Unit 4 - Lecture 19
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:36 PM on 4/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
1
New cards
What are the four proteins that cue for axon migration as well as regulate neural crest cell migration?
1. Ephrins
2. Semaphorins
3. Netrins
4. Slit
2
New cards
How are these proteins activated?
By particular Hox and Lim proteins along the body axis.
3
New cards
Ephrins, semaphorins, netrins, and Slit proteins can act to:
A) Promote attraction
B) Repulsion attraction
C) Passive
D) All of the above
A) Promote attraction
B) Repulsion attraction
C) Passive
D) All of the above
D) All of the above, depending on the nature of the receptors present on the axon.
4
New cards
The receptor present on an axon is dependent on what?
* The type of cell
* The time
* The time
5
New cards
**Ephrins**
membrane-anchored or transmembrane proteins that are recognized by the **Eph** receptor.
6
New cards
**Semaphorins**
transmembrane and secreted proteins that are recognized by the **neuropilin** receptors.
7
New cards
Ephrins and Semaphoring only act in repulsion (T/F).
False. in most cases they act in repulsion, but under some circumstances some can act in attraction.
8
New cards
**Netrins**
key diffusible **chemotactic** cues for neuron guidance.
9
New cards
Netrin-1 is recognized by two receptors found in axon growth cones, called:
A) Notch, Pax6
B) FGF8, BMP
C) DCC, DSCAM
A) Notch, Pax6
B) FGF8, BMP
C) DCC, DSCAM
C) **DCC** and **DSCAM**
10
New cards
Netrins usually are repulsive but can switch to attractive (T/F).
False. Netrins usually are attractive but can switch to repulsive.
11
New cards
Why would Netrins switch from attractive to repulsive?
When the axon reaches its intended destination, preventing further migration.
12
New cards
**Slit**
diffusible proteins generally acting in repulsion (chemorepulsion).
13
New cards
What is the receptor family for Slit?
**Robo**
14
New cards
Robo1/2
repulses neurons. Downregulation (-) allows **commissural neurons** to cross the body’s midline.
15
New cards
Robo3.1
opposite role of Robo1/2, promoting the crossing of the of the midline.
16
New cards
What happens when mutations are found in Robo3?
Humans are unable to coordinate eye movements.
17
New cards
Once a neuron reaches a group of cells in which lie its targets, it finds its specific target cells by responding to additional chemotactic peptides, two called?
* **Endothelins**
* **Neurotrophins**
* **Neurotrophins**
18
New cards
Endothelins
secreted by blood vessels that direct migration of certain neural crest cells and certain sympathetic axons that have endothelia receptors.
19
New cards
Endothelins acts to constrict blood vessels in adults (T/F).
True.
20
New cards
Neurotrophins
regulate development, maintenance, and function of vertebrate nervous systems.
21
New cards
Neurotrophins include five factors, called:
* Nerve growth factor (**NGF**)
* Brain derived neurotrophic factor (**BDNF**)
* Conserved dopamine neurotrophic factor (**CDNF**)
* Neurotrophins 3 (**NT3**)
* Neurotrophins 4/5 (**NT4/5**)
* Brain derived neurotrophic factor (**BDNF**)
* Conserved dopamine neurotrophic factor (**CDNF**)
* Neurotrophins 3 (**NT3**)
* Neurotrophins 4/5 (**NT4/5**)
22
New cards
Neurotrophins travel short distances and can also act as attractants or repulsive factors (T/F).
True.
23
New cards
**Synapse**
forms when an axon contacts its target.
24
New cards
Synapse formation involves the thickening of membranes of both cells at the region of contact, this is done by expression of;
* **B2-laminin** that stops further neuronal growth.
* **N-cadherin** to secure neuron-neuron connections.
* **N-cadherin** to secure neuron-neuron connections.
25
New cards
Neuronal cell death (**apoptosis**) occurs extensively in the central and peripheral nervous system. When does this happen?
When axons have successfully differentiated and extended axons to their correct targets.
26
New cards
Neurotrophin supply is limited (T/F).
True, and different neurotrophins are required to sustain populations of different neurons
27
New cards
Loss of neurotrophic production in adults can lead to serious diseases including:
* Huntington’s disease
* Parkinson disease
* Parkinson disease
28
New cards
Huntington’s disease
caused by the loss of Huntington protein, resulting in a lack of upregulation of BDNF.
29
New cards
Parkison disease
caused by loss of midbrain dopaminergic neurons, the survival of which may be enhanced by drugs that activate neurotrophic factors.
30
New cards
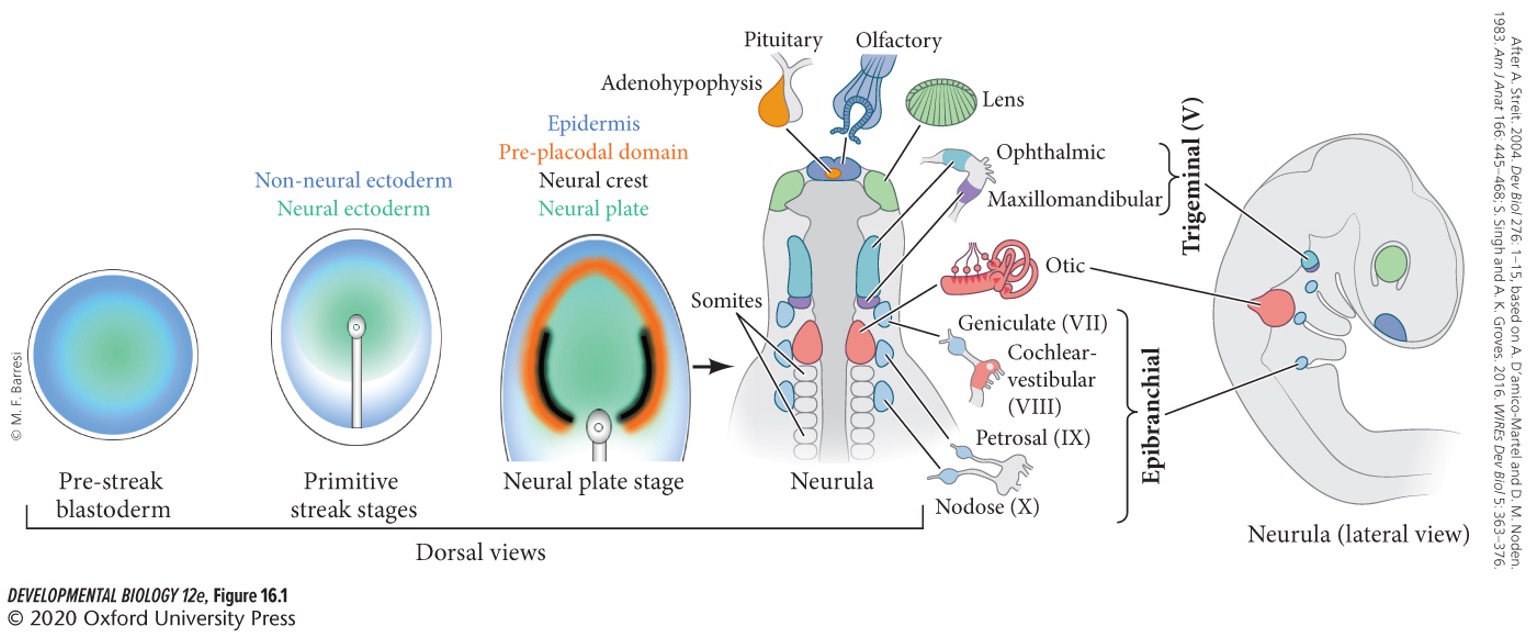
**Ecyodermal places**
thickenings of the surface ectoderm that become the rudiments of numerous organs.
