1404 Biochemistry- Nitrogen Metabolism (Protein Turnover)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Essential amino acids and their importance
Essential amino acids (histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine) cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from the diet. They are crucial for protein synthesis, tissue repair, and metabolic functions.
Ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS)
The UPS is the main pathway for targeted protein degradation in eukaryotic cells. It involves tagging proteins with ubiquitin and degrading them in the proteasome to regulate protein turnover and remove damaged proteins.
Role of ubiquitin in protein degradation
Ubiquitin serves as a molecular tag that marks proteins for degradation. At least four ubiquitin molecules must attach to a lysine residue on a target protein to signal its destruction in the proteasome.
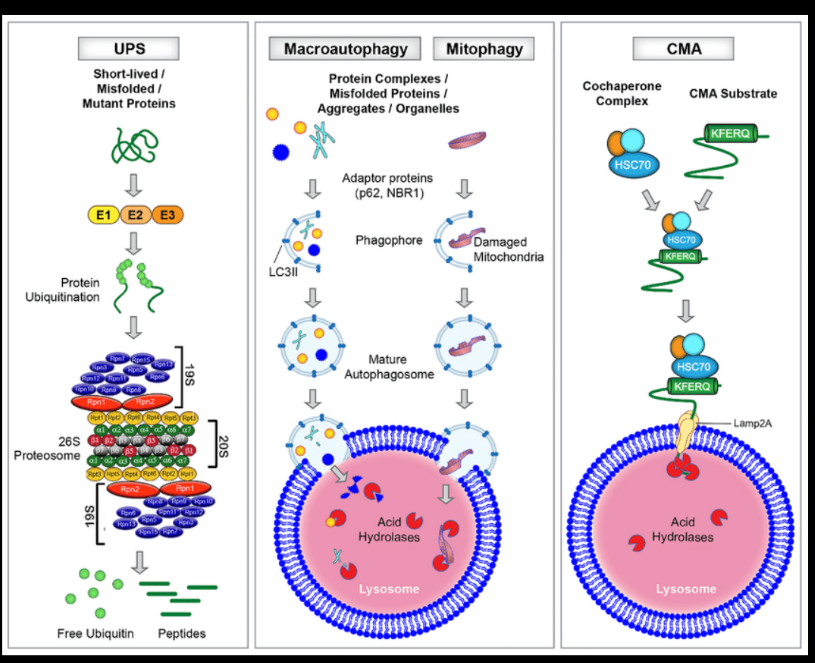
Autophagy vs. UPS
Autophagy degrades bulk cytoplasmic material and organelles through lysosomes, while the UPS selectively degrades short-lived proteins via proteasomes. Autophagy is more involved in cellular stress responses.
Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) and key proteins
CMA selectively degrades proteins with a KFERQ-like motif. Key proteins: HSC70 (binds target proteins) and LAMP2A (lysosomal receptor for protein translocation).
Nitrogen balance and its significance
Nitrogen balance reflects the difference between nitrogen intake and nitrogen excretion. Positive balance (intake > output) occurs in growth and pregnancy, while negative balance (output > intake) indicates muscle wasting or malnutrition.
Estimating nitrogen balance
Estimated by dividing daily protein intake (g) by 6.25. Primary nitrogen output component: Urinary urea nitrogen (UUN), measured in 24-hour urine samples.
Three factors affecting nitrogen balance
1. Dietary intake (protein/energy availability), 2. Physiological states (growth, pregnancy, illness), 3. Disease/trauma (catabolic states increase nitrogen loss).
Marasmus vs. Kwashiorkor
Marasmus: Total calorie deficiency → muscle and fat wasting. Kwashiorkor: Protein deficiency with sufficient calories → edema and fatty liver.
Disease linked to UPS dysfunction
Angelman syndrome: Caused by mutations in the E6-AP ubiquitin ligase (UBE3A), leading to neurodevelopmental impairments.