synaptic plasticity
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
how does the brain store info?
∆ing the amplitude/duration of synaptic events
potentiation
An increase in synaptic strength, making it easier for a neuron to fire in response to a given stimulus.
depression
A decrease in synaptic strength, making it harder for a neuron to fire in response to a stimulus.
synaptic strength can change by increasing/decreasing (3):
number of release sites
probability of neurotrans release
# or properties of postsynaptic ligand-gated receptors
n =
# of synapses
p =
probability of release
q =
quantal size
amplitude of the postsynaptic response to the glutamate from one vesicle
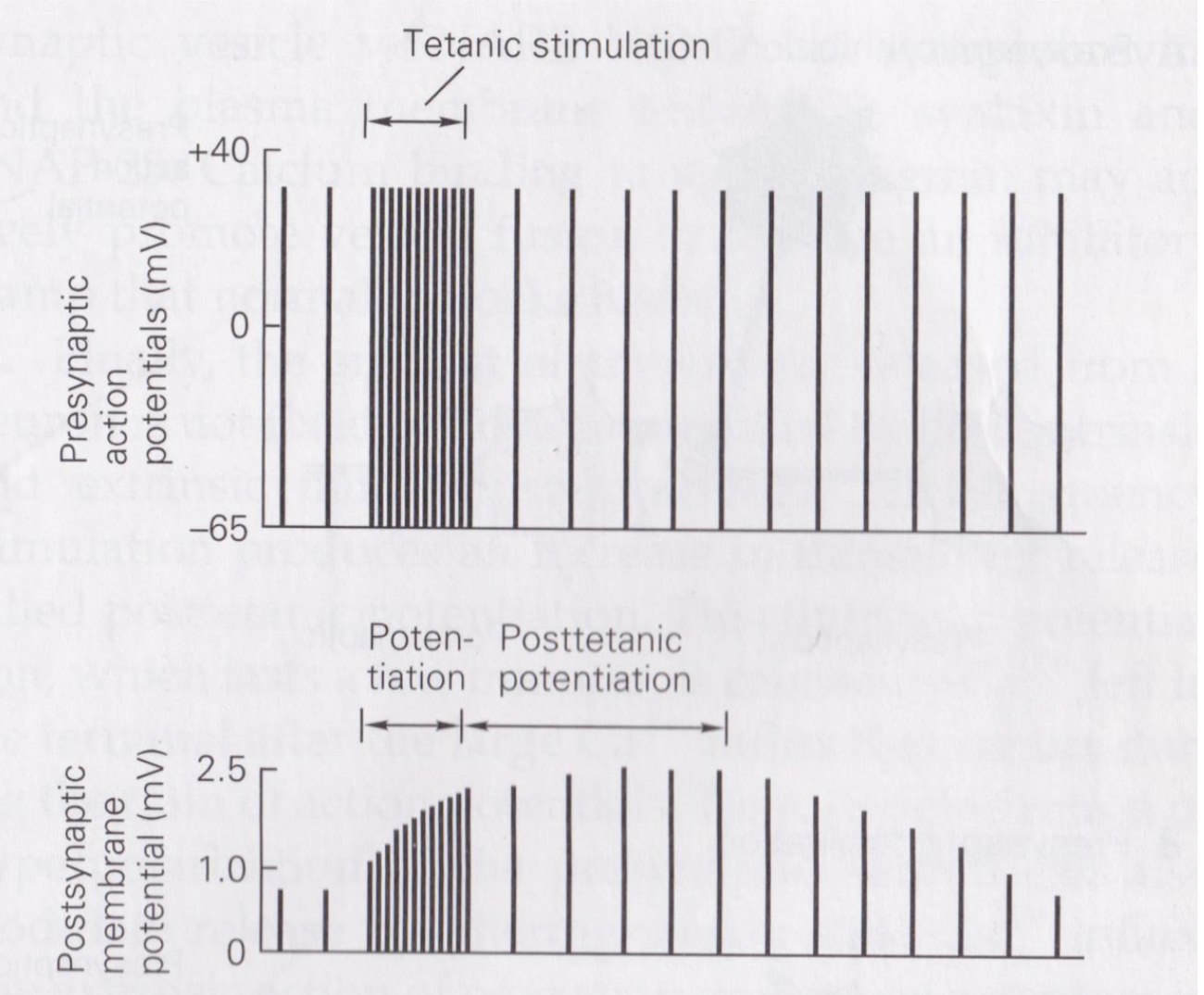
short-term facilitation
Ca2+ enters nerve terminal after 1st presynaptic AP
causes small amount of neurotrans release
2nd presynaptic AP → Ca2+ accumulates causing greater neurotrans release
post-tetanic potentiation
residual Ca2+ in presynaptic terminal caused by high frequency firing leads to short-term enhancement of synaptic transmission
caused by accumulation of Ca2+
short-term depression
occurs where release probability is initially high
