Procedures 1 & Image Analysis 1 CLASS 8 TEST (Tibia, Fibula, and Knee)
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Osteochondritis or inflammation of the tibial tuberosity- demonstrated on the lateral knee or tib-fib.
Bipartite
Patella in 2 parts connected by fibrous tissue, may be mistaken for fracture. Usually a congenital malformation.
Popliteal
Posterior depression, corresponds with knee joint and popliteal artery.
Gastrocnemius Muscle
Large muscle located in the posterior portion of the lower leg.
Comminuted fracture
A fracture in which the bone is broken, splintered or crushed into 2 or more pieces.
Compound fracture
A fracture in which the bone is sticking through the skin- also called an open fracture.
The purpose of the CR angle on the AP knee is:
Opens the joint space and projects patella above joint.
The purpose of the CR angle on the lateral knee is:
To project medial condyle out of joint space.
The projection that best demonstrates the proximal fibula:
AP oblique knee, medial rotation
The projection that best demonstrates the tibial tuberosity:
Lateral knee or lateral tib/fib
The projection that best demonstrates the intercondyloid fossa:
PA Axial, Camp - Coventry Method
The projection that best demonstrates arthritis of the knees:
Upright weight-bearing knees
The method name for a PA axial knee:
Camp-Coventry
The method name for a tangential patella:
Settegast
The PA axial knee for the intercondylar fossa should be flexed:
Between 40-50 degrees
For an AP oblique projection of the knee, the limb is rotated _____ degrees.
45
The two flat, superior surfaces of the tibia are called the:
tibial plateaus
In which position is the patient placed for a PA projection of the patella?
prone
The central-ray angle for an AP, bilateral weight-bearing knee is:
0 degrees
Where is the central ray directed for the tangential projection (Settegast method) of the patella?
