Chemical Processes Review
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
205 Terms
Bronsted lowry
Donor
Lewis
Acceptor
_________________ acid is a proton __________
_________________ acid is an electron __________
Kw=Ka*Kb
Equation for H3O and OH concentration
1.0*10^-14
Kw=
Ka
Kb
Molarity of H3O+ represented by _____
Molarity of OH- represented by ______
-log[H3O+]
pH=
HClO4
HCl
HBr
HI
H2SO4
HNO3
Six strong acids
-logKa
pKa=
Acidic
Neutral
Basic
Salts formed from strong acid and weak base are ___________
Salts formed from strong acid and strong base are ___________
Salts formed from weak acid and strong base are ___________
pH=pKa+log[A-]/[HA]
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
Used to find pH of buffer solution
14
pH + pOH =
Titrant
Titrand (Analyte)
Solution of known concentration (_______________) is used to titrate a solution of unknown concentration (______________)
Equivalence point
Point in titration where the titrant and titrand neutralize each other
Methyl red 4-6
Bromthymol blue 6-8
Phenolphthalein 8-10
Indicator that goes from red to yellow is _______________
Approximate pH range of ____________
Indicator that goes from yellow to blue is _______________
Approximate pH range of ____________
Indicator that goes from clear to pink is _______________
Approximate pH range of ____________
Acetate
(Ion name)
CH₃COO⁻
Permanganate
(Ion name)
MnO₄⁻
Nitrate
Nitrite
(Ion name)
NO₃⁻
NO₂⁻
Perchlorate
Chlorate
Chlorite
Hypochlorite
(Ion name)
ClO₄⁻
ClO₃⁻
ClO₂⁻
ClO⁻
Sulfate
Sulfite
(Ion name)
SO₄²⁻
SO₃²⁻
Carbonate
(Ion name)
CO₃²⁻
Bicarbonate (Hydrogen carbonate)
(Ion name)
HCO₃⁻
Phosphate
(Ion name)
PO₄³⁻
Chromate
(Ion name)
CrO₄²⁻
Dichromate
(Ion name)
Cr₂O₇²⁻
Oxalate
(Ion name)
C₂O₄²⁻
Peroxide
(Ion name)
O₂²⁻
Thiocyanate
(Ion name)
SCN⁻
Thiosulfate
(Ion name)
S₂O₃²⁻
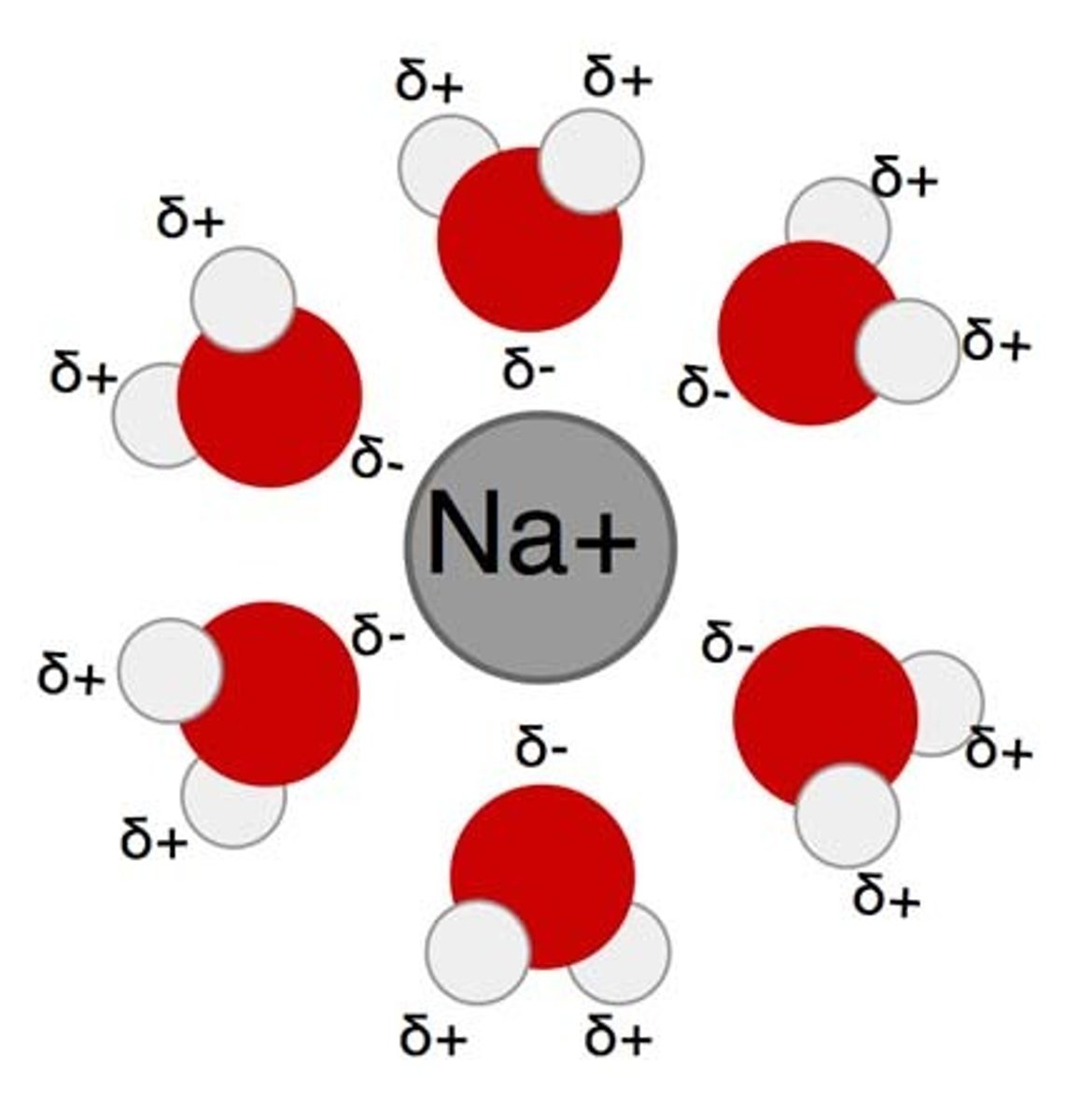
Hydration
Ion broken off and surrounded by polar water molecules
Ksp
Solubility constant (equilibrium constant for soluble compound in soultion)
Kf
Formation constant for complex ions
