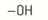organic chem
1/239
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
240 Terms
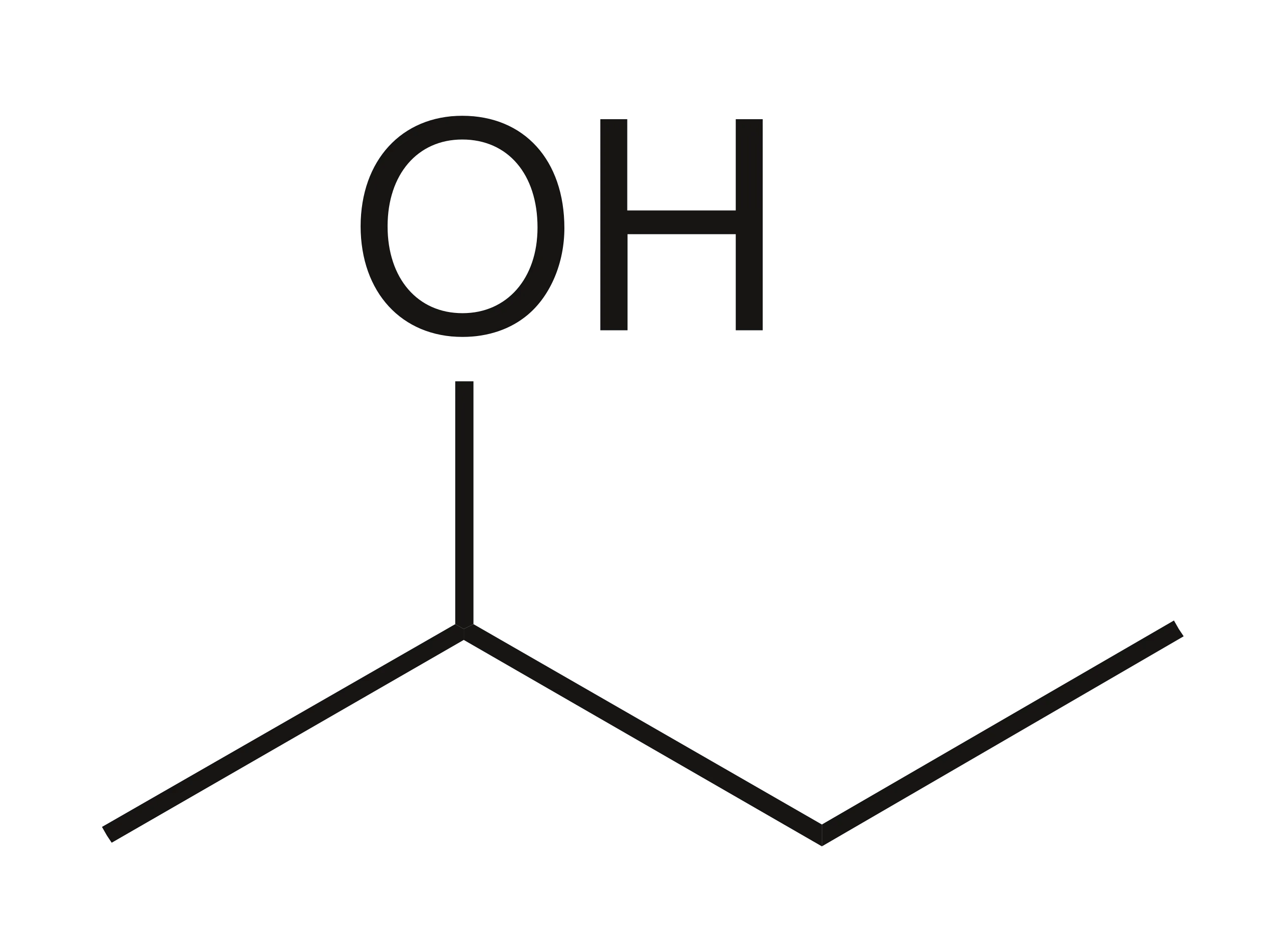
Skeletal formula definition
the simplified organic formula, shown by removing hydrogen atoms from alkyl chains, leaving just a carbon skeleton and associated functional groups e.g. for butan-2-ol:
Homologous series definition
a series of organic compounds having the same functional group but with each successive member differing by CH2
Functional group definition
a group of atoms responsible for the characteristic reactions of a compound
Alkyl group formula
CnH2n+1
Aliphatic definition
a compound containing carbon and hydrogen joined together in straight chains, branched chains or non-aromatic rings
Alicyclic meaning
an aliphatic compound arranged in non-aromatic rings with or without side chains
Aromatic meaning
A compound containing a benzene ring
What is a benzene ring
An aromatic functional group characterized by a ring of six carbon atoms, bonded by delocalised pi electron system
Saturated meaning
Only contains single carbon-carbon bonds
Unsaturated
The presence of multiple carbon-carbon bonds including C=C C=-C and aromatics rings
Structural isomer definition
Compounds with the same molecular formula but a different structural formula
Alkane definition
Saturated hydrocarbons containing single C-C and C-H sigma bonds
Why is there a tetrahedral shape around each carbon in an alkane
4 bonding regions and zero lone pairs result in equal repulsion and a 109.5 degree between each carbon
Why does boiling point increase in longer chain alkanes
higher surface area so more contact points so more london dispersion forces
Why does boiling point decrease with more branching
Branched alkanes has relatively small surface area for contact points, so less London dispersion force act among molecules
Why do alkanes have relatively low reactivities?
Due to the strong C-C and C-H bonds in the molecules that require a lot of energy to overcome or in the presence of strong catalysts
Complete combustion formula
Alkane+oxygen→ carbon dioxide+ water