31
New cards
**Cranial sensory placodes**
include olfactory (nasal), auditory (ear), lens (eye) placodes, etc.
32
New cards
Non-sensory placodes
give rise to cutaneous structures such as hair, teeth, feathers, and mammary and sweat glands.
33
New cards
Where are cranial sensory places located?
They are local and transient thickenings of the ectoderm in the head and neck between the prospective neural tube and epidermis.
34
New cards
Cranial placodes generate most of the peripheral neurons associated with ….
* hearing
* balance
* smell
* taste
* touch
* pain
* temperature
* balance
* smell
* taste
* touch
* pain
* temperature
35
New cards
The lens placed does not form neurons (T/F).
True.
36
New cards
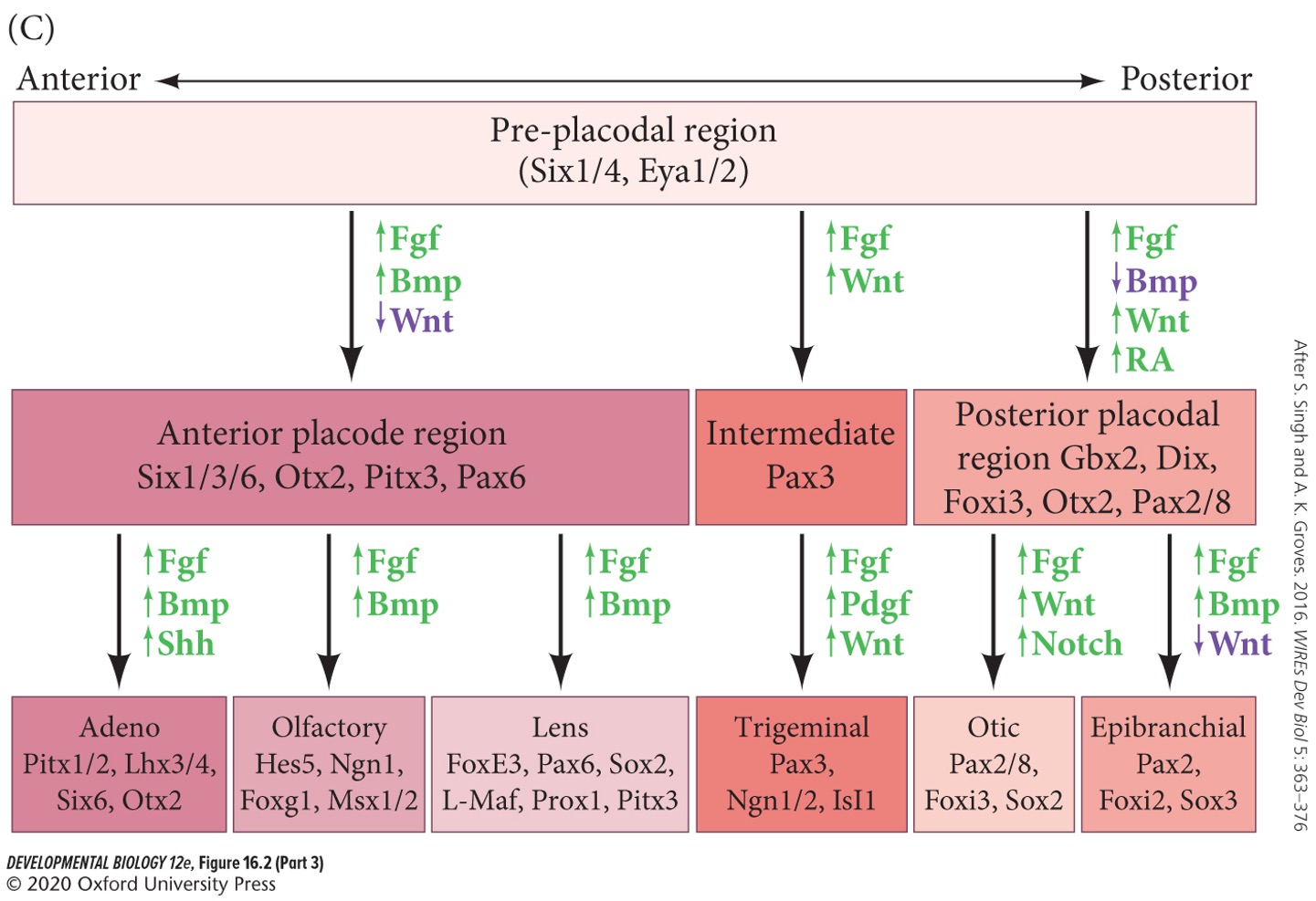
The **pan-placodal region/field** and each region of the specific placodes is specified by placement and timing of:
A) paracrine factor
B) proteins
C) gene expression
D) transcription factors
A) paracrine factor
B) proteins
C) gene expression
D) transcription factors
A) paracrine factor
37
New cards
The pre-pan-placodal field is specified by **Wnt** and **BMP**, how do these factors effect each other?
