Theme 1
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Describe the paternalistic leadership style
Leader consults other staff members but they make the final decision. Creates loyalty and morale, limits empowerment for employees
Describe the democratic leadership style
Leader involves the team in decision making. Good for motivation and creative ideas, however slow decision making and risk of disagreement
Describe the autocratic leadership style
They give orders without consultation. Quick decision making but low motivation
Describe laissez-faire leadership style
-leader allows the group members to make decisions
-this is utilized when group members are productive
-work output by staff is usually low in this situation.
-this style is to be used when group members are trusted and confident in the task at hand
What is the difference between a manager and a leader?
Leaders focus on motivation, achieving the business' aims; managers control day-to-day operations
What does a centralised and decentralised structure mean?
Centralised - decision making is done by the top management
Decentralised - decision making delegated to lower down staff
What is the chain of command in a business?
The reporting system from the top to the bottom --> tall structures have a long chain of command
Name some methods of recruitment
Media advertising
Job centres
Firm's own website
Recruitment agencies
Give pros and cons of internal recruitment
Pros:
Quicker and cheaper than external
Promotion opportunities can motivate employees
Less induction costs
Cons:
Less innovation
Could de-motivate workers who didnt get the role
What is a person specification?
The required skills, qualifications and personality for a vacant job
Define recruitment (selection)
Filling job vacancies by defining a job, advertising the job and selecting the best applicants to fill it
What are 2 ways of empowering employees?
Delegation - passing down authority to a lower "ranking" staff member
Consultation - asking for views of colleagues and taking them into your decision making process
What some financial reward systems?
Piecework - getting paid how by how many units are produced
Commission - earning extra income based on the sales you make
Profit share - sharing profits among employees
Performance related pay(PRP) - targets are set, those who exceed get bonuses
What did Herzberg believe about motivation?
Hygiene factors - minimum requirements (pay, job security etc)
Motivators - motivating staff (promotion, achievements)
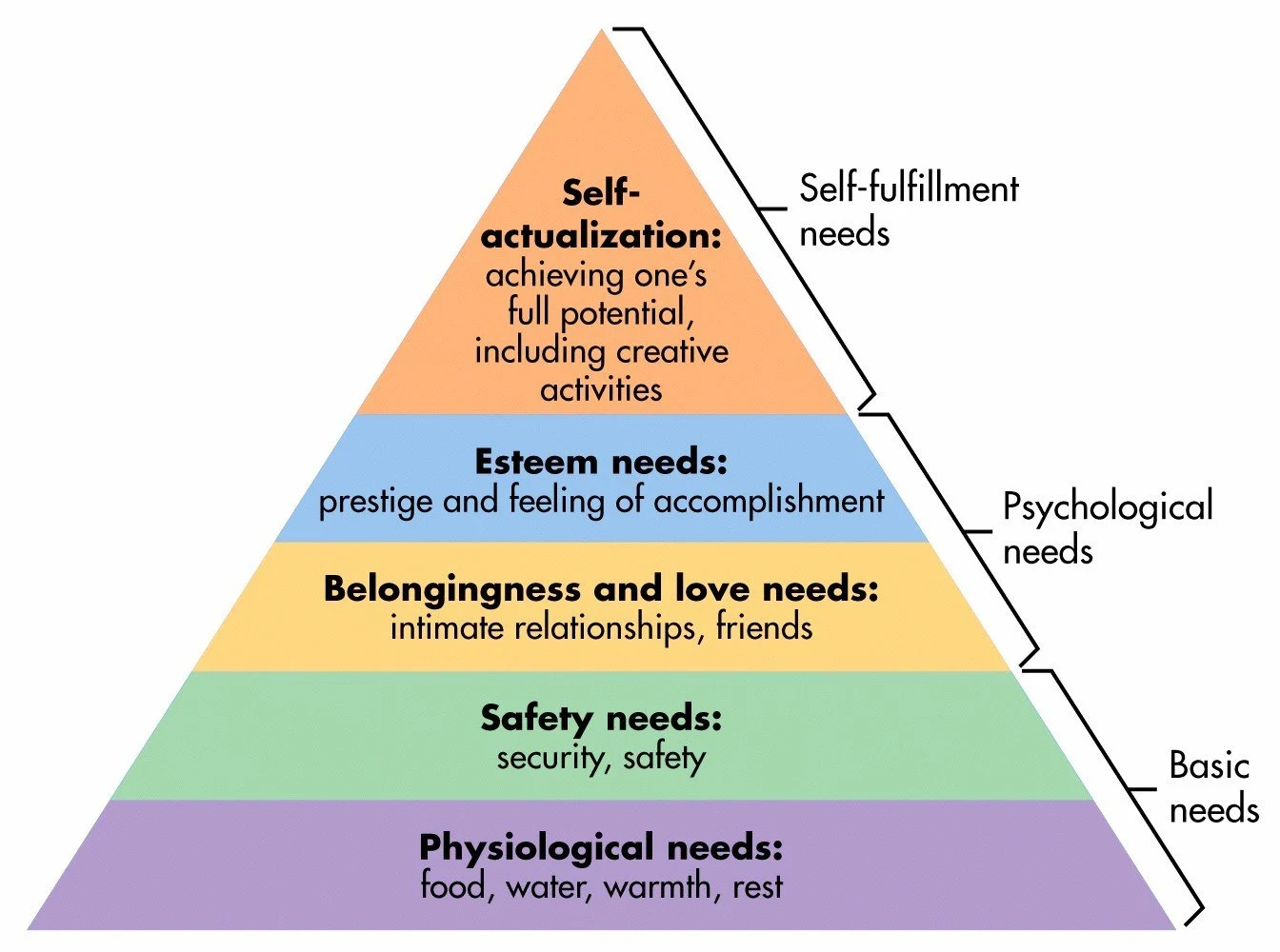
What are Maslow's heirachy of needs?
What did Mayo believe about motivation?
Workers are motivated by social needs, such as good relationships with bosses and feeling valued
What did Taylor believe about motivation?
Workers are primarily motivated by money. Work should be broken down into small more managable tasks to increase productivity. Workers should get payed by piece rate, not a fixed wage
Describe the "matrix" organisational structure for a business
Employees have multiple bosses, as they are involved in different departments. Can improve communication between departments but can lead to slow decisiin making
Describe the "flat" organisational structure for a business