Keq=Kf*Ksp
Formula to find equilibrium constant for solubility with complex ion formation
Linear
180
Molecular geometry for 2 electron groups
Bond angle=
Trigonal planar
120
Molecular geometry for 3 electron groups
Bond angle=
Tetrahedral
109.5
Molecular geometry for 4 electron groups
Bond angle=
Trigonal bipyramidal
120 equitorial
90 axial
Molecular geometry for 5 electron groups
Bond angle=
Octahedral
90
Molecular geometry for 6 electron groups
Bond angle=
Bent
<120
Molecular geometry for 3 electron groups, 1 lone pair
Bond angle=
Trigonal pyramidal
<109.5
Molecular geometry for 4 electron groups, 1 lone pair
Bond angle=
Bent
<109.5
Molecular geometry for 4 electron groups, 2 lone pairs
Bond angle=
Seesaw
<120 equitorial
<90 axial
Molecular geometry for 5 electron groups, 1 lone pair
Bond angle=
T shaped
<90
Molecular geometry for 5 electron groups, 2 lone pairs
Bond angle=
Linear
<180
Molecular geometry for 5 electron groups, 3 lone pairs
Bond angle=
Square pyramidal
<90
Molecular geometry for 6 electron groups, 1 lone pair
Bond angle=
Square planar
90
Molecular geometry for 6 electron groups, 2 lone pairs
Bond angle=
Enantiomers
Chiral (optically active) isomers that are mirror images of each other
+ (D)
- (L)
Enantiomer that rotates polarized light clockwise is represented by a _____
Enantiomer that rotates polarized light counterclockwise is represented by a _____
R
S
Chiral center where curved arrow from highest to lowest priority group is clockwise
Chiral center where curved arrow from highest to lowest priority group is counterclockwise
Enantiomeric excess
Measured excess of one enantiomer over the other in a racemic mixture
Teratogenic
______________ fetus develops horribly mishapen/misplaced parts (S-thalidomide does this)
Structural isomers (constitutional isomers)
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structure
Stereoisomers
Compounds with the same structural formula, but different 3D arrangement of bonds
Diastereomers