Incomplete combustion formula
Alkane+oxygen→ carbon monoxide/soot+ water
sigma bond
head on overlap of two p orbitals
pi bond
adjacent p orbitals overlap in a sideways orientation forming a cloud of electron density above and below the plane
what is a double bond made of
sigma and pi bond
is a sigma or pi bond stronger
sigma
what bond breaks with a double to single bond
pi bond as it is weaker
free radical mehcanism steps
initiation with Uv light to form radicals
propagation in which radicals and pairs make radicals and pairs
termination starts with radicals ends with pairs
stereoisomer definiton
same structural formula but different arrangement of atoms in space
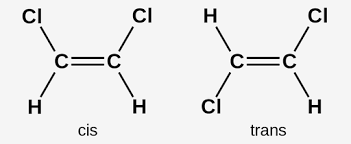
E/Z isomerism requirements
C=C double bond, different groups attatched to each carbon of the double bond
position isomers
structural isomers that can be viewed as differing only on the position of a functional group, substituent, or some other feature on the same "parent" structure

chain isomers
made up of two or more carbon or other compounds with the same molecular formula but different atomic arrangements, or branches
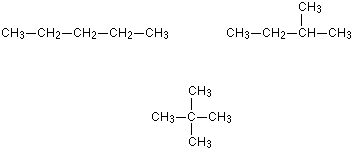
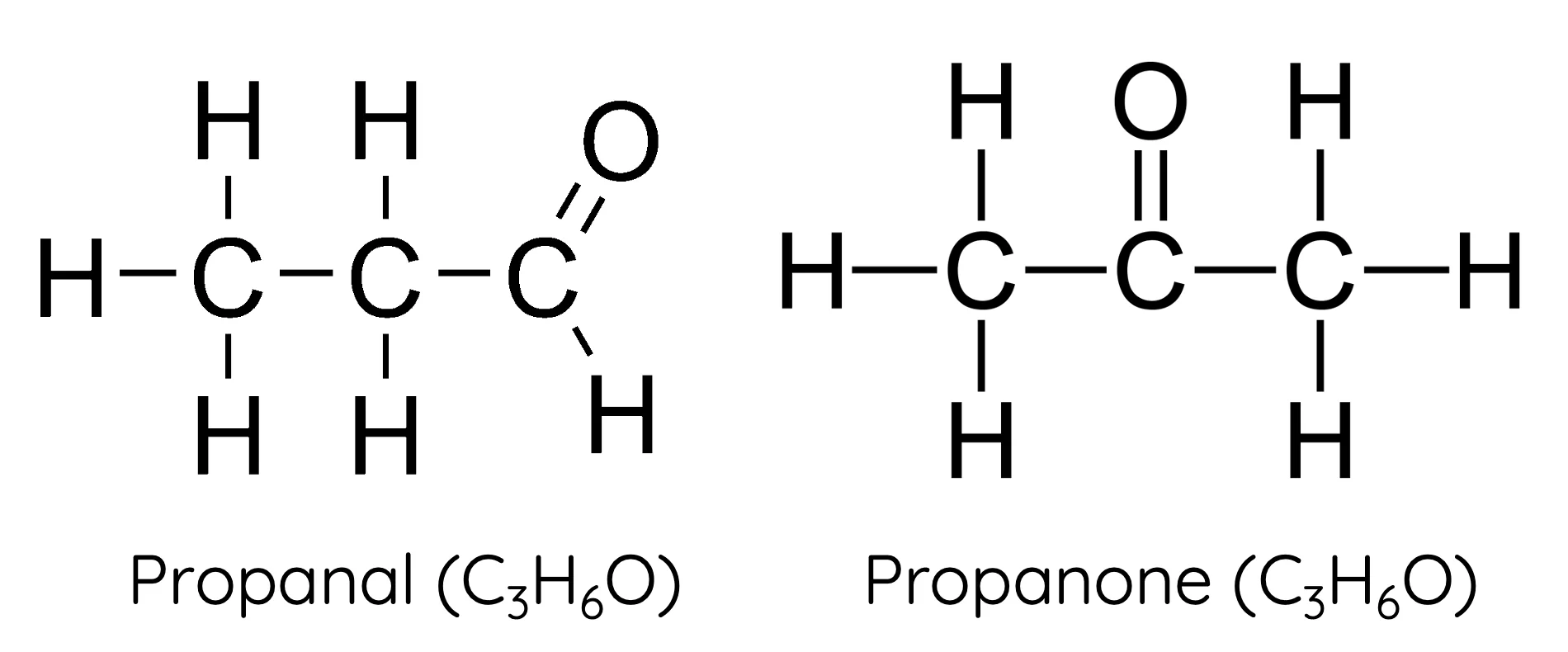
functional group isomers
molecules with the same molecular formula, but different functional groups
naming E/Z isomers rules
draw line in middle of C=C, assign priority on each side acoridng to alphabetical (directly bonded to C). same side Z opposite E
why do E/Z isomers need a double bond
because it restricts free rotation and means the groups attatched to the carbons can’t move
cis-trans isomers
a type of E/Z where two of the substituent groups on the C=C bond are the same
electrophilic meaning
electron pair acceptor
nucleophilic meaning
electron pair donor
why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes
-pi bonds are weaker so need less energy to overcome
-high electron density of C=C
what is a curly arrow used for?
showing where an electron pair is going. go from high to low electorn density
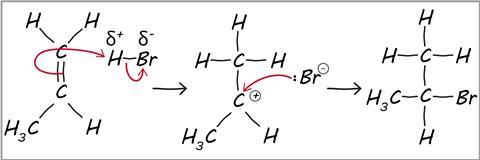
what is electrophilic addition
