Earth Science
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Earth
What is the only living planet discovered?
4 factors of habitability
Temperature
Energy
Atmosphere
Nutrients
Temperature
Which factor of habitability influences how quickly atoms and molecules move?
15°C - 115°C
What is the ideal temperature for a planet for life to exist?
Energy
Which factor of habitability is the light and chemical energy that run chemical reactions necessary for life.
Atmosphere
Which factor of habitability insulates, and provides protection from radiation.
Nutrients
Which factor of habitability involves the water cycle, and volcanoes to circulate nutrients.
The 4 Eons in the history of the Earth
Hadean
Archaean
Proterozoic
Phanerozoic
Eons
____ are the largest intervals of geologic time and are hundreds of millions of years in duration.
Phanerozoic Eon
What is the most recent eon and began more than 500 million years ago?
Eras
Eons are divided into smaller time intervals known as ____?
Periods
Eras are subdivided into ______.
Cenozoic Mesozoic and Paleozoic
Phanerozoic is divided into three eras:
Hadean
Which eon did not have that many evidence of existing except the discovery of Zircon Crystals?
Hades
Hadean eon was named after the Greek god and ruler of the underworld _____.
Archaean
Eon where life first emerged.
Proterozoic
Eon where unicellular life emerged also called the Precambrian period.
Paleozoic
What period in the geological time scale where fish diversified and marine organisms were very abundant, and where Pangea first formed.
Mesozoic
Era na may Dinosaurs.
Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous
What are the 3 periods of the Mesozoic Era?
Nicholas Steno
Danish scientist responsible for the modernization of Geology and the founder of Stratigraphy.
Stratigraphy
Study of Rock Layering
William Smith
Father of English Geology
Charles Lyell
Scottish scientist, author of the principles of Geology
Relative Dating
Determining which rock, fossil, or event came first, second, third, etc. (sequencing)
Absolute Dating
Determining the age of a rock, or fossil using radioactive decay and provide information.
Unifomitarianism
Law of nature that Earth’s cycles are constant but rates and intensity are varied through time
Fossils
Remnants of ancient creatures
The geologic time scale is an example of relative dating.
Geologic Time Scale is an example of what type of dating?
Law of Superposition
Law of Original Horizontality
Law of Cross-cutting relationship
Law of Lateral Continuity
What Laws of stratigraphy were proposed Nicholas Steno?
Law of Inclusions
What Laws of stratigraphy were proposed Charles Lyell?
Law of Faunal successions
What Law of stratigraphy were proposed William Smith?
crusts
sediments cannot form on ____ and can only be deposited on the bottom of a body of water.
Deposition
What is the collection of sediments called?
surface
Weathering cannot happen underwater, only on the ______ or if rocks emerge from a body of water.
Metamorphic Rocks
What is the whiskers called that are found in this image?
