Incisions and Retractions
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
What are Halsted’s Principles of Surgery?
gentle handling of tissue
meticulous haemostasis
preservation of blood supply
obliteration of dead space
minimum tension on tissues
accurate tissue apposition
strict aseptic technique
To achieve Halsted’s Principles what do we need to consider?
incisions
dissection
haemostasis
tissue retraction
tissue handling
lavage and suction
drains

What is this scalpel blade used for?
long straight skin incisions

What is this scalpel blade used for?
stab incisions

What’s this scalpel blade used for?
stitch removal

What’s this scalpel blade used for?
thinner skin, curved incisions, areas where we need to follow a contour (e.g. paws)

What’s this scalpel blade used for?
like 10 but larger (long straight skin incisions)
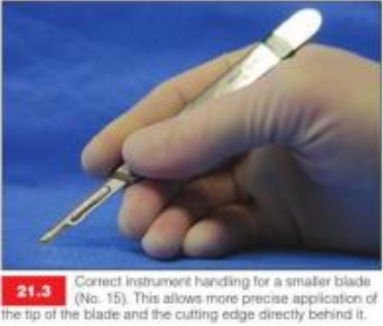
What does this image show?
pen-grip
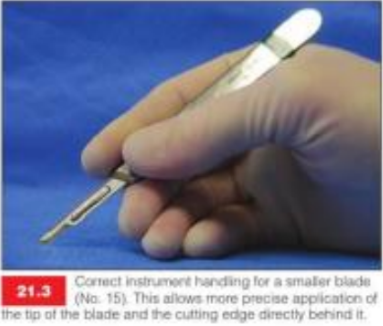
What is the pen grip useful for?
allows more precise control
useful for curves/achieving full thickness depth right into the corners of the incision
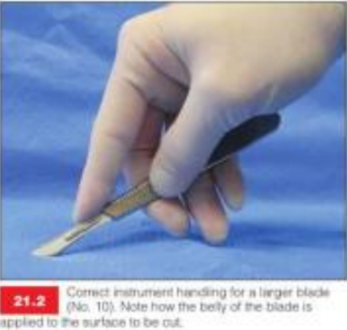
What does this image show?
shallower angle using more of the ‘belly’ of the blade than the tip
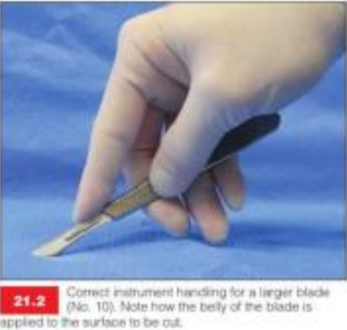
What is this grip useful for?
making long, straight incisions
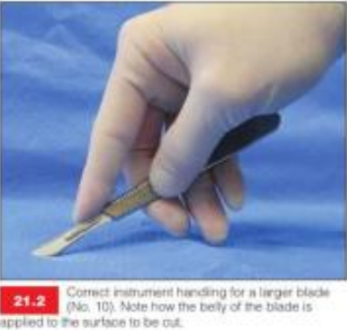
What is the sharpest part of the blade?
belly
What are the 2 ways to make an incision?
slide cutting
stab incision
How do you do slide cutting to make an incision?
stretch out/place tension on skin with free hand (non-dominant)
one smooth incision, using belly of the blade
How do you do the stab incision to make an incision?
one clean movement, using point of blade
may need to elevate tissue being incised, so that you don’t damage structures underneath (e.g. linea alba)
What are the tip tips for making incisions?
smooth incision - don’t go over multiple times - causes jagged edges
avoid incising blood vessels
don’t lean scalpel hand on patient whilst incising - hover
know landmarks
alter how firmly you’re pressing and angle of blade throughout incision to achieve consistent depth (press more firmly and steeper angle in corners, than the middle)
What size scalpel blade is best for excising a 2cm skin mass on the distal limb?
A) 10
B) 11
C) 12
D) 15
E) 20
D) 15
What are the 2 methods of dissection?
sharp
blunt
What does blunt dissection go along?
natural tissue planes or parallel to tissue fibres
Why do you need good visualisation and good anatomical knowledge when dissecting?
avoid damaging delicate structures in the area
Why should you avoid excessive dissection?
increase dead space
increase risk infection
What can you use to dissect?
digitally
scissors
Why is dissecting digitally useful?
for deep dissection so you don’t damage tissues you can’t see
What is undermining a form of?
dissection
What is undermining used for?
relieving tension when closing skin
Whilst making a skin incision, you cut through a small skin vessel which bleeds persistently. What is the best way to stop the bleeding?
apply pressure (e.g. clamp, swab)
ligating
Define ‘haemostasis’
stopping blood flow
Why is haemostasis important?
decrease blood loss
increase visibility surgical field
decrease seroma and haematoma formation
decrease dead space formation
decrease risk of infection
What are the 3 ways we can achieve haemostasis?
mechanical
thermal
chemical
How do you perform mechanical haemostasis?
digital pressure
haemostats
ligatures
What is the aim of mechanical haemostasis using digital pressure?
stem flow for long enough that platelets form plug
How do you do mechanical haemostasis using digital pressure?
press directly on vessel with single sterile gauze swab for 1-5 mins
What is digital pressure mechanical haemostasis NOT for?
medium-sized or large vessels
What is a benefit of using digital pressure for mechanical haemostasis?
minimal trauma
How do you use haemostats (clamps)?
place perpendicular to the long axis of the blood vessel
crushing stimulates coagulation
leave in place for at least 5 mins
How do you hold haemostats?
tripod grip
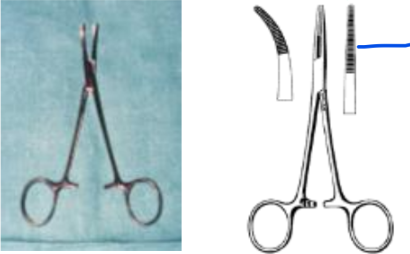
What do these images show?
haemostats
What do you place prior to ligation?
haemostat
What type of suture material do you use for ligatures?
absorbable
What ligature do you use for small vessels?
single
circumferential
What ligature do you use for pulsating or large vessels?
2
circumferential
for very large vessels you can use trans-fixing
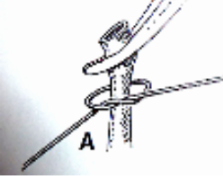
What type of ligature does this image show?
circumferential
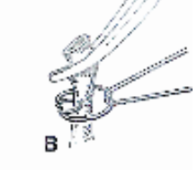
What type of ligature does this image show?
trans-fixing
What is used for thermal haemostasis?
electro-coagulation (diathermy/electrocautery)
How does thermal haemostasis using electro-coagulation work?
protein denaturation in tissue cells
What other products can be used for haemostasis?
cellulose/gelatin/collagen products
bone wax
How do cellulose/gelatine/collagen products achieve haemostasis?
provides scaffold and promotes clot formation
What are cellulose/gelatine/collagen products used for?
small volume, low-pressure bleeding
How frequently are cellulose/gelatine/collagen products used for haemostasis? why?
rarely - can delay wound healing and promote infection
When is bone wax used for haemostasis?
orthopaedic procedures
What chemicals can be used for haemostasis?
adrenaline
potassium permanganate, silver nitrate
When is adrenaline used for haemostasis?
used as an adjunct (e.g. digital pressure with adrenaline soaked swab) - not effective on it’s own
How does adrenaline work for haemostasis?
potent a2-adrenergic agonist causing vasoconstriction
When are potassium permanganate and silver nitrate used for haemostasis?
bleeding claws - NOT SURGERY
Why is tissue retraction important?
increase exposure and visibility
decrease tissue trauma and time
How do we achieve tissue retraction?
hand retraction (e.g. assistant)
instrument retraction (hand-held retractors, self-retaining retractors)
Is hand or instrument retraction preferred for tissue retraction?
instruments (more gentle)
What types of retractors are there for tissue retraction?
hand-held
self-retaining
What are hand-held retractors?
single handle and blade, used as extension of assistant’s hand (you still need a scrubbed assistant)
Name 2 types of hand-held retractors
Mathieu
Hohmann