a reaction in which a substrate is initially attacked by an electrophile, and the overall result is the addition of one or more relatively simple molecules across a double bond
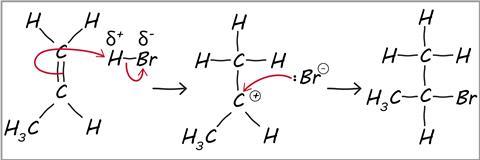
what is a reaction mechanism
a series of steps that show how a reaction takes place
Marvovnikoff’s rule
during electrophilic addition to alkenes/alkynes the h atom in the electrophile will be added to the C with less C/more H
primary carbocation 1°
the carbon which carries the positive charge is only attached to one other alkyl group
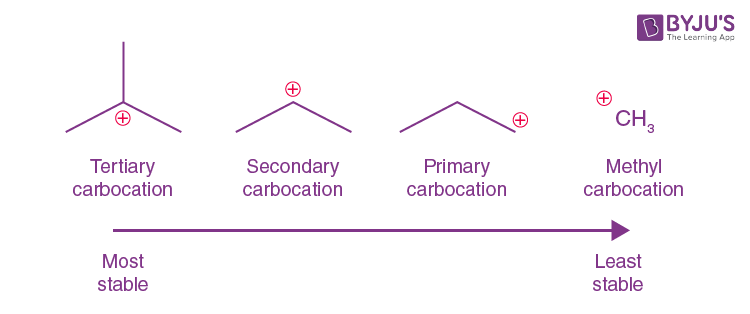
secondary (2°) carbocation
the carbon with the positive charge is attached to two other alkyl groups, which may be the same or different
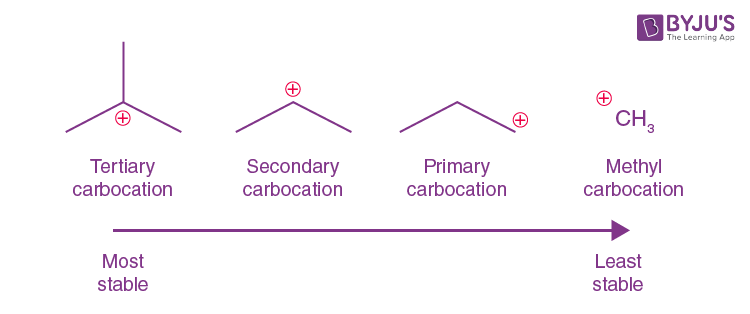
tertiary (3o) carbocation
the positive carbon atom is attached to three alkyl groups
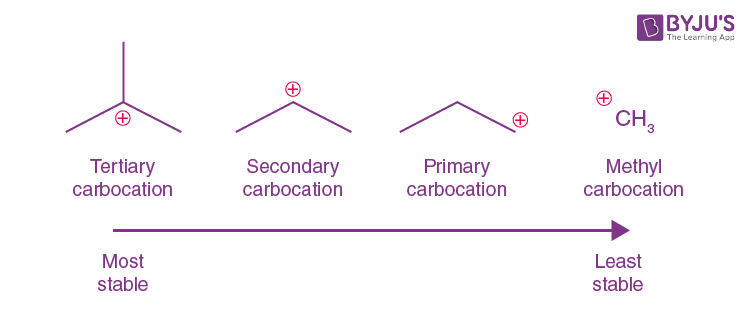
order of stability for carbocations and why
tertiary most primary least bceause the more chains the bigger the inductive effect
what is the inductive effect
The effect on electron density in one portion of a molecule due to electrophilic or nucleophilic groups elsewhere in the molecule
what determines the major product adding a hydrogen halide to an alkene
the C bonded to the least Cs
what happens in heterolytic fission
the pair of shared electrons is taken by one of the atoms
what happens in homolytic fission
the pair of electrons is split between the separated atoms
benefits of polymer use
readily availabile, cheap, more convenient than glass bottles, metal dustbins, paper bags and cardboard packaging, lack of reactivity
disadvantages of polymer use
challenge in disposal
mostly non-biodegradeable
killing marine life
recycling evaluation
reduces environmental impact
conserves finite fossil fuels
decreasing landfill buildup
sorted by type. can’t mix
chopped to flakes, washed, dried, melted
products may be weaker/less quality
PVC recycling evaluation
disposal and recycling is hazardous due to chlorine content and additives
landfill not sustainable
when burnt HCl gas is released it’s corrosive