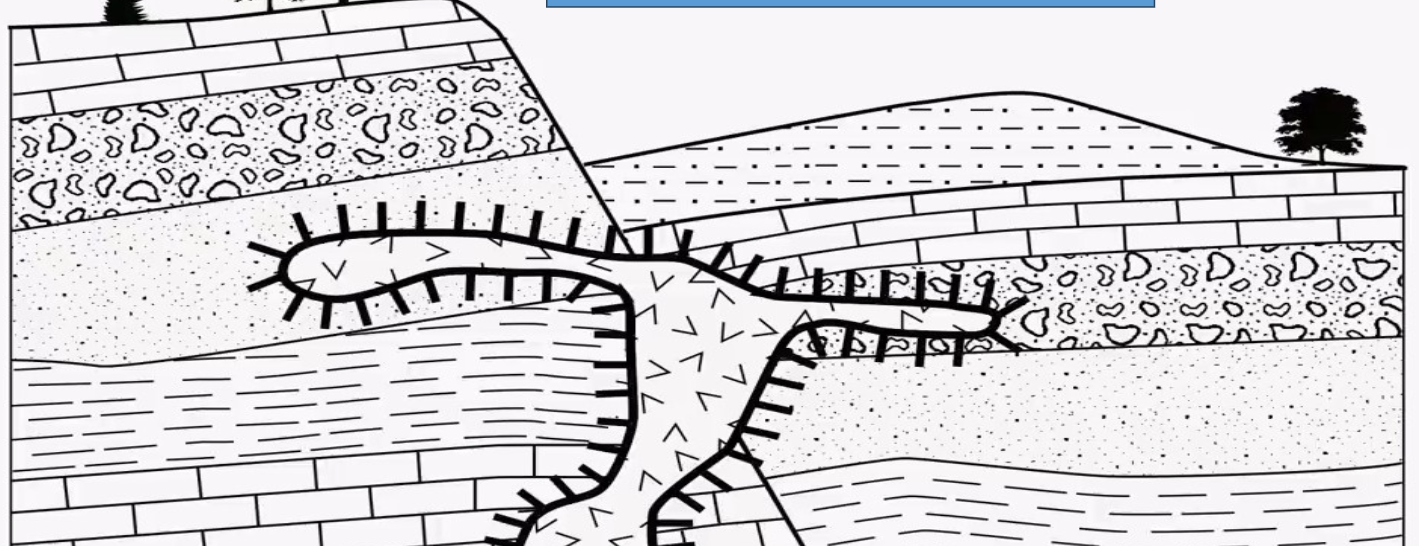
contact metamorphism
What is the process that is occurring on the whiskers in this image?
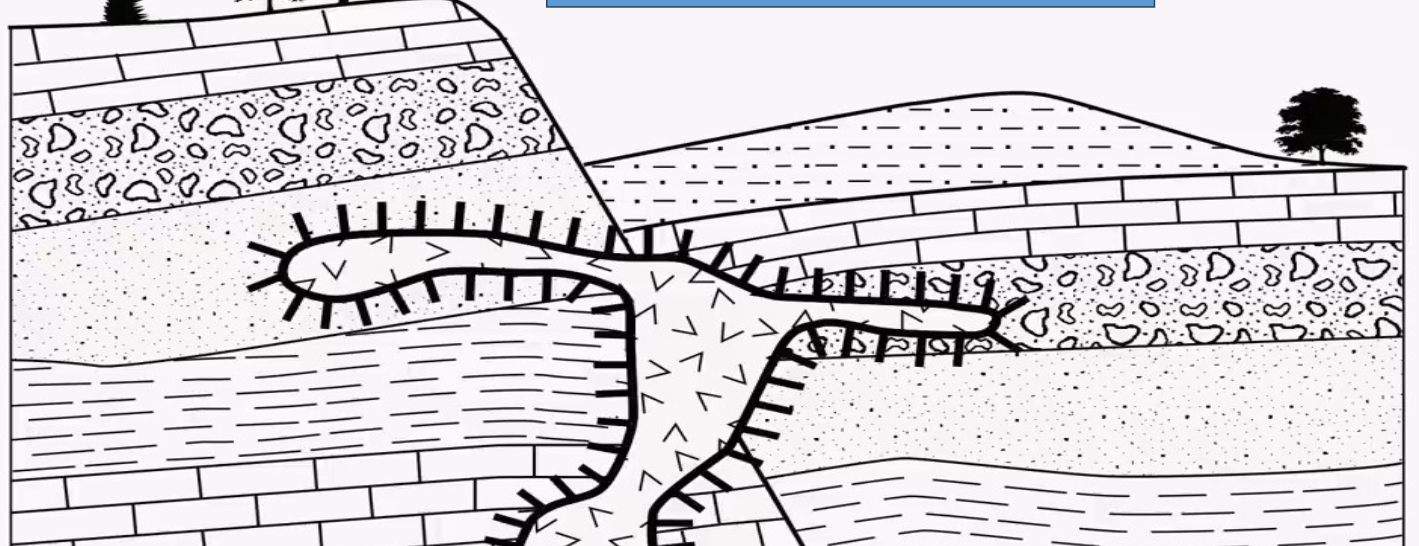
Law of Superposition of Strata
Younger layers of rock sit atop older layers
Law of Original Horizontality
Rocks are originally deposited flat
Law of Lateral Continuity
Layer of rock are continuous
Law of Cross-cutting relationship
When something cuts a sedimentary sequence then it is younger
Law of Inclusions
Inclusions are older than the rock they are deposited and layers are older than their intrusions
Near the bottom of rock layers
According to the Law of superstition, the oldest fossils are found
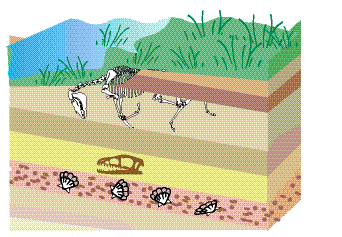
Sedimentary Rock type
Fossils are most common in what rock type?