What type of retractor is this?
Mathieu retractor

What type of retractor is this?
Hohmann retractor
What are self-retaining retractors?
blades of retractor placed within incision and opened until tissues on each side of incision are spread maximally
Do you need an assistant to hold self-retaining retractors?
NO
What do you need to be careful with when using self-retaining retractors?
avoid damage caused by tips
Name 2 types of self-retaining retractors
Gelpi
Weitlaner

What type of retractor is this?
gelpi retractor

How do you use a Gelpi retractor?
place 2 at 90 degrees to each other to create maximal exposure
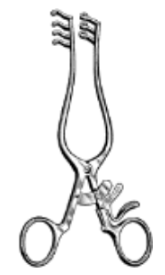
What is the name of this retractor?
Weitlaner retractor
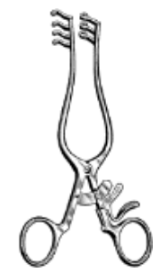
What is different about Weitlaner retractors (photo) compared to Gelpi?
retract larger area of tissue compared to Gelpi due to multiple prongs so can’t be used in as small wounds as Gelpi
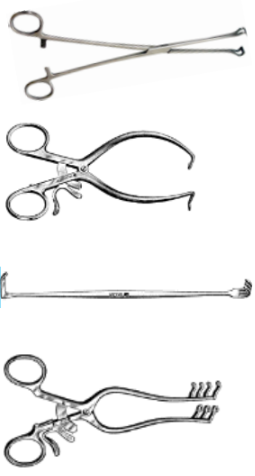
Which of these instruments typically require a scrubbed surgical assistant?
C
What are some top tips for good tissue handling?
make incision long enough to have good exposure
use natural tissue planes
use appropriate instruments
avoid excessive undermining
don’t let tissues dry out
How can you make sure tissues don’t dry out?
cover with moistened swabs
flush with sterile fluids