Wnt induction of BMP, followed by down regulation of Wnt.
38
New cards
**FGF** and **Cerberus**
Downregulate Wnt and BMP. Are active later.
39
New cards
Downregulation of Wnt and BMP leads to what?
Upregulation of **Six1/4** and **Eya1/2**.
40
New cards
**Six1/4** and **Eya1/2** specify what?
Placodes.
41
New cards
Otic-epbranchial development
ear development
42
New cards
How are hearing and balance accomplished?
Through the transformation of mechanical information into electrical stimuli by sensory hair cells in the inner ear.
43
New cards
Sounds waves are captured by the outer ear and channeled to where?
Tympanic membrane (ear drum).
44
New cards
Ear drum vibrations are amplified by the middle ear bones and transferred as waves to the fluid of the … of the inner ear.
**cochlea**
45
New cards
In mammals, the cochlea consists of three separate chambers:
1. Middle fluid-filled chamber
2. Epibranchial placode
46
New cards
Middle fluid-filled chamber
contains the **Organ of Corti**.
47
New cards
Organ of Corti
houses the sensory **hair cells**, which transform the movement of fluid into electrical signals.
48
New cards
Epibranchial placode
forms nearby and gives rise to three cranial nerves:
* Facial (VII)
* Glossopharyngeal (IX)
* Vagys (X)
Together controlling facial expression, sense of taste, speech, swallowing, heartbeat, sweating, peristalsis, etc.
* Facial (VII)
* Glossopharyngeal (IX)
* Vagys (X)
Together controlling facial expression, sense of taste, speech, swallowing, heartbeat, sweating, peristalsis, etc.
49
New cards
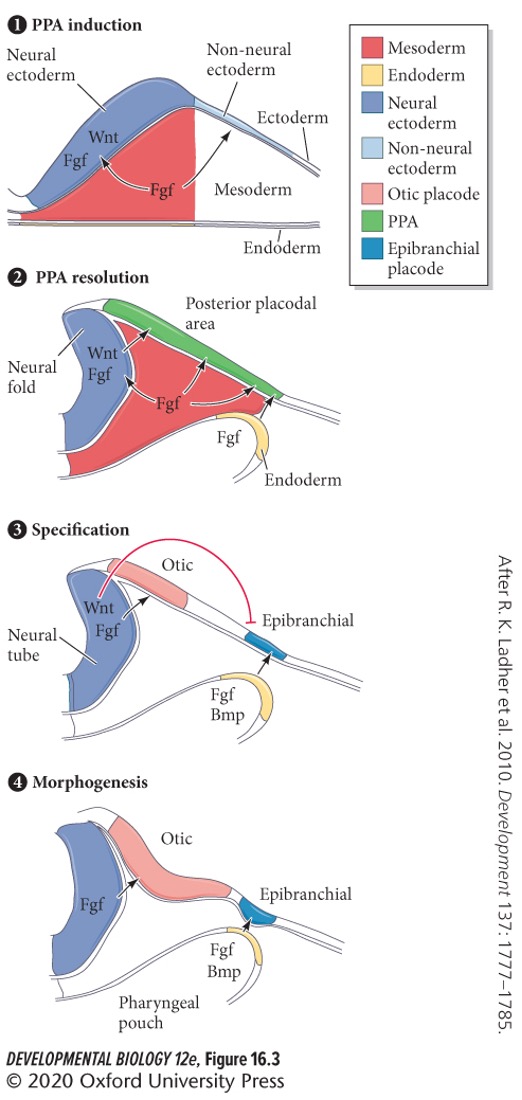
In the first step of otic specification, **Fgf** form head mesoderm specifying which region?
A) Posterior cocleovestibular ganglion
B) Anterior optic cup
C) Anterior lens placode
D) Posterior pre-placodal
A) Posterior cocleovestibular ganglion
B) Anterior optic cup
C) Anterior lens placode
D) Posterior pre-placodal
D) Posterior pre-placodal
50
New cards
The pre-placodal region is soon reinforced by Fgf from the … and ….
**Pharyngeal endoderm** and **neural plate**
51
New cards
Wnt signaling from the neural plate promotes otic identity and represses what at the same time?
**Epibranchial fate**.
52
New cards
Wnt represses epibranchial fate, what factors from the pharyngeal endoderm later promote epibranchial fate?
