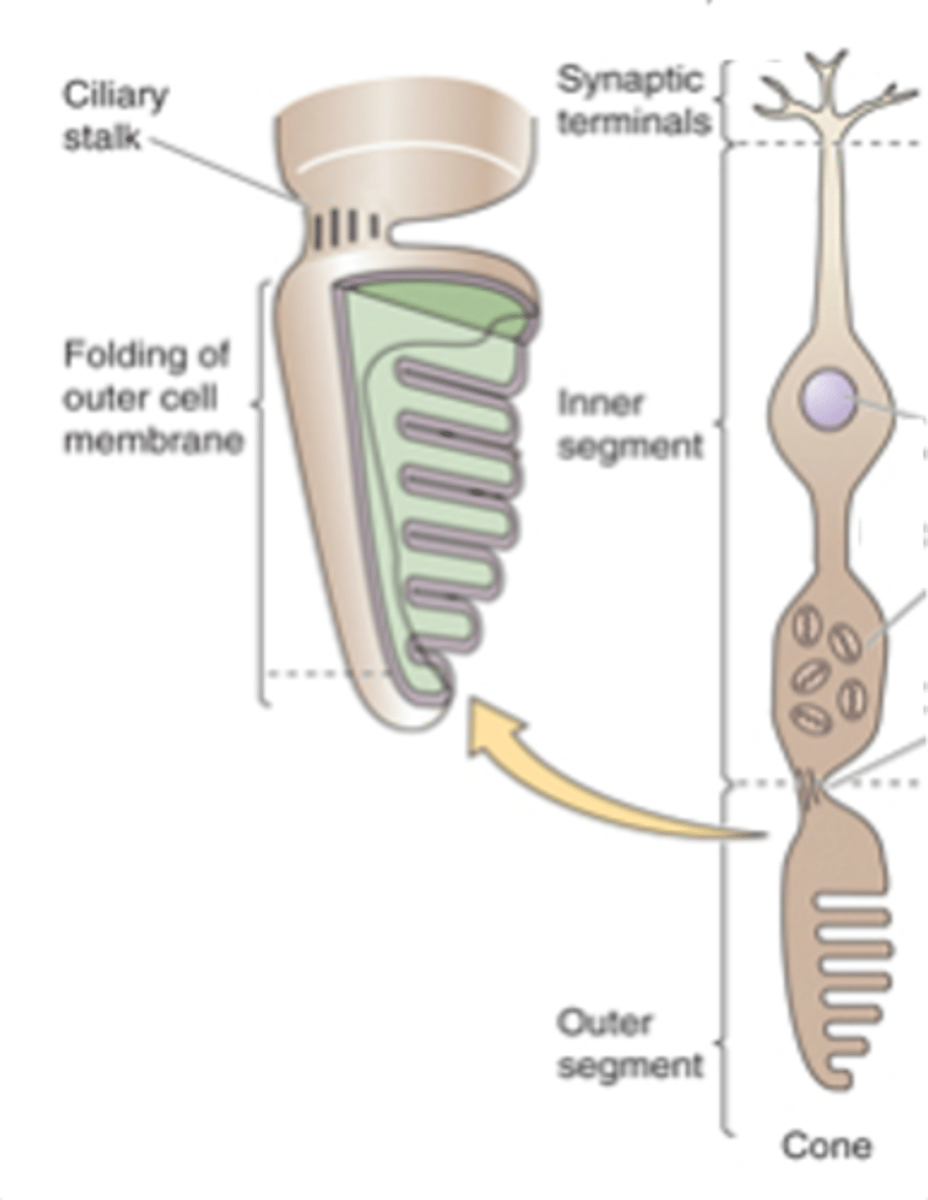
Sensory transducers, both rods and cones
What are photoreceptors?
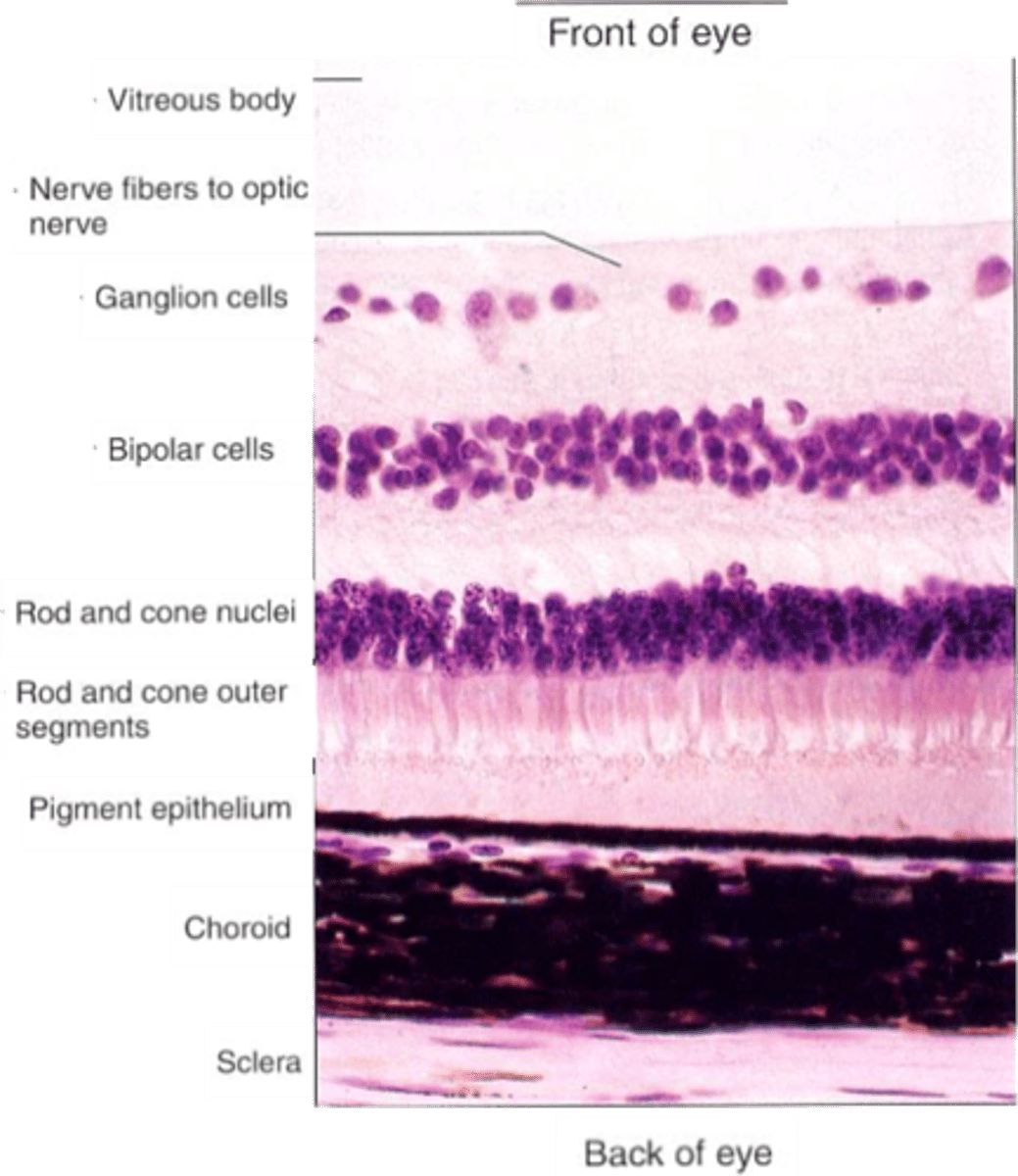
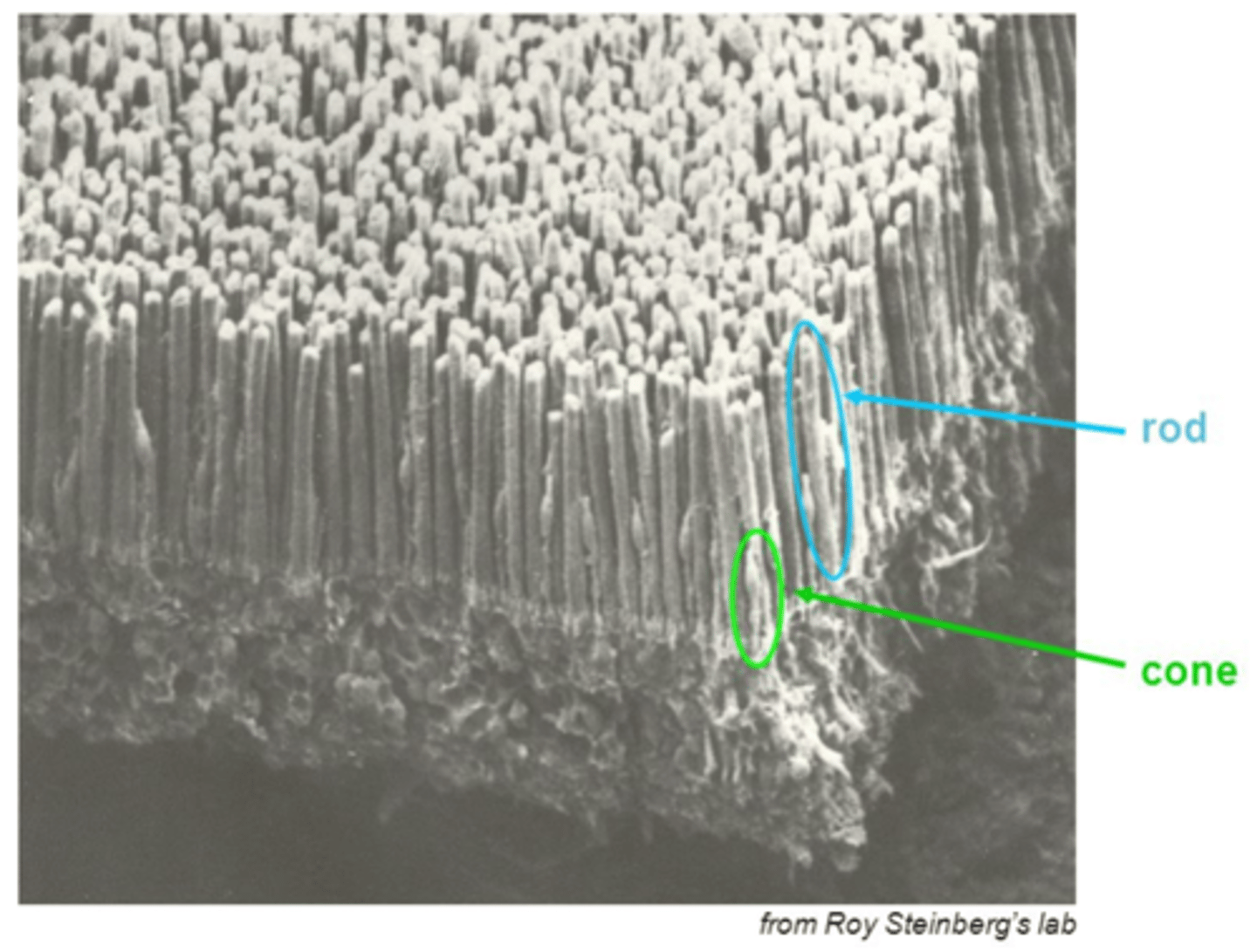
This image shows photoreceptors from the toad retina using scanning electron microscopy

Light-sensitive photopigments, light
Photoreceptors contain membranous disks which contain ______-___________ ______________ that absorb _______
Can't have high sensitivity and high resolution in single receptor
What is the duplicity theory?
True
There are separate systems for monochrome and colour (True or False)
Greater, higher, more
Rod photoreceptors have a _________ number of disks and a _________ photopigment concentration within each disk - meaning they are _____ likely to absorb photons
1000
Rods are ____ times more sensitive to light than cones
Vision in low light (scotopic) conditions (i.e. at night time)
What do rods enable?
