Elements, Nuclear Fusion, Spectra, and Doppler Effect
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
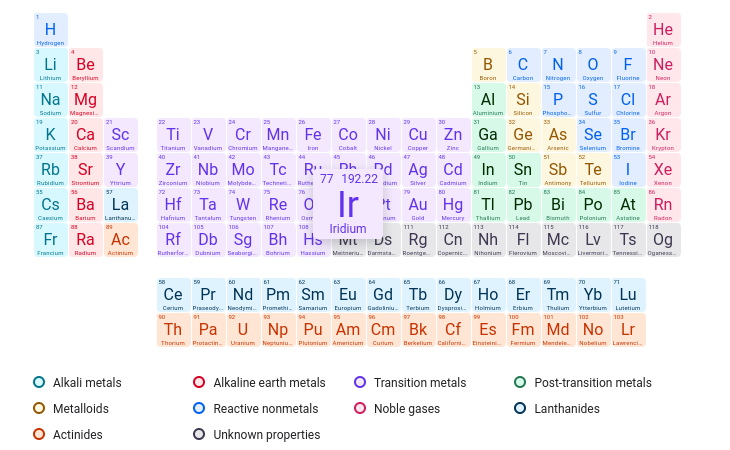
Which element has 60 protons in its nucleus?
Nd
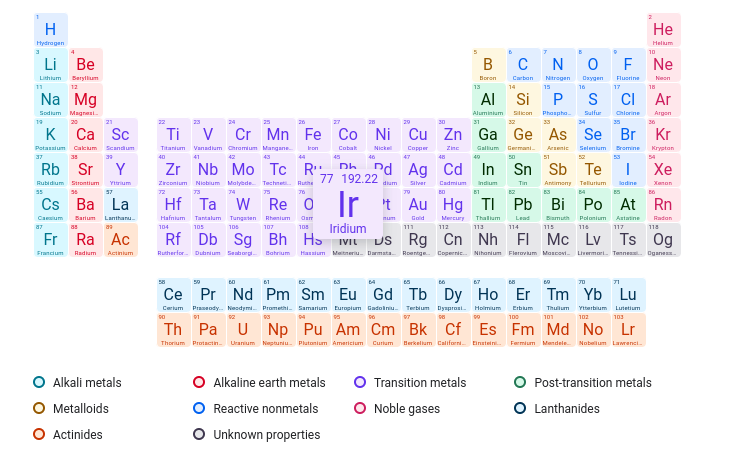
Which element has an atomic number of 75?
Re
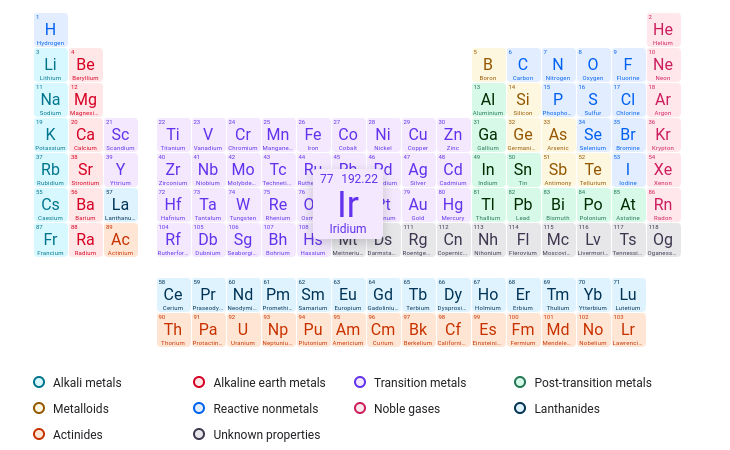
What element contains 35 neutrons and 31 protons?
Ga
If you were to write in isotopic notation, what 3 pieces of information does isotopic notation tell us?
Mass, element symbol, atomic number
What goes on the top in isotopic notation?