Large span of control allows for speedy vertical communication
Describe the "tall" organisational structure for a business
Lots of layers of management, each managing few people. Narrow span of control, good motivation
What is a trade union?
An organisation employees pay to join in order to gain more power and security at work
How can a firm have a flexible workforce?
Multi skilled workers - workers can carry out a variety of tasks
Part time / temporary workers
Working from home
What is public relations (PR)?
An attempt to better the consumer's image of a product without media advertising
What are the "below the line" methods of promotion?
Sales promotion
Direct mail
Personal selling
Sponsorships
Public relations
What is the "above the line" method of promotion?
Advertising
What is emotional branding?
When companies develop strong emotional connections with customers by appealing to values or beliefs
What is the Boston Matrix?
A model that shows a firm its products' market share and the growth of the markets in order to aid marketing strategies
What are the 4 groups in the Boston Matrix?
Problem child (?) - low market share in a fast growing market
Star - high market share in a fast growing market
Cash cow - high market share in a slow growing market
Dogs - low market share in a slow/stable growing market
What is an extension strategy?
The actions a business does to prevent a product entering the decline stage
Why are product life cycles important?
They help businesses plan their marketing activities for a product
What are the stages of the product life cycle
Research and development
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Decline
What are the types of distribution channels? Explain them
2 stage (Direct) = producer --> consumer
3 stage (Retailing) = producer --> retailer --> consumer
4 stage (Wholesaling) = producer --> wholesaler --> retailer --> consumer
What is distribution (place)?
The movement of goods from producer to consumer
What is an opportunity cost?
The cost of missing out on something when making a decision
What is a social enterprise?
A business thats main objective is to benefit society or the environment
What are the pros and cons of forming a limited company?
Pros:
Limited liability
Wider range of borrowing options
Cons:
Have to make financial information publicly available
Limited companies have to follow more expensive rules than unlimited liability
Describe what is meant by a partnership
When 2 or more people start a business without forming a comapany (like a sole trader). Unlimited liability and split 50/50 even if owners put in different effort
Describe what is meant by a sole trader
A business that only has one individual owner. Has unlimited liability and cannot use share capital. Hard to finance
Name 3 common business objectives
Survival
Profit maximisation
Sales maximisation
Market share
Minimise costs
Employee welfare
Social objectives
What is a business objective?
A target set by business owners for the business to achieve by a specified date
What are the factors that determine the appropriate pricing strategy?
Product differentiation
Strength of the brand
Amount of competition
PED
Stage in product life cycle
Costs
What are the pricing strategies for existing products?