Through the patellofemoral joint space
What is the degree of angulation for the tangential projection of the patella (Settegast method)?
Variable—depending on the degree of knee flexion
The incomplete separation or avulsion of the tibial tuberosity is known as:
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Posteriorly, the femoral condyles are separated by a deep depression called the:
intercondylar fossa
Which anatomic part must be identified on lateral radiographs of the knee in order to identify over- or under-rotation?
Adductor tubercle
If the knee is flexed 40 degrees for the PA axial intercondylar fossa (Camp-Coventry) projection, the central ray will be angled _____ degrees.
40
Which of the following bones does not bear body weight?
fibula
How much is the knee flexed for a lateral projection?
20-30 degrees
Which of the following is clearly demonstrated on an AP oblique projection of the knee in medial rotation?
Proximal Tibiofibular articulation
On the anterior surface of the tibia is a prominent process called the:
tibial tuberosity
Which of the following will ensure that the knee is in proper position for a lateral projection?1. Epicondyles perpendicular to the IR2. Patella perpendicular to the IR3. Leg flexed 20 to 30 degrees
1, 2, and 3
Which of the following positions can be used to perform the tangential projection (Settegast method) of the patella? 1. Seated 2. Supine 3. Prone
1, 2, and 3
Which of the following projections of the knee best demonstrates the narrowing of a joint space?
Bilateral AP weight-bearing
The central-ray angulation for a lateral projection of the knee is:
5 to 7 degrees cephalad
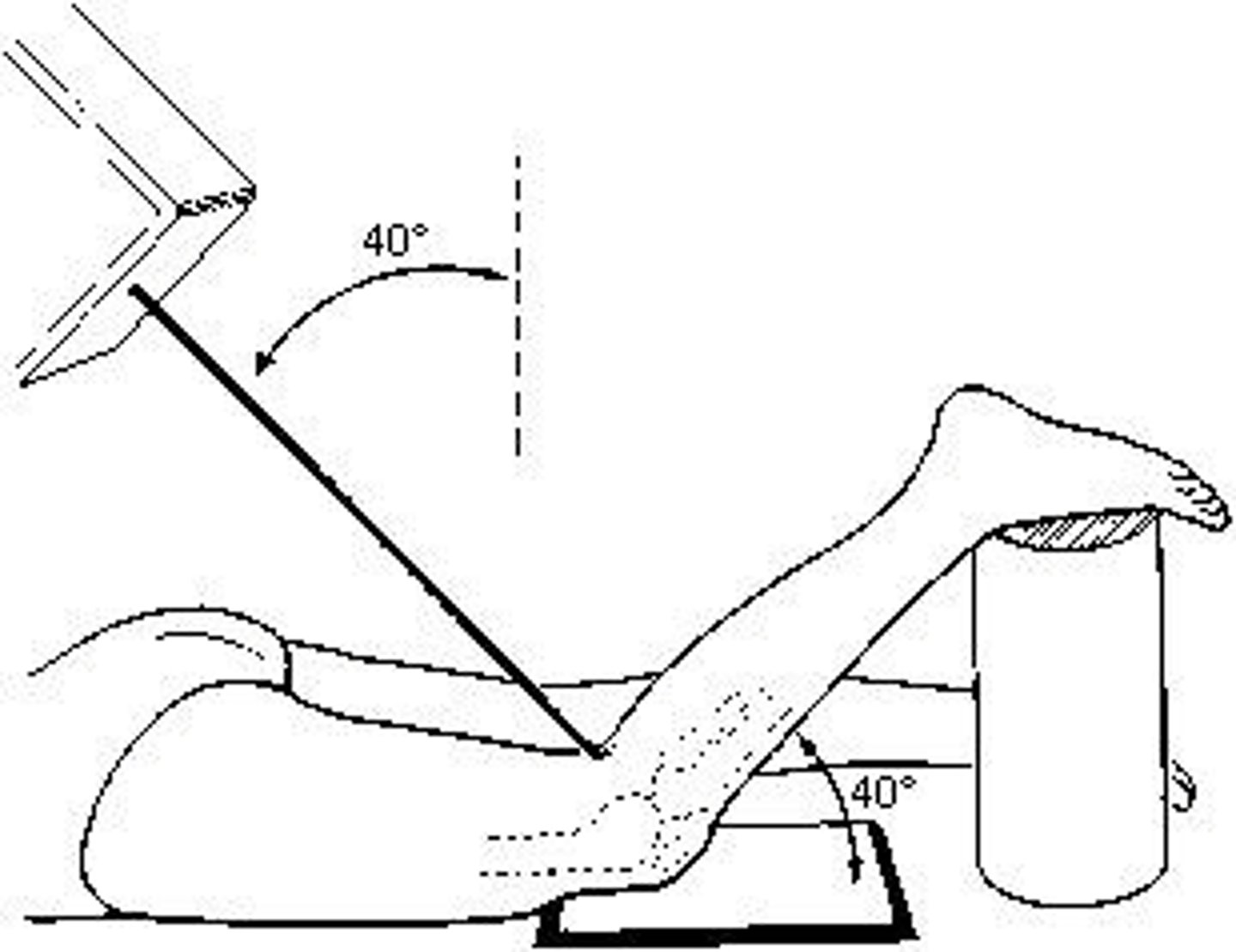
Camp-Coventry (intercondylar fossa)
The patient position and central-ray method demonstrated in the figure above is the:
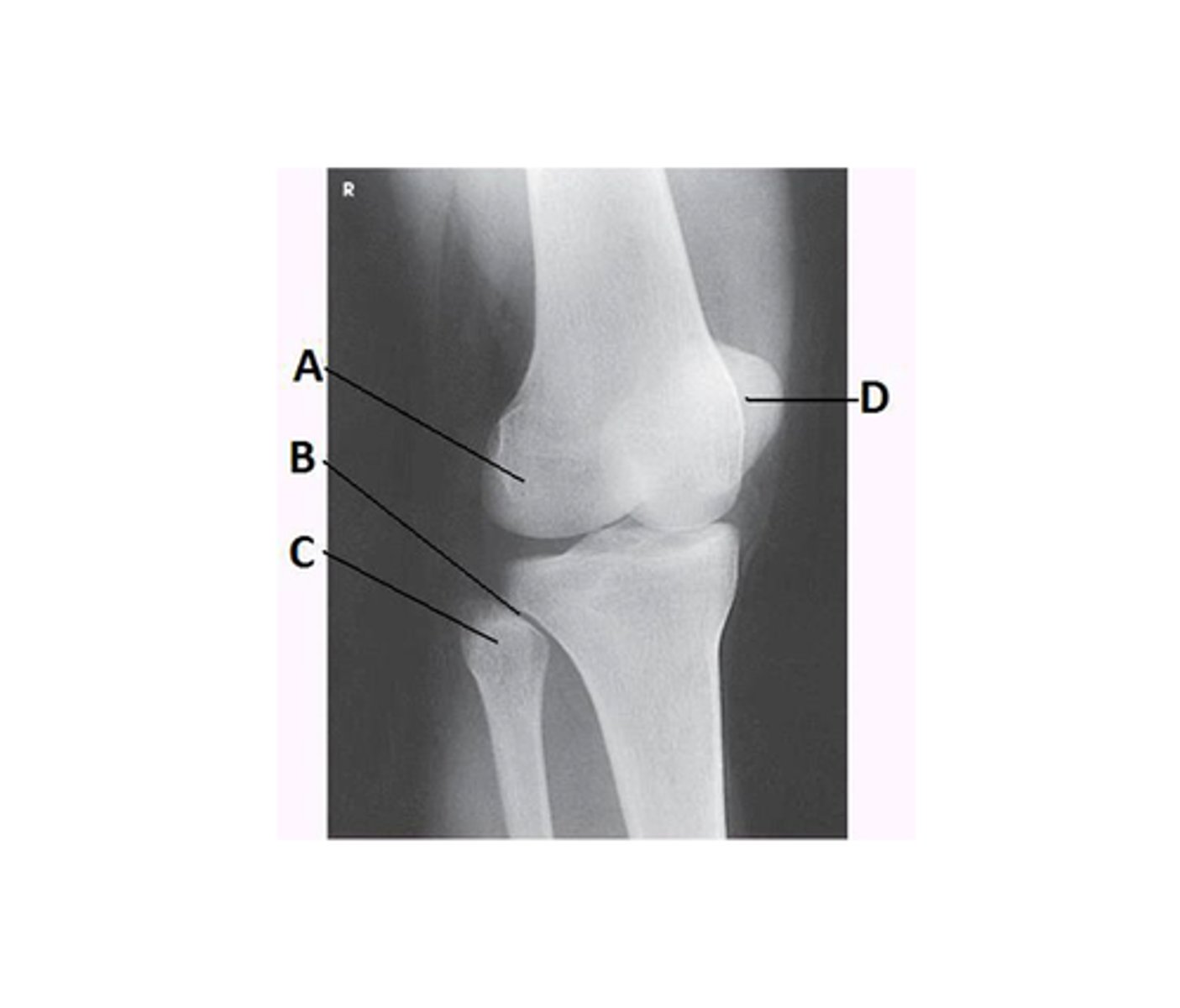
What anatomy is labeled with the letter B in the image below?