Visual acuity/resolution
Rod photoreceptors have low _______ _______/_____________
92 million
There are ~__ _________ rods in each human retina
Fewer, lower
Cone photoreceptors have ________ disks so ________ photopigment concentration
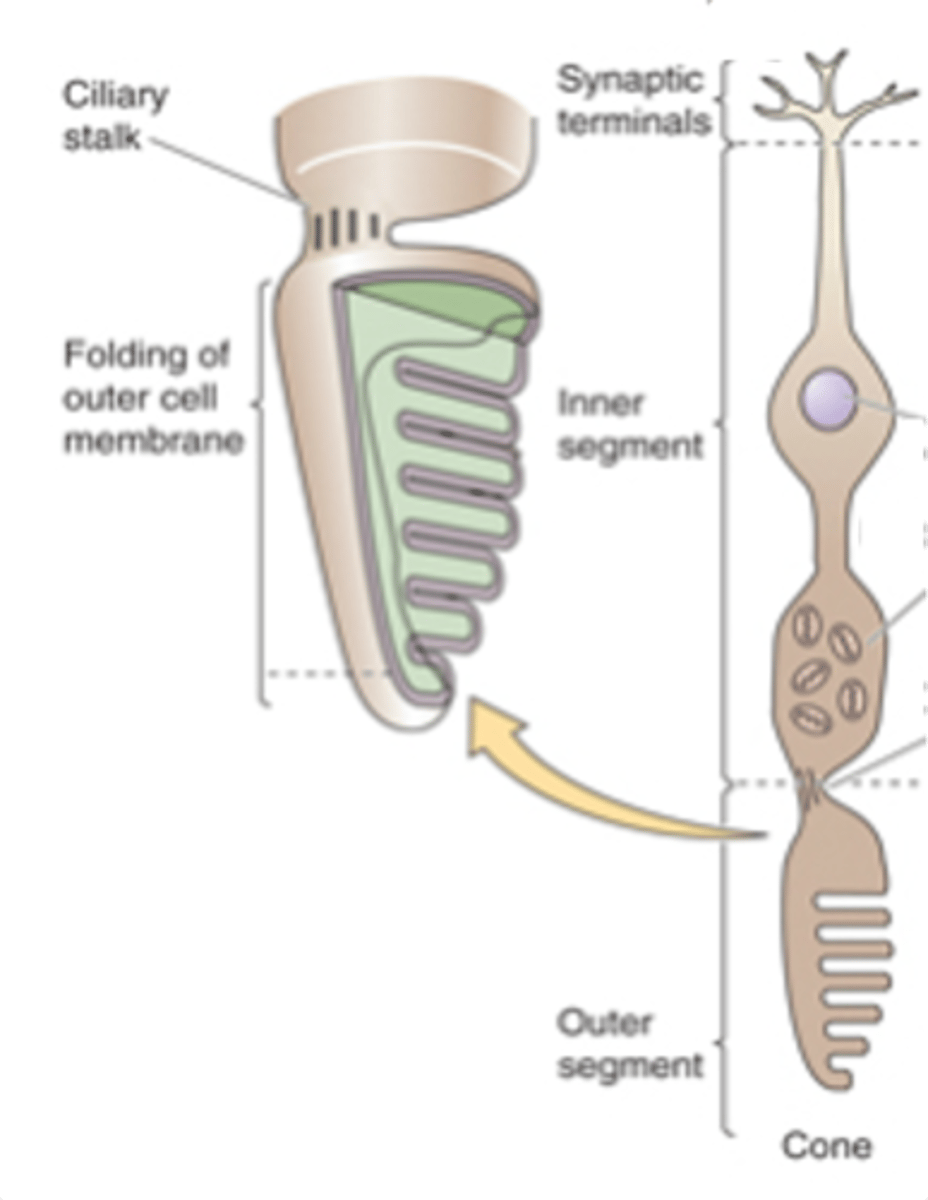
During daylight (photopic) conditions
When are cone photoreceptors used?
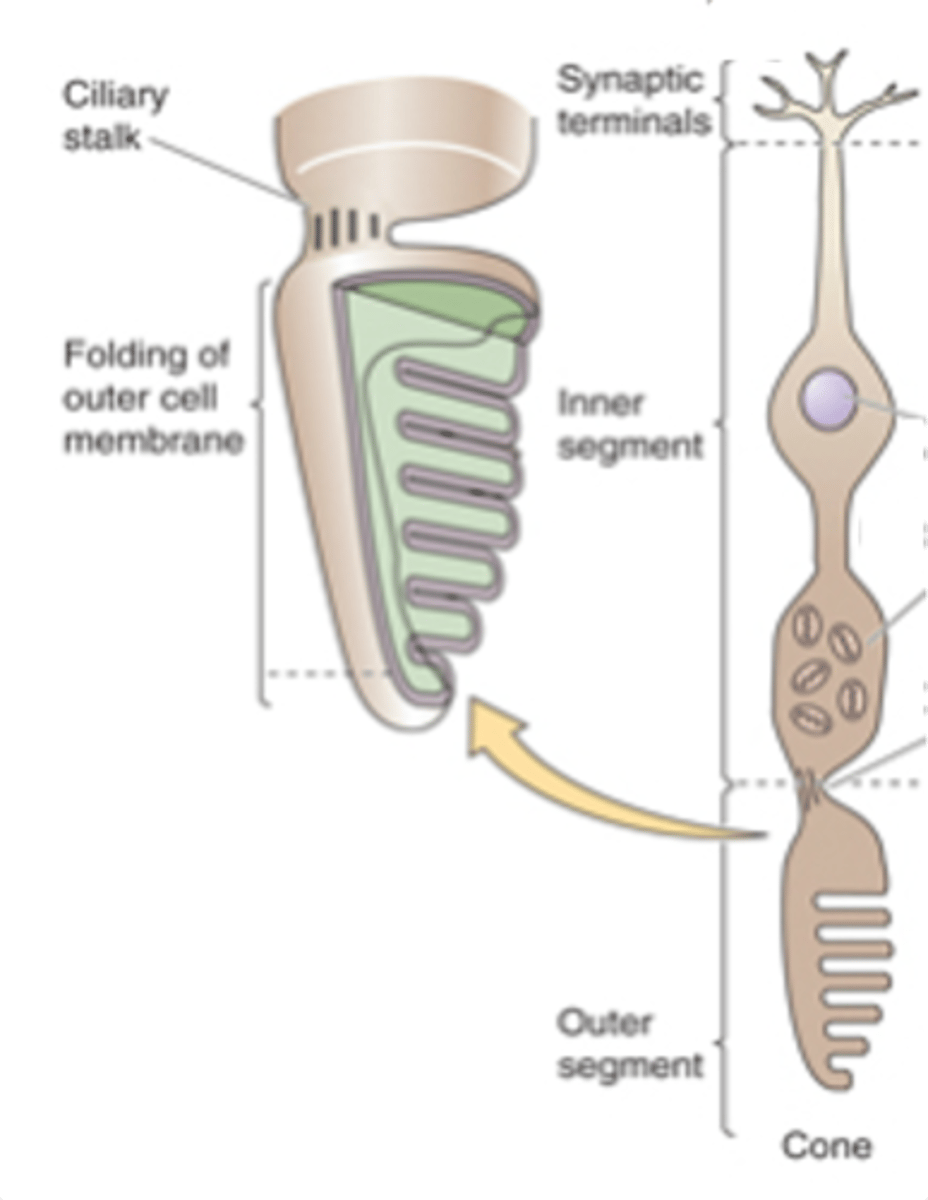
Colour vision
What do cone photoreceptors enable?