A) BMP
B) ET
C) FGF8
D) Shh
A) BMP
B) ET
C) FGF8
D) Shh
A) BMP
53
New cards
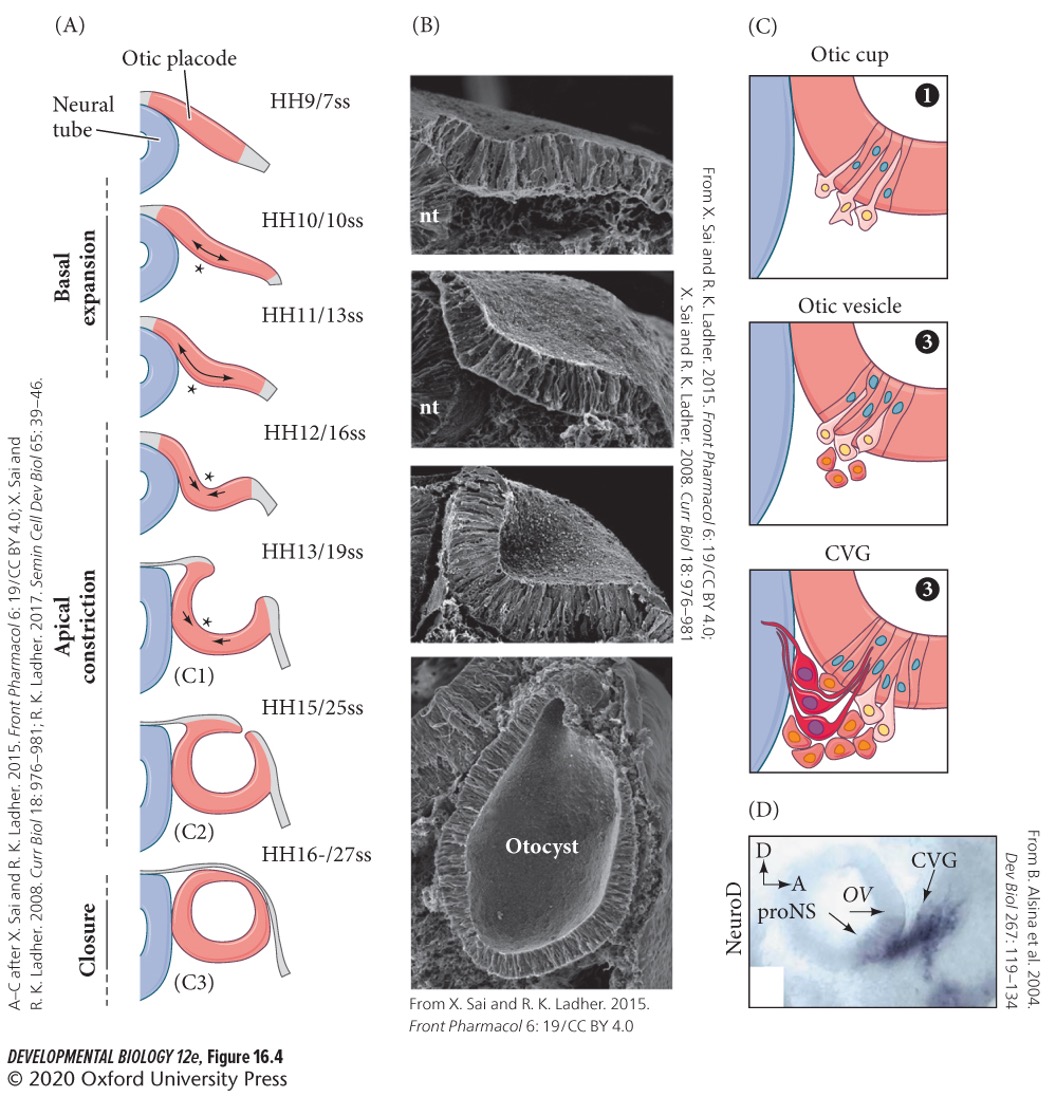
The otic vesicle forms by three steps:
1. First forming an indentation of the otic placode.
2. Forming an **otic pit**
3. Last forming an **otic cup**.
This pinches off to form the **otic vesicle**.
54
New cards
Otic vesicle is similar to neural tube formation and lens formation (T/F).
True.
55
New cards
Ganglia
sensory neurons formed by placodes.
56
New cards
How are ganglia generated?
By **delamination** of neuroblast cells.
57
New cards
**Otic neuroblast cells** will differentiate into the:
**cochleovestibular ganglion**.
58
New cards
Cochleovestibular ganglion will form what?
The major neural connection between the brain and inner ear structures.
59
New cards
Optic development
Lens
60
New cards
Using guidance cues from neural crest cells, epibranchial placodes will migrate ventrally or dorsally?
Dorsally.
61
New cards
The lens placed gives rise to the lens of the eye. Does is contribute to nerves as well?
No, unlike other cranial sensory placodes.
62
New cards
Early in development, prechordal plate mesoderm and head endoderm contact head ectoderm, activating …. in ectoderm and giving the head a lens-forming bias.
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Otx2
D) FGF8
E) Shh
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Otx2
D) FGF8
E) Shh
B) Pax6
63
New cards
After pax6 gives the head a lens-forming bias, which structure forms from bulges of the forebrain?
A) Optic nerve.
B) Optic vesicle
C) Optic cup
D) Lens placode
A) Optic nerve.
B) Optic vesicle
C) Optic cup
D) Lens placode
B) **Optic vesicles**
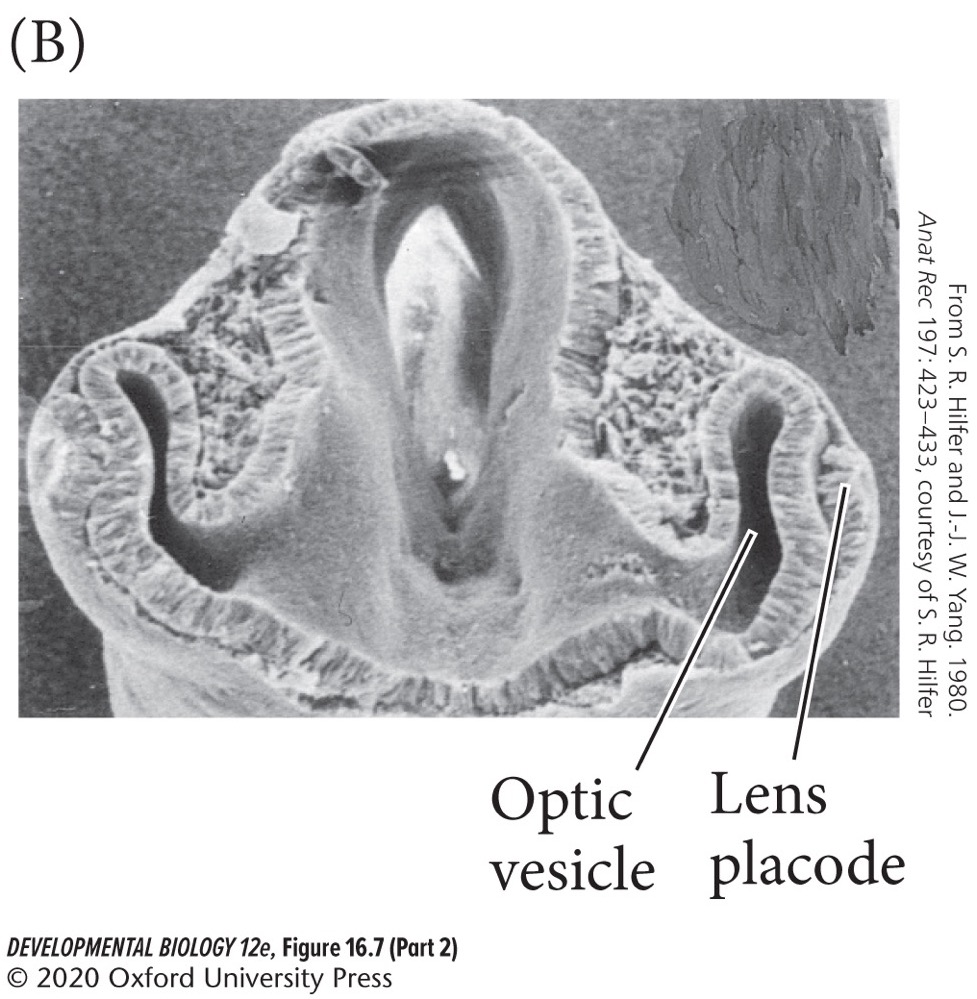
64
New cards
The optic vesicle induces the head ectoderm to form what structure?
