N470: Perfusion (exam 2)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
the process of nutrient delivery of arterial blood to a capillary bed
perfusion
what is the purpose of perfusion?
supply and organ or tissue with O2 and nutrients
noninvasive assessment of perfusion (7)
1) LOC
2) skin
3) urine output
4) color
5) BP
6)HR
7) capillary refill
perfusion scanning methods
- CT perfusion
- MRI perfusion- contrast injected and a series of fast images are taken
- nuclear medicine perfusion- uses radioactive isotopes
what are the two main factors of cardiac output?
HR and stroke volume
what are the three main determinants in stroke volume?
preload, afterload, contractility
what are the two main elements in preload?
CVP and PAWP
what are the two main elements in afterload?
SVR, PVR
what are the two main elements in contractility?
EF%, SV
the amount of volume/ blood ejected/ pumped from the heart in one minute
cardiac output
cardiac output formula
CO = HR x SV
Normal CO
4-8 L/min
The best indicator of cardiac function (vs CO) that corrects for body size?
CI
CI formula
CO/BSA (body surface area)
Normal CI
2.4-4 L/min
volume of blood pumped with each heartbeat
stroke volume (SV)
normal stroke volume
60-70 mL/beat
A severe increase in HR will cause the ______ ______ to decrease due to decreased _______ time, causing a _______ in CO
A severe increase in HR will cause the stroke volume to decrease due to decreased filling time, causing a decrease in CO
Influence of HR on CO*
- tachycardia
- afib
- bradycardia
- vtach
What are the four determinants of CO?
HR, preload, afterload, contractility
How does HR determine CO?
immediate increase in CO if SV constant
How does contractility determine CO?
it is the force of myocardial contraction and the pump function
amount of blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (stretch); end diastolic ventricular volume*
preload
the resistance the ventricle must overcome to eject blood; ventricular pressure at the end of systole*
afterload
Factors affecting preload
- volume: venous return, total blood volume, atrial kick
- compliance: stiffness and thickness of ventricular wall
Symptoms of decreased preload (7)
1) tachycardia
2) decreased U/O
3) increased specific gravity
4) dry mucous membranes
5) tented skin
6) sunken eyes
7) orthostatic hypotension
Symptoms of increased preload (7)
1) JVD
2) pedal edema
3) S3, S4
4) crackles
5) dyspnea
6) pink, frothy sputum
7) ascites, hepatic engorgement
what is a reliable indicator of volume/pressure in the right side of the heart?
JVD
an increase in JVD tells us about the patient's ___
CVP (central venous pressure)
Steps to measure JVD
- HOB 45 degrees
- head turned right
- identify sternal angle
- locate superior sternal notch
- measure distance between top pulsation and sternum in cm
- 4cm or less is normal
Medications affecting preload
fluids, diuretics, venodilators (nitrates, morphine, ace inhibitors)
increasing venous return, and therefore the filling pressure of the ventricle will lead to increased force of contraction and stroke volume
frank starling law of the heart
afterload is affected by...? (4)
1) aortic impedance
2) blood viscosity
3) blood volume
4) vascular tone
resistance to ejection from the left side of the heart
SVR (systemic vascular resistance)
SVR formula
MAP-CVP/CO x 80
Normal SVR
800-1200
resistance to ejection from the right side of the heart
PVR (pulmonary vascular resistance)
normal PVR
50-250
Symptoms of increased afterload (6)
1) pale, cool, clammy skin
2) HTN
3) non-healing wounds
4) thick, brittle nails
5) slow cap refill
6) decreased U/O
Symptoms of decreased afterload (3)
1) warm, flushed skin
2) increased CO
3) decreased BP
the ability of a muscle to shorten when stimulated; the force of myocardial contraction; measured as EF
contractility
Normal EF% range
60-70%
Symptoms of decreased contractility (5)
1) hypotension
2) fatigue
3) SOB
4) dizziness
5) low U/O
Symptoms of increased contractility (1)
increased BP
indications for hemodynamic monitoring
1) alterations in CO
2) alterations in fluid volume
3) alterations in tissue perfusion
What is the purpose of a CVP central line?*
reflects filling pressures in the right ventricle (preload of right heart); guides overall fluid balance
Noninvasive hemodynamic technologies (2)
1) impedance cardiography
2) doppler ultrasound
what noninvasive hemodynamic technology assesses cardiac function by measuring resistance to the blow of high frequency, low-amplitude current and measures SV, CO, SVR, and contractility?
