Organic Chemistry
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
organic chemistry
study of carbon, the compounds it makes, and hte reactions it undergoes
what are the five formulas in organic chemistry
molecular, empirical, structural, displayed, and skeletal
molecular formula
the exact number of atoms of each element present in the molecule (written in the subscript)
empirical formula
the simplest whole number ratio of atoms in the molecule (written in the subscript); ex. C2H5 could mean C4H10
structural formula
the minimal detail using conventional groups, for an unambiguous structure; ex. CH3CH2CH2CH3
displayed formula
shows both the relative placing of atoms and the number of bonds between them (basically lewis structure)
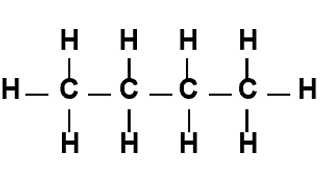
skeletal formula
shows a simplified organic formula by removing hydrogen
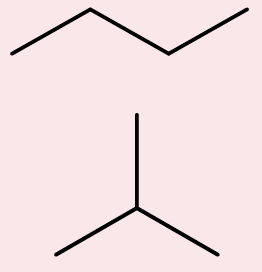
alkanes
hydrocarbon chains where all the bonds between carbons are single bonds; CnH2n+2
isomerism
where two or more compounds (isomers) have the same molecular formula but different arrangements (theres structural isomerism and stereoisomerism
what are the three types of structural isomerism
chain, positional, and functional isomerism
chain isomerism
the isomers differ specifically in the length of the main carbon chain and the placement of branches
positional isomerism
the isomers differ specifically in the position of the functional grop (like -OH or -Cl) or multiple bond (like C=C)
functional isomerism (or functional group isomerism)
the isomers differ specifically by their different functional groups
functional group
a specific atom or group of atoms responsible for the typical chemical reactions of a molecule
how to indicate that a substance is an alkane
use the suffix “-ane”
substituent
atom or group of atoms that replaces a hydrogen atom on a parent hydrocarbon chain or ring, acting as a “branch”
alkenes
have double bond between two or more of the carbons; are CnH2n
saturated hydrocarbons
have only single carbon-carbon bonds, holding the maximum number of hydrogen atoms, making them stable and less reactive; ex. alkanes
unsaturated hydrocarbons
have fewer hydrogens and extra bonds, making them more reactive and prone to addition reactions; ex. alkenes and alkynes
how to indicate that a substance is an alkene
use the suffix “-ene”