Mass
What goes on the bottom in isotopic notation?
Atomic number
What is fusion?
Two lighter elements combine to create one bigger element
What keeps a star stable?
Fusion in the core
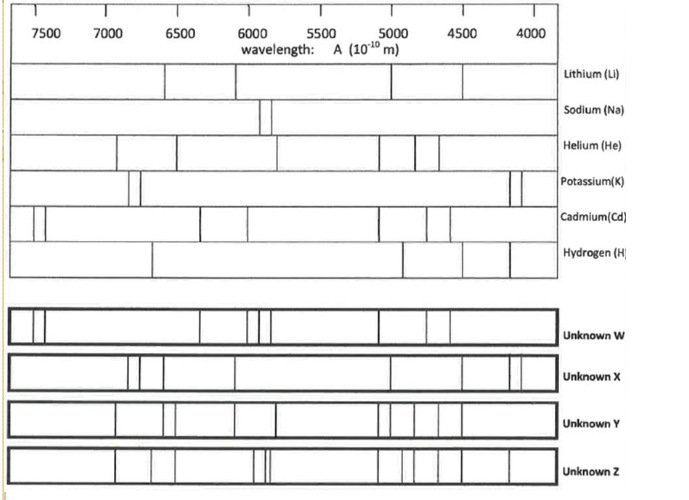
Determine the composition of Unknown X
K, Li
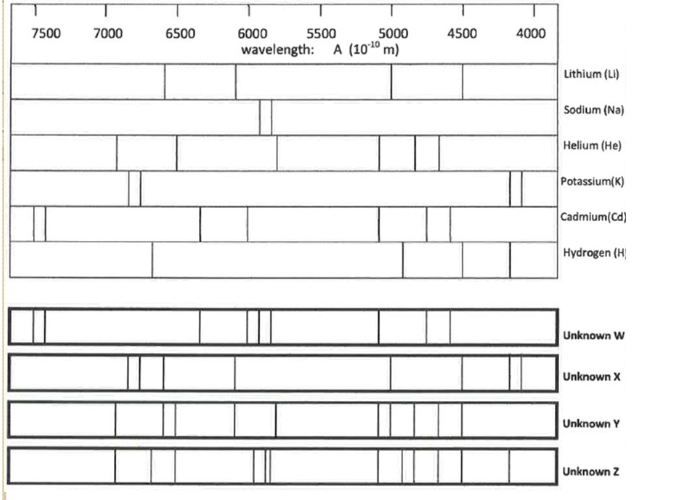
Determine the composition of Unknown Y
He, Li
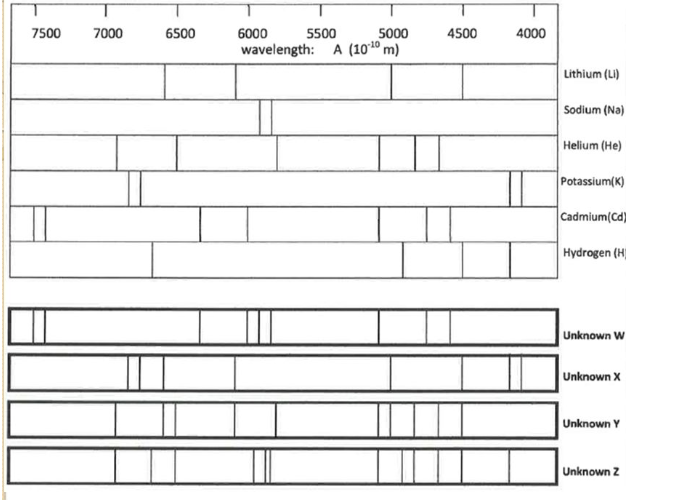
Would either of these stars (X and Y) produce a supernova? How would you be able to tell if it did?
Star X would probably produce a supernova. It produces potassium, which is an element high mass stars produce but low mass stars don’t. You would be able to tell if it was producing elements higher than 26.
