AI Quiz 2
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Prisoner's Dilemma
Imagine a scenario where both players have incentive to exploit each other, and a danger of being exploited. In additional, they both prefer mutual cooperation to mutual defection
Trust kind of structure / relationship → encourages them to cooperate
Benefit from mutual cooperation
Self interested behavior leads to suboptimal outcome
Anthropocentrism
People project human-like characteristics on non-human objects
People are more comfortable and trusting of things that look like them
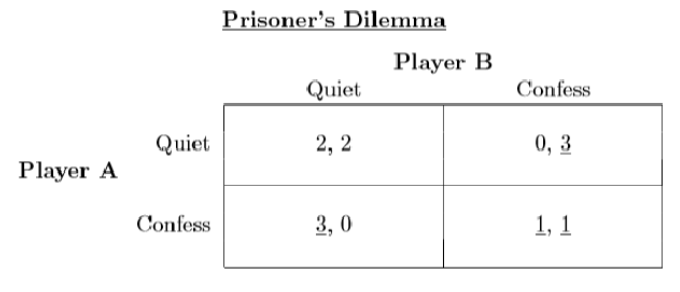
Uncanny Valley
People actually don’t like things that look human, but not quite
Polar express people → more comforted by Moana (looks less human than polar express)
Philosophical Theories of Love
Reductionism (desire)
No such thing as love; actually only __ (need, sexual desire, etc)
Union (merging desires)
Love = bringing together of things, become one (philia)
“Robust concern” (care and preserving)
Want to care / foster health and wellbeing of this person
Wanting good for them = love
Emotion views
All other positions are missing the feelings (passion) → something that moves you towards that person
*Under most of these positions, humans can have love with AI, union and robust concern might be harder to argue
Plato's Theory of Love
Valuing (judgements)
To love someone = to find someone valuable
Love value is connected to pride
Case Histories of Marriage Standards
Loving v. Virginia (1967)
Interracial marriage
Obergefell v. Hodges (2015)
same-sex marriage
Reynolds v. US (1878)
Restricts polygamy
Various state laws
Restrict child marriage
Technological Unemployment
Machines take over all human labor (extreme end of displacement effect)
Displacement Effect // Effects Counteracting the Displacement of Automation (e.g., Capital Accumulation and Productivity Increases)
Automation takes jobs because it lowers the cost of labor → “increase in automation causes a decrease in demand for human labor”
Counteracting the displacement (prevent technological unemployment)
Productivity effects (reduced cost)
Ask task becomes more automated, more opportunities for humans to work alongside machines
Also idea of human retraining
Gig economy → cheap to hire individuals but easy to replace; more and more humans free for labor, gig economy is an objection to this argument
Capital accumulation (increased outputs)
Automation → increase outputs; increase capital to put into company
Automation increases productivity → huge amounts of capital → reinvestment in human labor
Arguments for / against Displacement Effects
Arguments for: Cost reduction, increased efficiency and productivity
Arguments against: People lose motivation to pursue their dreams, job loss
Luddites
Group of people worked in manufacturing and they were upset that AI replacing jobs. Destroyed machines. (anti automation)
Autonomy
The ability of an individual or system to act independently and make decisions without external influence.