Proximal tibiofibular joint
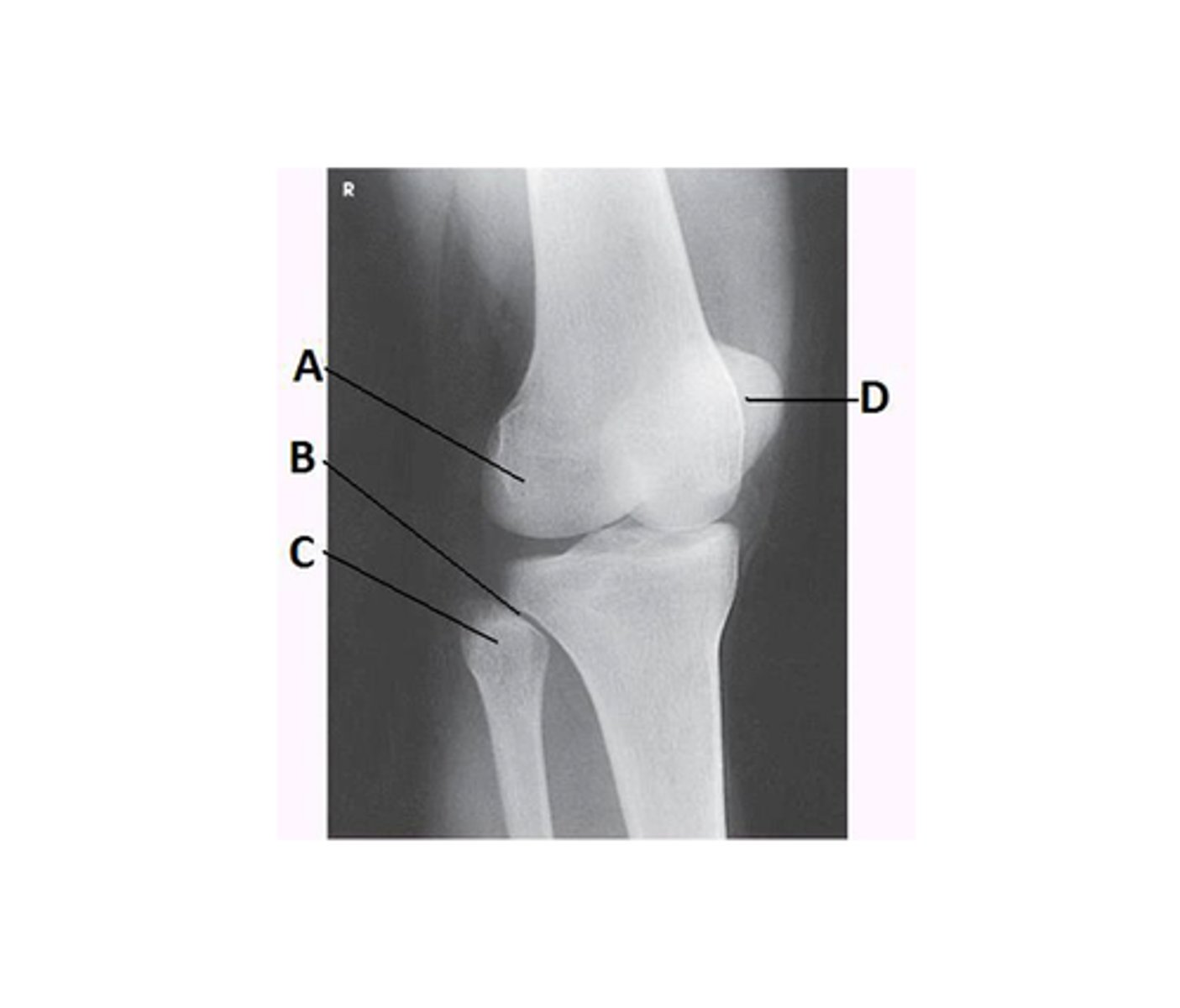
What lower limb position is required to obtain the image below?
45-degree medial rotation
What anatomy is best demonstrated on an AP oblique knee, medial rotation?
Prox tib/fib joint, head of the fibula, and lateral condyles
Which projection would best demonstrate the tibial tuberosity?
Lateral knee
What is the purpose of angling the CR on the lateral knee projection?
To project the medial condyle out of the joint space
What term means "patella in two parts"?
bi-partite
Which projection should visualize the proximal fibula in the lateral half of the tibia?
AP Oblique knee, lateral rotation (45 degrees)
What is the purpose of using a grid on a knee exam?
To reduce scatter and improve contrast
What is the centering point for an AP knee?
1/2 inferior to the apex of the patella
What is the method name for the tangential projection of the patella?
Settegast
What is the centering point for a lateral knee?
1" distal to the medial epicondyle
What is the CR direction and angle for a lateral knee?
5-7 degrees cephalic
What CR angle and direction is used on the Camp-Coventry when the lower leg is angled 40 degrees?
40 degrees caudal
When the thickness of the body part exceeds 10 cm or 4" a grid should be used. (T/F)
true
A tangential or 'sunrise' exam of the patella is contraindicated if a transverse fracture is suspected. (T/F)
true
The lateral condyle of the femur is inferior to the medial condyle. (T/F)
false
The medial condyle of the femur is inferior to the lateral condyle. (T/F)
true
Which projection best demonstrates arthritis in the knees?
AP bilateral weight-bearing knees
What is Osgood-Schlatter disease?
inflammation of the tibial tuberosity
If you cannot image the lower leg on one IR- how should you proceed?
Do a separate knee projection
Which projection best demonstrates a fabella of the knee?
Lateral Knee
The fabella of the knee is located in which muscle?
Gastrocnemius
Fabella
Fibrocartilage or bone that sometimes develops in the gastrocnemius muscle.
What is the range of the CR angle on an AP knee?
3-5 degrees
What is the centering point for an AP medial oblique knee?
1/2" inferior to the apex of the patella
The definition of a compound fracture:
A fracture where the bone is protruding through the skin
How much should the knee be flexed for a lateral projection?