What is the heaviest element that can be made in a star?
Iron (26)
Explain how the different colors of this spectrum are produced in terms of electrons, photons, and atomic energy levels.
Electron in ground state. It absorbs energy from heat, light, or electricity and jumps up to a higher energy level (excited state) (big jump, big energy and vice versa). Electron is unstable, emits its energy as a photon of light. Type of light determined by amount of energy released.
If an electron in a Hydrogen atom jumps from a high energy level (n=6), to a lower energy level (n=2), what would the color most likely be? Would it be a relatively higher or lower energy?
It would be violet because a lot of energy is released.
If an electron had a small jump down, what color would it be?
Red
True or false: The colors are IR, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet, and UV
False because IR and UV technically are not colors
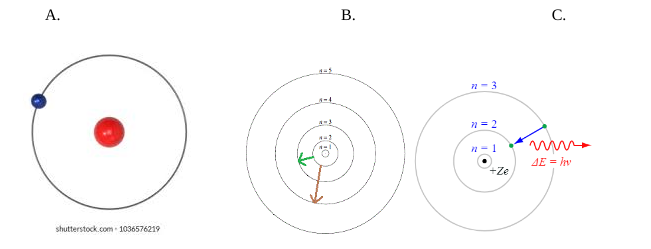
Which one of the following shows energy being absorbed by the electron?
B
A light wave is found with a wavelength of 4000nm in the IR region. Convert 4000nm to meters. Conversion factor: 1m=1E9 nm Report in correct units.
4 x 10^-6 m
If wavelength is 4 x 10^-6 m use the following equation to solve for the energy of a photon of 4000nm light. Energy=hc/wavelength h=6.63E-34 J*s c=3.00E8 m/s Report in correct units
4.9695E-20 J
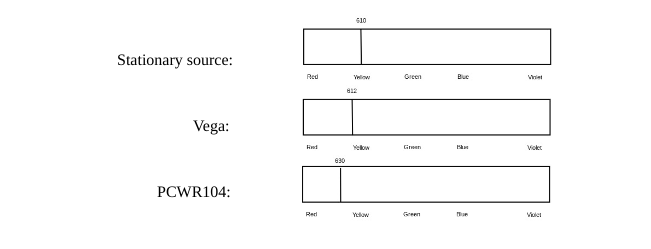
Explain why the yellow line from PCWR104 is shifted the way it is.
It is red shifted because it is moving away from the stationary source.
What would happen to the sound waves if a car was moving towards the observer?
They would move closer together and become higher pitched as they approach the observer
What is nucleosynthesis?
The process of element (nuclei) formation
True or false: Every element has the same atomic spectra
False
What does it mean if an object is blue shifted?
It is moving closer to us
What does it mean if an object is red shifted?
It is moving farther away from us
An ambulance is driving towards you. The sound waves would be…
small wavelength, high frequency
True or false: a blue shifted spectrum would have a wavelength longer than a red shifted spectrum
False
When an electron drops DOWN energy levels, it emits (releases) energy in the form of…
Light
True or false: A UV light wave has a small wavelength and high energy
True
What is the correct organization of the visible light spectrum from lowest to highest wavelength?
Violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, red
If an electron in Hydrogen falls from energy level N=6 to energy level N=2 what would its likely photon be?
UV
If an electron in Hydrogen falls from energy level N=2 to energy level N=1 what would its likely photon be?
IR
True or false: Absorption can be defined as when an electron takes in energy, becomes excited, and jumps an energy level
True
The three most common types of energy used to excite electrons come in the form of..
Heat, electricity, and light
Using atomic spectrum how could you tell a star has an older age?
By comparing the spectrum to known heavy elements like Iron and Cadmium
True or false: The identity of an atom is determined by its neutrons
False
The three types of nucleosynthesis are…
Stellar, Big Bang, and Supernova
True or false: The atomic mass is calculated by adding the number of protons and neutrons
True