substitution reactions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
how can esters be made apart from Fischer
react alcohols with acid halides (acid chlorides most common)
catalyst not needed as acid chlorides much more electrophilic
mechanism for this acid chloride + MeOH
explain any other reagents
reaction generates acidic by-product (HCl) so normally a non-nucleophilic base is included in the reaction to neutralise it - hence the presence of Et3N, triethylamine, a very common one
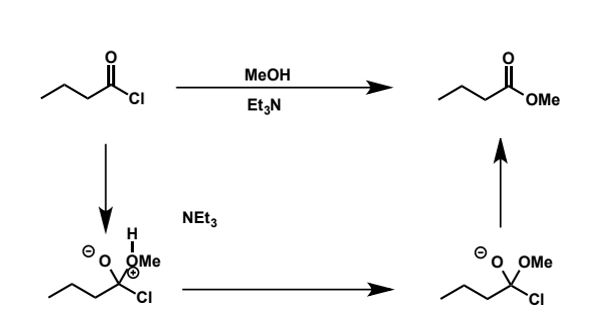
equilibrium for esters from acid chlorides
automatically shifted to product side as chloride is a good LG and not a particularly good Nu so formation of ester is favourable
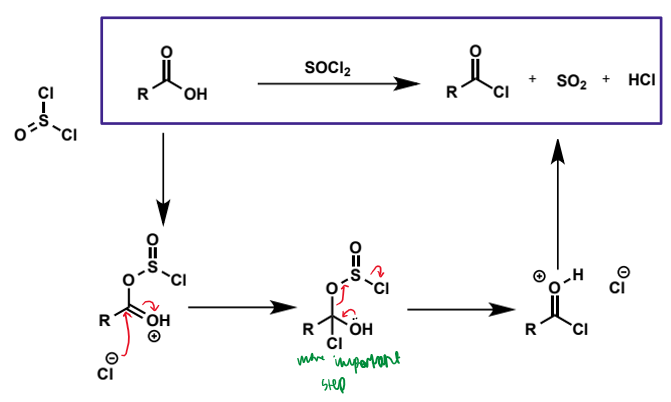
acid chloride synthesis
made from carboxylic acids and thionyl chlorides - same way as R-Cl is made from alcohols, but in this case it is addition/elimination
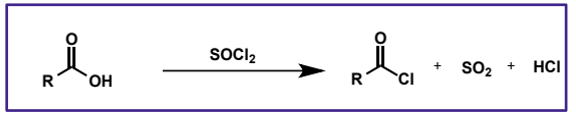
acid chloride synthesis mechanism
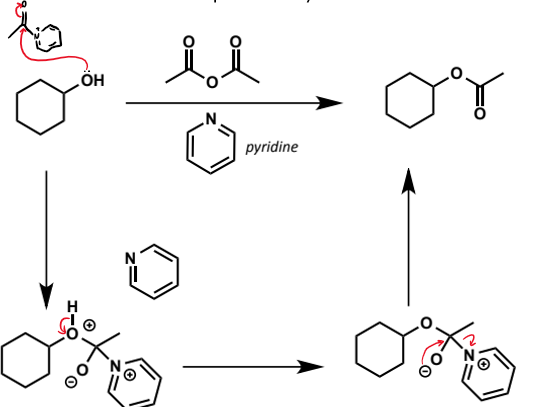
alternative reagent (to acid halides) for ester synthesis with alcohols
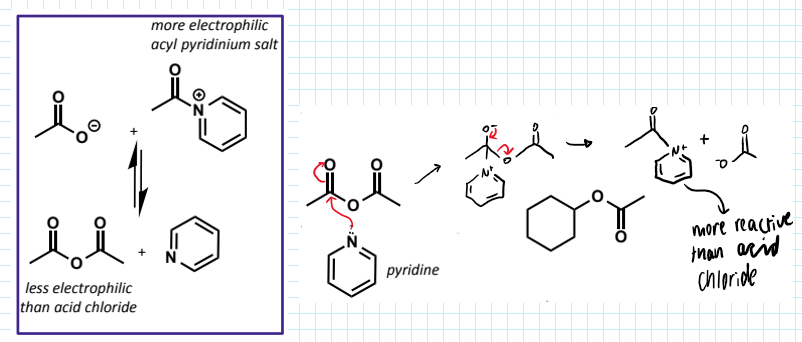
acid anhydrides - slightly less reactive than acid halides (chloride much better LG than acetate)