1st event: Ca2+ causes large amount of transmitter release
2nd event: not enough vesicles readily available for for an equally large transmitter release
synaptic events getting smaller
fewer release of vesicles in the readily releasable pool during refractory period
facilitation
occurs at synapses where release probability is low
not v. high chance of releasing
Ca2+ facilitates vesicle fusion
as time increases facilitation becomes less apparent bc no more Ca2+ accumulation
readily-releasable pool of vesicles
5-8 vesicles in the active zone
ready to be released one at a time
special synapses may release 2-3 at a time
reserve pool of vesicles
17-20 vesicles
spatially behind → move into place as vesicles are fusing
resting pool of vesicles
180 vesicles
helps replenish reserve pools
________ and ________ are important variables for short-term plasticity
# of vesicles in the readily releasable pool
how quickly the pool can be refilled
how to ∆ synaptic strength
postsynaptic receptor could become desensitized
OR could be phosphorylated → ∆ing their open time/conductance
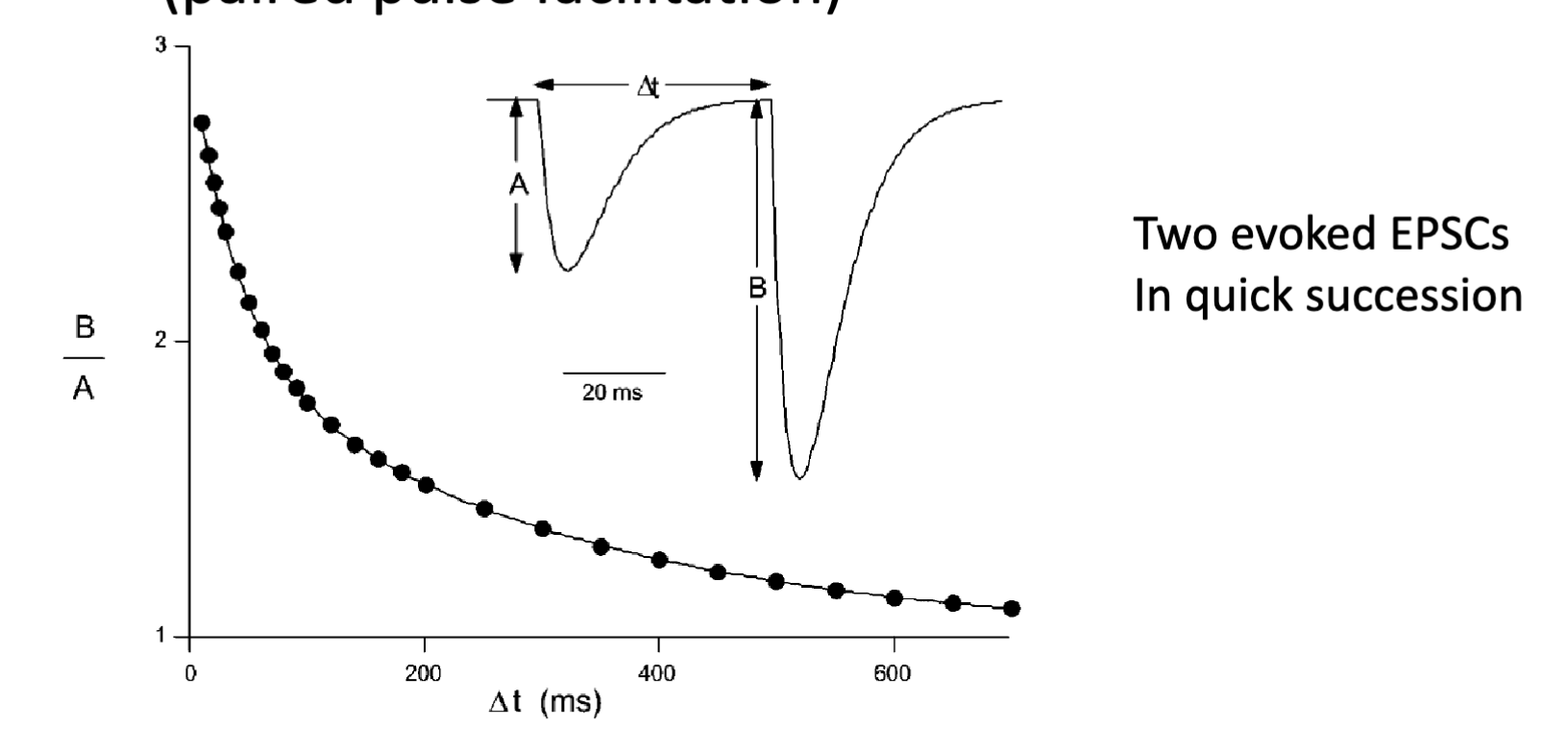
paired pulse ratio
second evoked current over the first