20-30 degrees
What is the range of the CR angle on a lateral knee?
5-7 degrees
What is the collimation for an AP Tib/Fib?
1" on sides and 1.5" beyond joints
What is the collimation for a Lateral Tib/Fib?
1" on sides and 1.5" beyond joints
What is the collimation for all knee projections except tangential and weight-bearing?
8 x 10
What is the collimation for a Tangential Patella (Settegast)?
4 x 4
What is the collimation for AP Weight-Bearing Knees?
14" x 17" then adjust collimation to within 1" on the sides
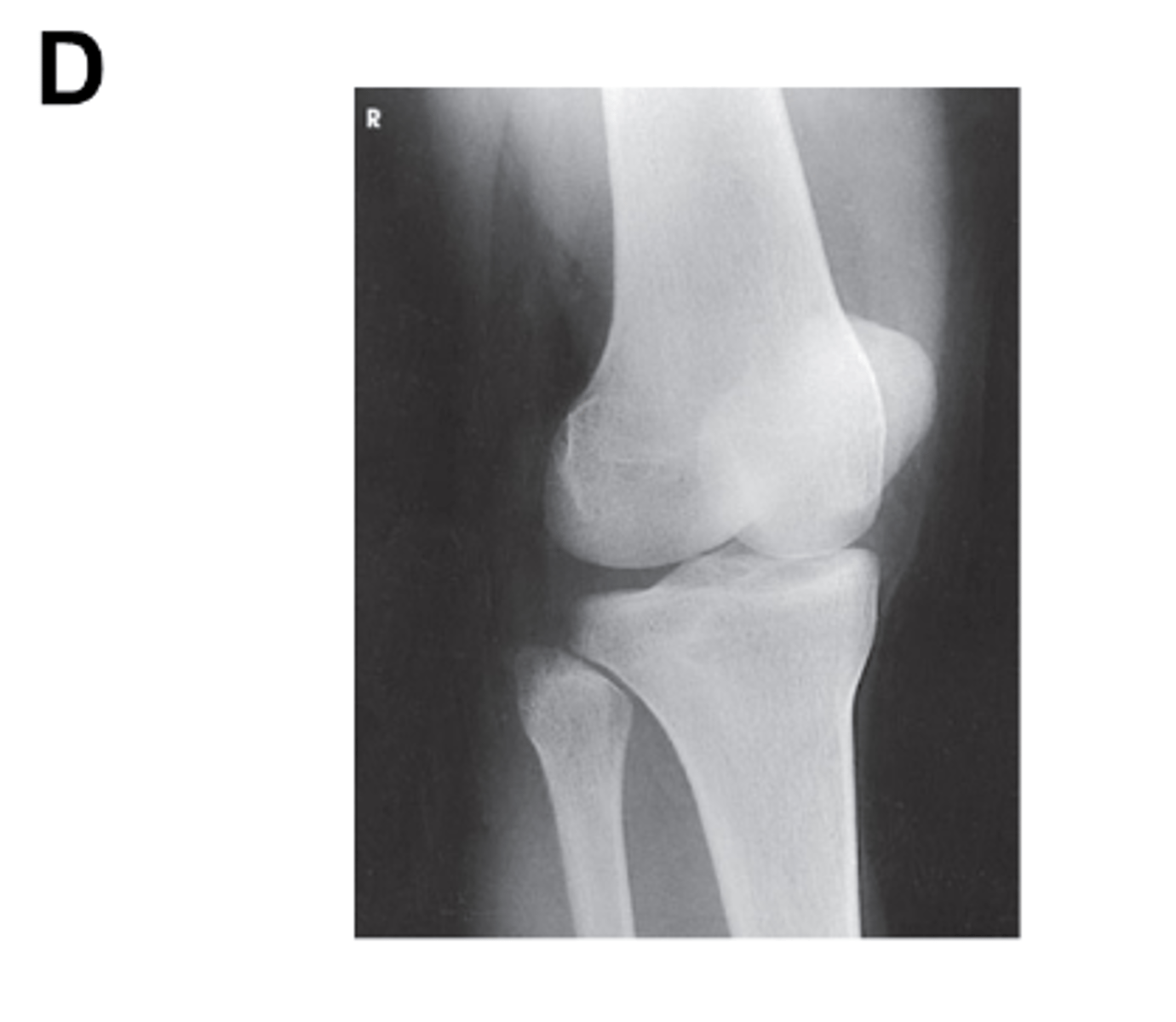
Identify the projection. (Be prepared to critique for positioning on the quiz)
AP Oblique Knee, medial rotation
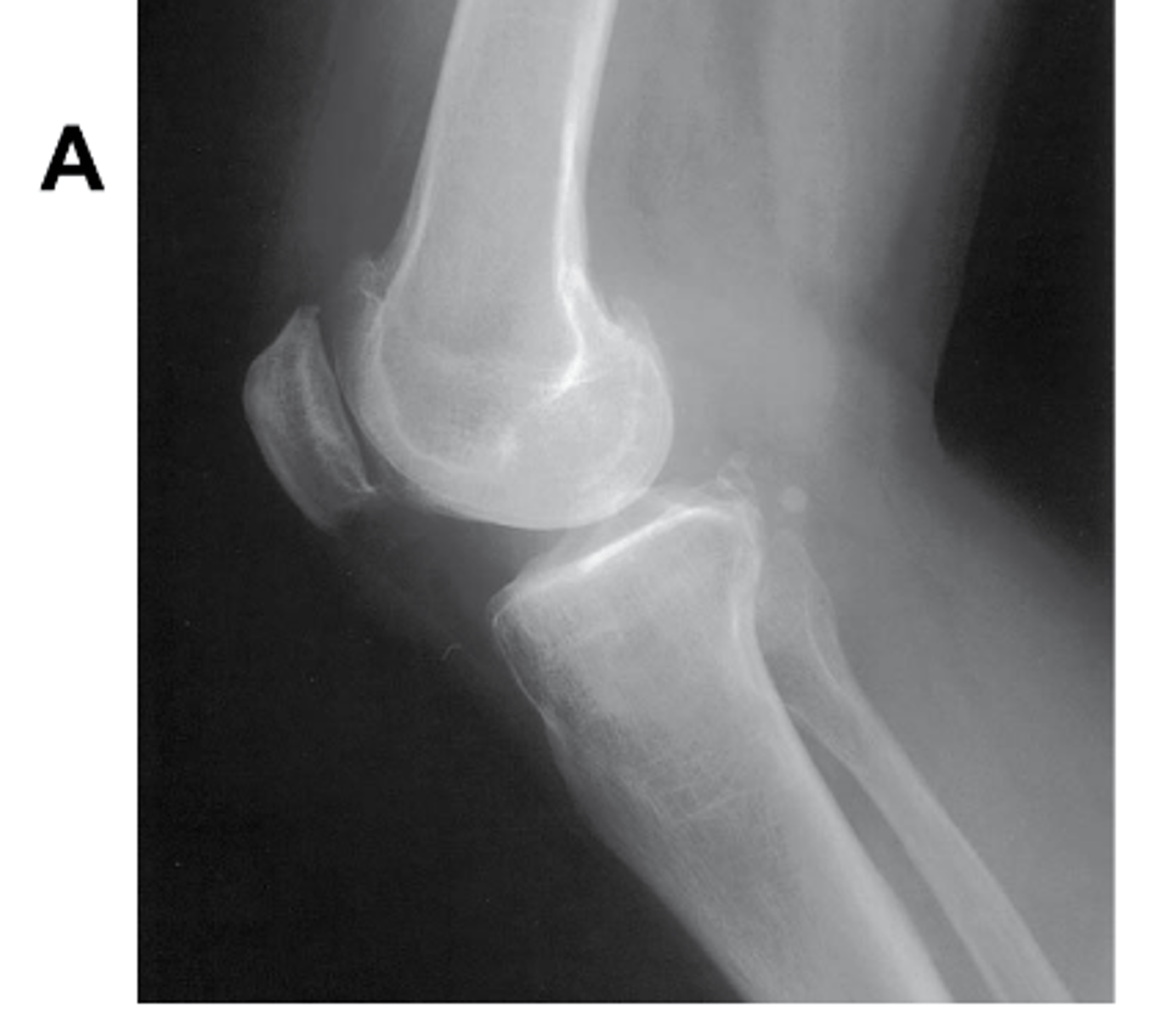