A) Optic nerve.
B) Optic vesicle
C) Optic cup
D) Lens placode
A) Optic nerve.
B) Optic vesicle
C) Optic cup
D) Lens placode
D) **Lens placode**.
65
New cards
The optic vesicle bends to form the two layered **optic cup**, which will draw the developing lens into the embryo by:
A) Ingression
B) Invagination
C) Delamination
A) Ingression
B) Invagination
C) Delamination
B) Invagination
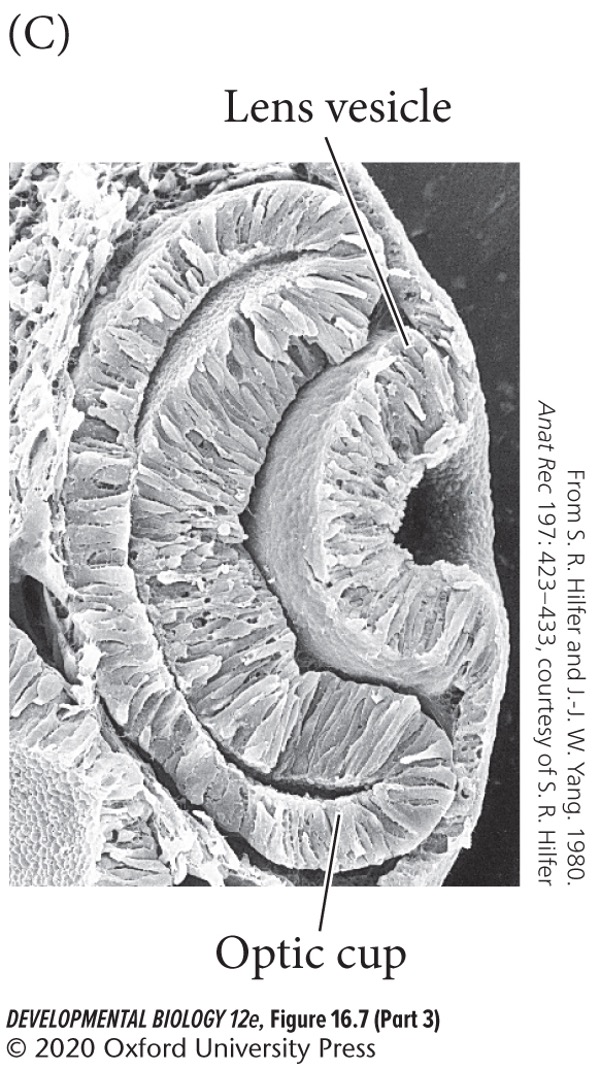
66
New cards
The outer layer (back) of the optic cup forms
A) Pigmented retina
B) Neural retina
A) Pigmented retina
B) Neural retina
A) **Pigmented retina**
67
New cards
The inner cells of the optic cup proliferate and differentiate into what three structures?
1. Photoreceptor neurons
2. Other neurons
3. Glia cells (**neural retina**)
68
New cards
The retinal ganglion cells of the neural retina send electric impulses to the brain. Their axons meet at the base of the eye and become the which structure?
A) Optic nerve.
B) Optic vesicle
C) Optic cup
D) Lens placode
A) Optic nerve.
B) Optic vesicle
C) Optic cup
D) Lens placode
A) Optic nerve.
69
New cards
The inner cells of the optic cells (become neural retina) induce the lens placode to invaginate and become which structure?
A) Optic nerve.
B) Glia cells
C) Lens placode
D) Lens vesicle
A) Optic nerve.
B) Glia cells
C) Lens placode
D) Lens vesicle
D) Lens vesicle
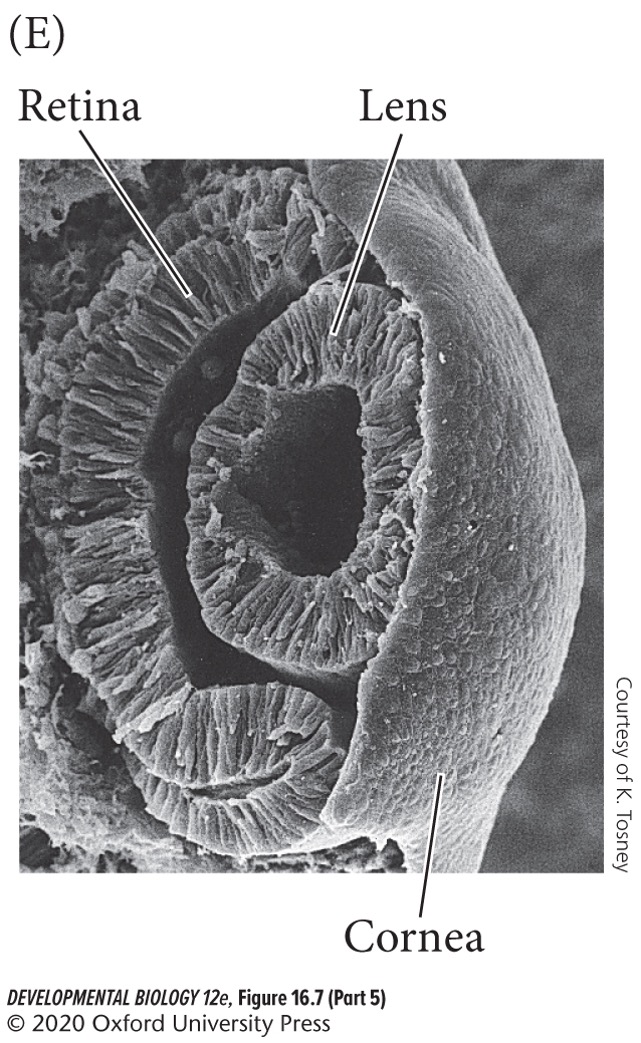
70
New cards
The first step in **eye field** specification of the anterior neural tube is the activation of the transcription factor:
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Otx2
D) FGF8
E) Shh
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Otx2
D) FGF8
E) Shh
C) **Otx2**
71
New cards
Activation of **Otx2** leads to the expression of which factor?