hence pyridine is often used as a base and nucleophilic catalyst for the reaction
mechanism for esterification with alcohol and acid anhydride
effect of pyridine on acid anhydride for reaction
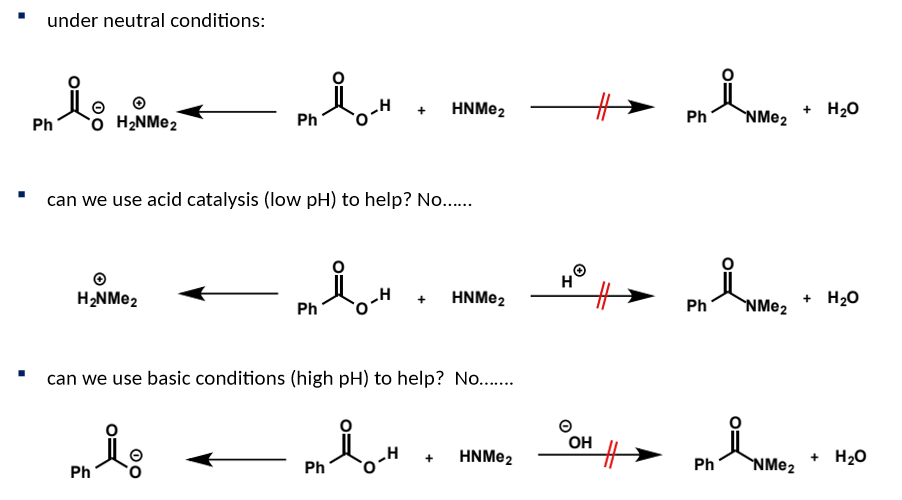
how would direct amide formation be attempted and why is it not successful (think 3 scenarios)
cannot be made directly from carboxylic acids and amines, analogously to forming esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols - even though this is a thermodynamically favourable process
this is due to the incompatibility of the reactants at any pH - in each scenario, Nu/E/both are converted into unreactive species
how can amides be successfully formed
use the amine with an acid chloride instead of a carboxylic acid
note that HCl produced again so need a base - can use excess amine or a different base
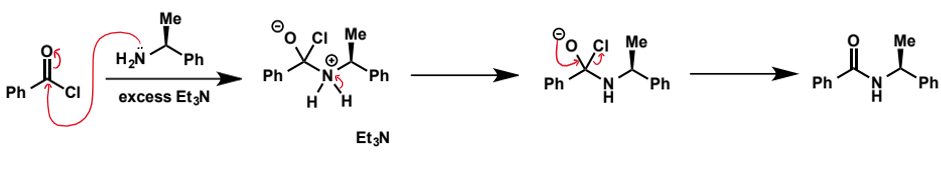
show amide formation from benzoyl chloride and dimethylamine using the nucleophile as the base
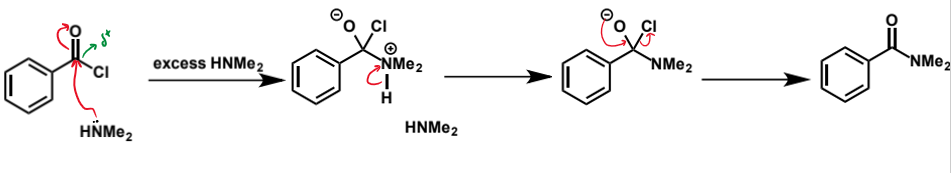
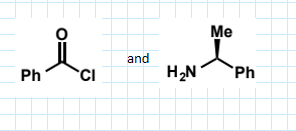
show amide formation from
with triethylamine base
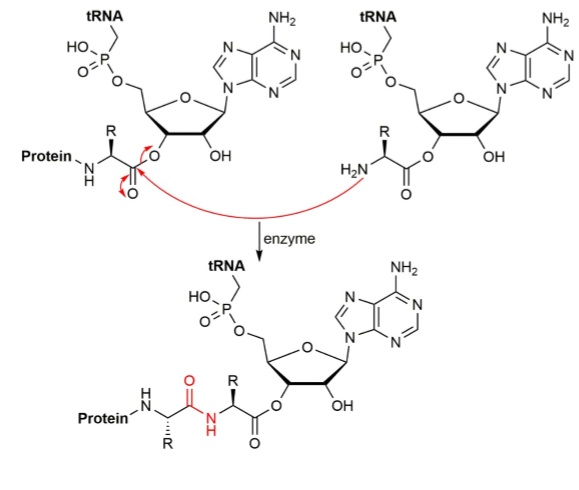