Is there an angle on the CR in this projection? (Be prepared to explain how you know on the quiz)
Yes
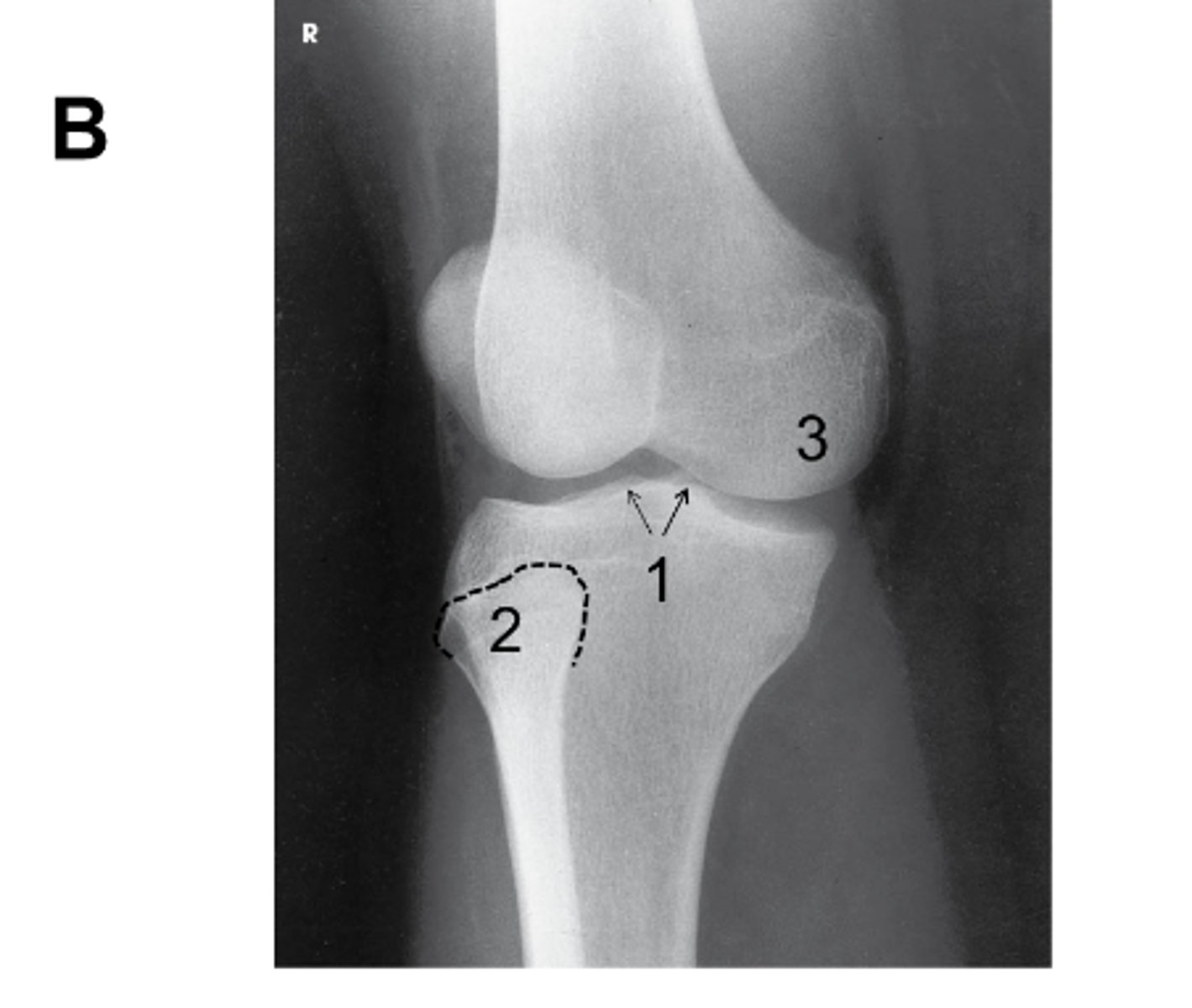
Identify the projection. (Be prepared to identify anatomy and critique for positioning on the quiz)
AP Oblique Knee, lateral rotation
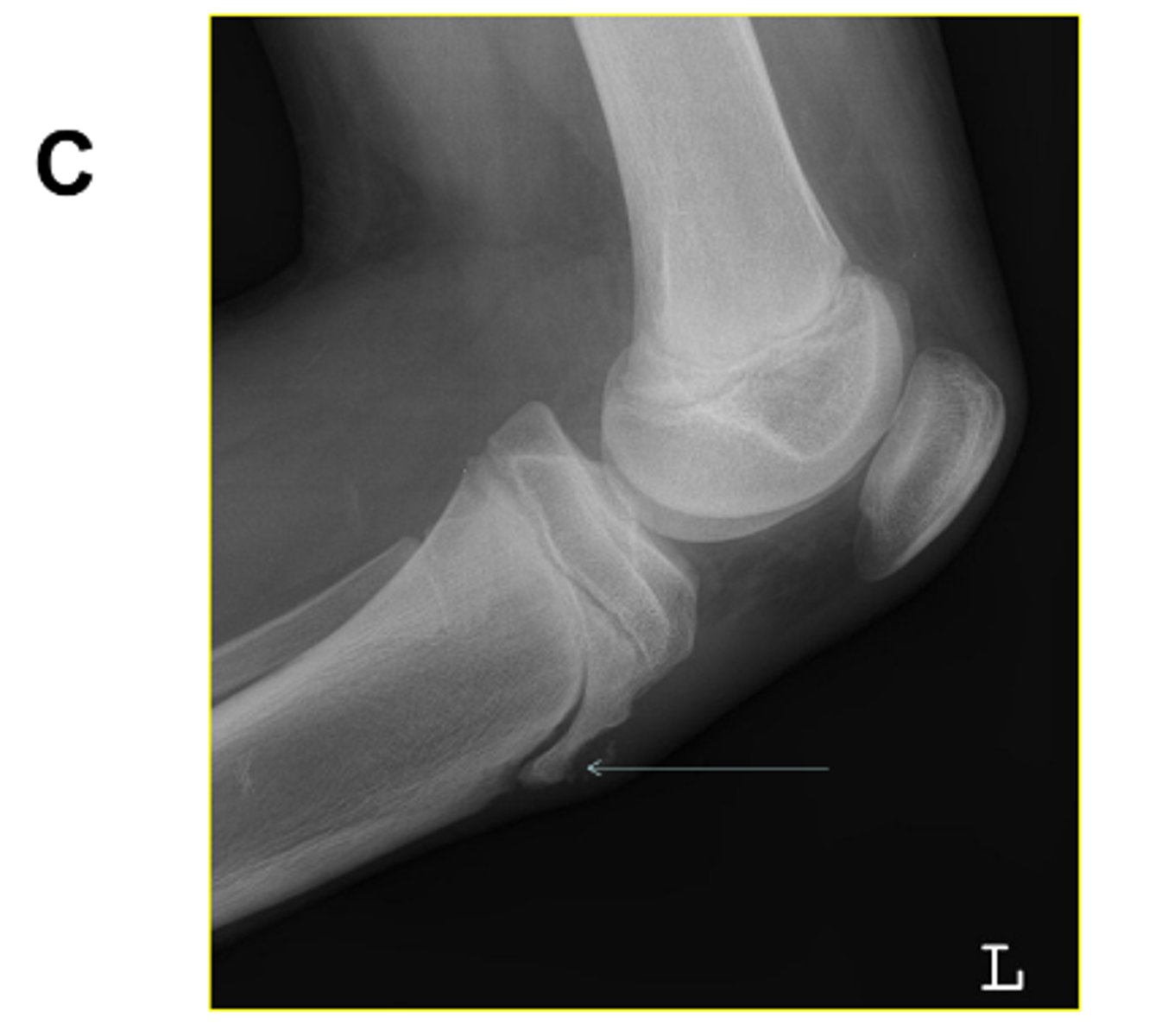
What pathology is visualized on this image?