B/A
increase in presynaptic efficacy effect on paired pulse ratio
decrease in paired pulse ratio (B/A < 1)
increase in miniature (EPSC) frequency
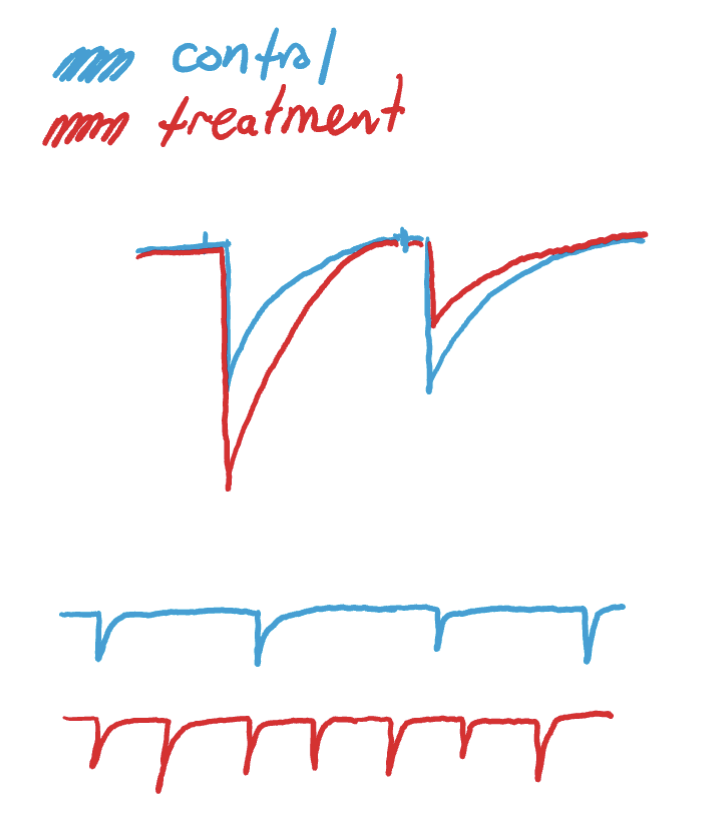
decrease in presynaptic efficacy effect on paired pulse ratio
increase in paired pulse ratio (B/A > 1)
decrease in miniature (EPSC) frequency
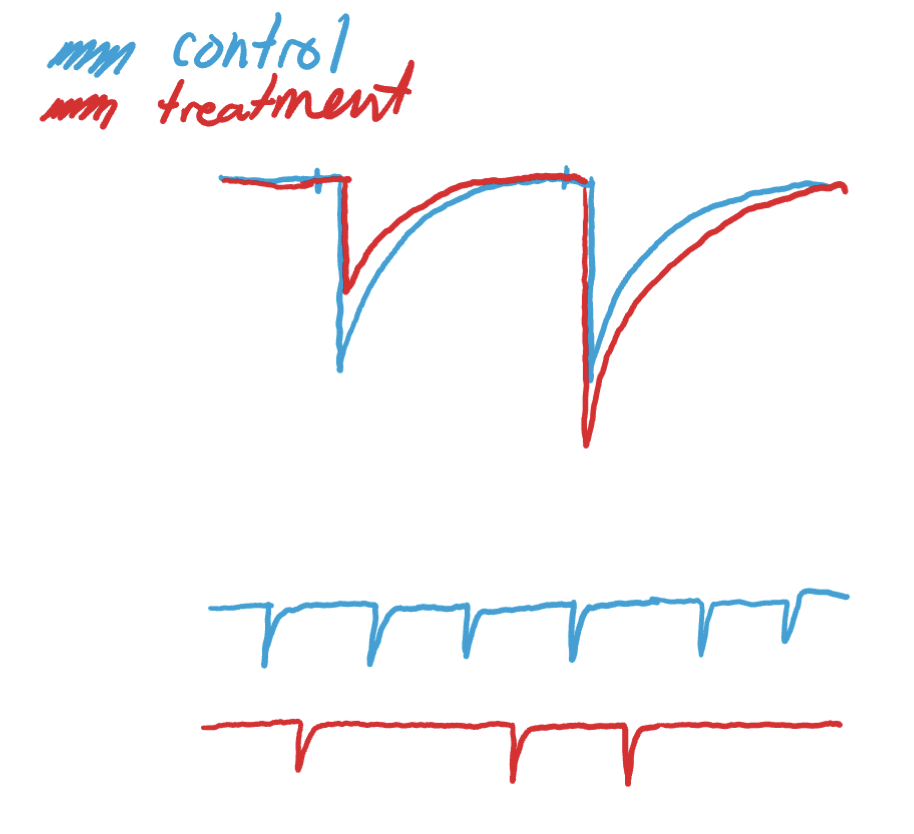
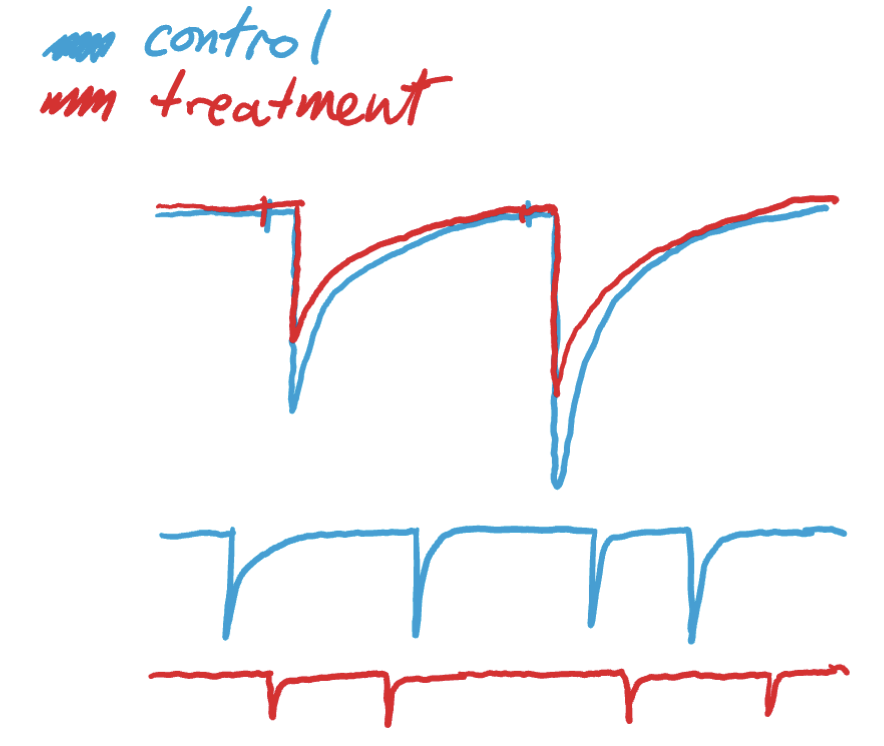
increase in postsynaptic efficacy effect on paired pulse ratio
no ∆ in paired pulse ratio (B/A) or miniature frequency
amplitude increase in all currents
current gets bigger but ratio doesn’t change (they both get bigger)
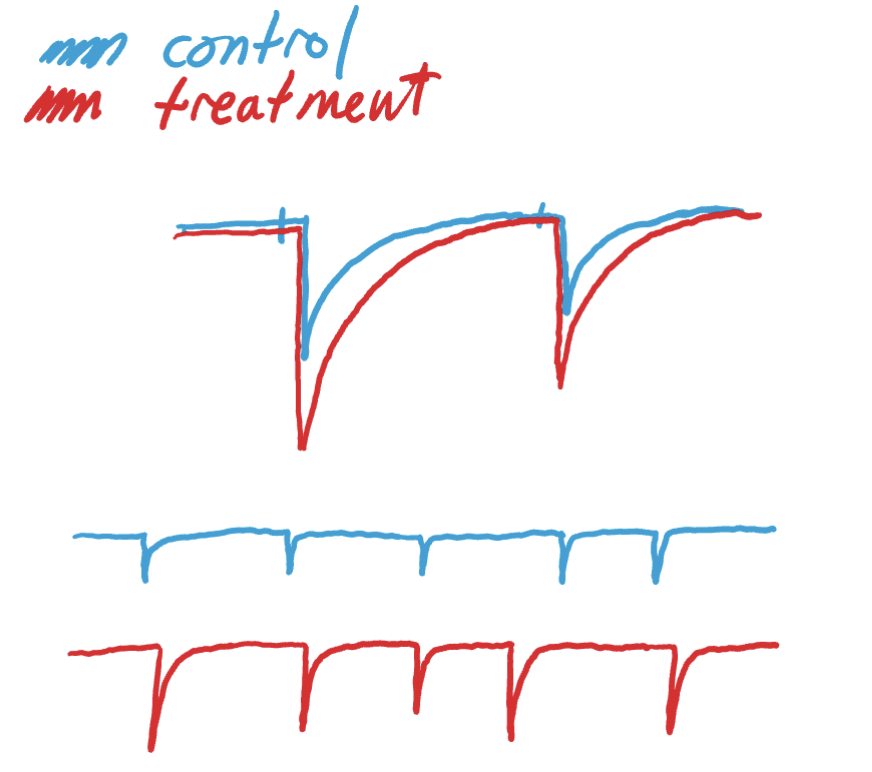
decrease in postsynaptic efficacy effect on paired pulse ratio
no ∆ in paired pulse ratio (B/A) or miniature frequency
amplitude decrease in all currents
both get smaller
could have changed quantal size = # of reeptors
phosphorylation of AMPA receptors
This suggests that phosphorylation of GluR4 enhances the synaptic response.
what happens to AMPA receptors when a cAMP blocker is added
inhibition of PKA prevents the effects of phosphorylation on AMPARs.
2-AG (2-arachidonoylglycerol)
