ID: W5L2 (L1 was exam) - Introduction to cognitive ability Lecture 4
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What’s the difference of focus between personality and intelligence
Personality decsirbes stable indi diffs that predispose behaviours
Intellgience: more concerned with ability
potentially harder to access ability in a questionanire
Explain lay theories of intelligence
After talking to a bunch of peopel in the street, Sternberg found that he could boil down to 3 dimensions
Practical problem solving ability: ability to think about multople solutions using available resources to solve a problem
Verbal ability: abiliity to confidently use language, slef expression and ability to see abstaract relationships betwen words
Social competence: ability to cooperate with otehrs, reoslve conflicts and correctly interpret social signals (kinda like EQ)
Later studis for other factors: goal orientation, fluid thought (thinking quickly and bstractly) , and learning from mistakes
Intellgence across the lifespan
During school: teacheros view social competence as most important in primary school VS verbal fluecny in scepndary VS logic and reasoning in post secondary
Interest and ability to cope with novelty judged as most important for younger adults (30s) vs practical probelm solving abilities for older adults
People also change what they consider to be intellegent as they ageFILL IN
Explain lay theories across cultures
What constutues intelleigence varies across cultures
Fairly consistent in North America, Eurppe, and Australia
Western world emphasizes individual mental processing, while non-Western countries emphasize social factors, self-understanding and huility
verbal skills are less often found or rated as less improtant
Explain the difference between rational or reasonable values (fill in)

Rational:
mathematical answer
Reasonable:
social answer
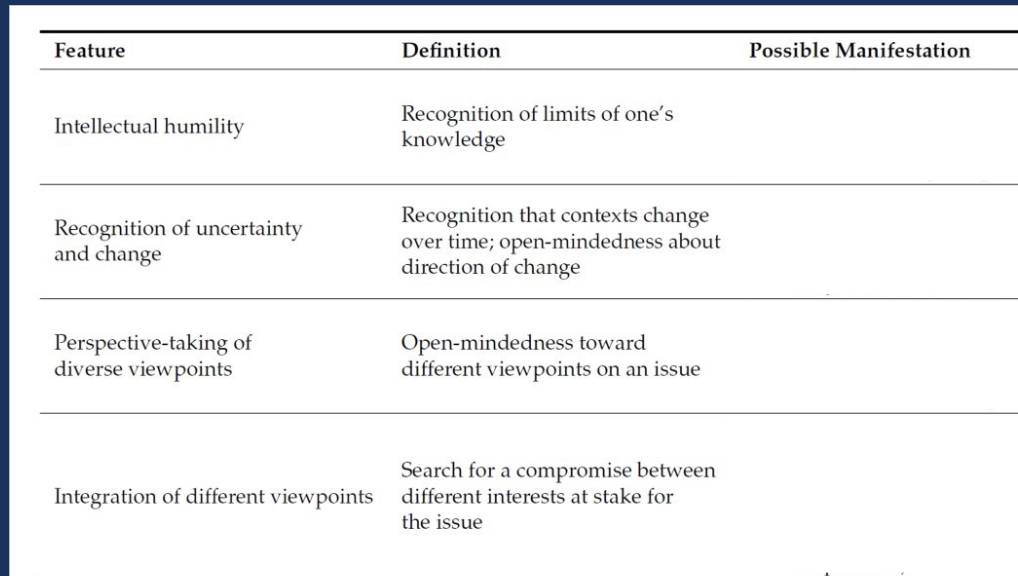
Explain wisdom vs intelligence
Wisdom:
intellectual humility, recognition of uncertanty, perspective-taking, and integration of different viewpoints
Wisdom increases with age, more life satisfaction and positive affect
negatively correlated with processing speed
What are some facets of wisdom (fill in possible manifestations)
Explain how what we beleif affects how we perceive intellegience (fill in)
Carol Dweck (fixed vs growth mindset)
fixed mindset: born with intelligence
growth mindset: can develop it
Research showcases that growth mindsets are more predictive of academic success
cultural differences: growth mindsets are effective for students from East Asia, North America while fixed mindsets are better for students in Europe
How do we define a genius?
IQ: over 130
Extradinary achievement: defined in retrospect after somebody accomplishses something significant
can include creatuve genuis, leadershp, sicentiifc or technical accomplishments, sports
How do we study genius
Psychometric:
start by looking at
longtudianl studies have trakced samples of intellectually gifted childern and tried to observe tehir achievemnt
pursued PhD’s at 50x the base rate
notable alumni: Lee Cronback (Cronbach;s alpha)
Historiometric:
Maslow is an example how he studied peoople who he thought already reached self-actualization
Howd they measure it
personality sketches: using independt rates to rate historicla figures personality based on biographeies, diaries, etc,
Develpment history: estimatng cognitive ability based on their development
IQ originally fomulated as the ratio of one’s mental age to one’s chronological age
Content analsyses: rating thoht processes forom written text (fill in)
Expert surveys: FILL IN
Explain how there’s variability in intelligence
FILL IN
What’s a “Mad Genius”
Mad Genius
Vincent van Gogh
Nikola Tesla, Beethoven
Historiometric research consistently finds a relationship between genius and psychopathology
particularly true for artists, rather than scientists or leaders
Explain heritability of intellgeince
a lot of intelligence is heritable but has big interaction with the environment
FILL IN
Summarize intelligence