Competitive
Predatory
Cost-plus
Phycological
Discrimination
What is cost-plus pricing?
A business calculates the production cost for a product then adds a desired markup to make a profit
What are the 2 types of pricing strategies for new products? Explain them
Penetration = Pricing much lower than existing similar products to gain market share
Skimming = At the start price is set high, price is lowered to find the optimal demand
Name 2 types of promotion for short term sales
Buy one get one free (BOGOF)
Seasonal price promotion
What are some ways to build a brand?
USPs
Advertising
Sponsorship
Digital media
What is promotion?
Part of the marketing mix that focuses on persuading people to buy the product
What does ethical sourcing mean?
When a business only buys products that are produced with fair working conditions and workers pay
What are some changes in the design mix that reflect social trends?
Concern over resource depletion
Designing for re-use and waste minimisation
Recycling
What does sustainability mean?
The purchase you make will not affect long term supplies of a product, because it has been automatically replenished
What are the 3 parts of the design mix?
Function
Aesthetics
Costs
What is the significance of income elasticity to businesses?
Used for sales forecasting
Financial planning
What are the 3 categories products can be placed in for YED?
Normal good - +0.5-+1.5
Luxury good - +1.5 or more
Inferior good - negative YED
What is income elasticity of demand?
The amount a change in a person's income changes the demand for a product
What does it mean for a product to have price-inelastic demand?
The product has a PED of below 1 - % change in price is greater than % change in demand
Addictive goods like alcohol and cigarettes are inelastic
What does it mean for a product to have price-elastic demand?
The product has a PED of above 1 - % change in demand is greater than % change in price
What are the main determinants of PED?
Degree of product differentiation from rivals
Availability of substitutes
Branding and brand loyalty
What is the formula for price elasticity of demand?
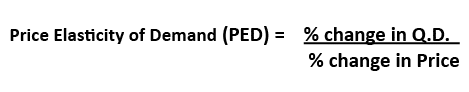
What is price elasticity of demand?
The extend demand changes for a product when price changes
What is equilibrium?
The point where there is a balance between supply and demand, this makes the price stable
What are the factors affecting supply?
Changes in cost of production
Introduction of new technology
Indirect taxes
Government subsidies
External shocks
Physical constraints
What are the two risks linked to demand?
Undiversified demand (not varied)
Overtrading - demand exceeds cash in the business
What is an entrepreneur?
A business owner that takes risks in order to profit financially
What is the purpose of product differentiation?
To insulate the product from competition#
To enable the business to increase its prices if costs go up
What is the main method of market positioning?
Market mapping
What is market positioning?
How a company/its products are positioned next to competitors by customers
What are the limitations to market research?
Expensive
Time consuming
Small / unrepresentative samples
Researcher bias
What is a product orientated business?
A business that focuses on what they do best before thinking about consumer preference
What is a market orientated business?
A business that takes the needs of customers before any other decision e.g. making products for a segment of a market
What is branding used for?
Product differentiation
Create customer loyalty
Help product recognition
Develop a brand image
Define market share
The proportion of a particular market that is held by a business/products
What are the advantages and disadvantages of niche marketing?
Advantages:
Little competition
Larger profit margins than mass marketing
Disadvantages:
Low amount of volume sold
If a large company enters niche market, it is hard to compete
What are the advantages and disadvantages of mass marketing?
Advantages:
High volume sold
Greater economies of scale
Disadvantages:
Lots of competition
What does economies of scale mean?
The benefits that occur from increasing the size of a business e.g. buying in bulk for cheaper if a larger company
What is a niche marketing
Identifying needs of customers that make up a niche market (a small segment of a large market) and producing products and services for those customers
What is mass marketing?
Creating products or services that target the whole market not specific people
What are the characteristics of effective marketing?
Identifying the target market - focus market research and advertisement
Segment your markets
Good brand image through good market mix
What are the 4 types of marketing mix?
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
Define marketing
The department tasked with targeting the right product at the right target market using a combination of price, promotion and place
Name the categories of goods sold in consumer markets
Fast Moving consumer goods - high volume, low unit value e.g. newspapers
Consumer durables - low volume but high unit value e.g. dishwashers
Soft goods - similar to consumer durables but dont last as long e.g clothes
Services e.g. hairdressing
Induction training
Initial training provided to new employees joining the business
On-the-job training
Employees gain skills directly at their workplace whilst working
Off-the-job training
Employees learn new skills away from their workplace