AP Bio Unit 1 Test
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Order
Property of life; Living things are highly organized in structure and function; Structure and function are related at all levels
Reproduction
Property of life; Organisms reproduce their own kind
Growth and Development
Property of life; Organisms increase in size and complexity (life grows by internal changes)
Energy Processing
Property of life; Organisms take in energy and transform it to do work; Organisms are “open” systems, they must continually take in energy
Response to Environment
Property of life; Organisms respond to changes/stimuli in their environment; The speed of the response may be “fast” or “slow”
Regulation
Property of life; Life processes must be controlled and adjusted; Organisms must maintain their internal environment within tolerable limits (homeostasis)
Evolution Adaptation
Property of life; Organisms change over time because of their adaptations to their environment; Organisms must adapt - move or die
Negative Feedback
When your body naturally reacts to get a system back into homeostatic range
ex: Glucose Levels; Your body releases insulin if your blood sugar gets too high
Positive Feedback
When your body responds to an unplanned event that makes systems overreact
ex: Cuts; platelets increase in order to clot the wound
Inductive Reasoning
Starting from a set of specific observations to reach a general conclusion
ex: humans require organic molecules, fish require organic molecules, therefore all animals must require organic molecules
Deductive Reasoning
A type of logic in which specific results are predicted from a general premise.
ex: All dogs have ears; golden retrievers are dogs, therefore they have ears
Matter
Anything with volume and mass
Macroelements
Elements needed in large quantities
ex: H, O, N, C (P, K, S, Ca, Fe, Mg, Na, Cl)
Microelements
Elements needed in small quantities (trace elements)
ex: Cu, Co, Zn, I, Mn
Atomic number
Number of protons in the nucleus
Atomic Mass
Number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different atomic masses (changes in the number of neutrons)
Radioactive Isotopes
Where the nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy
Heavy Isotopes
Has a stable nucleus, but masses more than the standard isotope for the element
Valence Electrons
The electrons on the outermost energy level (electrons available for chemical bonds)
Non-Polar Covalent Bonds
When electrons are shared equally between atoms (very strong bond)
Polar Covalent Bonds