releases other pollutants like toxic dioxins
new solvents that dissolve polymers and high grade PVC is recovered by precipitation. solvent reusable
waste polymers as fuel evaluation
some difficult to recycle
high stored energy value
incinerated to produce heat, generating steam to drive a turbine, producing electricity
feedstock recycling evaluation
the chemical and thermal process that can reclaim monomers gases and oils from waste polymers
products resemble those produced from crude oil in refineries
can be used as raw materials for new polymers
major benefit is that it can handle unsorted and unwashed polymers
bioplastics
produced from plant starch cellulose, plant oils, and proteins
renewable and sustainable alternative
protects environment and valuable oil reserves
biodegradeable polymers
broken down by microorganisms into water CO2 and biological compounds
usually made from starch/cellulose OR additives that alter the structure of traditional polymers so microorganisms can break them down
biodegradeable polymers EXAMPLES
poly(lactic acid)
plant starch/cellulose
sugar cane fibre
photodegradeable polymers
oil based
weakened by absorbing light to start degradation
general formula def
the simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous series) e.g. for an alkane: CnH2n+2
structural formula definition
the minimal detail that shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule) e.g. for butane: CH3CH2CH2CH3 or CH3(CH2)2CH3
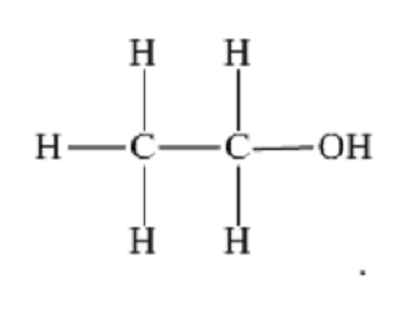
displayed formula definition
the relative positioning of atoms and the bonds between them e.g. for ethanol:
ozone depletion reaction
Cl + O3 → ClO + O2
ClO + O3 → Cl + 2O2
overall: 2O3 → 3O2
what is a CFC
chlorofluorohydrocarbon compound containing Cl, F, C, H
what is ozone
a form of oxygen O3
where is the ozone layer found
the stratosphere
what does ozone do
absorbs harmful Uv radiation which can damage DNA and cause skin cancer
what do CFCs do to ozone
CFCs break down from UV in stratosphere to form Cl radicals by breaking C-Cl. free radical chain reaction
why can one Cl radical destroy many ozone molecules