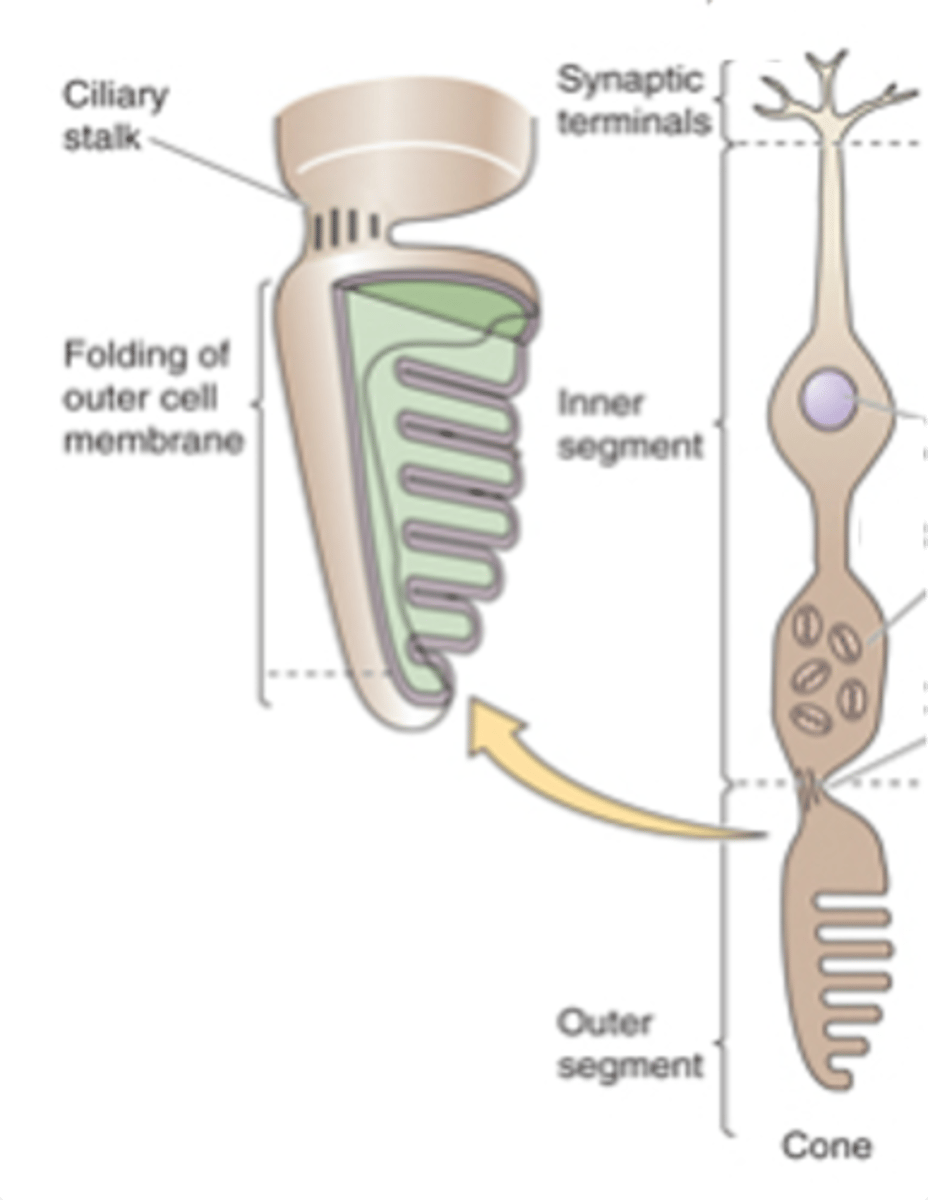
Visual acuity/resolution, sensitivity
Cone photoreceptors have high __________ _____/___________ and lower _____________
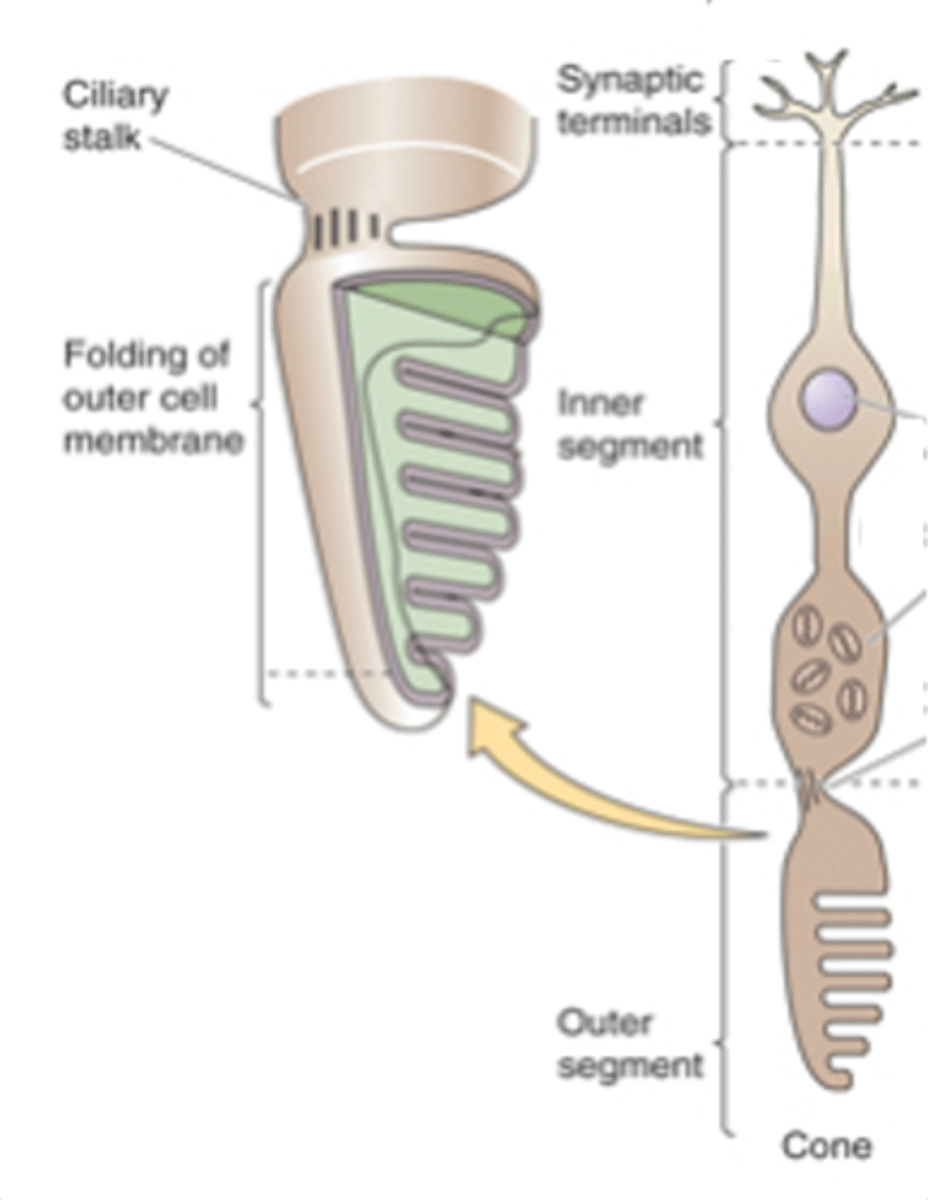
5 million