impedance cardiography
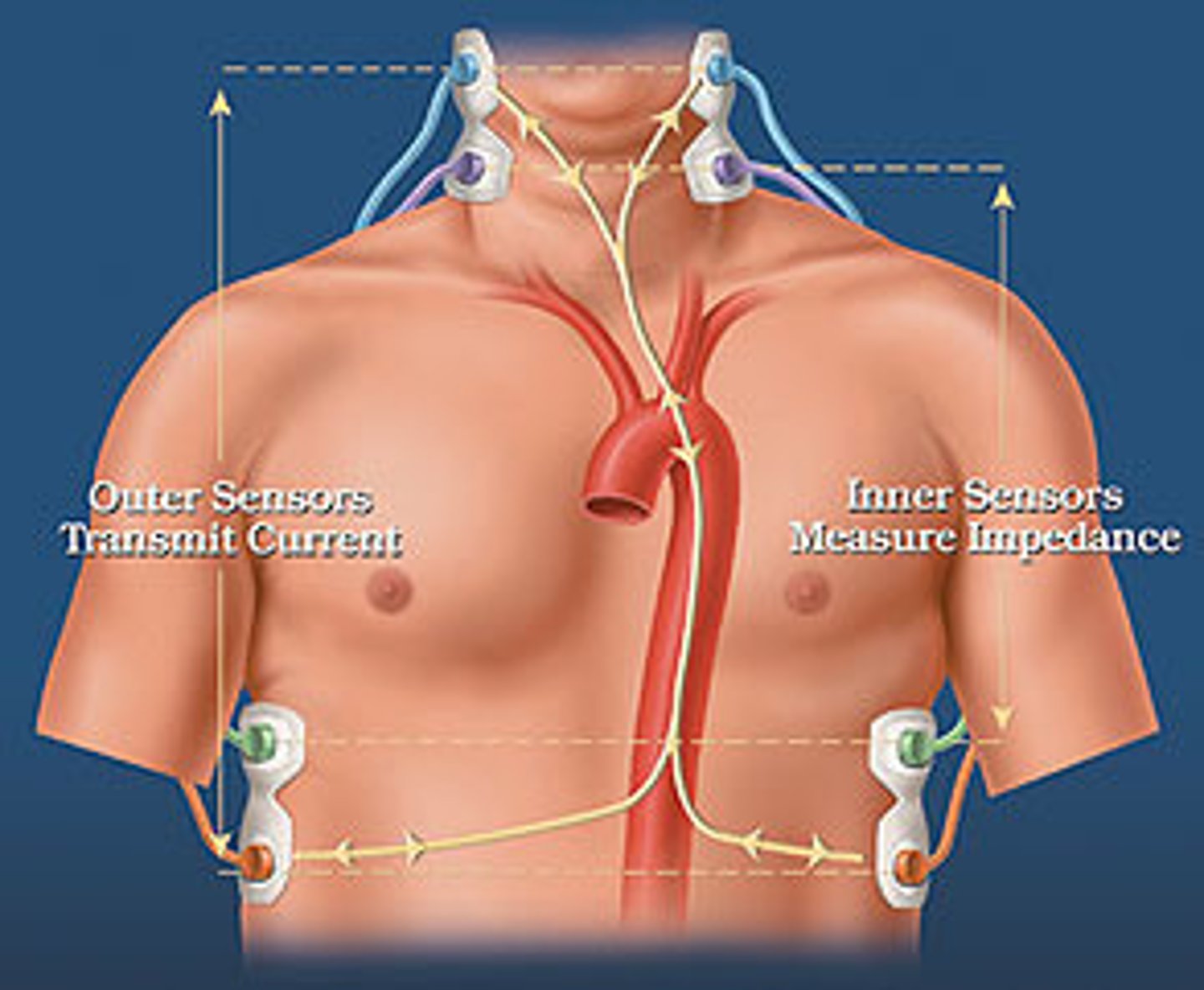
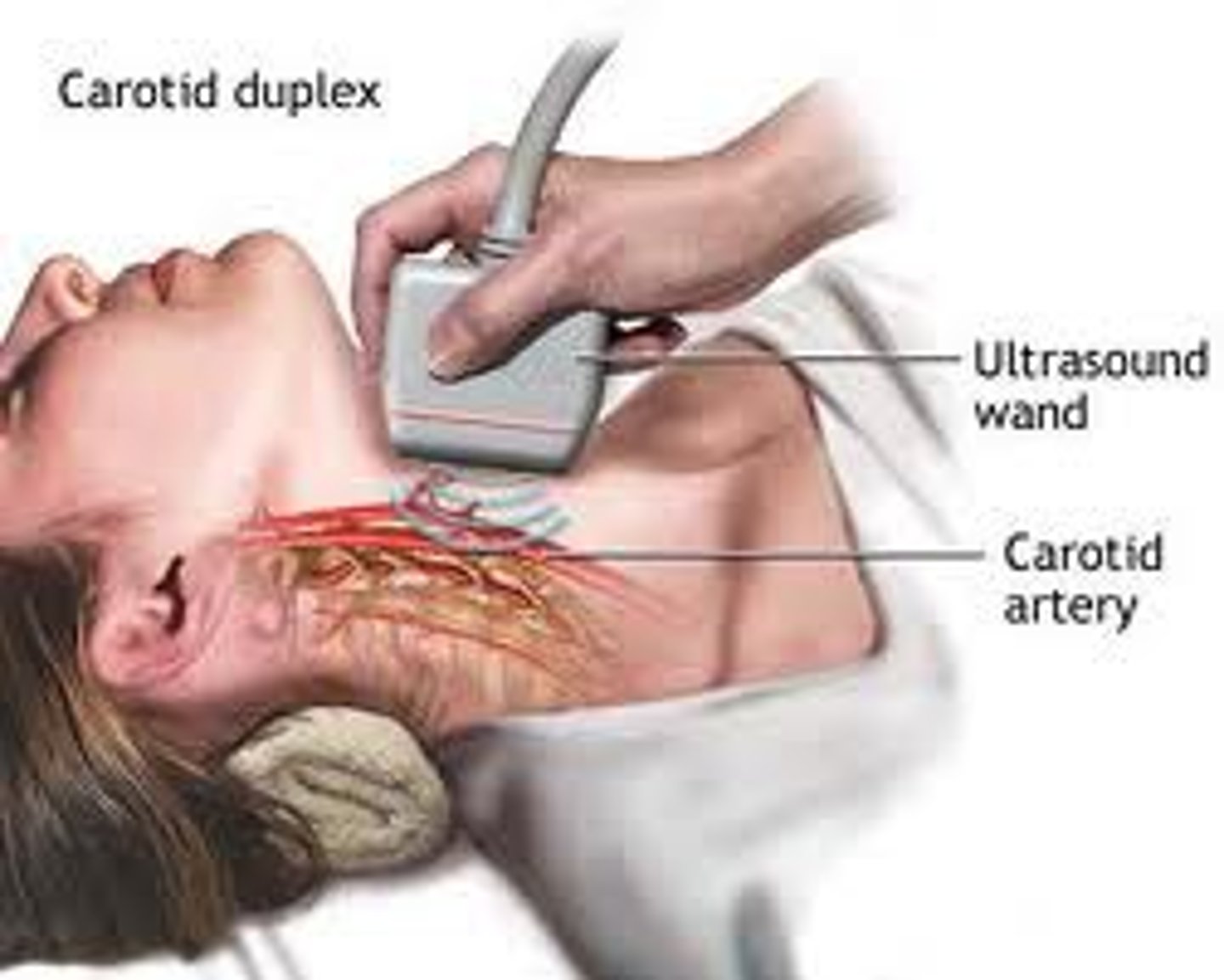
what noninvasive hemodynamic technology measures blood flow velocity in the vessel and helps to determine CO, preload, afterload, and contractility
doppler ultrasound
Minimally invasive hemodynamic technologies (3)