chain reaction which the radicals are not used up (they are reformed)
what is the montreal protocool
1987 many countries signed deal to ban CFC use. use has fallen dramatically. most effective environmental actions ever. ozone no longer depleting, [predicted to rise again
CFC alternatives
chemicals that do not contian chlorine. 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane for fridges
butane for aerosol propellant. can’t produce Cl radicals as no Cl.
still greenhouse gases, so problem there
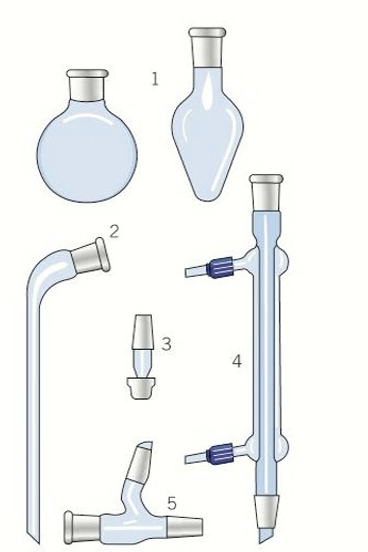
quickfit apparatus
-1 round bottom or pear shaped flask
-2 receiver
-3 screw tap adapter
-4 condenser
-5 still head
reflux setup
-bunsen burner/water bath if under 100C/ heating mantle for flammable liquids
-antibumping granules
-thin layer of grease to ground glass joints
-condenser upright
-clamp loosely
-no stopper or it will explode
-top tube linked to sink, bottom tube to tap

distillation setup
-purifies from incomplete reaction/by-products
-round bottom or pear shaped flask
-condenser
-rubber tubing
-heat source
-stands and clamps
-screw cap adaptor
-receiver adaptor
-still head
-thermometer

what is a receiver adaptor

what is a condenser
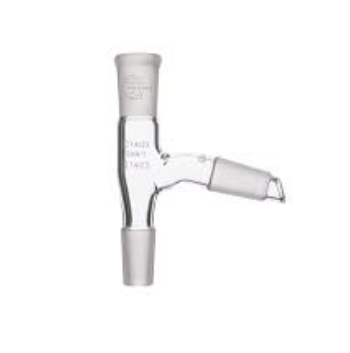
what is a screw cap adaptor

what is a still head
T shaped
what is a heating mantle

separating after organic synthesis of a liquid
-water may be obtained
-clear separation of 2 layers
-identify organic product by adding distilled water and seeing which layer increases - that is water
-conical flasks for collection
drying agents
-anhydrous inorganic salt
-CaCl2: specifically hydrocarbons
-CaSO4 and MgSO4 general drying agents
removing traces of water from organic synthesis
-drying agent
-add into flask with spatula
-add stopper, swirl
-if solid lump, water remains. add more
-add more until soft fine powder
-decant liquid into another flask. should be clear
why would you need to redistillate
-organic liquids can have close boiling points so impurities
-apparatus cleaned dried set up again
-only collect product with desired boiling point
