APHUG Unit 9 Agriculture
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
1
New cards
Agriculture
The deliberate effort to modify a portion of Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic gain.
2
New cards
Crop
Grain or fruit gathered from a field as a harvest during a particular season.
3
New cards
% of people in LDC's (Developing) that are farmers
around 42%
4
New cards
% of the World's farmers in LDC's (Developing)
around 90%
5
New cards
Hunter/Gatherer - Type of lifestyle prior to the invention of agriculture
* The method of obtaining food before agriculture (hunting for animals, fishing, gathering plants)
* Small groups (usually less than 50 people) for travelling reasons (traveled often)
* Work divided according to gender
* Small groups (usually less than 50 people) for travelling reasons (traveled often)
* Work divided according to gender
6
New cards
1st Agricultural Revolution
A transition from hunting and gathering societies to sedentary agricultural societies through the domestication of plants and animals that happened about 12,000 years ago.
7
New cards
2nd Agricultural Revolution
Period of technological change from the 1600s to mid-1900s beginning in Western Europe with industrial innovations to replace human labor with machines and to supplement natural fertilizers and pesticides with chemical ones.
8
New cards
4 Crop Hearths
* Southwest Asia: barley, wheat. lentils, and olives
* East Asia: rice and millet
* Sub-Saharan Africa: sorghum, yams, millet, and rice
* Latin America: beans, cotton, potatoes, maize
* East Asia: rice and millet
* Sub-Saharan Africa: sorghum, yams, millet, and rice
* Latin America: beans, cotton, potatoes, maize
9
New cards
SW Asia and Animal Hearths
* Thought to have been the hearth for the domestication of the largest number of animals that would prove to be the most important for agriculture between 8000-9000 years ago
* Horses thought to be domesticated in Central Asia, along with cattle, sheep, and goats
* Horses thought to be domesticated in Central Asia, along with cattle, sheep, and goats
10
New cards
Subsistence Agriculture
Agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family usually found in LDCs
* Larger percentage of farmers in the labor force
* 44% of people involved in agricultural processes
* Larger percentage of farmers in the labor force
* 44% of people involved in agricultural processes
11
New cards
Commercial Agriculture
The production of food primarily for sale off the farm usually found in MDCs
* Bigger farm size
* Heavy use of machinery
* 5% of people involved in agricultural processes
* Bigger farm size
* Heavy use of machinery
* 5% of people involved in agricultural processes
12
New cards
Loss of farmland due to expanding suburbs
US is losing about 3 million acres of farmland because of the expansion of urban areas
13
New cards
Dietary Energy Consumption
The amount of food that an individual consumes.
* Average person needs 1844 calories to survive
* Developing Country: 2,800
* Developed Country: 3,400
* Average person needs 1844 calories to survive
* Developing Country: 2,800
* Developed Country: 3,400
14
New cards
Cereal Grain
A grass that yields grain for food
* Grain is the seed from a cereal grass
* Grain is the seed from a cereal grass
15
New cards
3 leading cereal grains
Wheat, rice, and maize (corn)
16
New cards
Primary source of protein - Developed vs Developing
* Developed: Meat Products
* Developing: Cereal Grains
* Developing: Cereal Grains
17
New cards
Food Security
Physical, social, and economic access at all times to safe and nutritious food sufficient to meet dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
* 10% of the world does not have food security
* 10% of the world does not have food security
18
New cards
Undernourishment
Dietary energy consumption that is continuously below the minimum requirement for maintaining a healthy life and carrying out light physical activity.
19
New cards
Intensive Farming
A form of subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relatively large amount of effort to produce the maximum feasible yield from a parcel of land.
* Smaller farms
* High agricultural density
* Practiced in LDCs
* Smaller farms
* High agricultural density
* Practiced in LDCs
20
New cards
Extensive Farming
Agriculture that uses fewer inputs of capital and paid labor relative to the amount of space being used
* Bigger farms
* Practiced in MDCs
* Bigger farms
* Practiced in MDCs
21
New cards
Pastoral Nomadism
A form of subsistence agriculture based on the herding of domesticated animals in dry climates.
* Rely on camels, sheep, goats, and horses
* Decreasing because pasture lands are being developed; governments are also giving incentives to tribes or groups of nomads for settling down
* Rely on camels, sheep, goats, and horses
* Decreasing because pasture lands are being developed; governments are also giving incentives to tribes or groups of nomads for settling down
22
New cards
Transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.
23
New cards
Shifting Cultivation
A form of subsistence agriculture in which people shift activity from one field to another.
* Southeast Asia: Rice
* South America: Maize (corn) and manioc (cassava)
* Africa: Millet and sorghum
* Southeast Asia: Rice
* South America: Maize (corn) and manioc (cassava)
* Africa: Millet and sorghum
24
New cards
Slash and Burn Agriculture
Farmers clear land for planting by slashing vegetation and burning the debris (slash and burn agriculture)
25
New cards
Fallow Land
Farmers grow crops on a cleared field for only a few years, until soil nutrients are depleted, and then leave it fallow (with nothing planted) for many years so the soil can recover.