1) CVPs- transducer/computer based and visual
2) arterial access line
3) MAP
MAP formula
(SBP + 2(DBP))/3
Locations for arterial line placement (5)
1) radial
2) DP
3) femoral
4) axillary
5) brachial
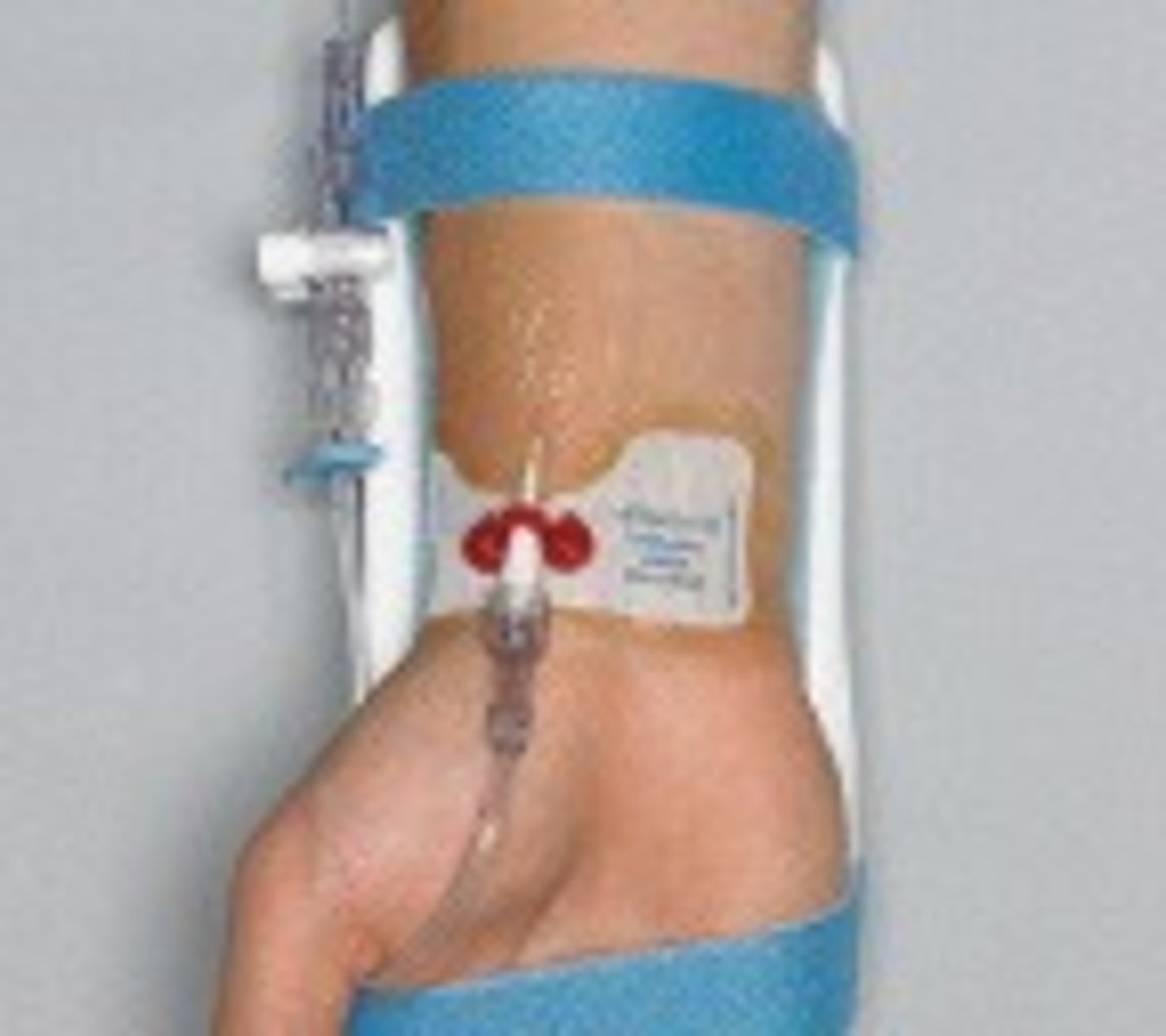
indications for an art line (3)
1) monitoring BP
2) frequent ABGs
3) if low CO or shock cuff is unreliable
Difference between an art line and a BP cuff
- art line- measures flow inside artery
- cuff- measures flow from outside artery
- may measure 5-10 mmHg differently
Vigileo FloTrac Benefits
- Minimally invasive; Connects to existing arterial line.