Osgood-Schlatter disease
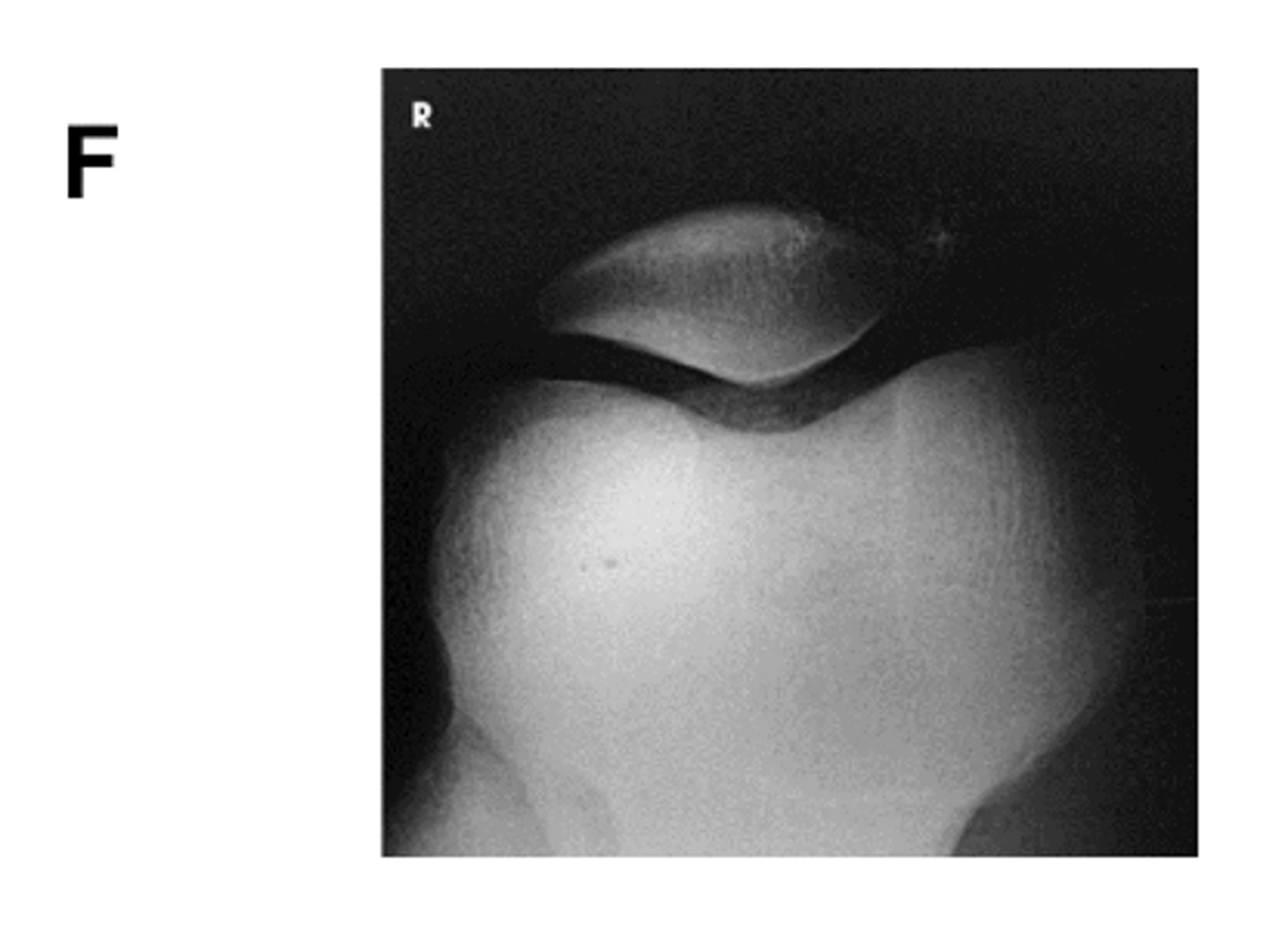
Identify the projection:
Tangential Patella (Settegast Method)
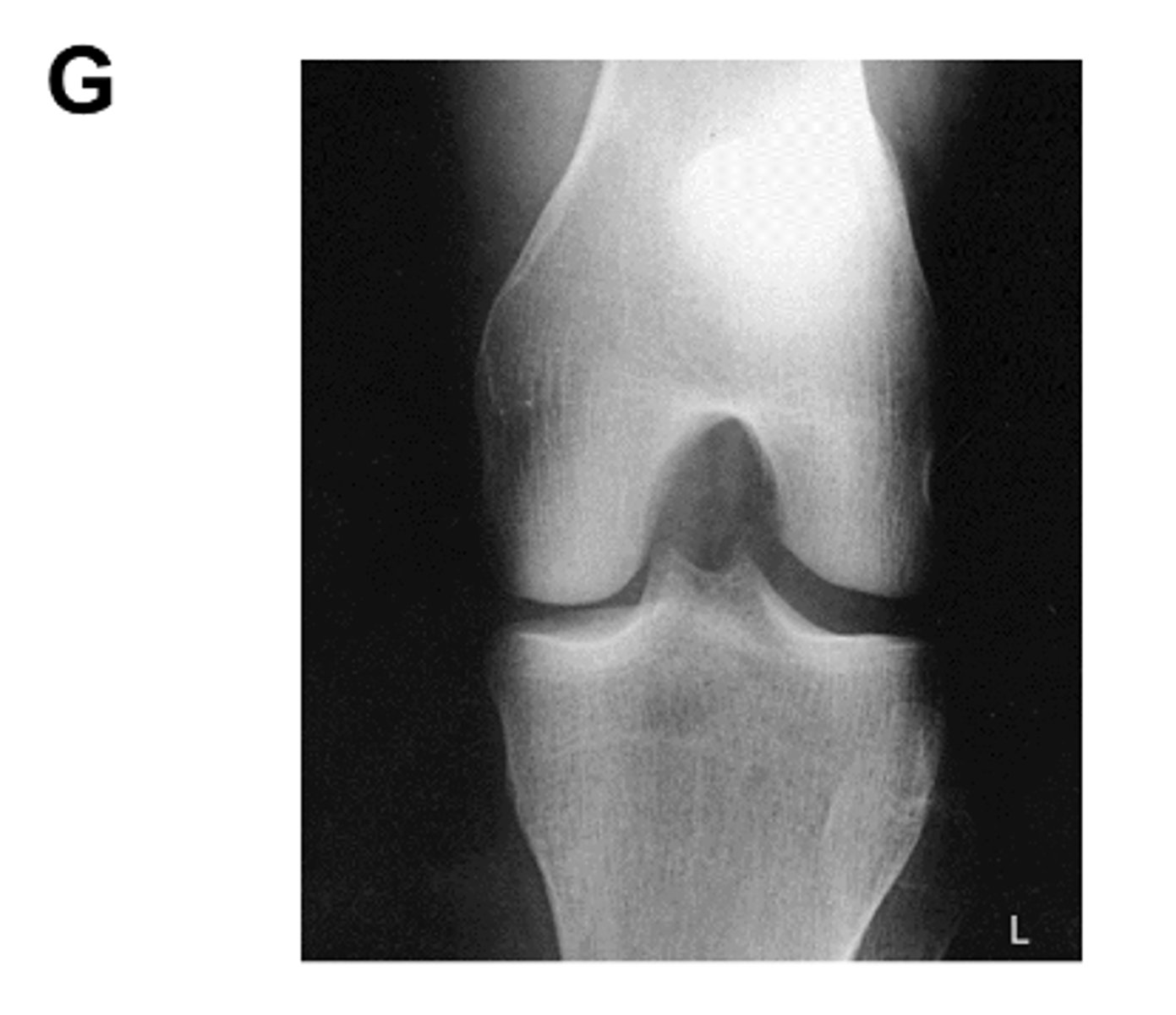
What is the AOI in this projection?
