CHEM EXAM 1: Concepts, Definitions, and other facts
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Matter
anything that has mass and occupies space
Fact
A basic statement established by experiment or observation that is true under specific conditions of the observation
Hypothesis
tentative(can be changed) explanation that can be tested by further investigation
Theory
Well-supported explanation of observations, aren’t likely to change
Law
Principles that can be used to predict the behavior of the natural world (patterns)
Qualitive vs Quantitative Observations
Qualitive observations describe using senses
Quantitative observations are measured, include number values
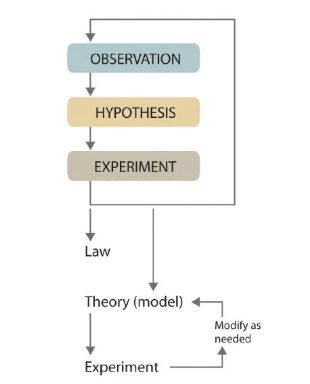
Scientific Method
Make observations
Formulate a hypothesis
Test the hypothesis through experimentation
Accept or modify the hypothesis
Develop into a law and/or a theory
Scientific Notation
N ×10n where N is less than 10 and n is any integer
Sig Fig rule when multiplying/dividing
count the number of sig figs in each factor and limit the sig figs in the answer to the least # of sig fig in the factors (use rounding)

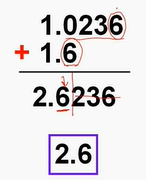
Sig Fig rule when adding/subtracting
limit the sig figs in the answer to the digits that both numbers have in common
accuracy vs precision
accuracy is how close a measurement is to the true value
precision is how close a series of measurements are to each other and if hey give reproducible results
Sig Fig Rules
All nonzero digits in a measurement are significant
Zeroes that appear between other nonzero digits (middle zeros) are always significant
Zeros that appears in front of all the nonzero digits (leading zeros) are never significant
Zeros that appear after all nonzero digits (trailing zeros) are ambiguous
Zeros after the decimal pt are significant, but not if they are leading zeros
Mass vs Weight
Mass measures amount of matter
Weight is the force of gravity
Volume
amount of space occupied by matter
Temperature
measure of the average amount of energy of motion (kinetic energy) a system contains
Density
the mass of an object divided by its volume; can be used as a conversion factor between mass and volume
Atoms
building blocks of matter and the universe
Molecules
bonded atoms, can be combined in different ways, have properties like shape, size, color, boiling point, volatility, conductivity, etc.
Stages of Matter
Solid: particles are in a fixed position, shape and volume are definite
Liquid: particles are in contact but not fixed, shape is not definite by volume is
Gas: particles are in random positions, shape and volume aren’t definite
Pure substance
matter that has constant composition and properties are constant throughout the sample
Mixture
matter consisting of two or more substances that retain their individual identities and can be separated by physical methods
Homogenous mixture: mixtures that have a uniform composition and properties throughout (ie AJ and tea)
Heterogeneous mixture: mixtures that aren’t uniform (ie guac and trail mix)
Element
substance that cannot be broken down into chemically simpler components; composed of the same type of atom
Compound
substance that are made up of more than one type of atom; can be separated into simpler substances and elements by chemical methods
Physical vs Chemical Properties
Physical properties: characteristics that can be observed or measured
Ex: conductivity, malleability, color, hardness, solubility, density
Chemical properties: describe a sample’s potential to undergo a chemical reaction by virtue of its composition
Ex: burn, rot, explode, decompose, ferment, rust, flammability
Physical vs Chemical Change
Physical: no bonds are broken or formed
Ex: change of state, separation of a mixture, deformation, making solutions
Chemical: bonds are broken and/or formed
Indicators: temp changes, light produced, color changes, bubbles, different smell or taste, precipitate
Conservation of mass
No matter can be created or destroyed
Heat
energy that is transferred from a hot object to a cooler object due to the difference in their temperature
Work
transferred energy as a result of a force applied over distance
Kinetic and Potential Energy
Kinetic: energy of motion
Potential: stored energy that depends on the position of an object rea=lative to another object
Endothermic Processes
Where a system absorbs heat and the temperature of the surroundings get cooler; the system gets hotter (q>0)
Exothermic Processes