Non superimposable non mirror images (some chirality centers are opposite, some are the same)
Cis
Trans
Isomer with identical groups on same side of double bond
Isomer with identical groups on opposite side of double bond
Z
E
Isomer with higher priority groups on same side of double bond
Isomer with higher priority groups on opposite side of double bond
Staggered
Eclipsed
Conformation around C-C single bond where substituents are evenly spaced
Conformation around C-C single bond where substituents overlap
Intramolecular
Intermolecular
___________________ forces are between two atoms within a molecule
__________________ forces are between two different molecules
Metallic
Ionic
Polar covalent
Nonpolar covalent
Order of four intramolecular forces from strongest to weakest
Hydrogen bond
Dipole dipole
Van der waal (London dispersion)
Order of three intermolecular forces from strongest to weakest
F
O
N
Atoms that participate in hydrogen bonding
Sigma
Pi
___________ bond is formed by direct overlap of two orbitals
___________ bond is formed by side-by-side overlap of two orbitals
Steric number
Number of sigma bonds + number of lone pairs; reveals hybridization of molecule
Eluent
Eluate
Solvent being poured into a chromatography column is _________________
Fluid exiting chromatography column is ______________
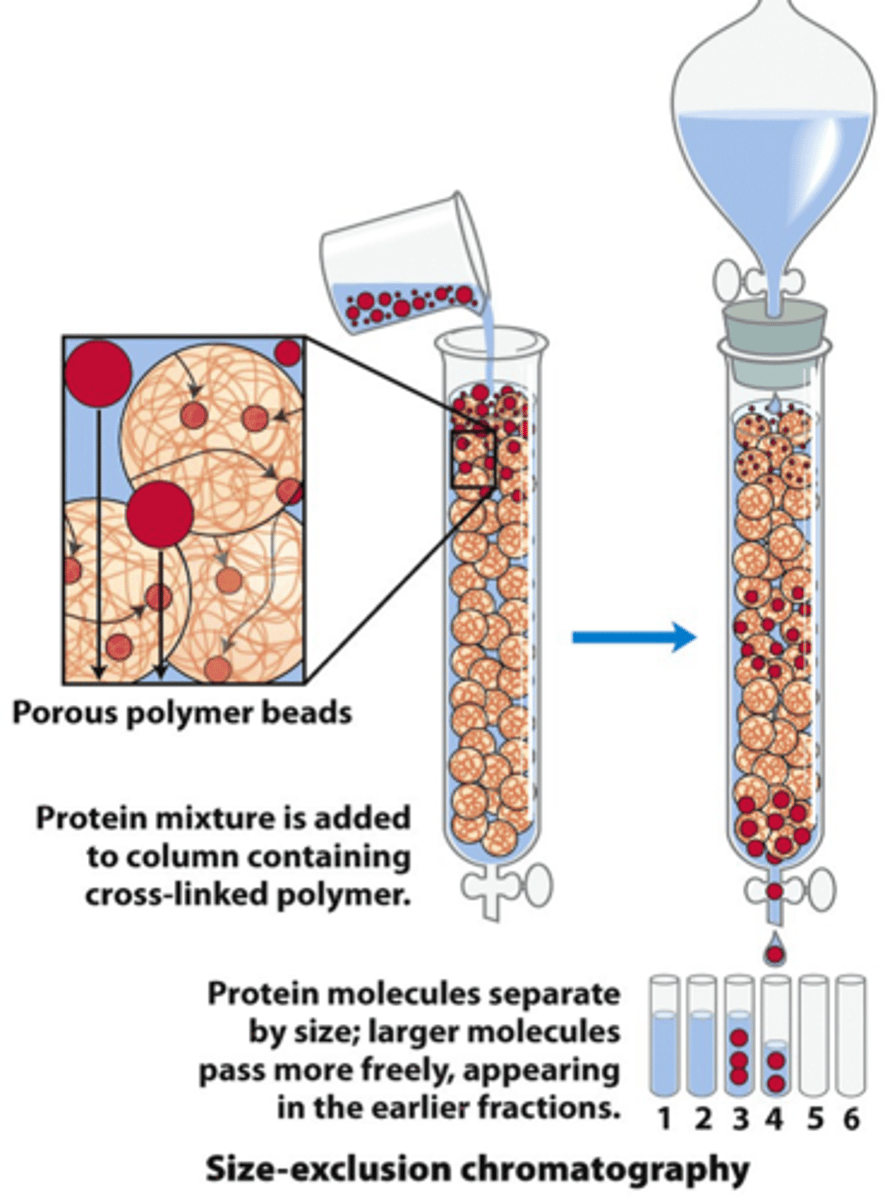
Size exclusion chromatography
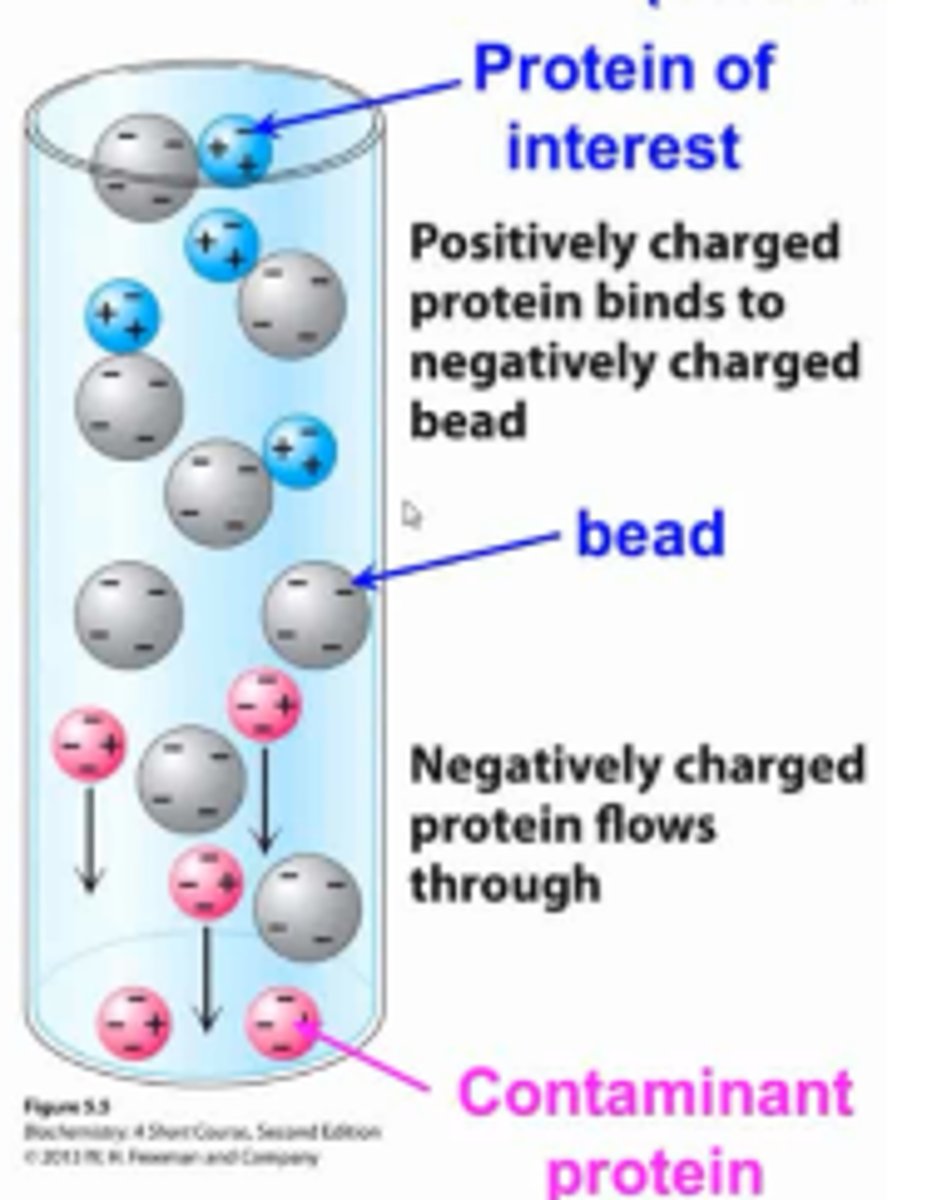
Ion exchange chromatography
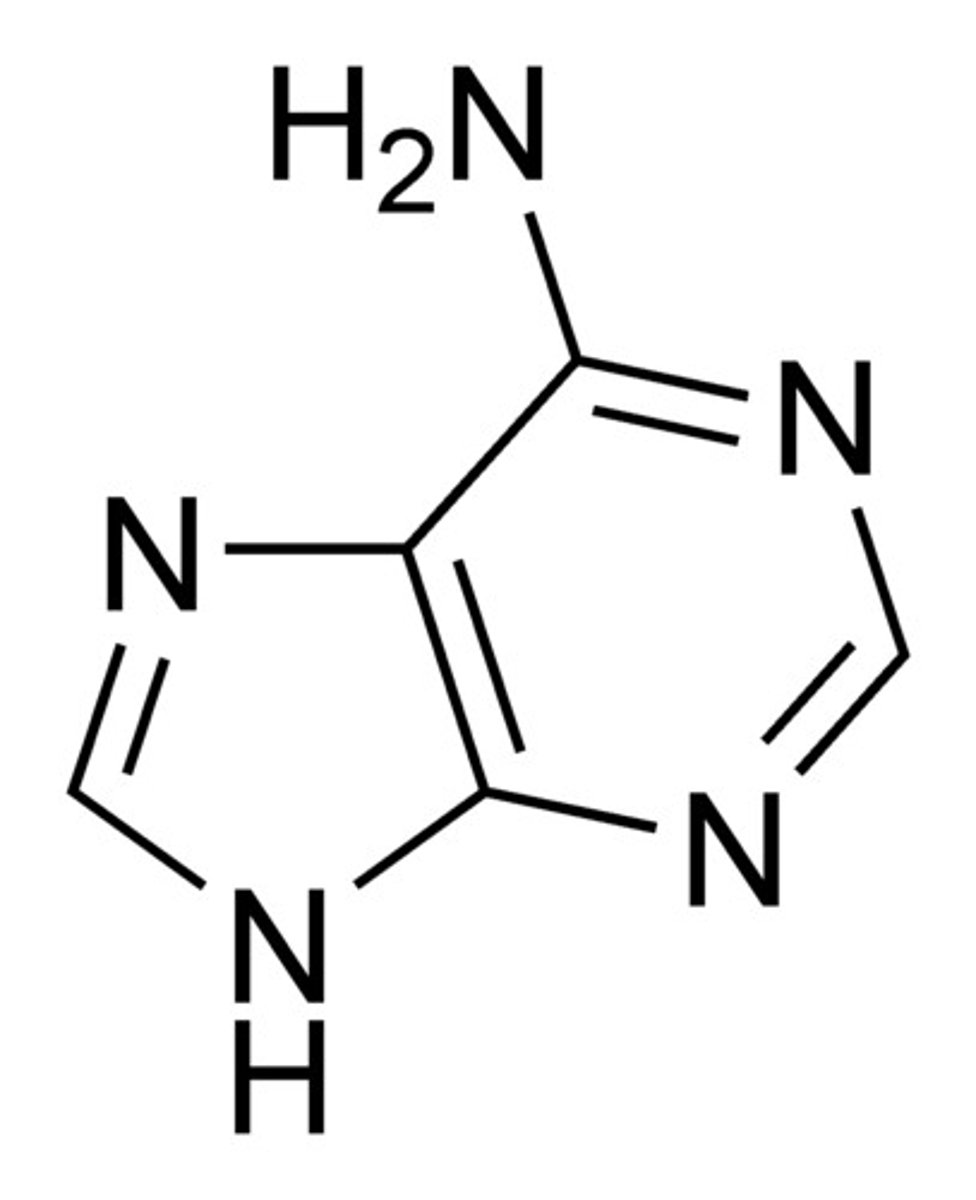
Adenine
Guanine
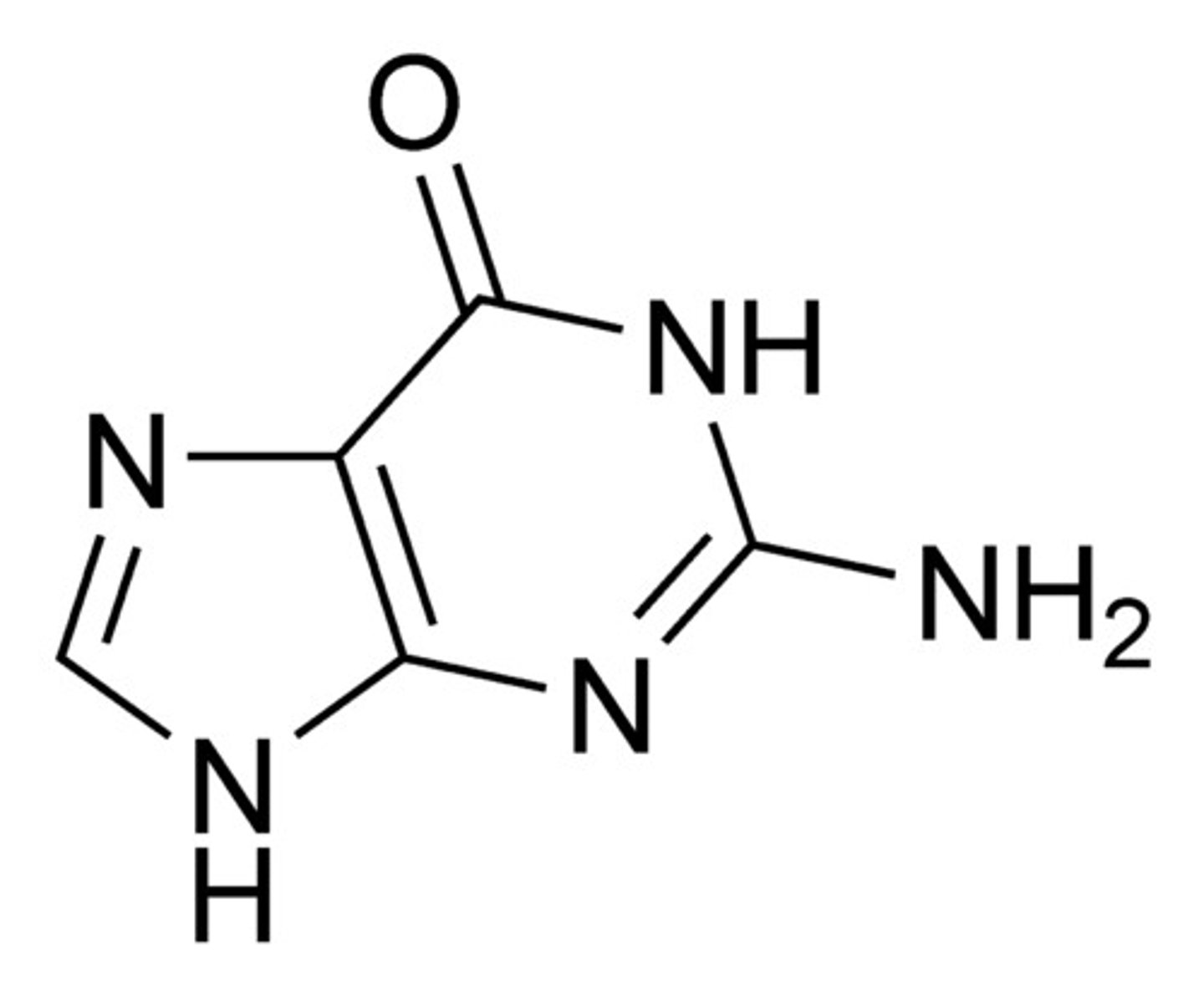
Thymine
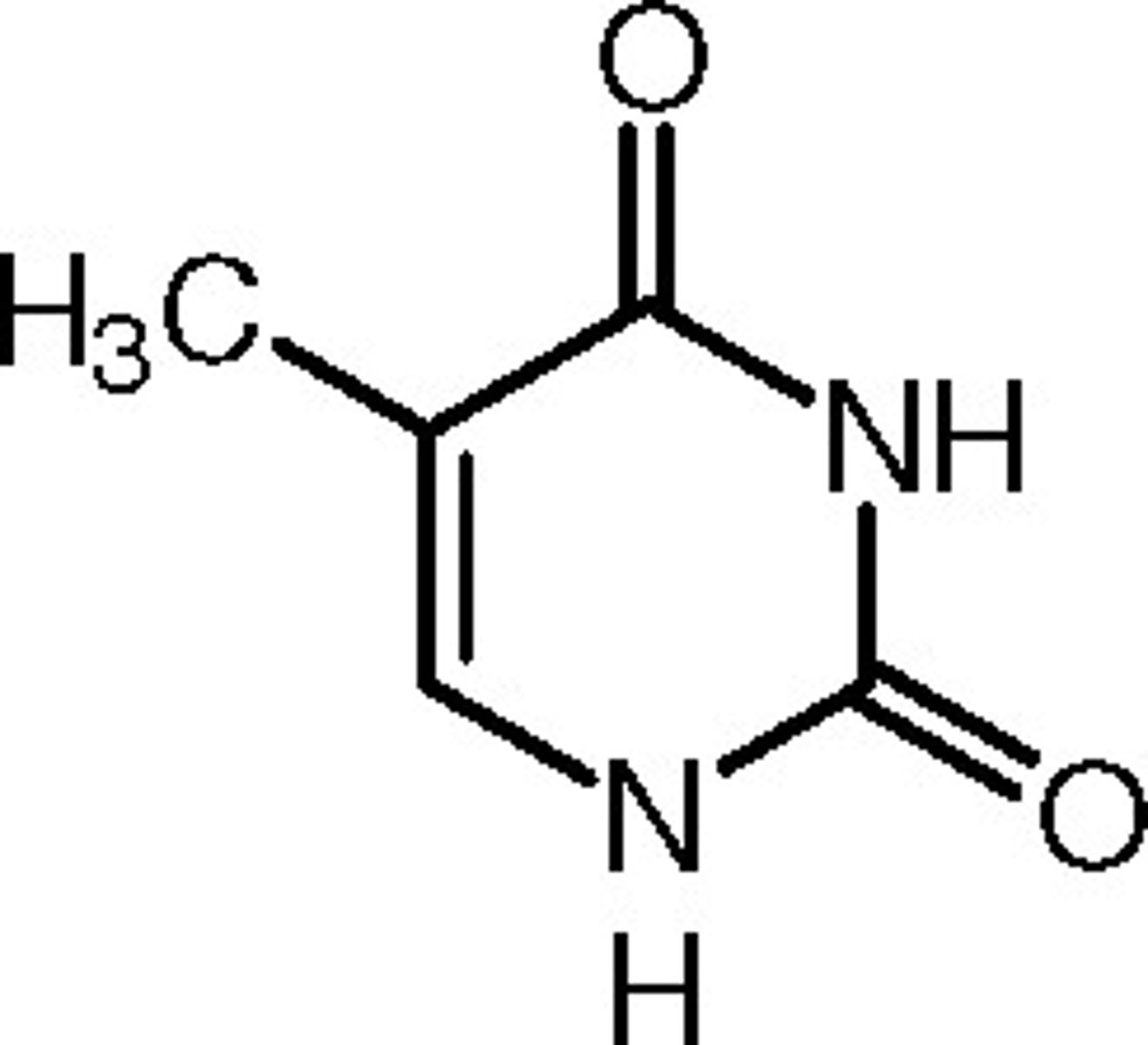
Cytosine

Uracil
Saponification (Base-catalyzed ester hydrolysis)
Starting point for all fat metabolism reactions
Hydrolyzable
Nonhydrolyzable
_______________ lipids can be broken down (used for energy)
______________ lipids function as signaling molecules/cofactors
Sphingolipid
Lipid found in myelin sheath
Non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
Drug such as aspirin or ibuprofen that stops production of prostaglandins
Prostaglandins
