hematologic and renal emergencies
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
blood is solide components suspended in liquid called…
plasma
solid components of blood created in the…
bone marrow
blood comps. filtered out by…
spleen and liver
red blood cells have…..important for carrying O2
hemoglobin
platelets
fragments of larger cells crucial for forming clots
aspirin prevents aggregation of…
platelets
clotting factors are proteins produced in the…
liver
coagulopathy
abnormal clotting of blood
patients with liver cirrhosis
struggle to produce adequate clotting factors that form stable clots
hemophillia
don’t produce certain clotting factors
Von Willebrand’s disease
1/1000, normal number of platelets, but functionally defective
common blood thinners
Coumadin, Pradaxa, Eliquis, Xarelto, Lovenox
patients with a-fib usually on…
blood thinners
why? Blood pools in atrium and clots
anemia
deficiency in # of RBC’s
acute anemia
can be caused by trauma or big GI bleed —> SHOCK
checking for chronic anemia
color of patient conjuctiva on lower eyelid, anemic pateints very pale as opposed to ormal red/pink
sickle cell
results in sickle cell anemia
RBC’s sickled
lead to premature destruction of RBC
causes blockages in small blood vessels
destruction of spleen (blocked by sickled cells) - infection prone
sick cell crisis- block caps = severe pain
acute chest syndrome = shortness breath + chest pain due to hypoxia
priapism = sickle blockage prevent normal blood drainage
stroke = sickle blockage
jaundice = liver overwhelmed with breakdown of RBC = turn yellow
treatment of sickle
give O2 if chest pain/shortness of breath
monitor those with acute chest sydrome for respiratory failure and use BVM if needed
monitor fever and hypoperfusion patients for shock
transport stroke patients to stroke center
should I request ALS to provide pain control for sickle crisis
UTI’s caused by…
bacteria in the urinary tract
if infection acend to kidney = pyelonephritis (complain of unilateral flank pain)
very bad if bacteria gets into bloodstream (for old people)
kidney stone
calcium buildup in kidney
unilateral flank pain that radiates to groin when stone descends
lodged in ureter and unable to blass into bladder
naseua vomitting
renal failure
kidneys lose ability to filter blood = toxins buildup
end stage = need dialysis
long term damage cuased by diabetes or high blood pressure
fistula
connects arterial and venous flow
flow between surgically connected artery and vein makes noise called thrill when palpated
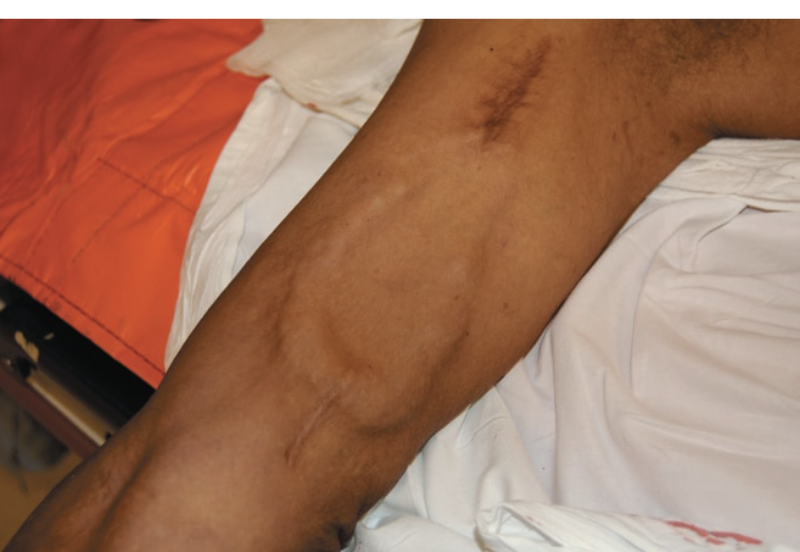
BP on other arm!
peritoneal dialysis
in home
slower
multiple treatments everyday
SA inside periotneal cavity that surround abdominal organs used to filter toxins and excess fluid
patients have catheter in ab wall and into peritonneal cavity
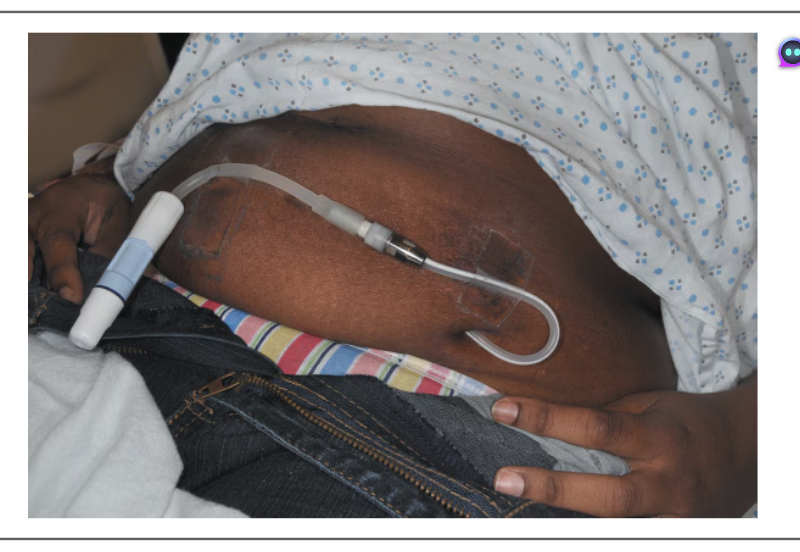
2 complications with end stage
loss of normal kidney function
missed dialysis
most dialysis patients have diabetes and high bp
missed dialysis
present with signs and symtoms similar to congestive heart failure
shortness of breath due to fluid buildup in lungs and elsewhere (hands, face, feet, ankles)
no longer balanced electrolytes = electrical disturbances in heart = dysrhythmias
elevated K+ levels can lead to patient death
fistula not working
hard to the touch and no more thrill sound when palpated
common complication with peritonneal dialysis
peritonitis - infection of peritoneal cavity
ab pain, fever, dialysis fluid appears cloudy when drained from peritonneal cavity (looks like chicken broth)
ABC’s, control bleeding (elevation + hemostatic dressing), tourniqeut last resort if bleeding cant be stopped, O2, if peritonitis and presenting with shock, supine and keep warm and transport back of dialysis fluid with patient so it can be tested for bacteria