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Rx
D) FGF8
E) Shh
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Rx
D) FGF8
E) Shh
A) **ET**
72
New cards
What factor does **ET** induce?
A) Otx2
B) Pax6
C) Rx
D) FGF8
E) Shh
A) Otx2
B) Pax6
C) Rx
D) FGF8
E) Shh
C) **Rx** (Retinal homeobox)
73
New cards
What does **Rx** specify?
**Retina**.
74
New cards
Rx induces the major gene that specifies the eye field in the anterior neural plate called:
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Otx2
D) FGF8
E) Shh
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Otx2
D) FGF8
E) Shh
B) **Pax6**
75
New cards
The role of Pax6 is specifying photoreceptor cells and is only seen in humans (T/F).
False, common among lots of animals.
76
New cards
What happens to humans and mice that are heterozygous for *Pax6* mutants.
They have small eyes.
77
New cards
What happens to humans, mice, and *Drosophila* that are homozygous for *Pax6*?
No eyes
78
New cards
**Sonic hedgehog** is secreted by the prechordal plate mesoderm. What is its role in optic development?
Split eye field in two.
79
New cards
Shh secreted by the prechordal plate suppresses …. expression in the center of the neural tube.
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Otx2
D) FGF8
E) Rx
A) ET
B) Pax6
C) Otx2
D) FGF8
E) Rx
B) Pax6
80
New cards
Inhibition or mutation of Shh results in what?
Cyclopia (no split of the eyes)
81
New cards
What happens if shh secretion is in excess?
Loss of eyes.
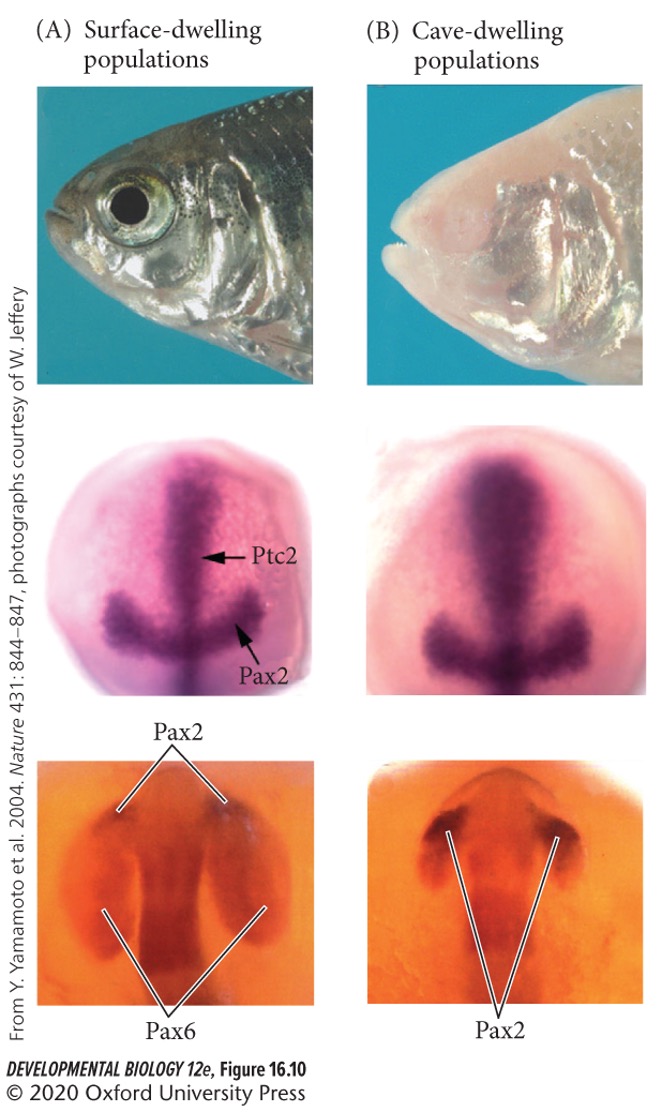
82
New cards
Lens-retinal induction cascade
An example of reciprocal and sequential inductions.
83
New cards
During the lens-retinal indication cascade, the optic vesicle produced different factors to induce lens placodes in competent head ectoderm. Which main factor induces?
**FGF8**
84
New cards
The lens placode secretes more FGFs to induce the optic vesicle to form which structure?
A) Neural retina
B) Cornea
C) Optic cup
D) Lens fiber
A) Neural retina
B) Cornea
C) Optic cup
D) Lens fiber
C) Optic cup.