Where a system releases/loses heat and the temperature of the surroundings get warmer; the system gets colder (q<0)
Heat Capacity vs Specific Heat
Heat capacity: the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of an object by 1 °C
Specific Heat: the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 °C
Diatomic Atoms
Hydrogen (H)
Oxygen (O)
Fluorine (F)
Bromine (Br)
Iodine (I)
Nitrogen (N)
Chlorine (Cl)
John Dalton and Modern Atomic Theory
all matter is composed of extremely small atoms
atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties
atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed
atoms of different elements can combine in numerous rations to form chemical compounds
in chemical reaction, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged
Plum Pudding model by J.J. Thompson
electrons are like blueberries on a muffin or plums in pudding embedded in a uniform sphere of positive charge
Nuclear Model by Rutherford
all of the positive charge and majority of the mass of the atom must be concentrated in the atom’s nucleus
Nucleus is the central core of the atoms that is composed of protons and neutrons
Electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy most of the volume of the atom
Electrons
contribute virtually nothing to the total mass of an atom
found orbiting nucleus
charge of -1
symbol: e-
Protons
found in the nucleus
charge of +1
mass of 1 amu
symbol: p+
Neutrons
in all atoms except hydrogen
no charge
mass of 1 amu
symbol: n0
Periodic Table
Developed by Dmitri Mendeleev
Rows of the table are called periods
Columns of the table are called groups
Each element has unique symbol and atomic number
Metal
a substance that is shiny, an excellent conductor of electricity and heat, and malleable and ductile
Metalloid
elements with properties intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals
Nonmetal
dull, poor conductor, and brittle
Group 1
The Alkali Metals; common in nature and daily life
Lithium (Li), atomic # of 3
Sodium (Na), atomic # of 11
Potassium (K), atomic # of 19
Rubidium (Rb), atomic # of 37
Cesium (Cs), atomic # of 55
Francium (Fr), atomic # of 87
“Lisa Saw Patrick Rob Cane’s Fries”
Group 2
The Alkaline Earth Metals
Beryllium (Be), atom # of 4
Magnesium (Mg), atom # of 12
Calcium (Ca), atom # of 20
Strontium (Sr), atom # of 38
Barium (Ba), atom # of 56
Radium (Ra), atom # of 88
“Bart Might Cause Some Bad Rukus”
Group 7
Halogens; react readily with metals to form compounds
Florine (F), atomic # of 9
Chlorine (Cl), atomic # of 17
Bromine (Br), atomic # of 35
Iodine (I), atomic # of 53
Astatine (At), atomic # of 85
“Flanders Can Bake Incredible Apple-pie”
Group 8
Noble Gases; compromised of single atoms aka monatomic; unreactive
Helium (He), atomic # of 2
Neon (Ne), atomic # of 10
Argon (Ar), atomic # of 18
Krypton (Kr), atomic # of 36
Xenon (Xe), atomic # of 54
Radon (Rn), atomic # of 86
“Home Needs All Krustry’s Extras Ribs”
Ions
Atoms that have a charge because they have more protons than electrons pr vice versa
cations: have a positive charge because they lost an electron; metals become cations (groups 1 & 2 become cations)
anions: have a negative charge because they gained an electron; nonmetals become anions (groups 7 become anion)
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that differ in their number of neutrons
have different mass numbers
can be denoted like so:
Nickel-59 where # is the mass number
Mass Number (A)
total number of protons and neutrons
Chemical Potential Energy
Potential Energy stored in atoms
Physical Chemistry
Study of macroscopic properties, atomic properties, and phenomena in chemical systems
Organic Chemistry
Study of chemicals containing carbon
Inorganic Chemistry
Study of chemicals found in rocks and minerals
Analytical Chemistry
Study of composition of matter through separation, identification, and quantification of chemicals in samples of matter
Biochemistry
Study of chemical processes that occur in living systems
Alchemy
Study of matter based on fire, water, earth, and air that believed changing proportions of these in a substance could change its composition
Robert Boyle
Developed basic ideas about behavior of gases
Joseph Priestly
Isolated and characterized Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, etc.
C. W. Scheele
Discovered Chlorine gas
Lavoiser
Father of chemistry
discovered nitrogen gas
discovered the role of oxygen in combustion
formulated the law of conservation of matter
Amadeo Avogadro
Pioneered quantitative approach to chemistry by calculating the number of particles in a given amount of gas