There are ~_ _________ cones in the human retina
Intermediate
Rods and cones are used together in _______________ (mesopic) light conditions
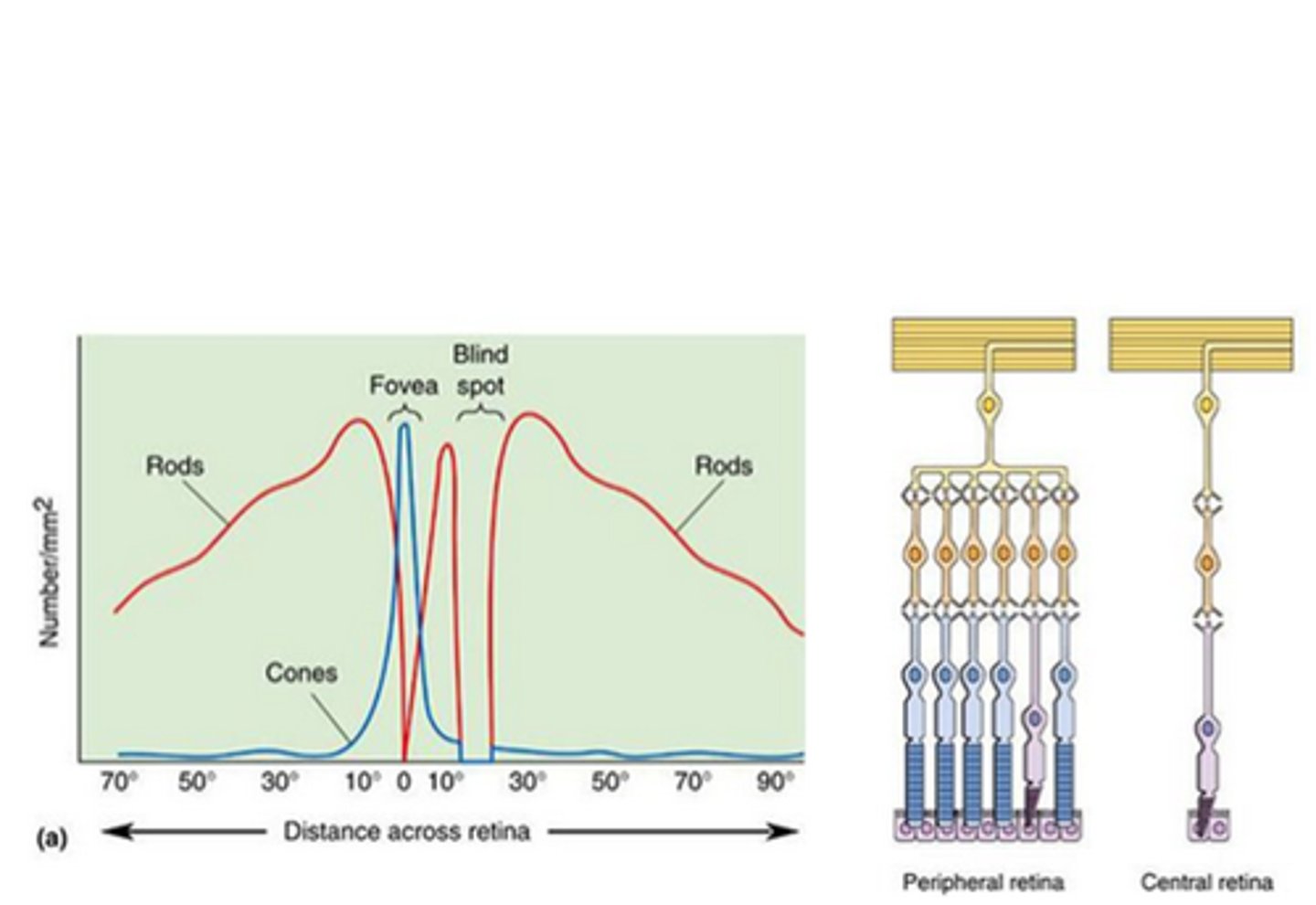
The fovea
What contains most of the 5 million cones and no rods?