Hormones that are inhibited by NSAIDs
Eicosanoids
20-Carbon lipids that signal effect in immediate area
(includes prostglandins)
A
D
E
K
Four fat soluble vitamins
A (retinol)
Vitamin ___ is needed for light sensitivity and healthy mucus membranes
D
Vitamin ___ regulates phosphorus and calcium metabolism
E
Vitamin ___ is an antioxidant that protects neurological function
K
Vitamin ___ regulates the synthesis of prothrombin
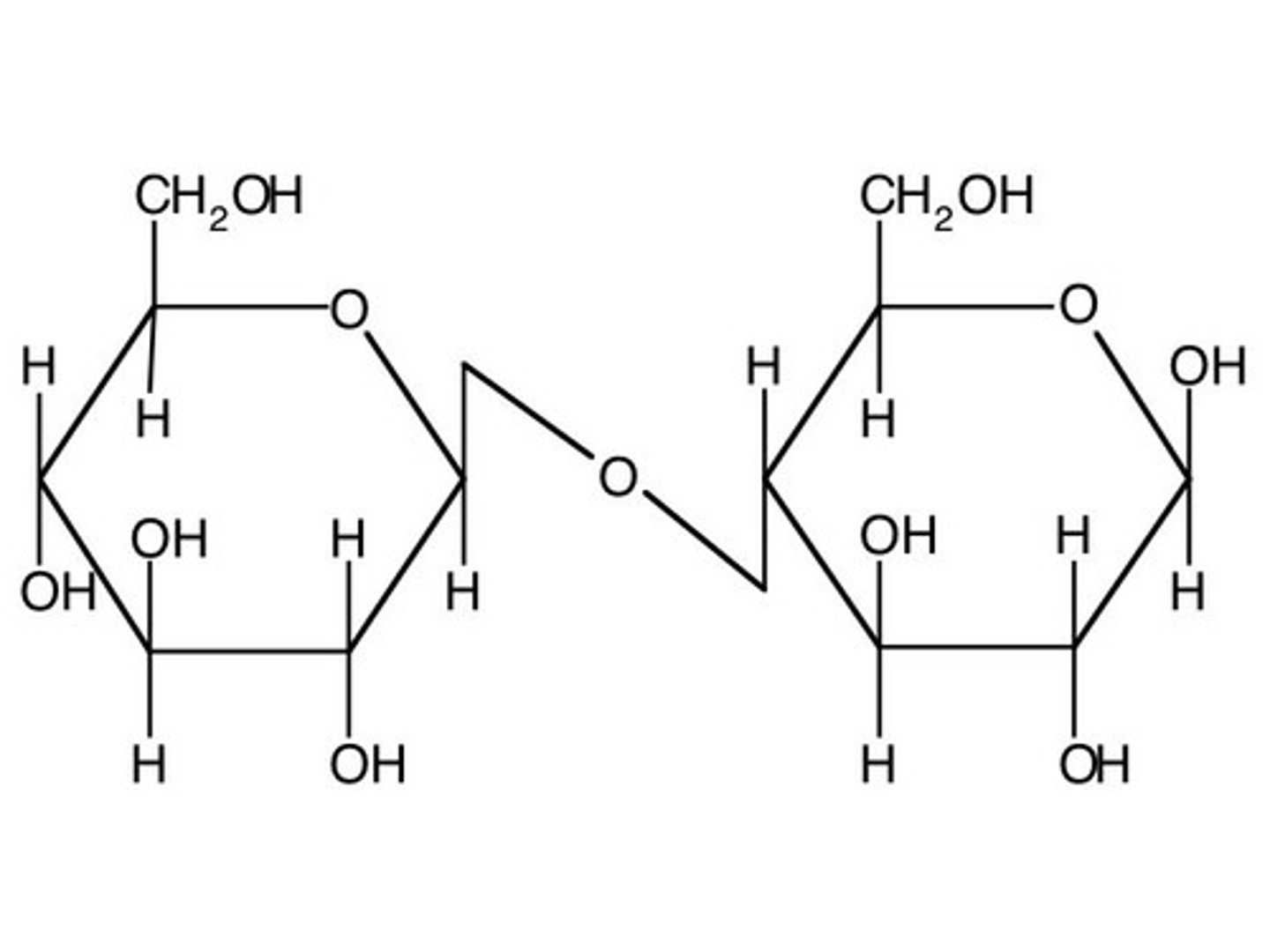
Glycoside hydrolysis
Reaction that forms glycosidic bonds
Beta
Alpha
Glycosidic linkage from cis OH groups (both equitorial or both axial)
Glycosidic linkage from trans OH groups (one equitorial one axial)
Non reducing
_______________ sugar
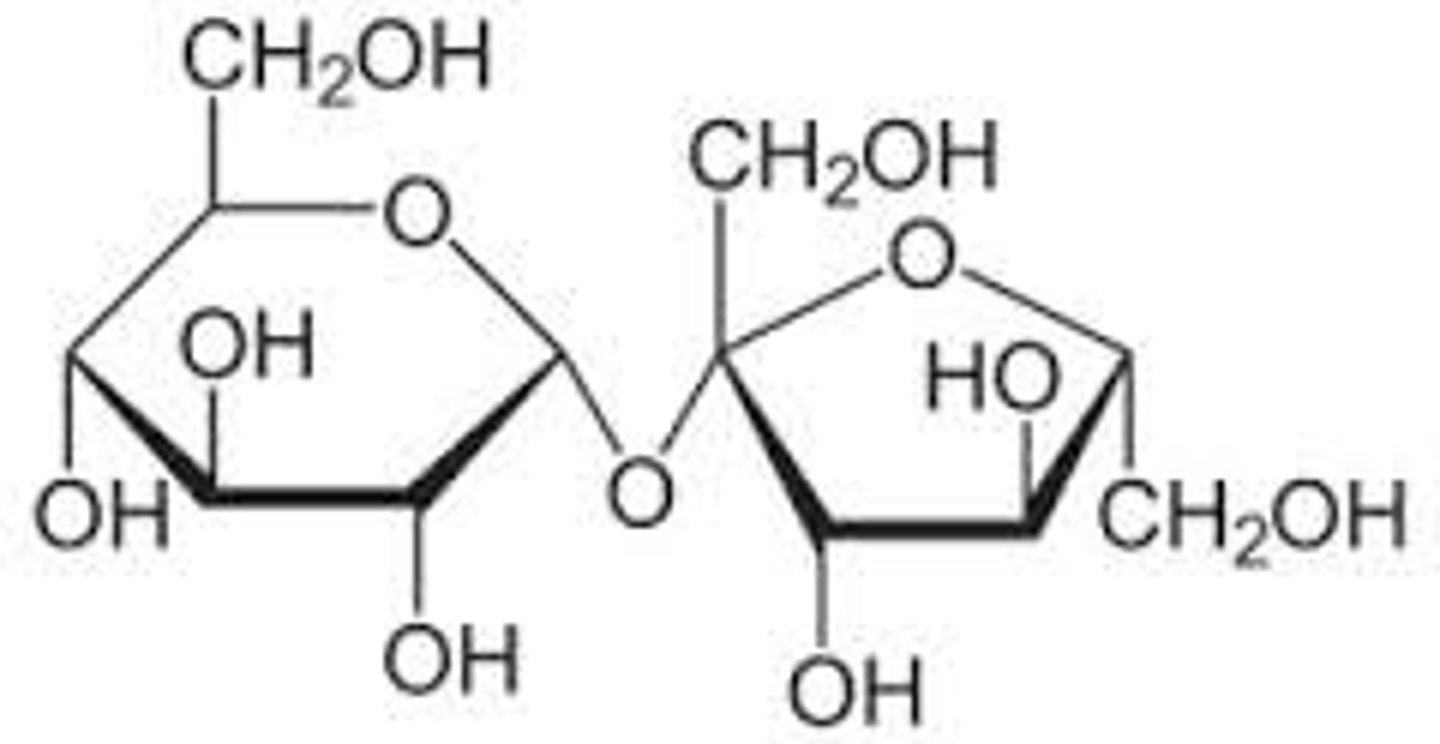
Reducing
_______________ sugar
First
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
__________ step of citric acid cycle uses aldol reaction
Cleavage of ____________________________ in glycolysis and formation of it in gluconeogenesis are aldol and retro-aldol reactions