-narrower bp range → purer product
do alcohols with the same chain length have a higher or lower bp and mp that alkanes and why
they have a higher b.p and m.p than alkanes because of their polar -OH group which forms H bonds
what’s more volatile alcohol or alkanes and why
alkanes because they only have weak london forces but alcohols have hydrogen bonds
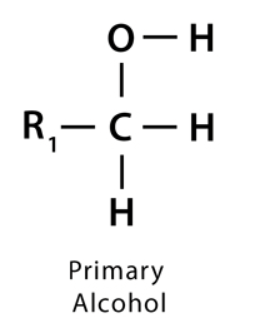
what is a primary alcohol
an alcohol whose -OH group is bonded to a carbon only directly bonded to 1 other methyl groups
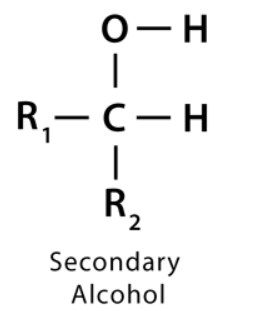
what is a secondary alcohol
an alcohol whose -OH group is bonded to a carbon directly bonded to 2 other methyl groups
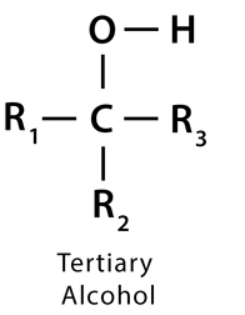
what is a tertiary alcohol
an alcohol whose -OH group is bonded to a carbon directly bonded to 3 other methyl groups
oxidising agents for alcohols
-acidified potassium dichromate (VI) or Cr2O72-/H+, K2Cr2O7, H2SO4.
-represented as [O] in equation
-heat in water bath
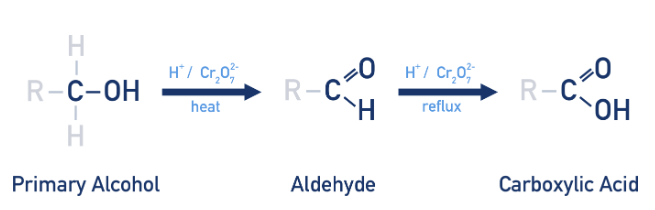
product of oxidation of primary alcohols
aldehydes under heat with agent. further oxidation. under reflux produces carboxylic acids
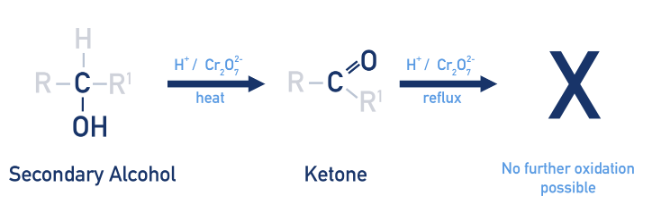
product of oxidation of secondary alcohols
ketones
how to avoid further oxidation of aldehydes
heat while distilling to remove products from reaction vessel before they can react further
oxidation of tertiary alcohols
not possible
dehydration of alcohols conditions
acid catalyst - H3PO4 or H2SO4 and heat
dehydration of alcohols product
alkenes
alcohol substitution with halide ions conditions
halide ions in the presence of acid catalyst such as (NaBr and H2SO4)
halide substitution of alcohols product
haloalkanes
haloalkane hydrolysis product
alcohol
what primary haloalkane hydrolyses fastest
C-I, C-Br, C-Cl, C-F in order of fastest to slowest. because bond enthalpy decreases down the group due to larger atomic radius, more shielding, less charge
organic synthesis
the preparation of complex materials from simple starting materials
alkene functional group
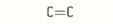
alcohol functional group
-OH