2.10-2.12 Vocab
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Migration
the permanent or semipermanent relocation of people from one place to another
Voluntary Migration
movement made by choice
Push Factors
negative circumstances, events, or conditions present where a person lives that compels them to leave
Pull Factors
Destination chosen based on its positive conditions and circumstances
Emigrate
when people migrate away from somewhere else
Economic Push Factors
Lack jobs & economic opportunities (ex: unemployment; less available jobs)
Economic Pull Factors
greater chance for economic prosperity
more or new job opportunities
Social Push Factors
discrimination or persecution because of ethnicity, race, gender, or religion; violence
Social Pull Factors
kinship links
safe environment to practice culture; safer social conditions
Political Push Factors
disagree with government policies
discrimination, arrest, persecution
Political Pull Factors
protection/safe from government
Environment Push Factors
natural disasters, drought; environmental stress
unfavorable environmental conditions
Environmental Pull Factors
favorable environmental conditions
Demographic Push and Pull Factors
unbalanced demographics (ex: gender imbalance)
too young → overpopulation
Migration Transition Model
countries in stage 2 & 3 of the DTM: rapid pop. growth and overcrowding = push factor
Stage 4 & 5: economic opportunity and aging pop. = pull factors
Demographic Pull Factors
aging population
more space (not overpopulated)
more balanced demographics
Intervening Obstacles
barriers that make reaching the desired destination more difficult
Intervening opportunities
Migrants encounter opportunities en route that disrupt their original migration plan
ex: finding a job along the way
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration
migration tendencies and demographics → migration theory
Short Distance
Urban Areas
Multiple Steps
Rural to Urban
Counter Migration
Youth
Gender Patterns
Distance Decay
the further apart two places are, the less likely it is that people will migrate between those places
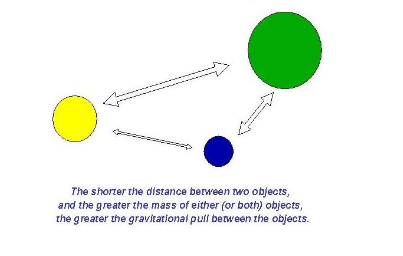
Gravity model of migration
model that assumes the size and distance between two cities or counties will influence the amount of interaction that include migration, travel, and economic activity
Step migration
a process in which migrants reach their eventual destination through a series of smaller moves
counter migration
each migration flow produces a movement in the opposite direction
Forced Migration
migrants have no choice but to move
Internally displaced persons (IDPs)
If forced migrants move to another part of the same country
Refugees
If forced migrants cross international borders
Asylum
protection granted by one country to an immigrant from another country who has a legitimate fear of harm or death if they return
internal migration
voluntary movement that occurs within a country
Transnational Migration
when people voluntarily move from one country to another; internationally
chain migration
Migrants’ decision to settle where others from their home country, family members, friends, or those from their culture group have previously settled
Guest Workers
transnational migrants who relocate to a new country to provide labor that isn’t available locally
Transhumance
process of herders moving with their animals to different pastures during different seasons
Homestead Act
policy that attracted immigrants
U.S. gov. gave land to settlers willing to stay and farm it for 5 years
Guest-worker policies
regulate the number of workers who can temporarily enter each country to work in specific industries for a defined amount of time
family reunification
policies that allow migrants to sponsor family members who migrate to the country
xenophobia
a strong dislike of people of another culture
remittances
money sent to family and friends in the country a migrant left
brain drain
when migration out of a country is made up of many highly skilled people
ethnic enclaves
neighborhoods filled primarily with people of the same ethnic group
ex: Little Italy, Chinatown
The Great Migration
Americans migrated from South to cities in the rest of the country
Pull Factors: Factory Jobs
Push Factors: racial discrimination, violence, poverty
Sun Belt Migration
Migration from Northeast & Midwest to the South
Highway systems & house subsidies → move anywhere
Pull Factors: hot climates, stable benefits for retirees, lower costs of living in Sun Belt
Push Factors: cold climates, decline in job opportunity