- Requires no manual calibration.
- Automatically calculates hemodynamic values every 20 seconds.
- Accurate when validated against Swan catheter
Which data does Vigileo produce?
- CO
- CI
- central venous oxygen saturation
- SV
- SV variation
- SVR
central venous oxygen saturation
determines oxygen extraction vs demand (O2 utilization)
Which hemodynamic parameter assesses ventricular performance?
SV
What is stroke volume variation?
variation in SV given as %; >15% may indicate hypovolemia
Which hemodynamic parameter is an indicator of afterload?
SVR
SWAN/PA catheter measurements
- PAP (pulmonary artery pressure) - systolic, diastolic, mean
- PAWP (pulmonary artery wedge pressure)
- CVP (central venous pressure)
- CO
- CI
- SVR
- PVR
PA catheter advantages
- real-time data
- simultaneously measures a variety of hemodynamic parameters
- able to rapidly assess pt response to interventions
PA catheter disadvantages
- infection
- insertion complications (pneumothorax, bleeding, damage to blood vessels, or heart dysrhythmias)
- air emboli, exsanguination
- balloon rupture (rare)
- pulmonary artery rupture (rare)
What does PAWP reflect?
left sided preload
normal PAWP
4-12 mm Hg
What does CVP reflect?
right sided preload
normal CVP
2-6 mmHg
What does PAP measure?
blood pressure in the lungs
normal PAP
20-30/ 10s mmHg
What does CO/CI measure?
volume ejected/min with each beat
Normal CO and CI
CO = 4-8L/min
CI = 2.5-4 L/min
What does PVR reflect?
right sided afterload
What does SVR reflect?
left sided afterload
Normal PVR
50-250 dynes/sec/cm-5
Normal SVR
800-1200 50-250 dynes/sec/cm-5
conditions that elevate PA pressures (2)
1) pulmonic valve stenosis/calcification
2) pulmonary HTN
a condition elevating PA pressures; insidious process that happens over time with increased afterload on right ventricle
pulmonic valve stenosis/calcification
a condition elevating PA pressures; increased afterload on right ventricle which impacts right ventricular emptying (incomplete emptying)
pulmonary hypertension
Interventions for elevated PA pressures
- find cause
- reduce preload (circulating volume)
- decrease venous return to the right side
- increase/improve contractility
- meds
- Na and fluid restriction
- valve replacement/repair
meds for increased PA pressures
1) vasodilators (viagra)
2) diuretics
The degree of stretch in myocardial fibers at the end of diastole *
preload/ventricular filling
According to the Frank Sterling law, the more you stretch the ventricle during , the stronger the contraction in *
According to the Frank Sterling law, the more you stretch the ventricle during diastole, the stronger the contraction in systole
The most common cause of pulmonary HTN*
aortic valve disease/stenosis