3.3
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Investments -
Strategic decisions with long term consequences
Techniques for investment definition
Allows the business to assess the forecast of financial returns and make comparisons between investments. Accounting rate of return, payback and Net present value.
For these techniques you need
initial capital cost
yearly cash inflows
cash outflows
Lifespan of investment
Payback
The amount of time is takes for a project to return its initial investment outlay
Payback equation
Amount required /Net cash flow un a year of payback x 12
Pros and cons of payback
Pros- Focusses on cash, emphasises speed of return, Important in dynamic markets
Cons- Ignores cash flow which arises from payback, lead to short terminist, Ignores qualitative factors. JUST A FORECAST
Accounting rate of return
Measures the overall profitability of an investment as a % of the intial cost
Steps for ARR
Add up the total forecasted return and - the investment cost
Divide the figure by the expected life of investment
Calculate the % of the initial capital cost
Pros and Cons of ARR
Pros- Looks at profitability, considers returns from the whole life of the project
Cons- Treats profits arriving late the same as treating them if they were early, Cashflows could be bias, Reduce reliability if data is incorrect.
NPV- Net Present Value
What money in the future is worth now
Steps of NPV
List out NCF for product life
Select discount factors
Discounts x cashflow
add up all values
Pros and cons of NPV
Pros- Takes into account of time and value of money, looks at all cashflows involved through the whole project, decision making, takes opportunity cost into account
Cons- Complicated for users, difficult to select most appropriate discount rate, Difficult to compare.
Decision trees
A mathematical model used to help make decisions. Helps decide if net gain is worth while. looking at probabilities
Probability
The chance of an outcome occurring
expected outcome-
The anticipated value of an investment (multiplying each outcome with the likelihood of it happening).
Pros and cons of Probability trees-
Pros- Forces managers to decide all options, more useful then investment appraisal, helps business see worst and best case scenarios
Cons- Only good if data is accurate, Bias, Does not focus on qualitative data.
Business growth measured through-
revenue
volume
profit
value
market share
Companies may want to grow because-
achieve economies of scale
increase market power
increased market share
increased profitability
Economies of scale
Unit costs fall as output increases
Internal economies of scale
Business/ individual enjoys Unit costs lowers
External economies of scale
Falling unit costs are enjoyed by all businesses
Three types of internal economies of scale
Technical- new technology
Purchasing- bulk buying
Managerial- Specialist staff e.g. accountant to lower unit costs
Three types of external economies of scale
Expertise- Country or area being known for a particular industry
Cooperation- Good communication means greater effectiveness
Supports services- when services specialise in particular industry
Market power over customers and suppliers
Customers- Higher prices and brand loyalty
Suppliers- Stronger negotiation power and securing raw materials.
How can a business achieve profitability
Lower costs, charge higher prices, increased productivity
Reasons for diseconomies of scale
Wider span of control, Longer chain of command, create risk of distortion and too much technology
Over trading
When a business grows too fast without sufficient resources to fund the expansion. Businesses may use their cash up too quickly and as a result go insolvement. -too much capital, trade credit.
Three negatives of growth
Alienation, Co-ordination and control, Internal communication
Organic growth-
Occurs when a business expands through size- eg new stores, control, expansion and time consuming
External inorganic growth
Growth occurs when expanding in size by either merging or taking over another business. This is high risk
Methods of growing organically
New products
New markets
new routes to markets
franchising
diversification
Pros and cons of organic growth
Pros- Less risky, greater consistently, less loss of control, less brand dilution
Cons- Lack of shared expertise, missed opportunities and lack of competitiveness
Merger-
Two or more businesses agree to become integrated to form one business under joint ownership
Takeover-
One business gains control over one business and becomes the owner if they buy 51% of shares.
Horizontal merger
Two businesses at the same stage of integration and selling the same product
Vertical merger- 2 types
Forwards- Vertical joins with business at the next stage of the production process. Manufacturing to retailer
Backwards- Joins with a business at an earlier stage in the process e.g. manufacturers with suppliers
Conglomerate merger
Two unrelated businesses integrate
Joint venture
Businesses and arrangements which two or more parties agree to. Can be a new product of any other business activity
Reasons for external growth
Synergy
Secure suppliers
Secure outlets
distribution
foothold in the market
benefits from expertise
intellectual property
brand recognition
achieve corporate objectives
External growth-
When a business expands through mergers and takeovers rather than their operations.
Financial risks and rewards of takeovers
Risks- Costs of integrating operations, research is costly, impact on share value, very risky
Rewards- greater revenues, economies of scale, market share and profits
Why might a business grow too fast?
Over trading-, cultural clashes, taking on debt, uncertainty, strain on resources, diseconomies of scale.
Why do some businesses want to remain small?
owners preference
operate in a niche market
offer personal services
tradition
less administration procedures
Methods of business survival
Product differentiation
Offer unique products , tailor made, good reputation
Flexibility to respond to customer needs
closer relationship, greater control, less formal structure
Customer service
More personal, long term relationships, local
E- Commerce
Low start up costs, niche market and global markets
why are sales forecasts useful
prudcing a cashflow forecast, planning resources, stocking
Steps of Time series analysis
Step 1- work out moving averages
Step 2- Plot them on a graph and draw a line of best fit
Step 3- Extrapolate the line of best fit to forecast future sales.
Pros and cons of time series analysis
Pros- Good for a stabilised future
Cons- Sales are influenced internally- PESTLE
Variation
Actual data- trend data
Average cyclical variation equation
Total of all cyclical variation for a quarter/ Number of results for this quarter
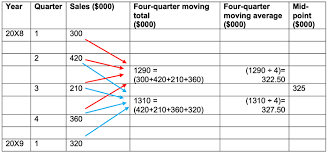
Steps of Four point moving averages
Add up all the periods for the total
add two totals together
then divide them by 8
repeat for all figures
Critical path analyses
Technique used to identify the order in which all activities need to be competed when planning a complex project.
The critical path
The set of activities that will lengthen the duration of the project if they are delayed
EST
LFT
Node Number
Est- earliest starting time TOP OF NODE
Lft- Latest starting times BOTTOM OF NODE
Node number- What node is numbered- 1,2,3,4
Calculating the float
LFT - Duration - EST
Pros and cons of critical path analysis
Pros- speeds up the time of projects, helps gain first mover advantage from the speed, improves working capital and improves efficiency
Cons- Reliability depends on accuracy of data used, estimates are vulnerable, managers must ensure that the estimates are actually achieved- could have issues with motivation.