What type of tissue forceps?
treves (rat-toothed)

What are Treves (rat-toothed) tissue forceps for?
dense tissue (e.g. skin)

What is an advantage to using Treves (Rat-toothed) tissue forceps?
allow good grip without tissue slipping away

What type of tissue forceps are pictured?
Adson

What are characteristics of Adson tissue forceps (pictured)?
less traumatic rat-toothed
mini rat-tooth - finer tip so can only grasp tiny amount of tissue

What are these forceps?
Adson - brown tissue forceps

What are the characteristics of Adson - brown tissue forceps?
2 longitudinal rows intermeshing teeth
broad yet delicate grip without major trauma

What type of forceps are these?
dressing forceps

What are the characteristics of dressing forceps?
transverse sections

What type of forceps are these?
DeBakey and other smooth tissue forceps

What are the characteristics of DeBakey and other small tissue forceps?
least traumatic
smooth longitudinal grips
use for delicate tissues (e.g. bowel, blood vessels)
Name the foreceps from most trauma/grip/dense tissues to least trauma/grip/dense tissues
Treves (rat-toothed)
adson
adson - brown tissue forceps
dressing forceps
DeBakey (and other smooth tissues forceps)

Which image shows the correct way to hold thumb forceps?
image on the left
How should you hold thumb forceps?
pencil grip
What are forceps for?
manipulate and stabilise tissue during incising and closing

What is this?
Allis tissue forceps

What is this?
Babcock tissue forceps
What are locking forceps used for?
when prolonged tissue handling is required

What are Babcock tissue forceps used for?
less traumatic so used in more delicate tissue

What are Allis tissue forceps used for?
saw-toothed edge and crush tissue so should' not be used for delicate structures
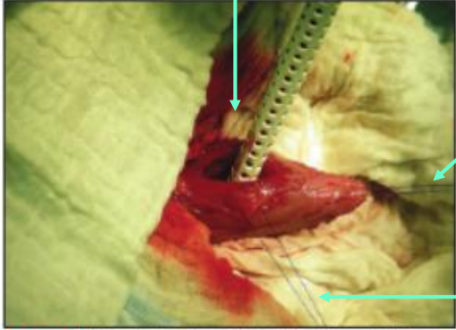
What does this image show?
stay sutures
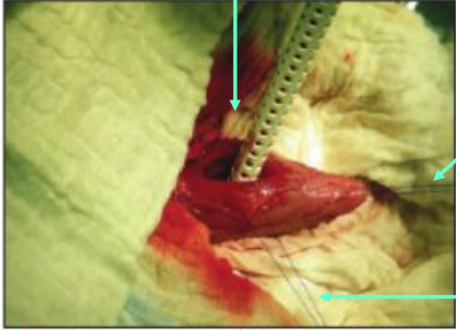
What are stay sutures used for?
minimally traumatic - use for delicate tissues (e.g. bladder wall)
confined areas where retractor instruments too bulky
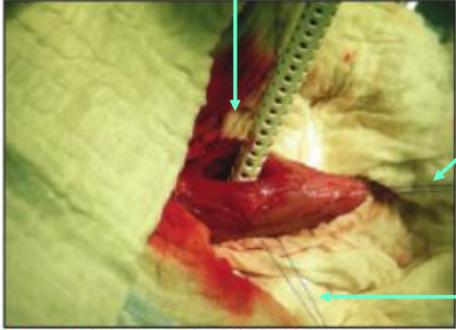
What type of suture should you use for stay sutures?
synthetic monofilament suture
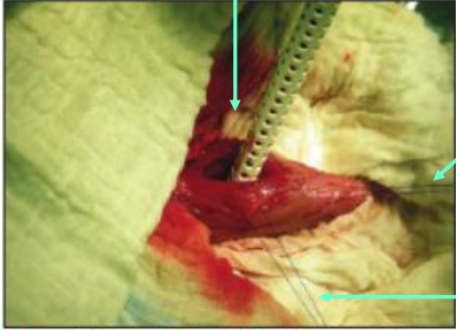
How do you apply a stay suture?
clamp 2 ends in haemostat and held by assistant/line on patient/table
large diameter suture & placed with taperpoint needle to avoid cheese-wiring/tearing through tissue
What can you use for tissue handling?
thumb forceps
tissue forceps
stay sutures
What should you use to hold the skin whilst you are suturing it closed?
Treves - rat toothed forceps
Why lavage?
decrease infection
moistening of tissues
increase visibility by removing blood