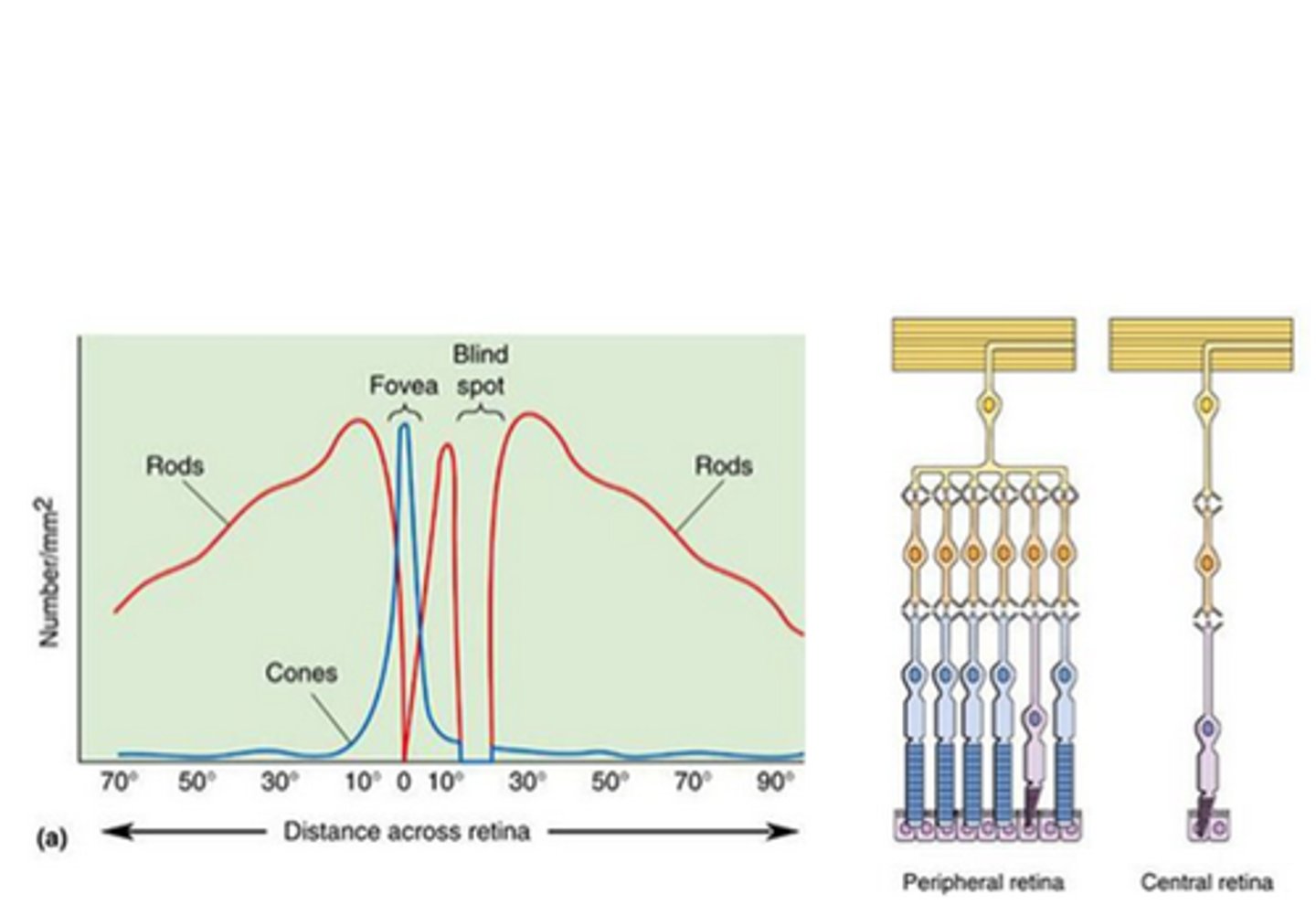
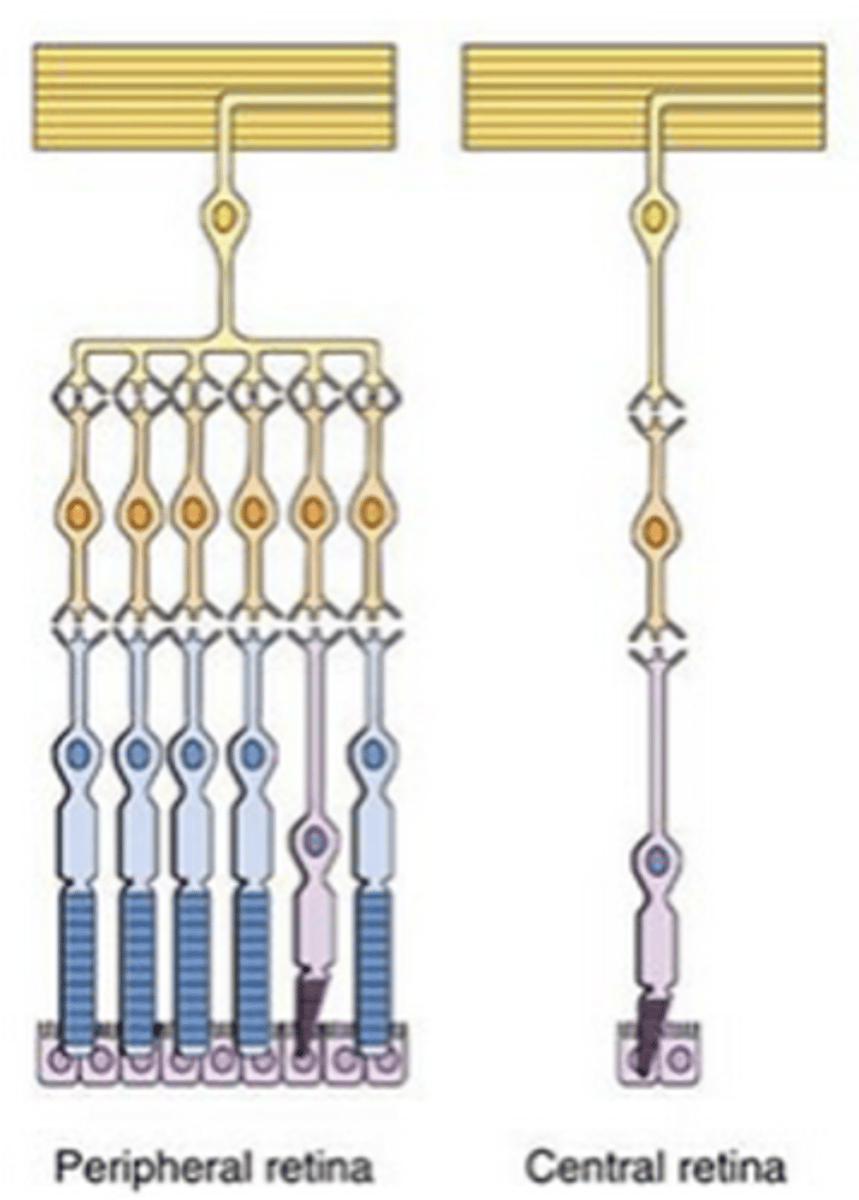
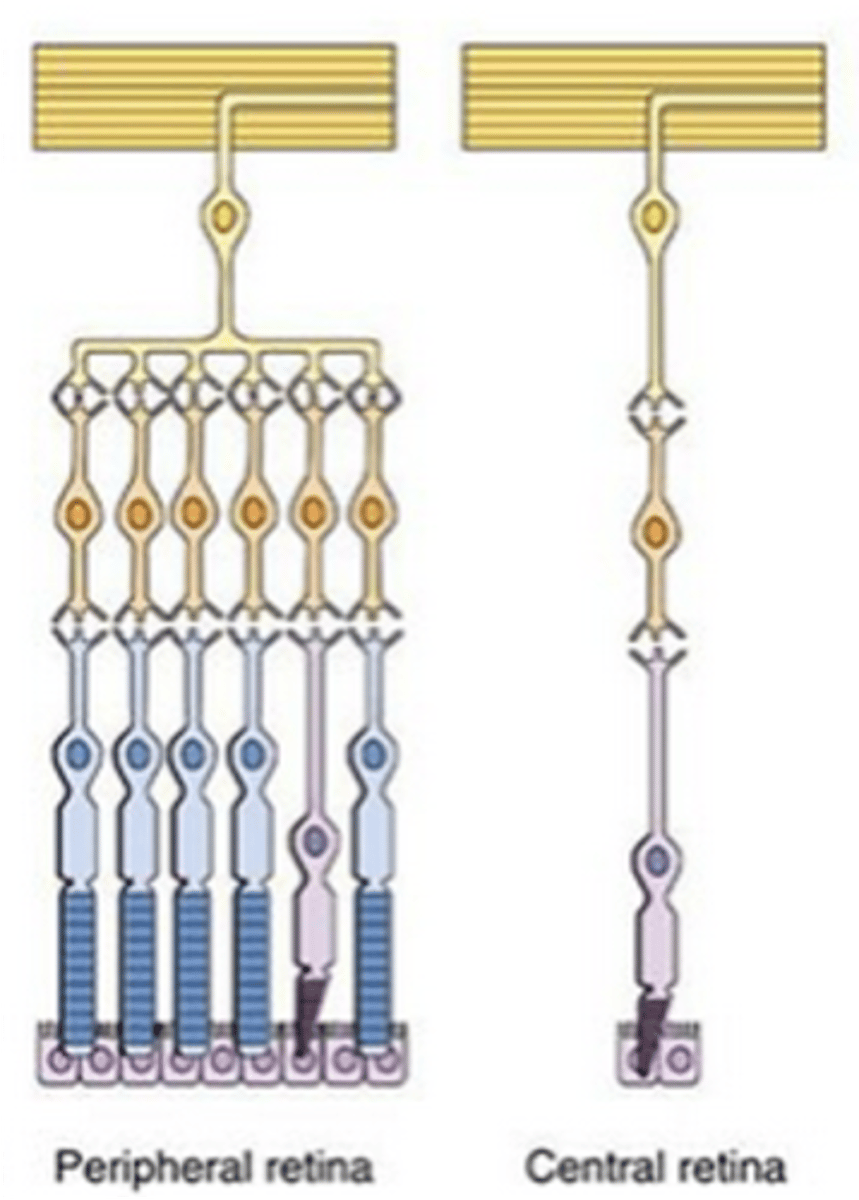
Low, low, high
The central retina has ____ convergence, _____ sensitivity and _____ resolution
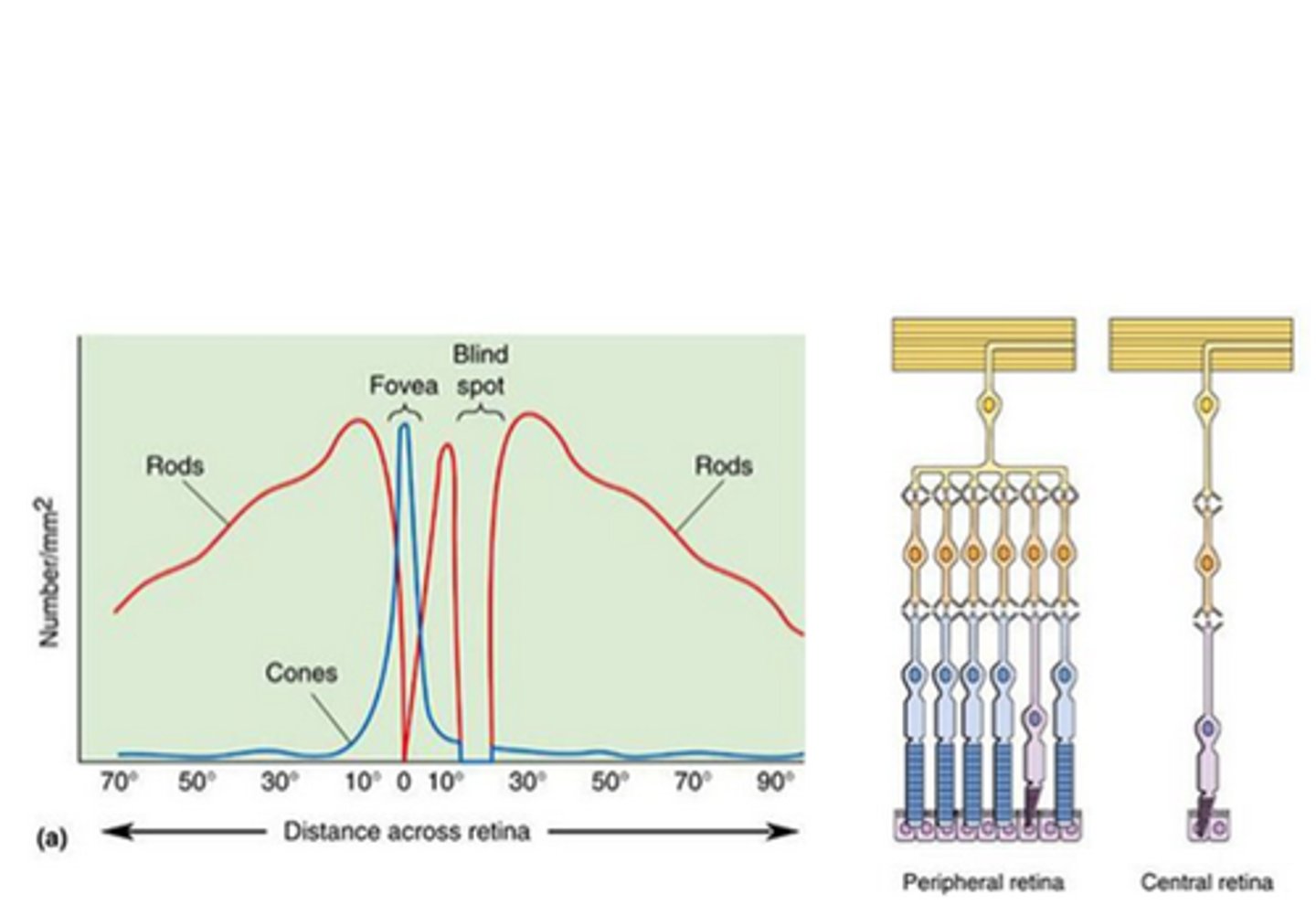
High, high, low