absolute
If you say something occurred 12 million years ago, you are using _____ time.
Atmosphere
Earth subsystem (air)
Geosphere
Earth subsystem (land)
Hydrosphere
Earth subsystem (water)
Biosphere
Earth subsystem (life)
Troposphere
The only layer in the atmosphere clouds reside.
Ozone Layer
Part of the Stratosphere responsible for protection from UV radiation.
Mesosphere
Part of the Atmosphere responsible for the defense from space debris through friction.
Thermosphere
Part of the Atmosphere where particles are ionized/charged (magnetic field)
Exosphere
Part of the atmosphere where a small portion of our atmosphere “leaks”
Inner core
hottest, iron and nickel rich solid layer of the Earth where our magnetic field comes from
Outer Core
Second hottest, iron and nickel rich liquid layer of the Earth
Intense pressure
Why is the Inner core solid?
The Mesosphere and Asthenosphere
The mantle is divided into two layers which are?
Asthenosphere
What layer of the Earth that is fluid, moves the tectonic plates?
1.5 cm or 0.6 in
How many centimeters do the tectonic plates move yearly?
Oceanic and Continental Crust
Two kinds of crust
71%
How many % of the Earth is water
97%
How many % of the water in Earth is salt water?
69%
How many % of the freshwater is frozen
1%
How many % of the fresh water is surface water
Rocks
Aggregate of Minerals
Geology
Study of the changes of the Earth over time
Standards of a mineral
naturally occurring
chemically inorganic
homogenous solids
ordered internal structure
definite chemical composition
Streak
Color of mineral in powdered form
Hardness
Resistance to scratch
Cleavage
resistance from being broken into a semi smooth surface
diaphenity
transparency; ability for light to pass through
luster
how light is reflected on a surface
tenacity
reaction to stress
sectility
sliced by a knife
intrusive
still cooling rock
extrusive
already cool igneous rock
glassy texture (extrusive)
Silica-rich
vesicular texture (extrusive)
trapped gasses (buslot-buslot)
pyroclastic (extrusive)
rocks ejected during an explosive volcanic eruption
Aphanitic (extrusive)
fine-grained texture, crystals cannot be seen by the naked eye
porphoraytic (intrusive)
almost at the surface (still inside the crust)
phaneritic (intrusive)
crystals have melted, slow cooling process, high crystallization.
sediments
rocks broken into small pieces
compacting
_____ occurs when deposited sediments have lesser amounts of water
cementation
____ occurs when there is crystallization
Clastic sedimentary rocks
Conglomerate
Sandstone
Shale
non-clastic sedimentary rocks
Coal
Rock Salt
Limestone
Metamorphic rock type
rocks that have gone through intense heat and pressure (squeezing)
crystals, glassy or sparkly, and ribbon-feather-like structures
Metamorphic rocks have?
marble
an example of a metamorphic rock is?
obsidian
an example of a igneous rock is?
Glassy surface, and gas bubbles
Igneous rocks have?