When electrons are shared unequally between atoms (water)
Ionic Bonds
Formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another and ions are formed (weak bond)
Cation
Loses electrons (positive charge)
Anion
Gains electrons (negative charge)
Hydrogen Bonds
When a hydrogen atom bonded to one molecule is attracted to the slightly negative area (N or O) of another molecule (weak individual bond, but strong when there are a lot of them)
Cohesion
Water sticks to water (hydrogen bonding); helps to facilitate photosynthesis
Adhesion
Water sticks to other (polar) molecules (hydrogen bonding); helps water move through plant vessels
Surface Tension
The surface of water is very difficult to stretch or break (hydrogen bonding); bugs can walk on water and collect nutrients
High Specific Heat
It takes a lot of energy to raise one gram of water one degree C (hydrogen bonding); water can stabilize temperature
High Heat of Vaporization
It takes a lot of heat for water to convert to vapor; (hydrogen bonding); water cools organisms from excessive heat buildup
Water expands when it freezes
The distance between water molecules increases from the liquid to the solid form; forms crystalline structure; ice can float; (Hydrogen bonding)
Why is water known as a ‘Universal Solvent’
Water’s unique chemical properties give it the ability to dissolve many different materials, which is why it is known as a universal solvent.
Hydrophillic
Materials that dissolve in water (have polar regions on their molecules for H+ bonds)
Hydrophobic
Materials that repel water (have non-polar bonds)
pH Scale
Logarithmic scale for showing H+ concentration; each pH unit is a 10x change in H+
Acids
pH < 7
Bases
pH > 7
Buffers
Materials that have both acid and base properties; resists pH shifts
Hydrocarbon
Organic molecules made of ONLY hydrogen and carbon (fatty acids are hydrocarbons)
Isomer
Compounds with the same molecular formula, but different structures; results in different molecular and chemical properties
Structural Isomers
Different in covalent arrangements of their atoms
Geometric Isomers
Same covalent partnership but different in spacial arrangements
Enantiomers
Molecules that are mirror images of each other
Functional Groups
A group of atoms attached to a carbon skeleton (have consistent properties)
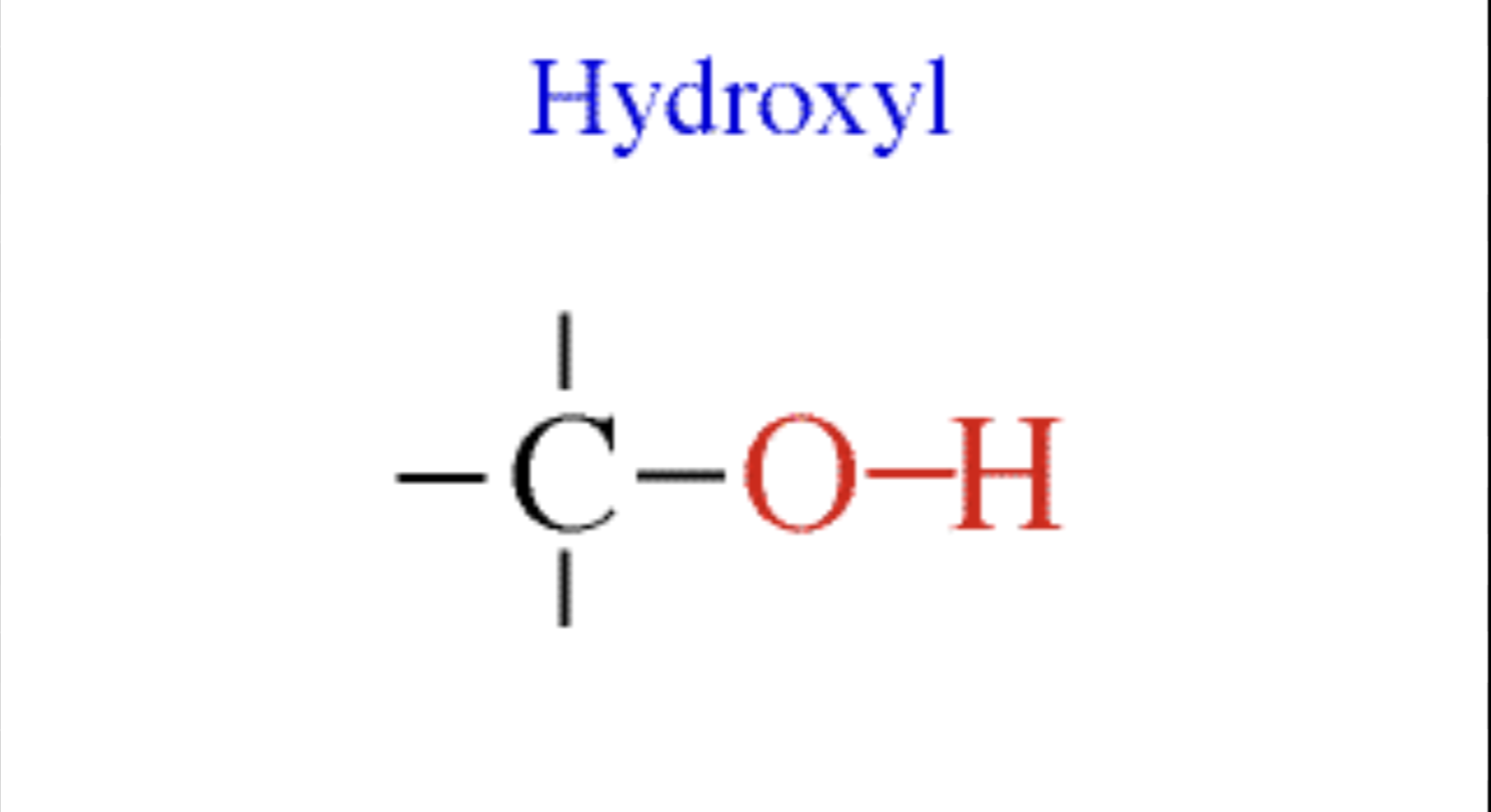
Hydroxyl
Polar; can form hydrogen bonds easily
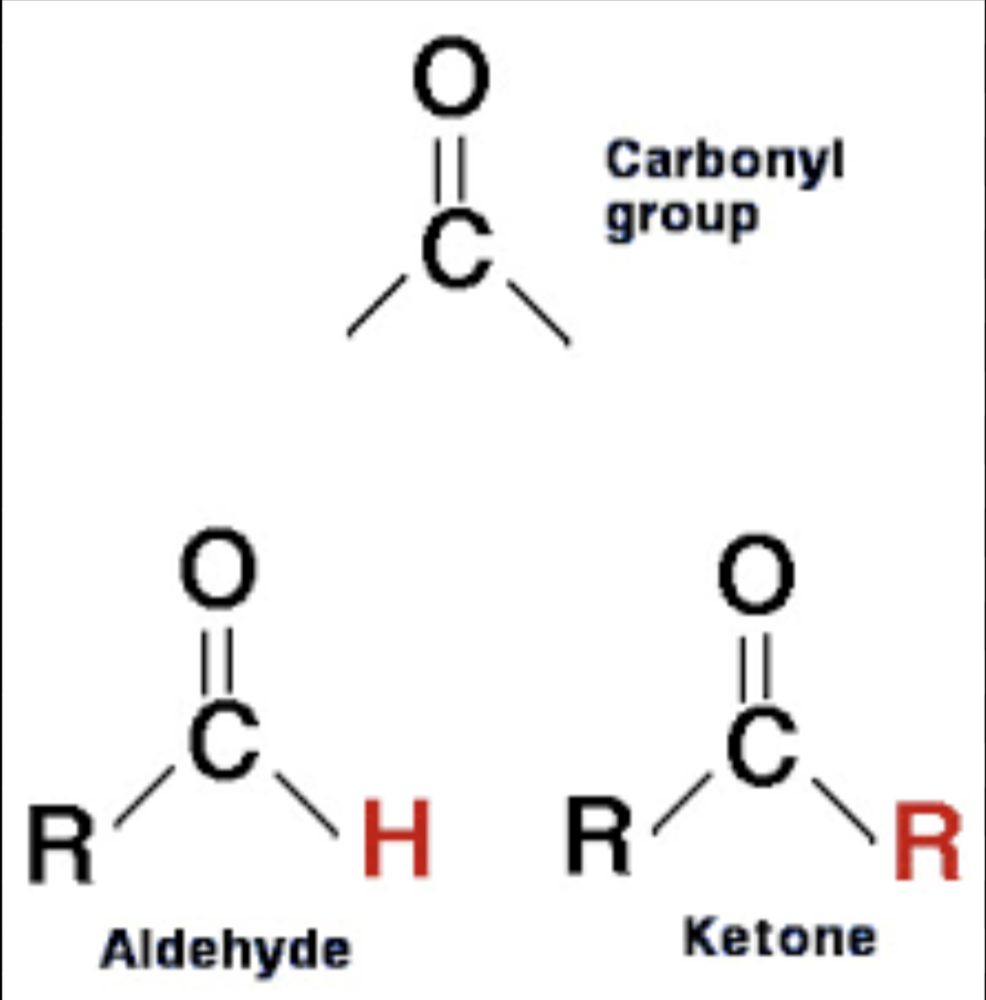
Carbonyl
Non-polar; found in sugars;