Reactant
Product
pKa(___________ acid) - pKa(__________ acid) = pKeq
Kinetic
Thermodynamic
________________ enolate forms faster
______________ enolate is more stable
Small
High
Large
Low
_______________ base and __________ temperature favors thermodynamic enolate
_______________ base and __________ temperature favors kinetic enolate
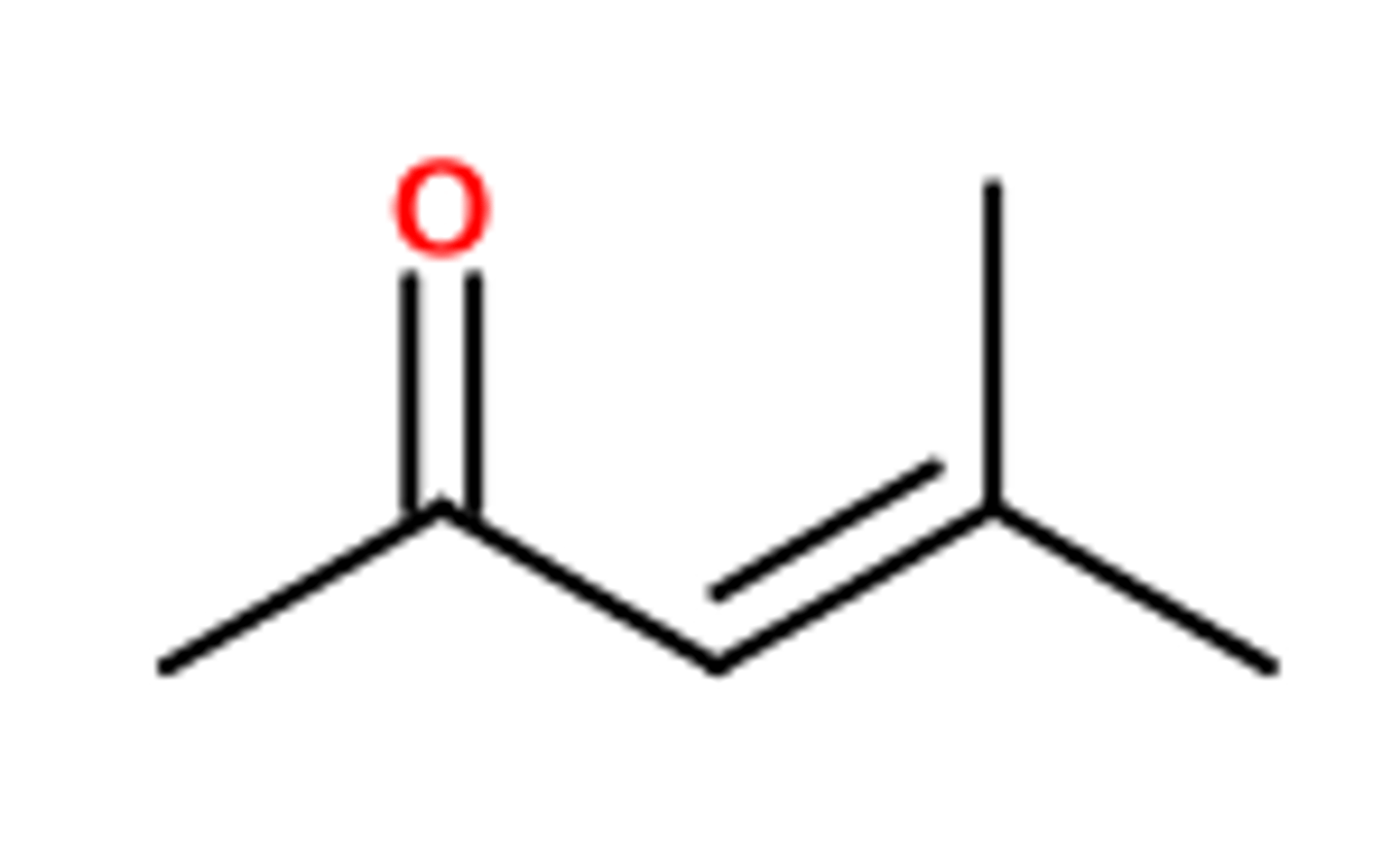
Aldol
al
one
carbaldehyde
Suffix for aldehydes=
Suffix for ketones=
Suffix for aldehyde attached to a ring=
Dione
Molecule with two ketones
Hemiacetal

Hemiketal
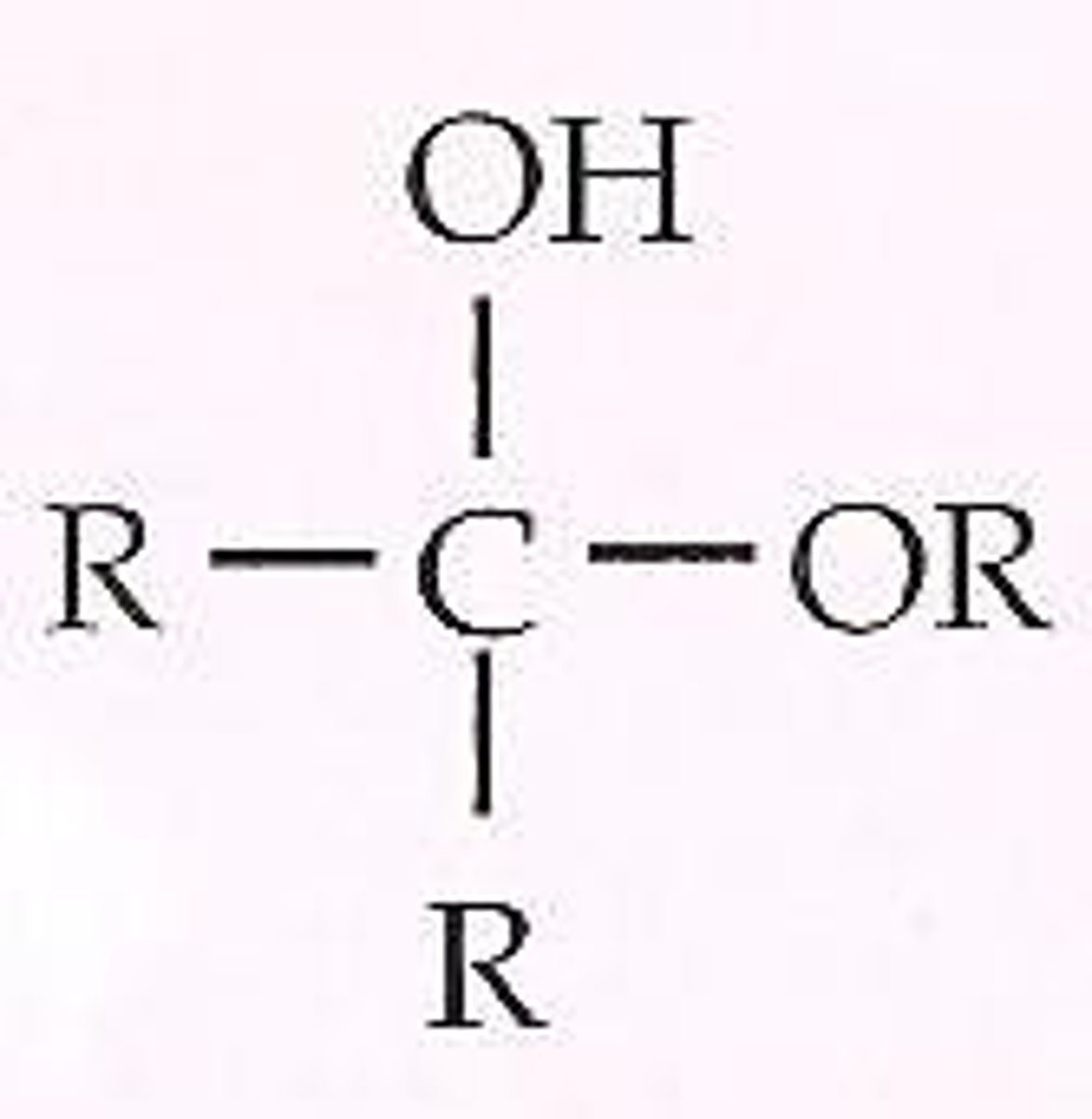
Acetal
Aldehyde or ketone + excess alcohol in acidic environment ⇌ ____________________
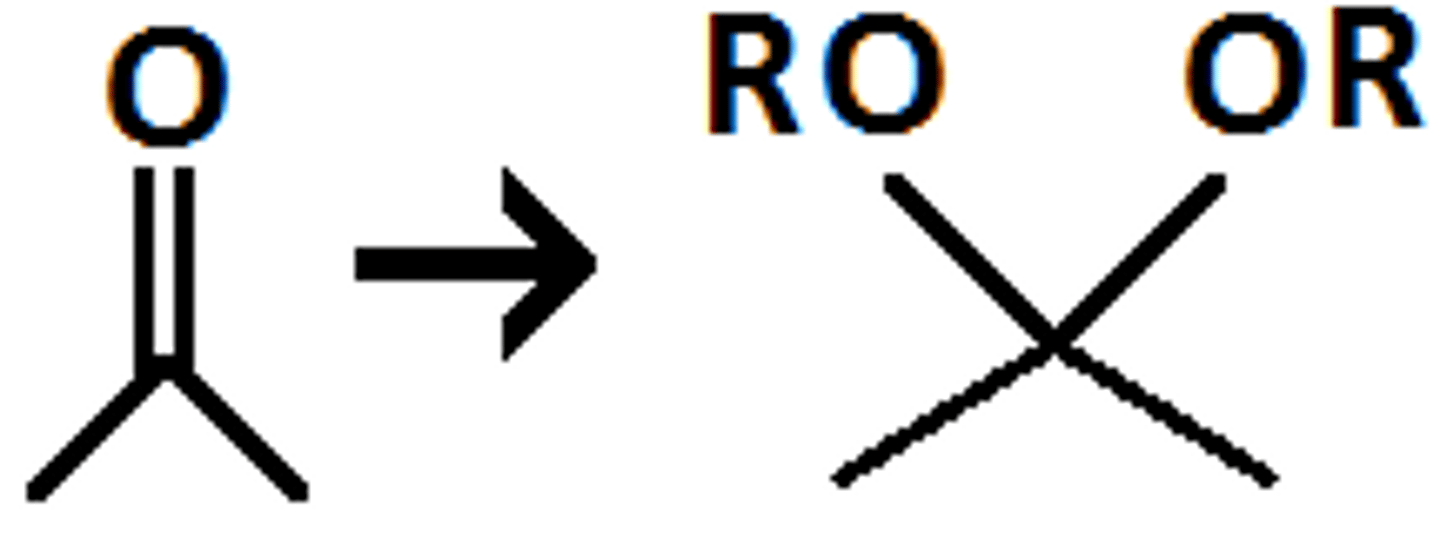
Basic
Acetals are stable in ______________ conditions
Thioacetal
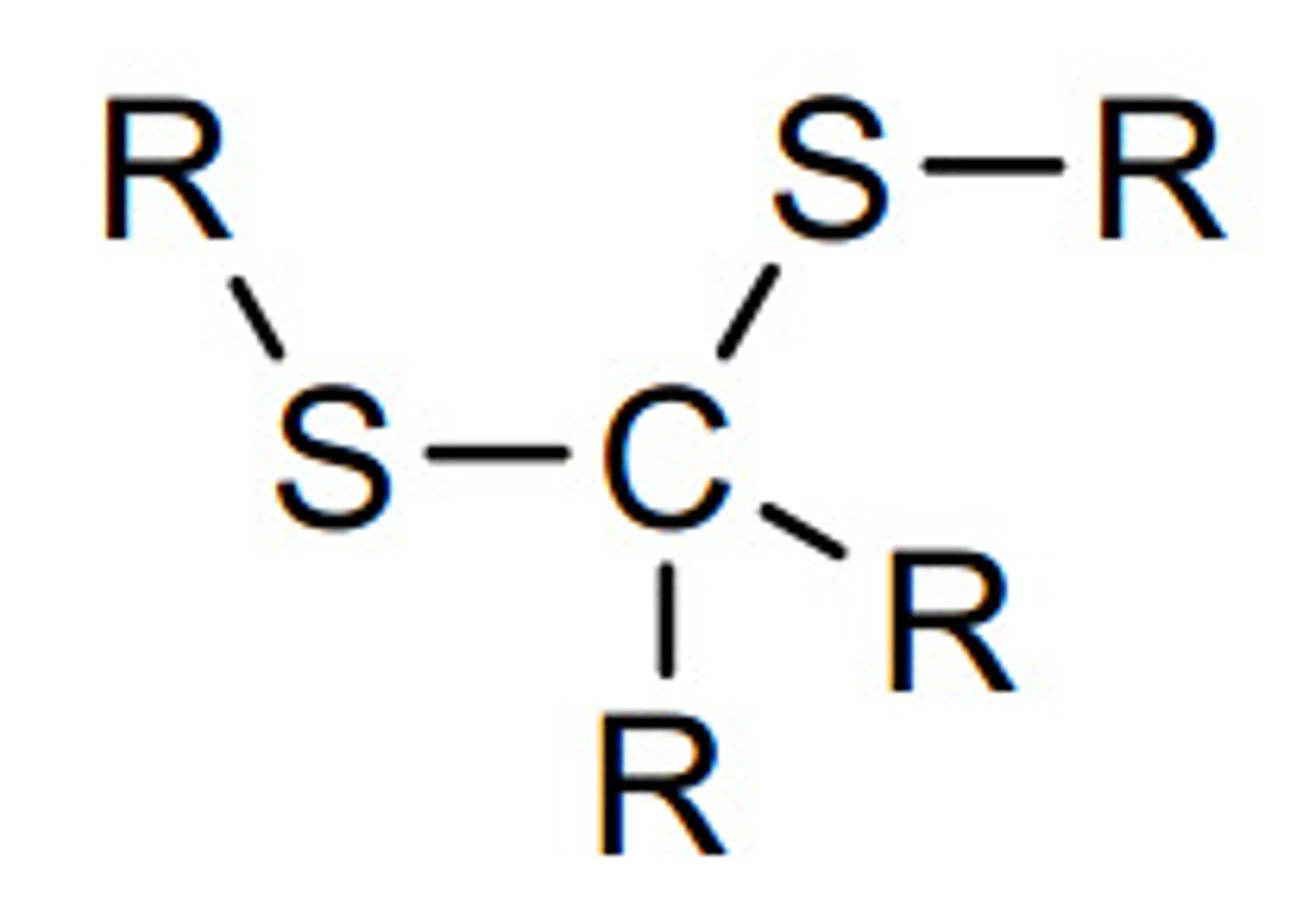
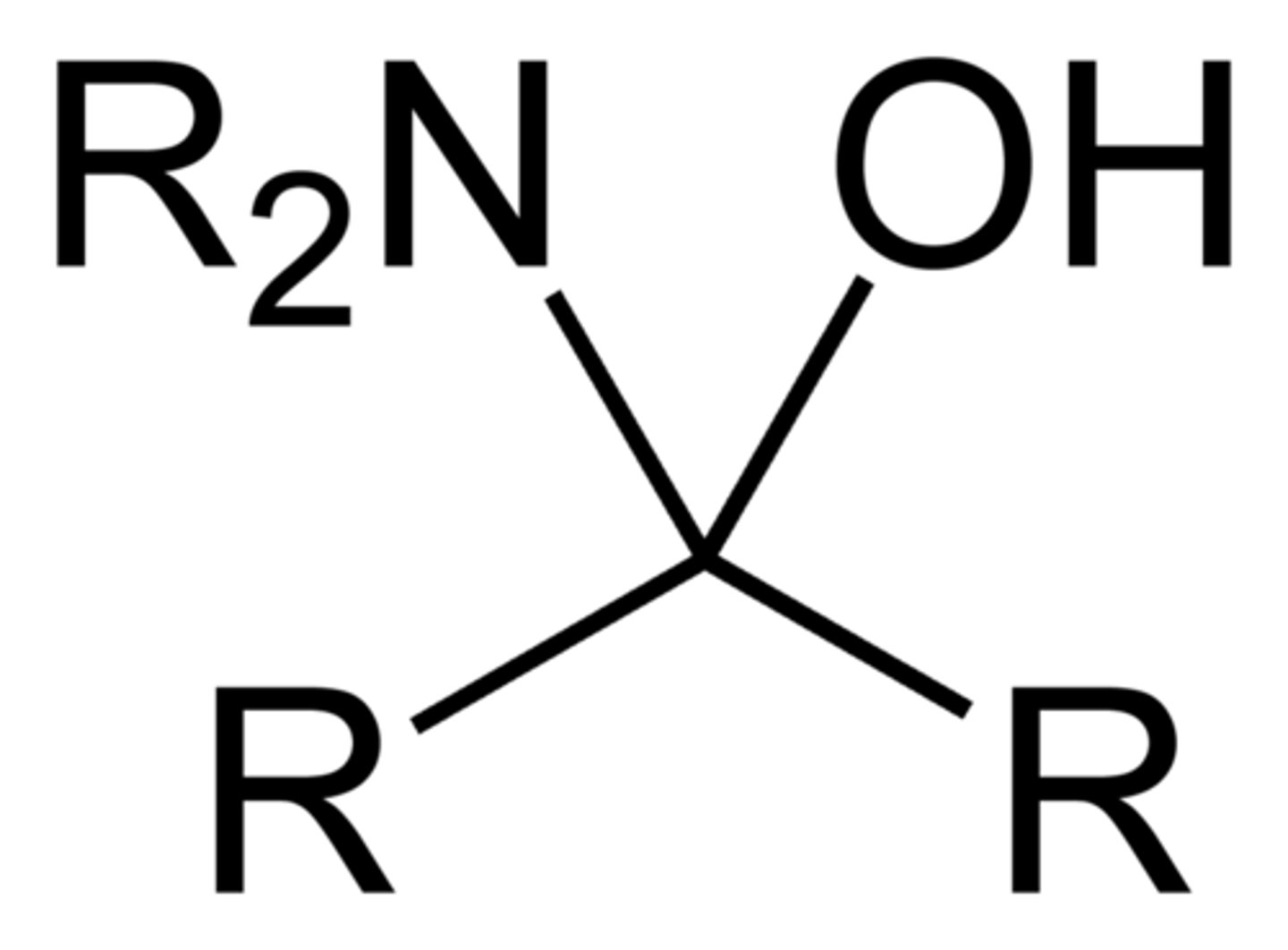
Carbinolamine
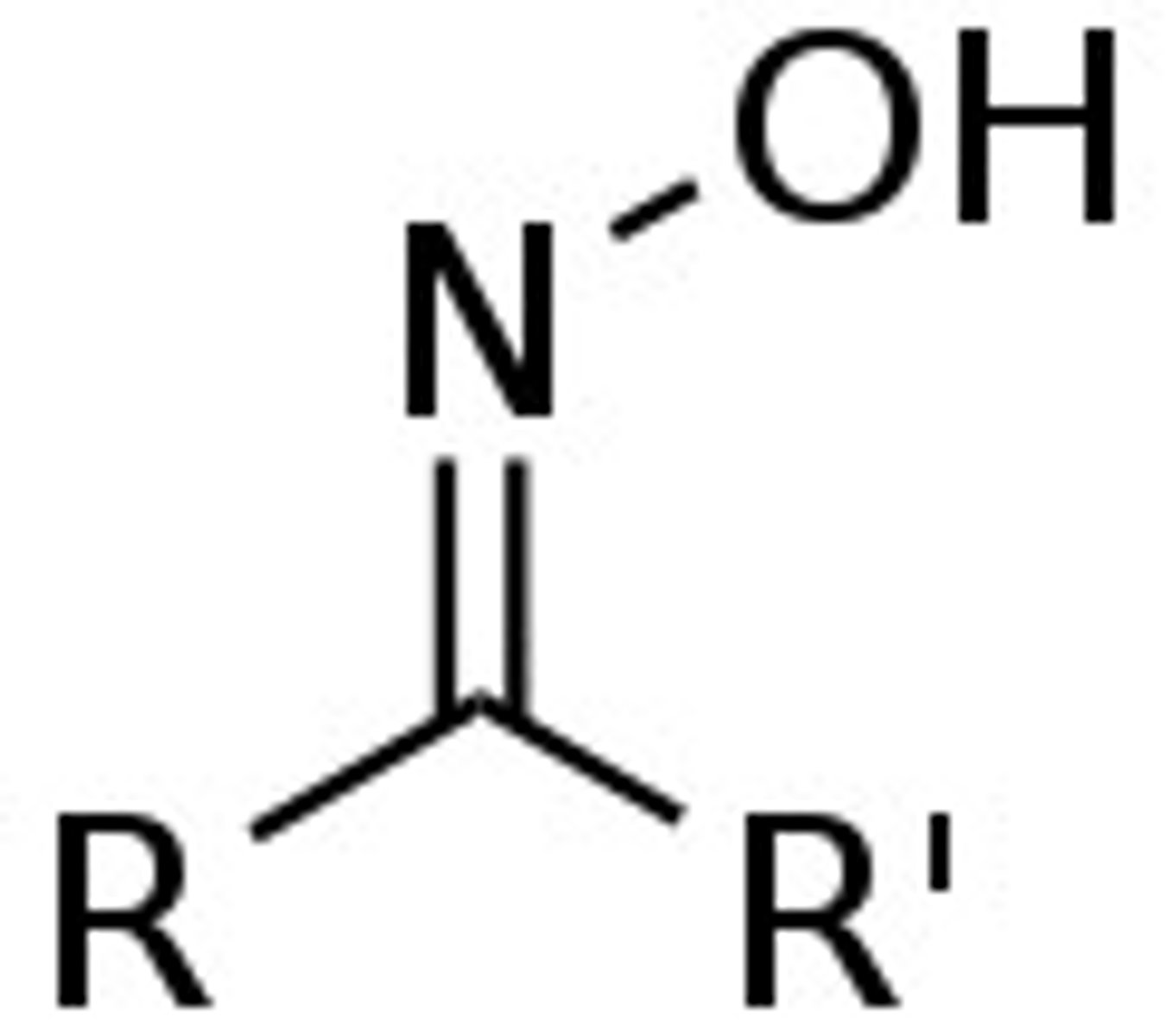
Oxime
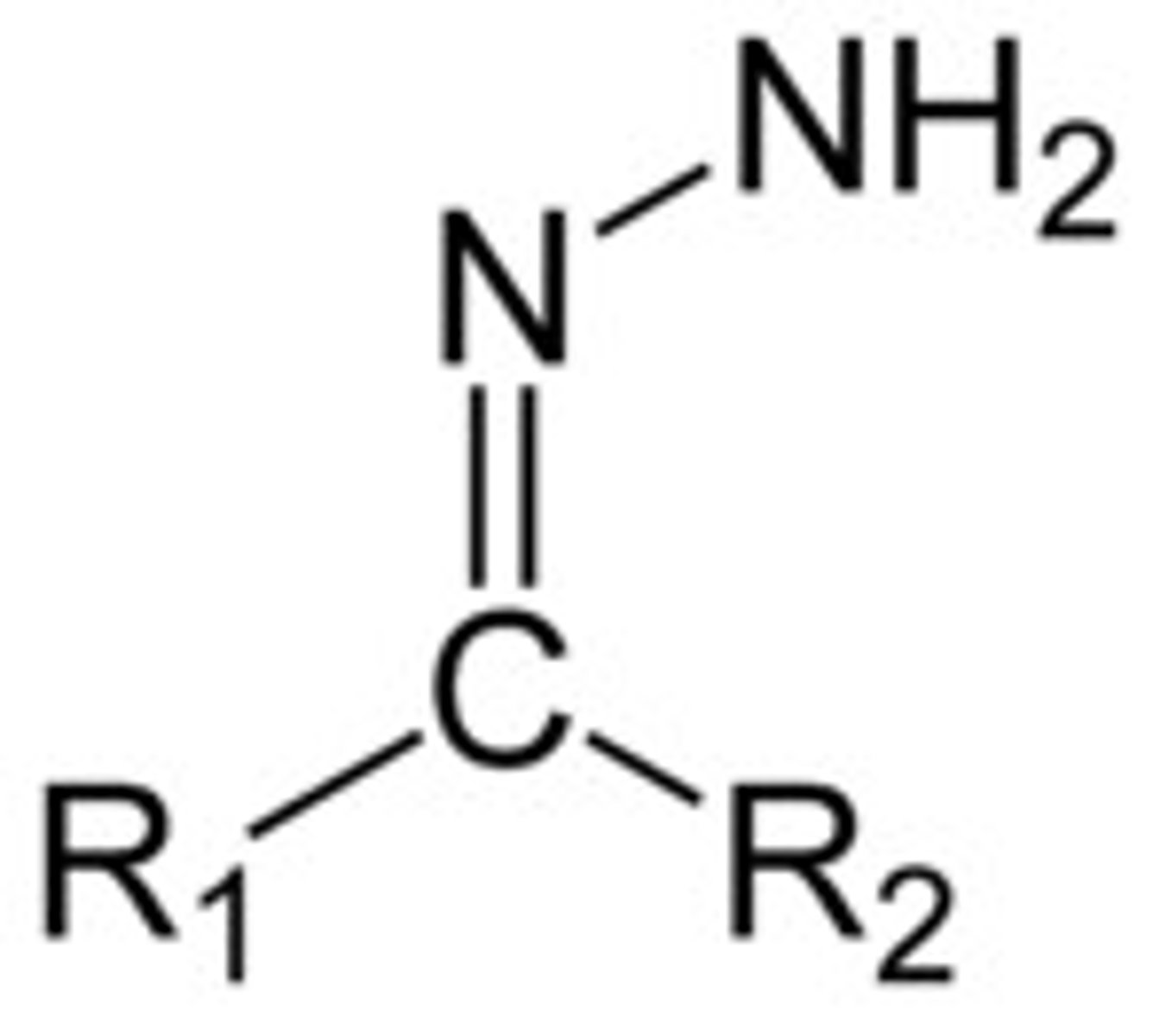
Hydrazone
Alcohol
Ketone or aldehyde + NaBH4 → ____________