The peripheral retina has ____ convergence, ____ sensitivity and _____ resolution
Sensitive, night vision
Rod photoreceptors are highly ___________ to light, allowing _______ _______
Photopigments, colour
Cone photoreceptors contain one of three ______________, enabling ________ perception during daylight
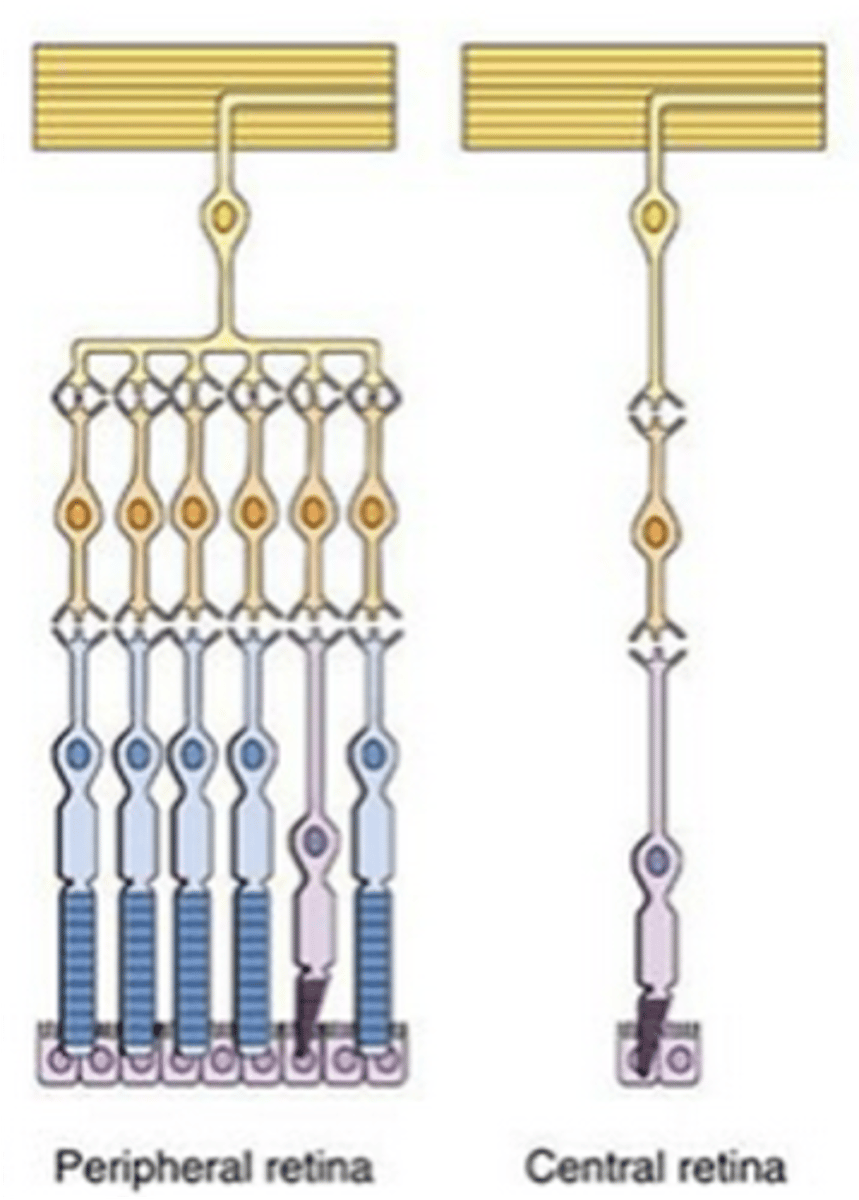
High, low, high resolution vision
The fovea contains a _____ concentration of cones, with a ____ convergence on retinal ganglion cells, making this area better for ______ ____________ _______