Keytones = found in the middle of a molecule Aldehyde = found on the ends of molecules
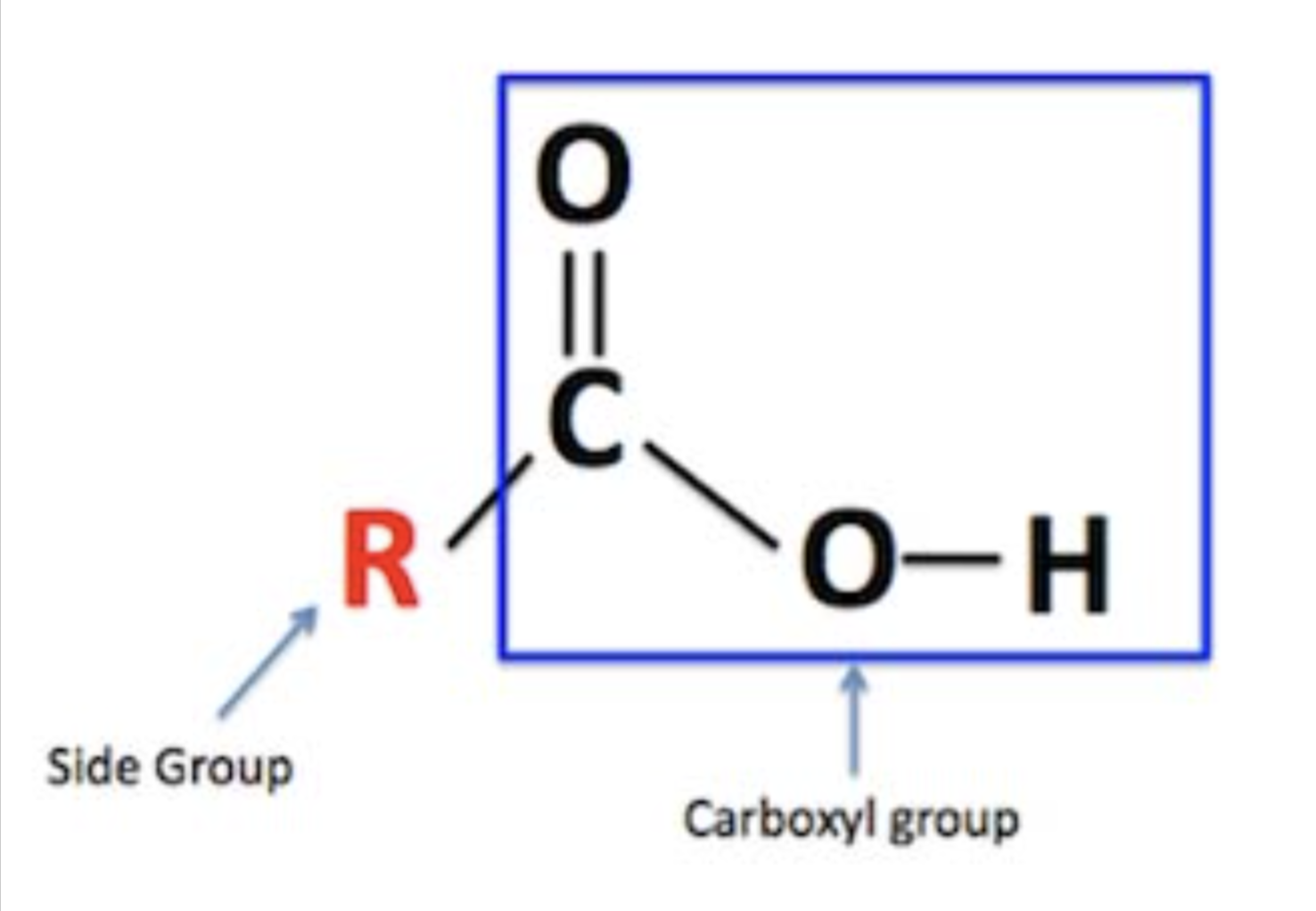
Carboxyl
Tends to be acidic; slightly polar (gives H+ away)
Amino
Tends to be basic; proteins; (looking for H+)
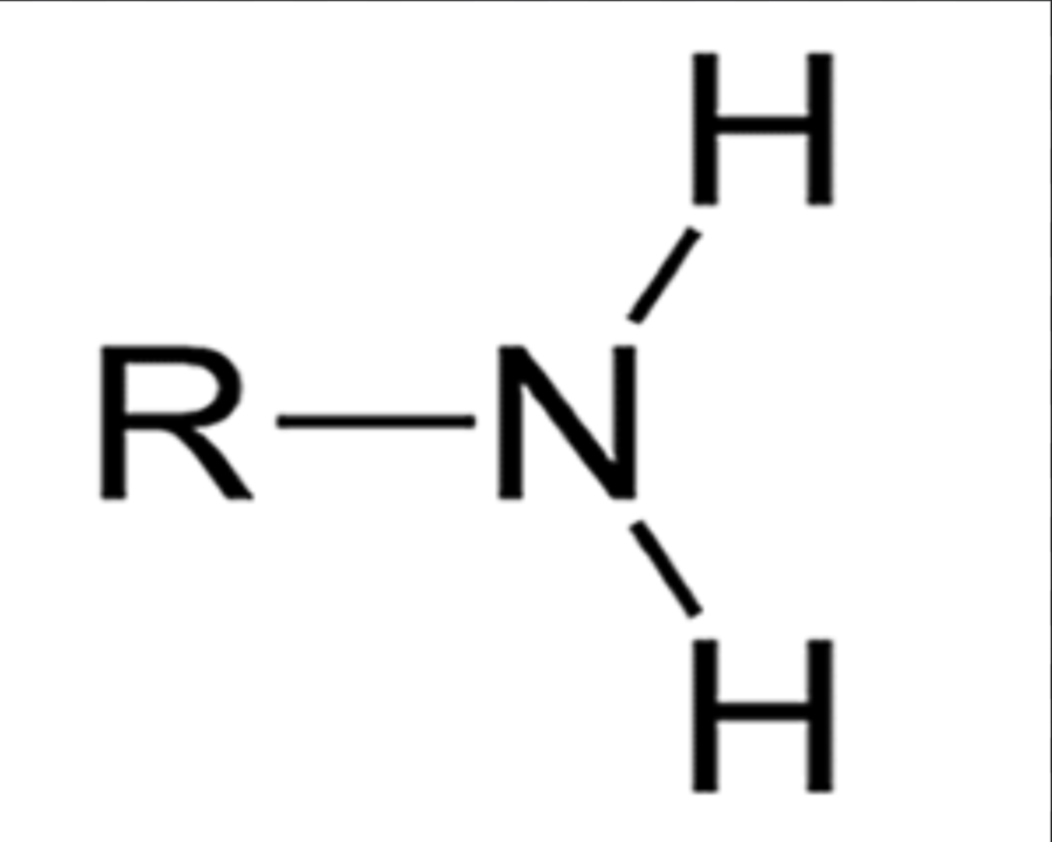
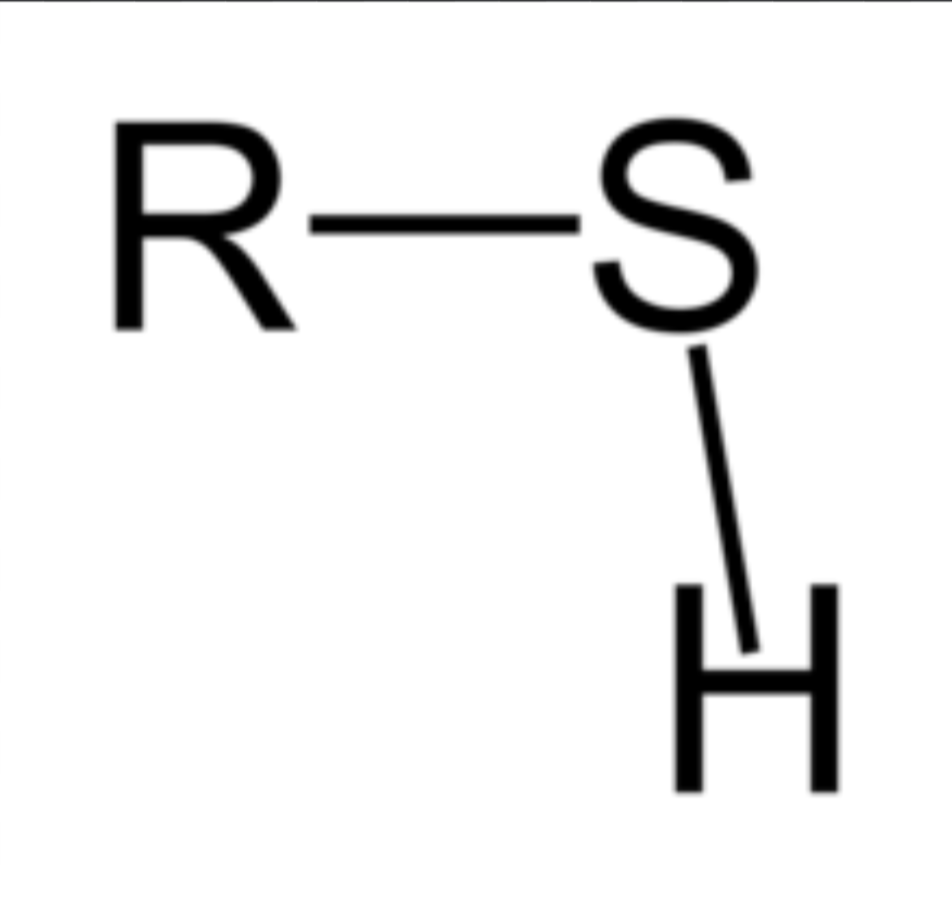
Sulfhydryl
Only wants to bond with Sulfur; forms disulfide bridges
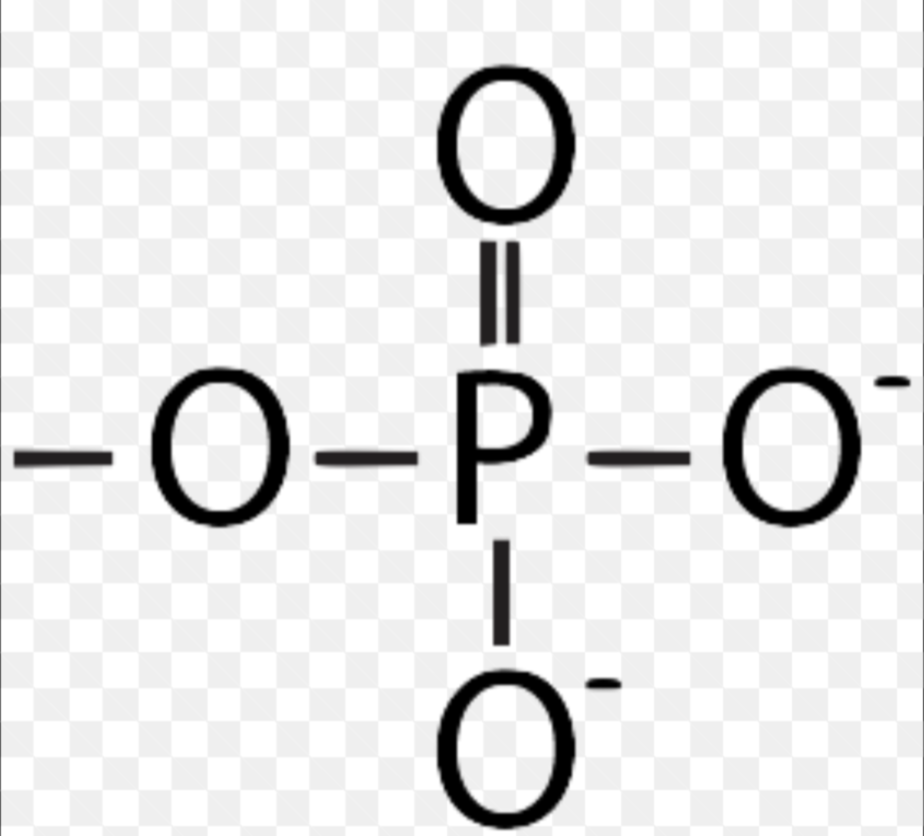
Phosphate
Polar; contributes negative charge; ATP
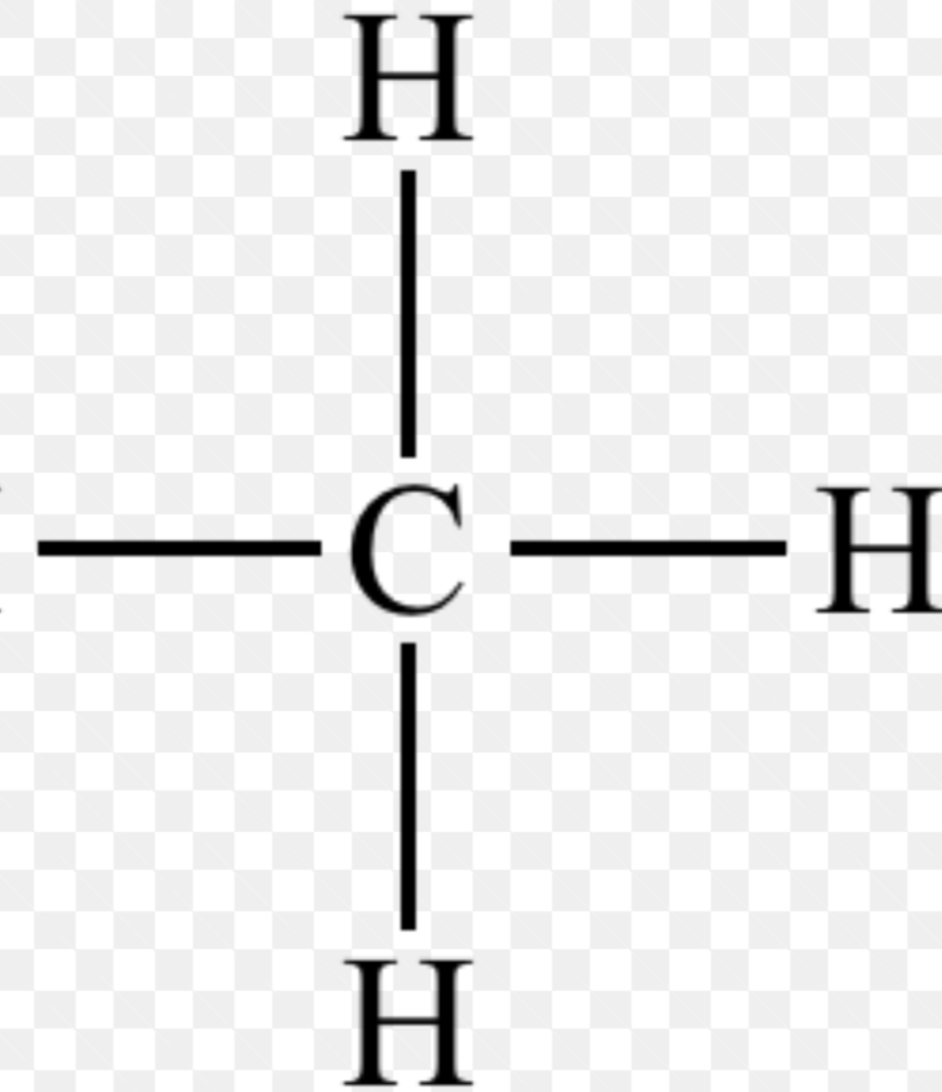
Methyl
Non-polar; DNA; Hormones
Carbohydrates: Uses
Fuel, building materials, receptions
Carbohydrates: Made of
C, H, O; C:H:O ratio is 1:2:1
Carbohydrates: general formula
CH2O
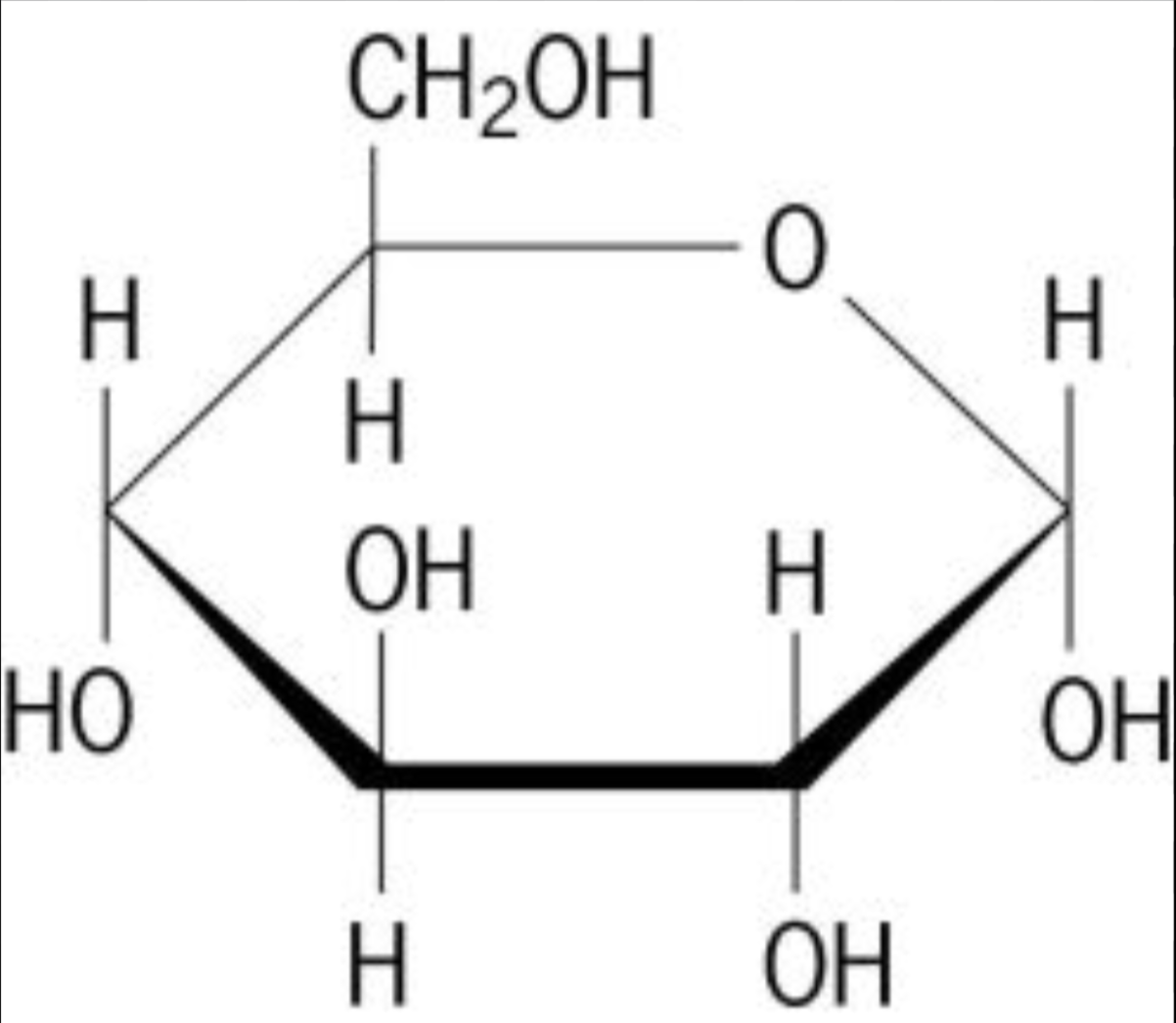
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars, can be in linear or ring form; 3-7 Carbons;
ex: glucose, galactose, ribose, fructose
Disaccharides
Sugar formed by joining two monosaccharides; double the amount of Carbons
ex: Maltose = glucose + glucose; Lactose = glucose + galactose; Sucrose = glucose + fructose (sweetest)
Oligosaccharides
Used in cell membranes; 2-10 joined simple sugars
Polysaccharides
Many joined simple sugars; used for storage or structure;
ex: Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen (ALL made of only glucose)