intercondylar fossa
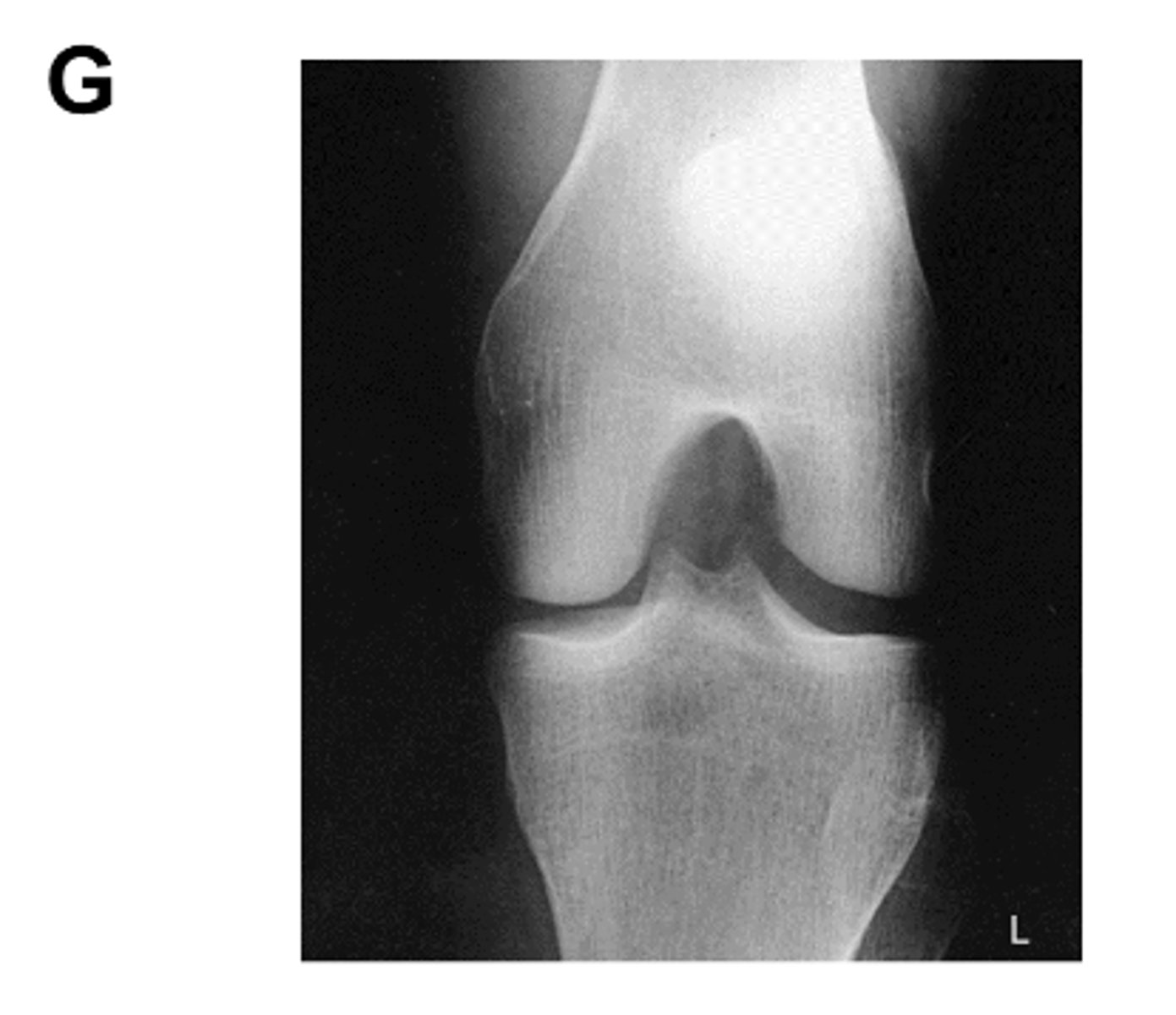
Identify the projection:
PA Axial Knee (Camp-Coventry Method)