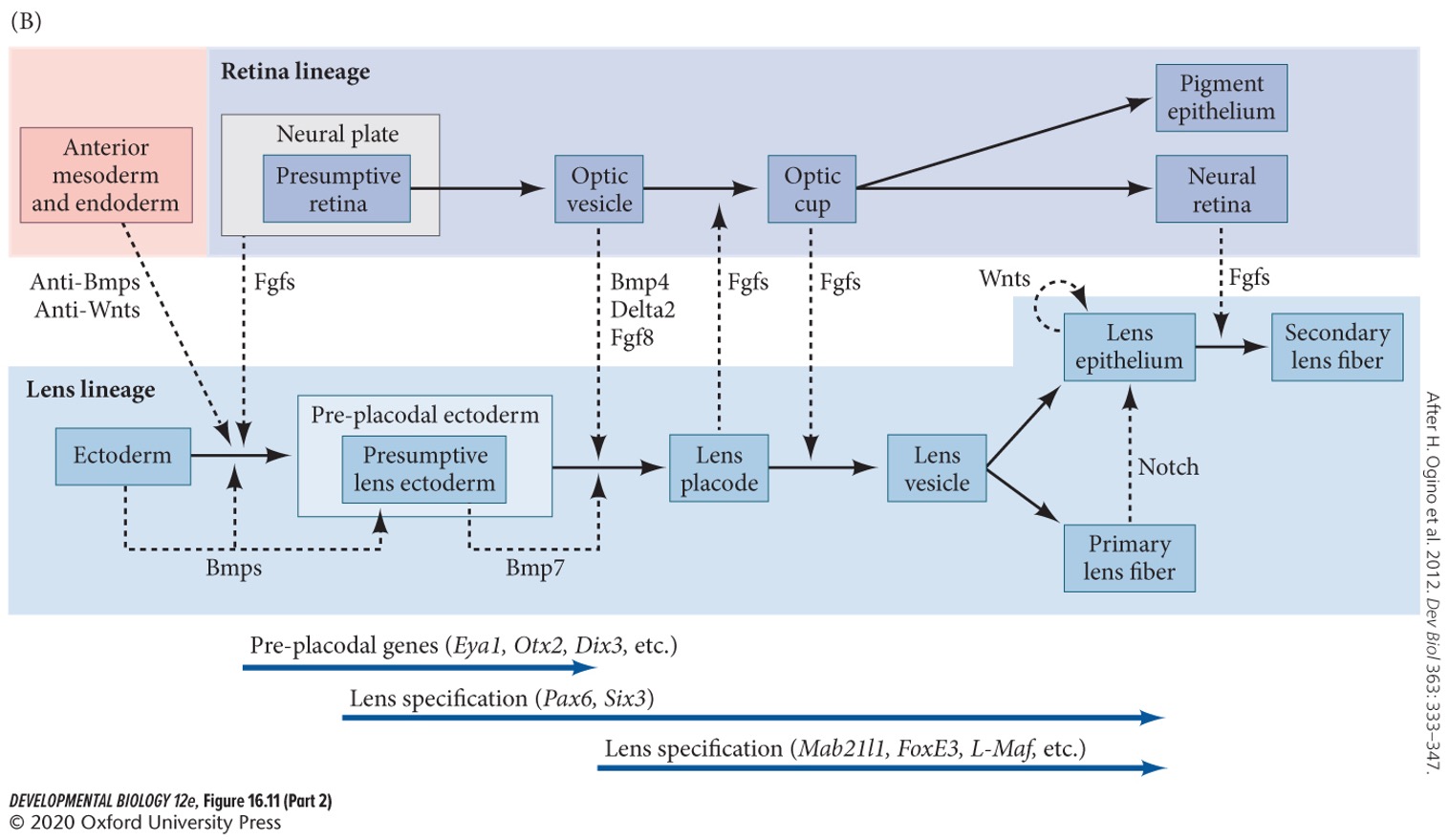
85
New cards
The invaginated lens induces the remaining ectoderm above it to become which structure?
A) Neural retina
B) Cornea
C) Optic cup
D) Lens fiber
A) Neural retina
B) Cornea
C) Optic cup
D) Lens fiber
B) Cornea.
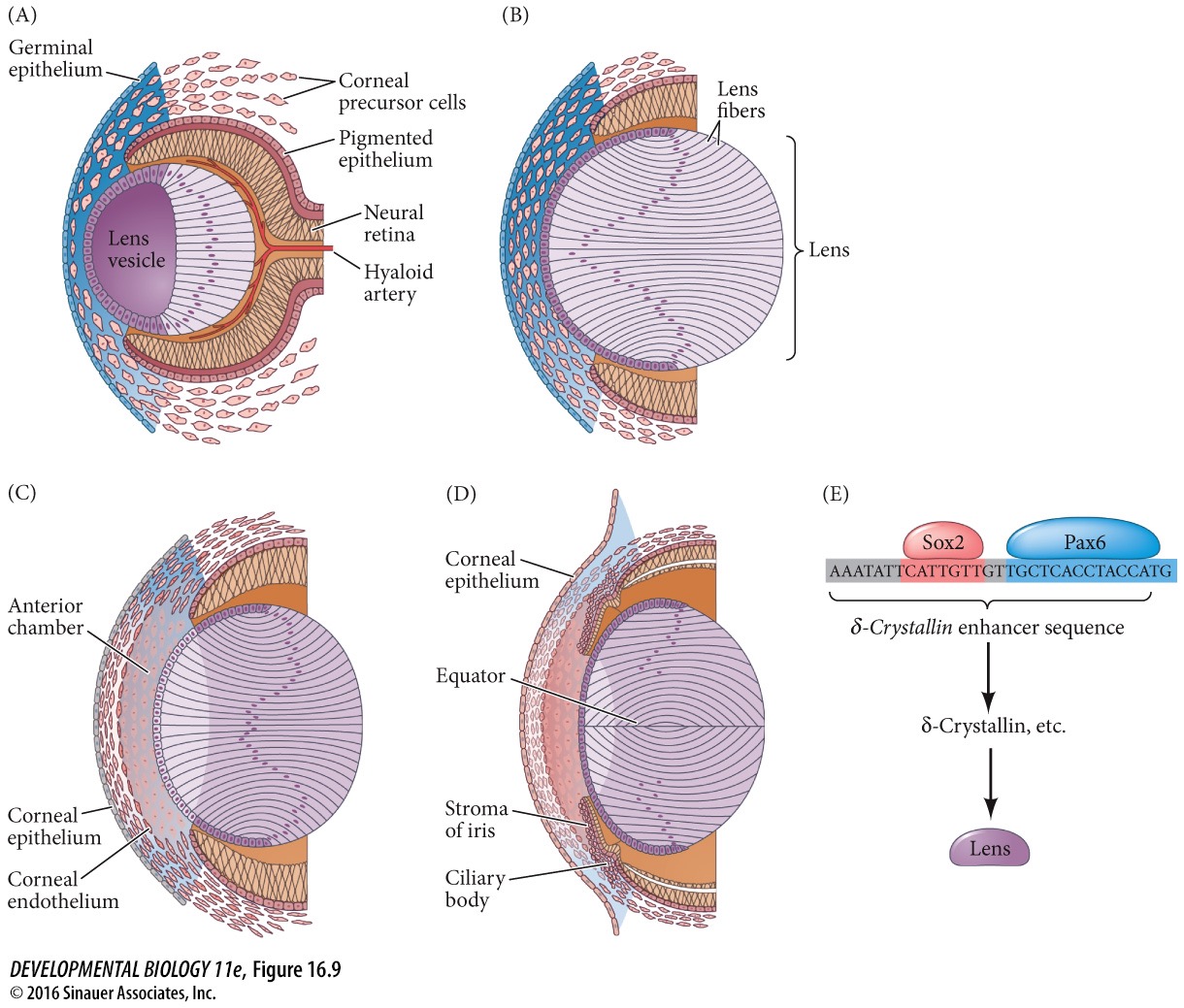
86
New cards
1\. The optic vesicle induces the head ectoderm to form the ____________.