Starch
Fuel storage in plants- very easy to break down
Cellulose
Used for structure in plant cell walls (humans cannot break it down- fiber)
Glycogen
Found in liver and muscle cells
Lipids
Diverse hydrophobic molecules
Lipids: Made of & C:O ratio
C, H, O; no general formula; C:O ratio is very high in C
Fats
Solid at room temp
Oils
Liquid at room temp
Hydrophobic = ??
Non-Polar
Fatty Acids
A long carbon chain (12-18 Carbons) with a -COOCH (carboxyl group) (acid) on one end, and a -CH3 (methyl group) (fat) on the other
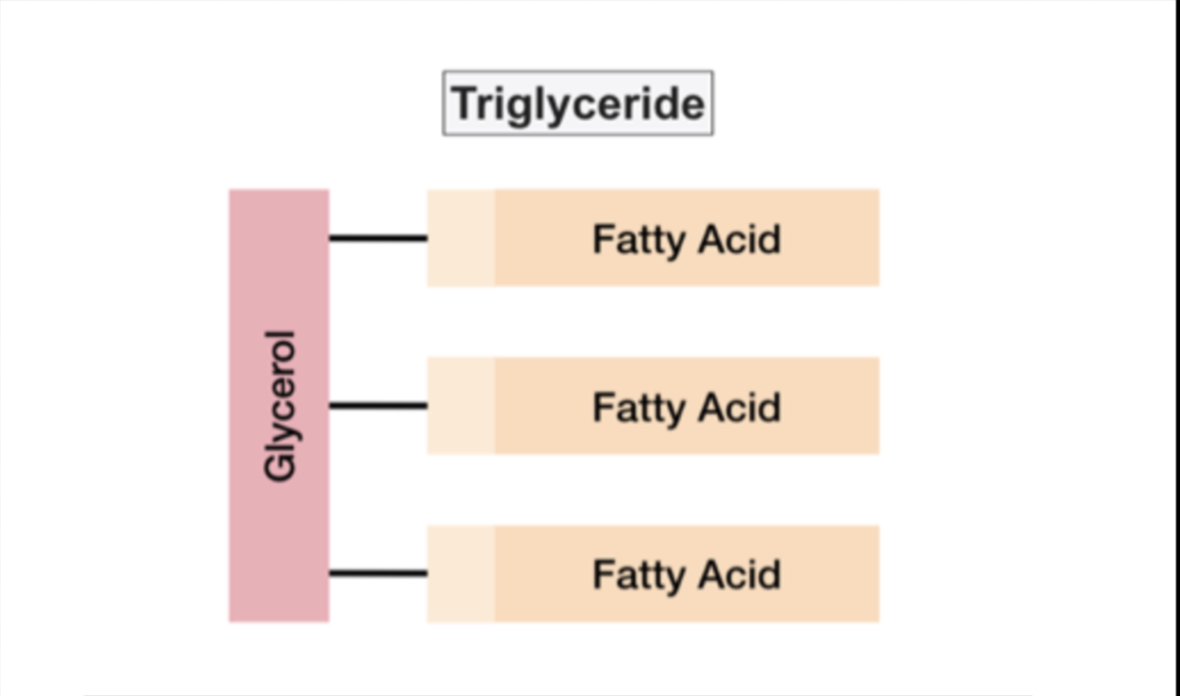
Triglycerides
Most fats have 3 fatty acids attached to the glycerol
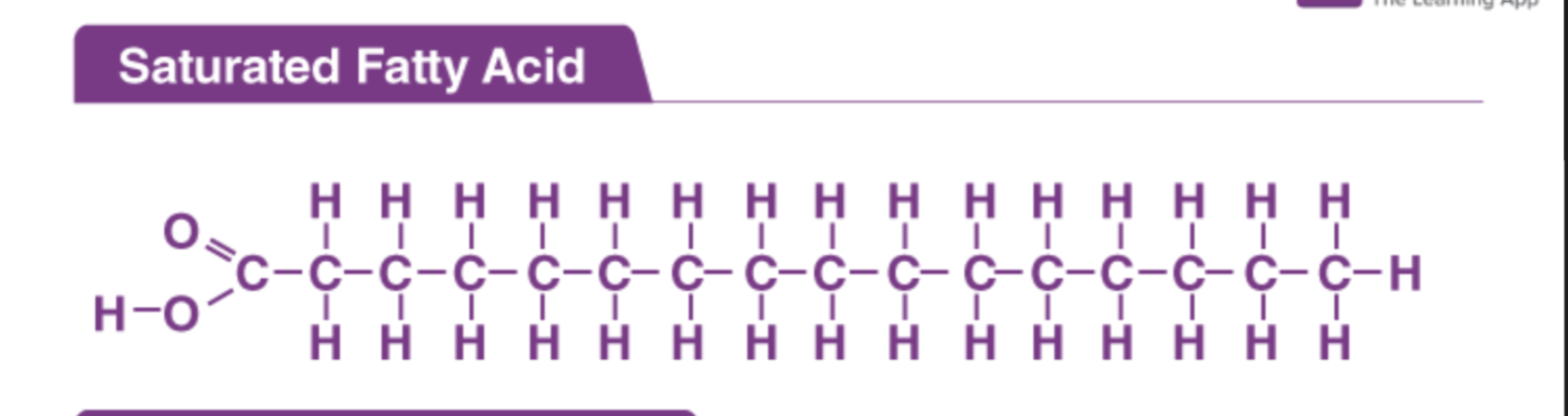
Saturated fats
No double bonds (tend to be solid)
Unsaturated fats
One or more C=C bonds; can accept more hydrogens; double bonds put kinks in the molecule’s shape

Fats are used for:
Energy storage, cushions for organs, insulation
Phospholipids
Similar to fats, but only have two fatty acids; the third -OH of glycerol is joined to a phosphate-containing molecule
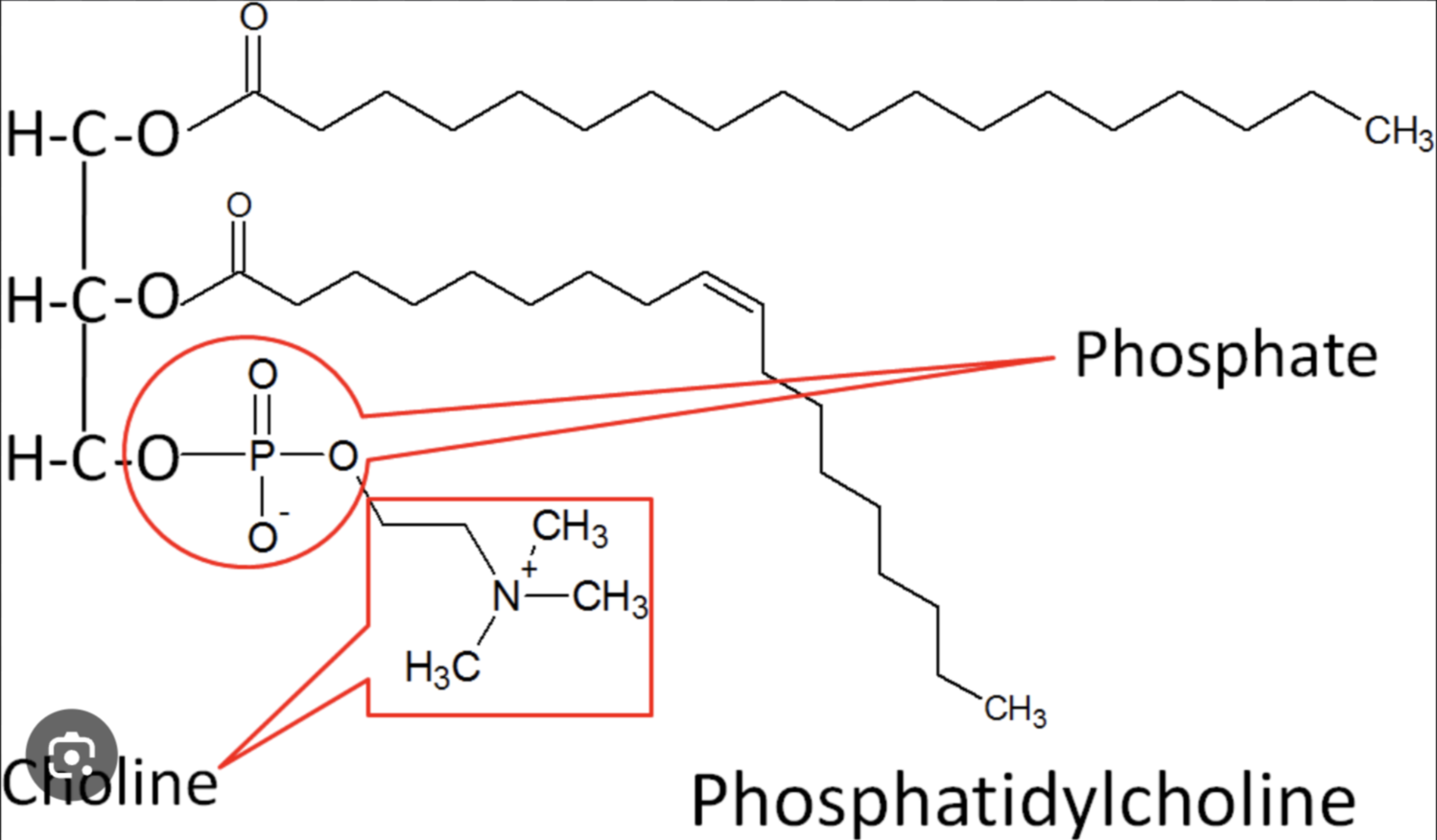
Phospholipid Structure
Have a hydrophilic head, and hydrophobic tails; self assembles into bilayers, as an important part of cell membranes
Steroids