Automation Bias
an automated medical diagnosis tool may overlook important symptoms or risk factors, leading to incorrect treatment decisions
Humans slowly and gradually rely on automation more and more
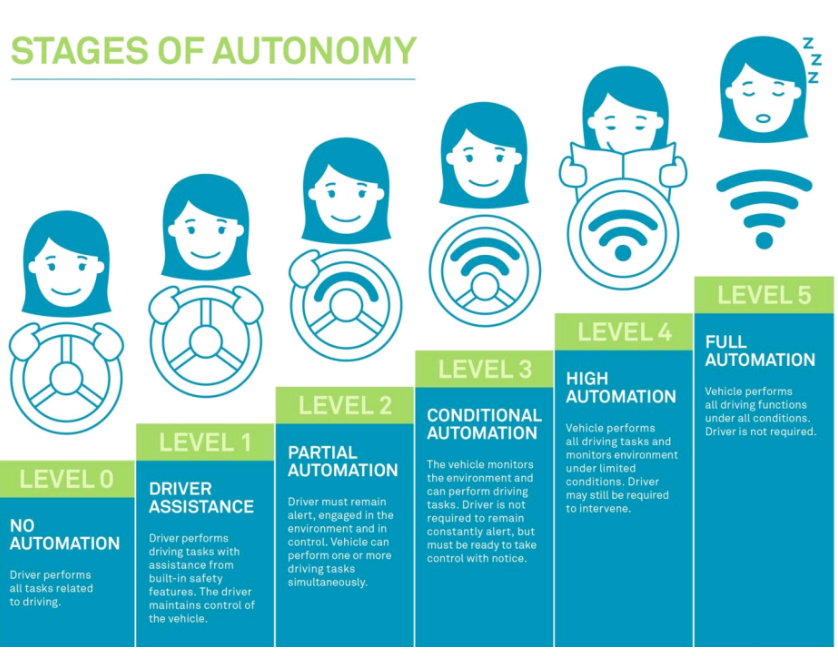
SAE Standards for Autonomous Vehicles
Objectivism/Subjectivism about Meaningful Lives
Objectivism
“meaningfulness of life is independent of subjective beliefs and desires”
Subjectivism
If you feel and think that life is meaningful then it is
Hedonism → happy life = meaningful life
Compatibilism/Incompatibilism about Free Will
Compatibilism is the view that free will and determinism are compatible. It argues that it is possible for an individual to possess free will even if their actions are determined by prior causes.
Aristotle's Theory of Citizenship
Equal capacity (Aristotle)
Differences in ability → mean more or less legal rights?
Citizenship based on capacity
Locke's Theory of Property
Labor is how people acquire property; property is something that you can buy and sell
Used as justification for colonialists
Capitalism and property ownership
“The theory is rooted in laws of nature that Locke identifies, which permit individuals to appropriate, and exercise control rights over, things in the world, like land and other material resources.”
Marx's Theory of Labor
Capitalism is bad economically and for identity
Work is a part of who you are
When sell labor, turn you into an object (commodification)
Trade part of yourself for a wage
Metaphysics of it
Taking away labor from people is taking away part of who they are
Organ selling is illegal in all countries except Iran
Part of who you are (Marx says)
Same thing about labor
Utilitarianism
An ethical theory that asserts that the best action is the one that maximizes overall happiness or pleasure. (in consequence-based family // J.S. Mill)
An action is right just because it brings about good consequences → increases well-being
Maximize net well-being
Natural Rights
John Locke’s Life, Property, Liberty
“all individuals are equal in the sense that they are born with certain "inalienable" natural rights” → life, property, liberty (negative rights // Locke)
Never cross a rights-boundary without consent
Contractarianism
Contract with government, social contract, give up some of freedoms for moral space, pretty much goal of Constitution
Hobbes
“Contractarianism, which stems from the Hobbesian line of social contract thought, holds that persons are primarily self-interested, and that a rational assessment of the best strategy for attaining the maximization of their self-interest will lead them to act morally (where the moral norms are determined by the maximization of joint interest) and to consent to governmental authority.” (source)
Always provide people with what they are owed (positive rights // Rawls)
Virtue Ethics
Perform the action that is consistent with good intentions/character (agent based // Aristotle)
mirroring a virtuous person, or someone who has model characteristics, and their actions provides the guidelines for morality (aristotle)
Moral Relativism
Rejects objective moral value
Make morality relative to ___
Positions on Political Equality
Equal value (Locke)
Everyone created equally
Equal capacity (Aristotle)
Differences in ability → mean more or less legal rights?
Equal treatment (Kant)
Either have rights or don’t
Reflects on your own responsibilities (good to treat things equally
Institutions of equality (Rawls)
Positions on Free Will
Two people plan to murder someone. Person B will make person A pull the trigger if person A chickens out. Does Person A have free will.
Dualist
Need soul to have free will (problem of other minds; causal interaction problem)
Materialist
Material object in material world
Eliminitavist
Free will doesn’t exist (problem of responsibility)
Arguments for AI Rights
Robots should be slaves article
AI should not have rights
Why does Bryceson think that AI shouldn’t have rights
Cost to individuals if they are treating machines as people rather than interacting with other real people
Cost to institutions protecting rights to objects, giving resources
Other kinds of costs