A) optic cup
B) lens placode
C) cochleovestibular ganglion
D) pigmented retina
E) neural retina
A) optic cup
B) lens placode
C) cochleovestibular ganglion
D) pigmented retina
E) neural retina
B) lens placode
87
New cards
The epidermis →
Skin
88
New cards
The skin
the largest organ in our body. It protects against dehydration, injury, and infection, and is constantly renewed via stem cells.
89
New cards
What are the three major components of skin?
1. **Epidermis**
2. **Dermis**
3. Neural crest-derived **meloncytes**
90
New cards
What is dermis made of?
**Firoblasts**, loosely packed and derived from mesoderm
91
New cards
Where does the melanocytes stay?
In the basal epidermis and in hair follicles.
92
New cards
Mammalian epidermis starts as one layer but soon becomes a two layered structure. What does the outer layer give rise to?
**Periderm**
93
New cards
Periderm
Temporary covering that is shed once the inner layer differentiates to form the true epidermis.
94
New cards
The inner layer is also referred to as what?
**Basal layer** or **stratum germinativum**
95
New cards
The inner layer contains what?
Epithelial epidermal stem cells attached to a **basal lamina** (basement membrane) that the stem cells help to make.
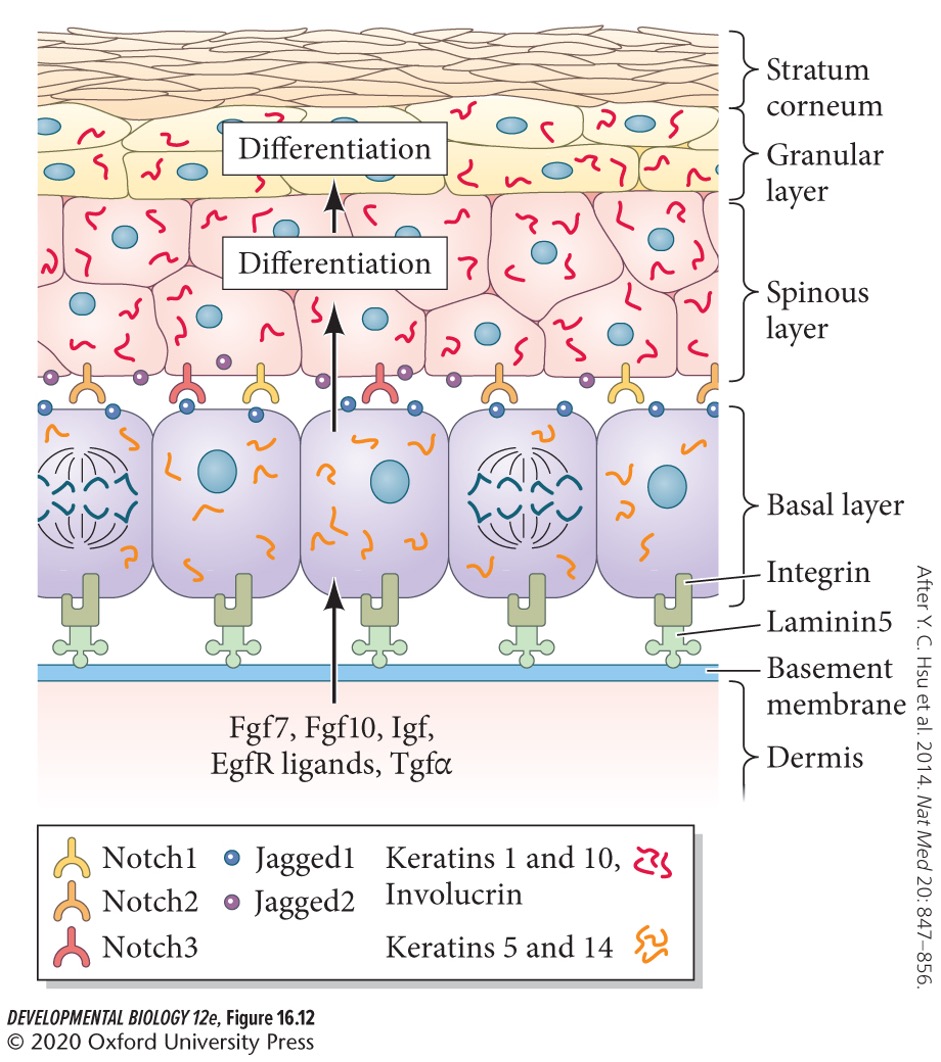
96
New cards
Stem cells divide asymmetrically, producing two daughter stem cells. What are their functions?
* One stem cell remains attached to the basal lamina.
* One stem cell differentiate to a **keratinocyte**.
* One stem cell differentiate to a **keratinocyte**.
97
New cards
What signal promotes differentiation of keratinocytes?
A) Notch
B) FGF8
C) Shh
D) Pax6
E) BMP
A) Notch
B) FGF8
C) Shh
D) Pax6
E) BMP
A) **Notch**
98
New cards
What does induction of keratinocytes produce?
**Keratin**
99
New cards
Keratin
intermediate filament protein.
100
New cards
What does absence of Notch lead to?
Hyperproliferation of the dividing cells.