role of addition/elimination in peptide synthesis
an enzyme catalyses the reaction of the free amino group of the aminoacyl tRNA with the ester at the end of the growing protein to form a new amide/peptide bond (shown in red)
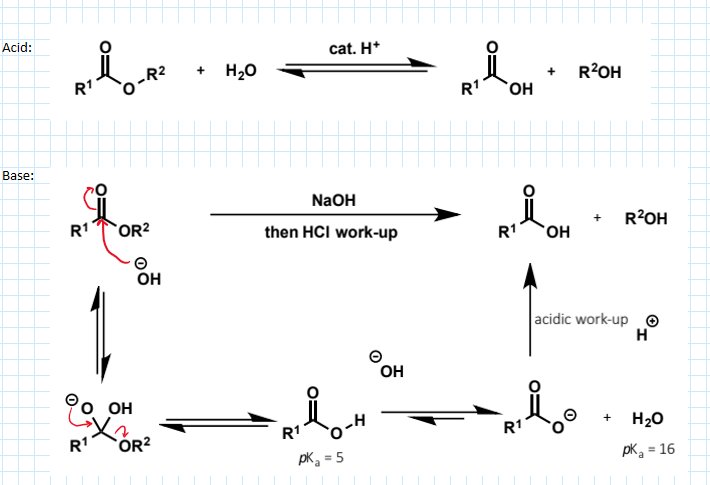
ester hydrolysis
can be hydrolysed by water but the reactions are slow at neutral pH. it can be catalysed by acid and this mechanism is the exact reverse of the Fischer process, but as with formation the reaction will be an equilibrium
instead esters can be hydrolysed under basic conditions. the equilibrium is displaced towards the product by the favourable deprotonation of the initially formed carboxylic acid.
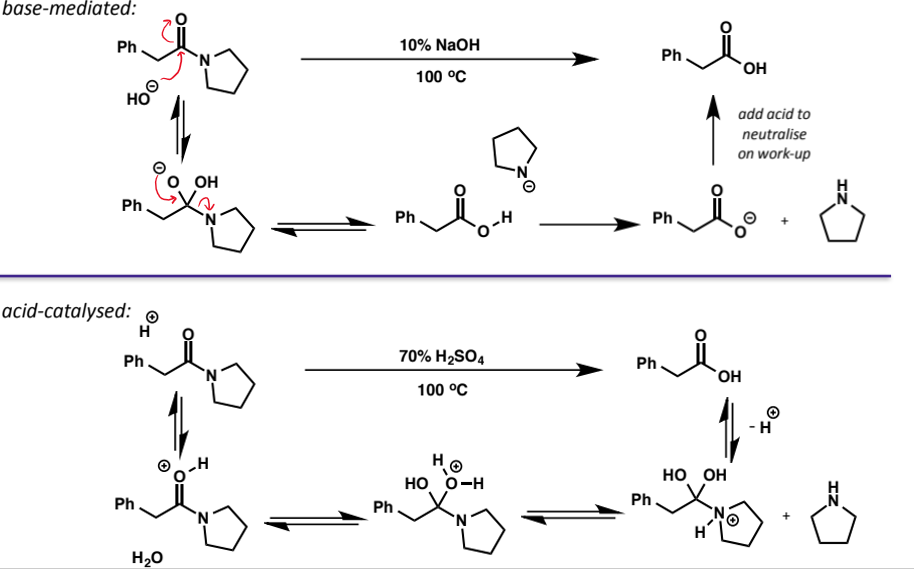
amide hydrolysis
can be hydrolysed under acidic or basic conditions but the reactions require more forcing than for esters (high T, more concentrated cat, longer reactions)
peptide hydrolysis
protease enzymes very effective at catalysing peptide hydrolysis. the enzymes have a nucleophilic alcohol that will react with an amide to form an ester. the enzymes have groups perfectly placed to stabilise the tetrahedral intermediates in both steps of the overall hydrolysis reaction