Lipids with 4 fused rings, differ in functional groups attached to the rings
ex: Cholesterol & Sex hormones
Protein: Uses
Molecular tools of the cell
Used for: Structure, enzymes, antibodies, transport, movement, receptors, hormones
Protein: Made of
C, H, O, N, (sometimes S); no general formula
Protein Structure
Polypeptide chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
Amino Acids
All have a carbon with 4 attachments
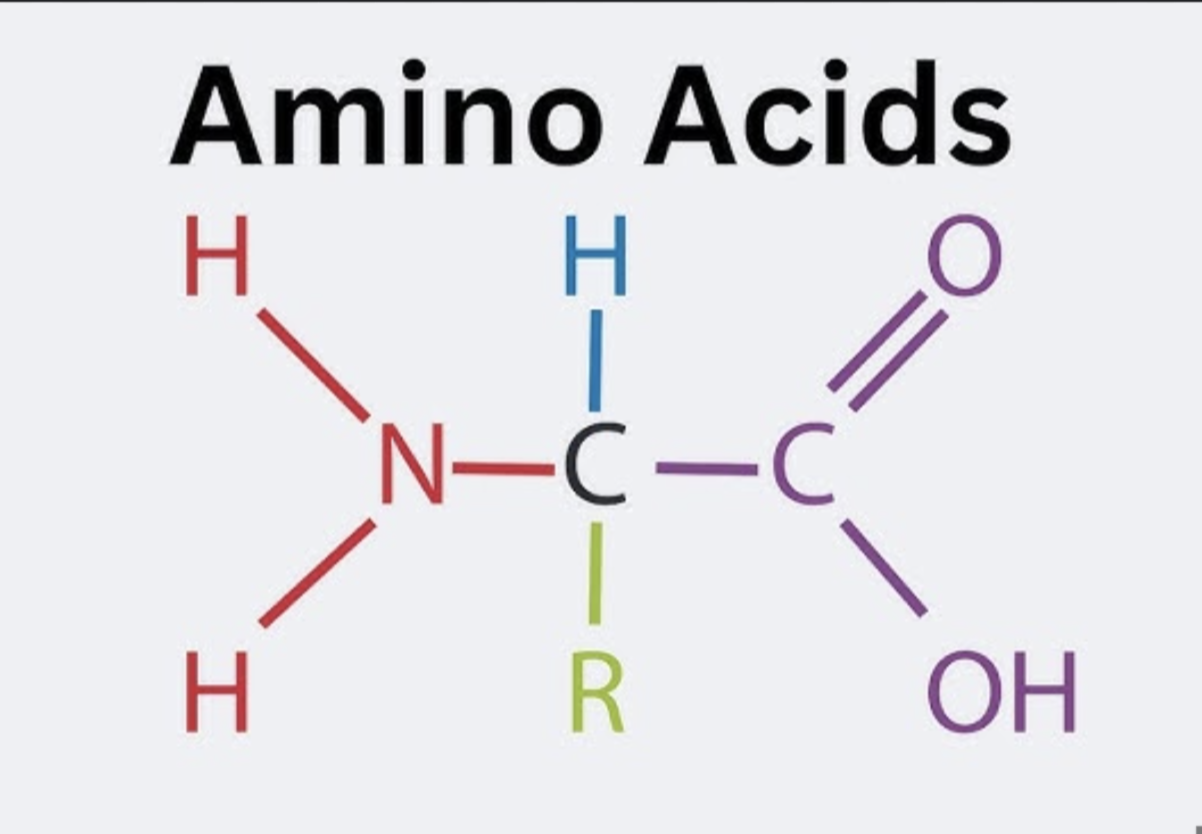
R Groups
20 different kinds; Properties of R groups determine the properties of the protein
Polypeptide chains
Formed by dehydration synthesis between the Carboxyl group of one Amino Acid and the Amino group of another Amino Acid
Protein Structure Levels: Primary
Sequence of Amino Acids in the polypeptide chain; Peptide bonds
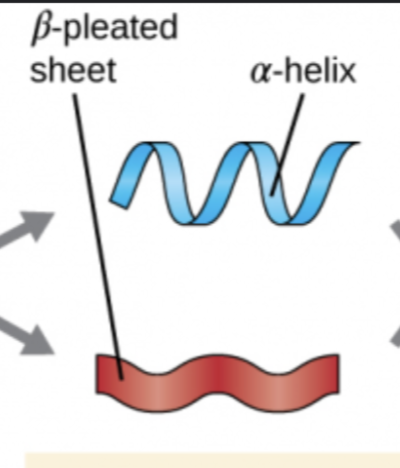
Protein Structure Levels: Secondary
3-D structure formed by bonding between parts of the peptide backbone; Two main structures: Helix & Pleated sheets; Hydrogen Bonding
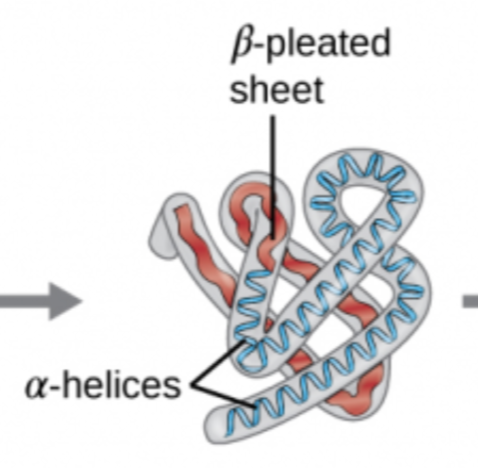
Protein Structure Levels: Tertiary
Bonding between the R-Groups; Ionic bonding; Disulfide bridges (covalent bond)
ex: hydrophobic interactions
Protein Structure Levels: Quaternary
When two or more polypeptides unite to form a functional protein
ex: hemoglobin
Denaturing of a Protein
Events that cause a protein to lose its structure (and function)
ex: pH shifts, high salt concentrations, heat
Chaperone Proteins
Large protein complexes that help fold other proteins into their correct shape; Often used when cell are stressed to keep the proteins intact and functioning
Nucleic Acids: uses
Informational polymers- used in DNA and RNA
Nucleic Acids: Made of
C, H, O, N, P; no general formula
Parts of Nucleotide
Nitrogenous Base, Pentose Sugar, Phosphate
Nitrogenous Bases
Rings of C & N; N atoms take up H+ (base);
Two types: Pyrimidines (single ring) and Purines (double ring)
Pentose Sugar
5-C sugar;
Ribose (RNA) & Deoxyribose (DNA) differ in an -OH group on their second Carbon
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid; makes up genes; genetic information for life; double helix
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid; structure and protein synthesis; genetic information for a few viruses only; single helix
Dehydration Synthesis
The chemical reaction that joins monomers into polymers; covalent bonds are formed by the removal of a water molecule between the monomers
Hydrolysis
Reverse of dehydration synthesis; breaks polymers into monomers by adding water