26
New cards
Swidden
A patch of land cleared for planting through slashing and burning.
27
New cards
How much of the world's land area shifting cultivation occupies and % of people in the world that participate in shifting cultivation
* 1/4 occupied by shifting cultivation
* only 5% of the world participates
* only 5% of the world participates
28
New cards
Why was shifting cultivation sustainable in the past?
Supported small villages and populations
29
New cards
Why shifting cultivation is expected to diminish during the twenty-first century.
Declining because of more effective development strategies like logging, cattle ranching, and the cultivation of cash crops
30
New cards
Double Cropping
To grow two or more crops on the same land.
* Practiced in places with warm winters such as southern China and Taiwan
* Practiced in places with warm winters such as southern China and Taiwan
31
New cards
Crop Rotation
The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil.
* Practiced in places with milder climates
* Practiced in places with milder climates
32
New cards
Wet Rice
Rice planted on dry land in a nursery and then moved to a deliberately flooded field to promote growth
33
New cards
Wet Rice Not Dominant
Climate discourages farmers from growing wet rice in portions of Asia, especially where summer precipitation levels are too low and winters are too harsh.
34
New cards
Intertillage
The clearing of rows in the field through the use of hoes, rakes, & other manual equipment
35
New cards
Plantation
A large farm in tropical and subtropical climates that specializes in the production of one or two crops for sale, usually to a more developed country.
36
New cards
Horticulture
The growing of fruits, vegetables, flowers and tree crops
37
New cards
Truck Farming
Commercial gardening and fruit farming, so named because truck was a Middle English word meaning bartering or the exchange of commodities.
* Grow produce that is demanded by people in developed countries and tend to be towards urbanized areas
* Grow produce that is demanded by people in developed countries and tend to be towards urbanized areas
38
New cards
Milkshed
A ring surrounding a city from which milk can be supplied without spoiling.
39
New cards
Ranching
A form of commercial agriculture in which livestock graze over an extensive area.
40
New cards
Mixed Crop and Livestock Farming
Commercial farming characterized by integration of crops and livestock
* Most of the crops are fed to animals rather than consumed directly by humans.
* Most of the crops are fed to animals rather than consumed directly by humans.
41
New cards
Dairy Farming
A farm that produces milk or milk products, and are usually around big urban areas
42
New cards
Grain Farming
A type of commercial agriculture, is considered extensive and mechanized, that produces mainly wheat.
43
New cards
Livestock Ranching
The raising of domesticated animals for the production of meat and other byproducts such as leather and wool.
44
New cards
Agribusiness
A system of commercial farming found in developed countries
45
New cards
Two issues that influence the choice of crops grown in developing countries
* Subsistence farmers must feed an increasing number of people because of rapid population growth in developing countries
* Farmers who traditionally do subsistence farming are pressured to grow food for export instead of for direct consumption due to the adoption of the international trade approach to development
* Farmers who traditionally do subsistence farming are pressured to grow food for export instead of for direct consumption due to the adoption of the international trade approach to development
46
New cards
Drug crops
Crops that can be converted into drugs
47
New cards
Asian Carp and Chicago's Economy
Asian carp is an aggressive and invasive species, constituting 97% of the Mississippi and Illinois rivers. The only effective way to keep the carp out is to shut the canals but they play a major role in sustaining Chicago's economy and could devastate their economy if shut down.
48
New cards
Challenges for Farmers in Developed Countries
* Overproduction in commercial farming due to the mass production and efficient technology, farmers have low incomes.
* Importance of access to markets; Distance from the market to farm influences the farmer's choice in crop.
* Importance of access to markets; Distance from the market to farm influences the farmer's choice in crop.