endocannabinoid
acts as retrograde messenger in brain
Endocannabinoids
produced by postsynaptic neurons and act on presynaptic receptors to modulate neurotransmitter release
in GABAergic synapse, CB1 receptors (cannabinoid receptors) are activated by
2-AG, leading to the short-term depression (DSI) of synaptic transmission through a cascade involving Gi/o proteins.
in glutamatergic synapse, CB1 receptors (cannabinoid receptors) are activated by
2-AG and leads to short-term depression (DSE).
Significance of DSI/DSE
important for modulating synaptic activity and maintaining balance between excitation and inhibition in neural circuits.
help to prevent excessive excitation or inhibition, ensuring proper neuronal network functioning.
what happens to IPSC current when a CB1 agonist is added
activation of CB1
decrease in IPSC amplitude following the application of WIN
significant increase in the paired-pulse ratio with WIN (p < 0.05),
indicating that the CB1 receptor activation by WIN affects synaptic function, likely by reducing neurotransmitter release or affecting synaptic plasticity.
what happens to IPSC current when a CB1 antagonist is added
block CB1 receptor signalling
a return to baseline when SR14 is applied, indicating a reversal of the effects of WIN by the antagonist
what does a high paired pulse ratio suggest
A higher ratio typically suggests reduced synaptic depression or altered neurotransmitter release.
long-term potentiation (LTP)
long-lasting enhancement in signal transmission between two neurons that results from stimulating them synchronously
Long-term depression (LTD)
long-lasting attenuation in signal transmission between two neurons.
NMDA receptor
permeable to Ca2+ in addition to K+ and Na+
requires d-serine/glycine as a cofactor
voltage dependent (Mg+ block)
opens + closes slowly
where to ∆ # of AMPA receptors for long-term potentiation/depression
in the post synapse
negative membrane potentials (around -100 mV), there is little to no current passing through the NMDA receptor channel because
magnesium (Mg²⁺) ions block the channel at resting membrane potential (typically negative).
what happens to NMDA receptor when membrane potential becomes more positive (towards 0 mV and beyond)
magnesium block is relieved due to the depolarization of the membrane, and current starts to flow