49
New cards
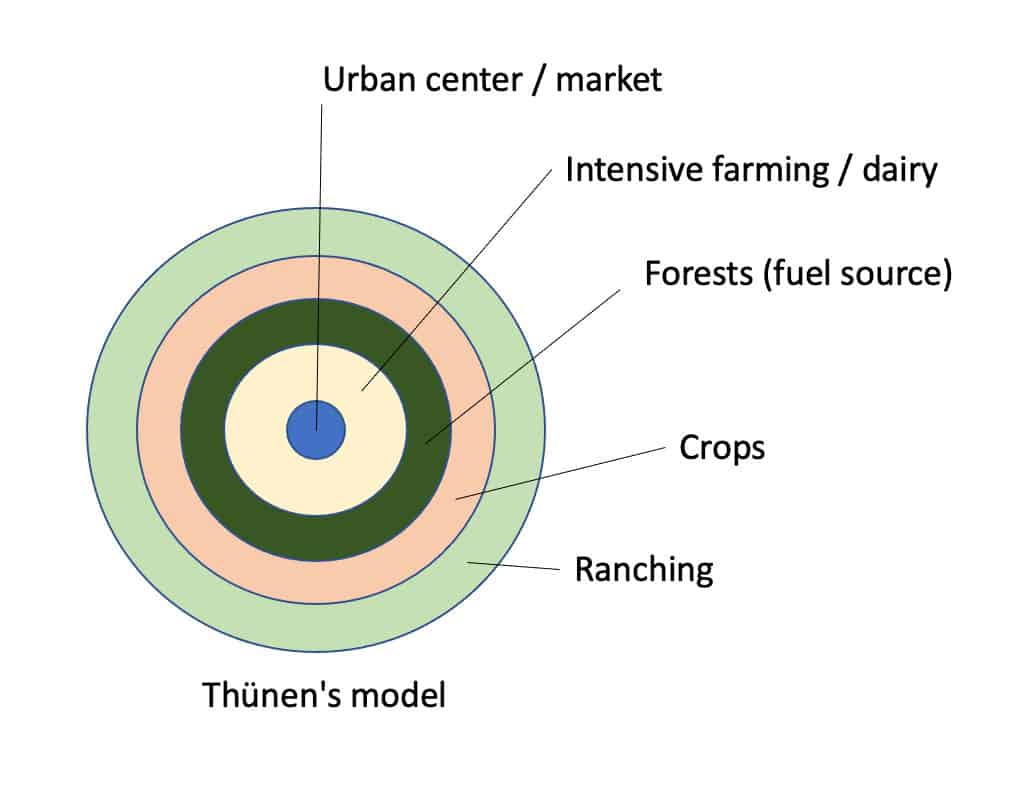
Von Thünen's Model
Model that shows the importance of access to the market and considers which crops to cultivate and what animals to raise based on the market location
* ==Cost of land and Cost of Transporting it to Market==
* **First Ring**: market-oriented garden milk (expensive)
* **Second Ring:** wood/timber for fuel (weight)
* **Third Ring:** crop pasture
* **Fourth Ring:** animal grazing (most space needed)
* ==Cost of land and Cost of Transporting it to Market==
* **First Ring**: market-oriented garden milk (expensive)
* **Second Ring:** wood/timber for fuel (weight)
* **Third Ring:** crop pasture
* **Fourth Ring:** animal grazing (most space needed)
50
New cards
4 Strategies being employed to distribute food to everyone in the world
* Increasing exports from countries with surplus: in other countries, production wasn't able to keep up with rapid population growth; assistance needed
* Expanding the agricultural land: people think there is still land to use, but it's not arable (cities, flooded, or desert)
* Expanding fishing: people don't eat fish often, but overfishing and unregulated problems with agriculture pose a risk
* Increasing productivity of agricultural land: the green revolution, GMOs
* Expanding the agricultural land: people think there is still land to use, but it's not arable (cities, flooded, or desert)
* Expanding fishing: people don't eat fish often, but overfishing and unregulated problems with agriculture pose a risk
* Increasing productivity of agricultural land: the green revolution, GMOs
51
New cards
Desertification
Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting.
52
New cards
Aquaculture/Aquafarming
The cultivation of seafood under controlled conditions
53
New cards
Overfishing
The capturing fish faster than they can reproduce
54
New cards
3rd Agricultural Revolution
Currently in progress, the Third Agricultural Revolution has as its principal orientation the development of Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO's)
55
New cards
Green Revolution
Rapid diffusion of new agricultural technology, especially new high-yield seeds and fertilizers.
56
New cards
Gene Revolution
Using genetic engineering to develop genetically improved strains of crops and livestock animals.
57
New cards
Genetically Modified (GM) crops and characteristics
* The USA promotes the usage of GMOs in order to increase food supplies and because it supplies benefits such as higher yields, increased nutrition, and more resistance to pests.
* Countries in Africa oppose the usage of GMOs because of health problems, export problems, and having an increased dependence on the United States
* Countries in Africa oppose the usage of GMOs because of health problems, export problems, and having an increased dependence on the United States
58
New cards
Sustainable Agriculture (Organic Farming)
An agricultural practice that preserves and enhances environmental quality
\-3 Principle Practices: sensitive land management (ridge tillage), limited use of chemicals, integrated crop and livestock (free-range, wholesome for animals)
\-3 Principle Practices: sensitive land management (ridge tillage), limited use of chemicals, integrated crop and livestock (free-range, wholesome for animals)
59
New cards
King Corn
Corn is an ingredient that is found in almost every consumable across the globe. Because of this, governments provide farms with subsidies and in return, these farms mass produce corn to supply the demand.
60
New cards
How do our U.S. farm subsidies affect LDC farmers who live halfway around the world?
LDC farmers don't have the support that Americans do, so American exports are pouring into other countries, while LDC's can't compete, so they aren't exporting as much and subsequently aren't earning profit.