Exam 3
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Arrange the following alkenes in order of decreasing stability. (see pic)
D>C>A>B
Choose the more stable alkene in each of the following pairs. Explain your reasoning:
1-Methylcyclohexene or 3-methylcyclohexene
1-Methylcyclohexene because it has a trisubstituted double bond
Choose the more stable alkene from the following pair. (see pic)
The second structure because a double bond in a six membered ring is less strained
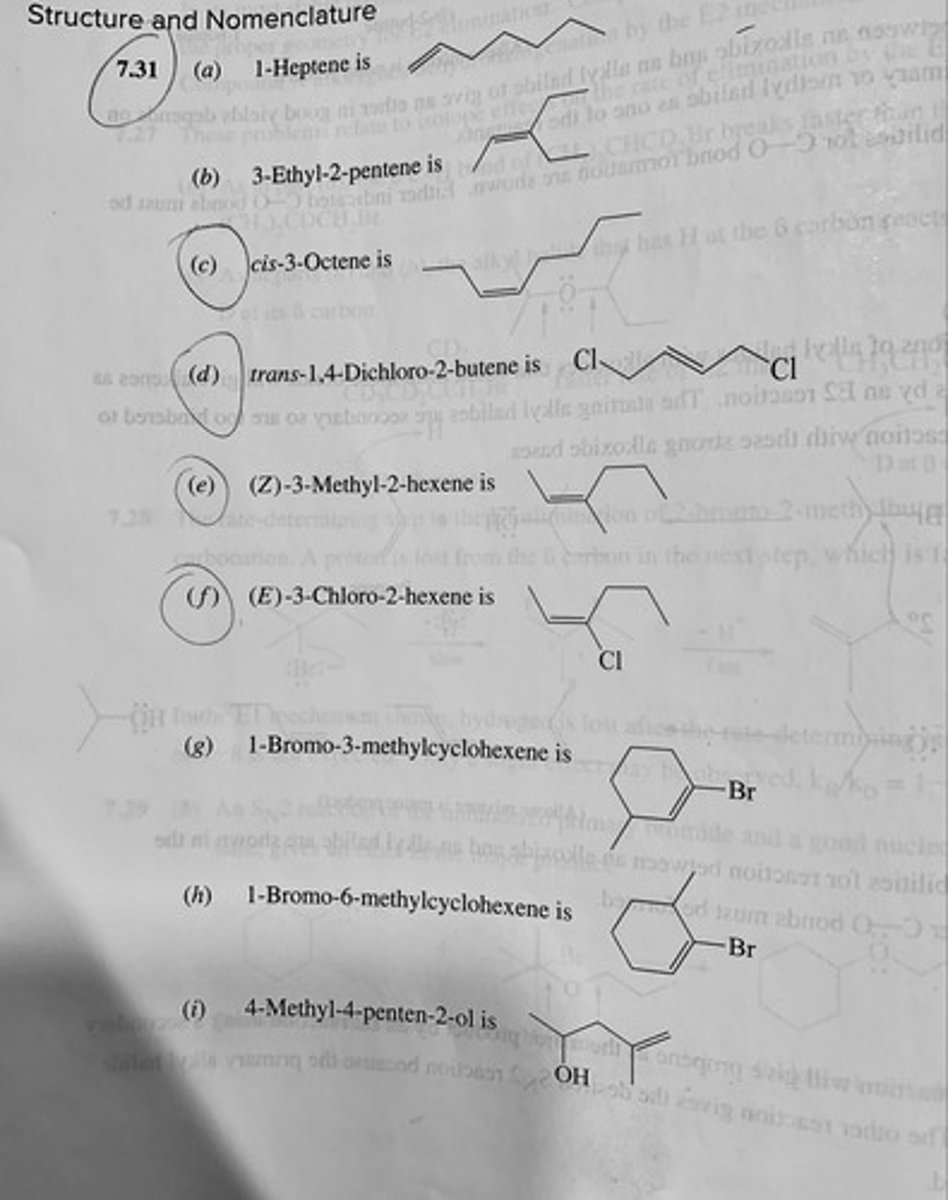
Write structural formulas for each of the following:
(a) 1-Heptene
(b) 3-Ethyl-2-pentene
(c) cis-3-Octene
(d) trans-1,4-Dichloro-2-butene
(e) (Z)-3-Methyl-2-hexene
(f) (E)-3-Chloro-2-hexene
(g) 1-Bromo-3-methylcyclohexene
(h) 1-Bromo-6-methylcyclohexene
(i) 4-Methyl-4-penten-2-ol
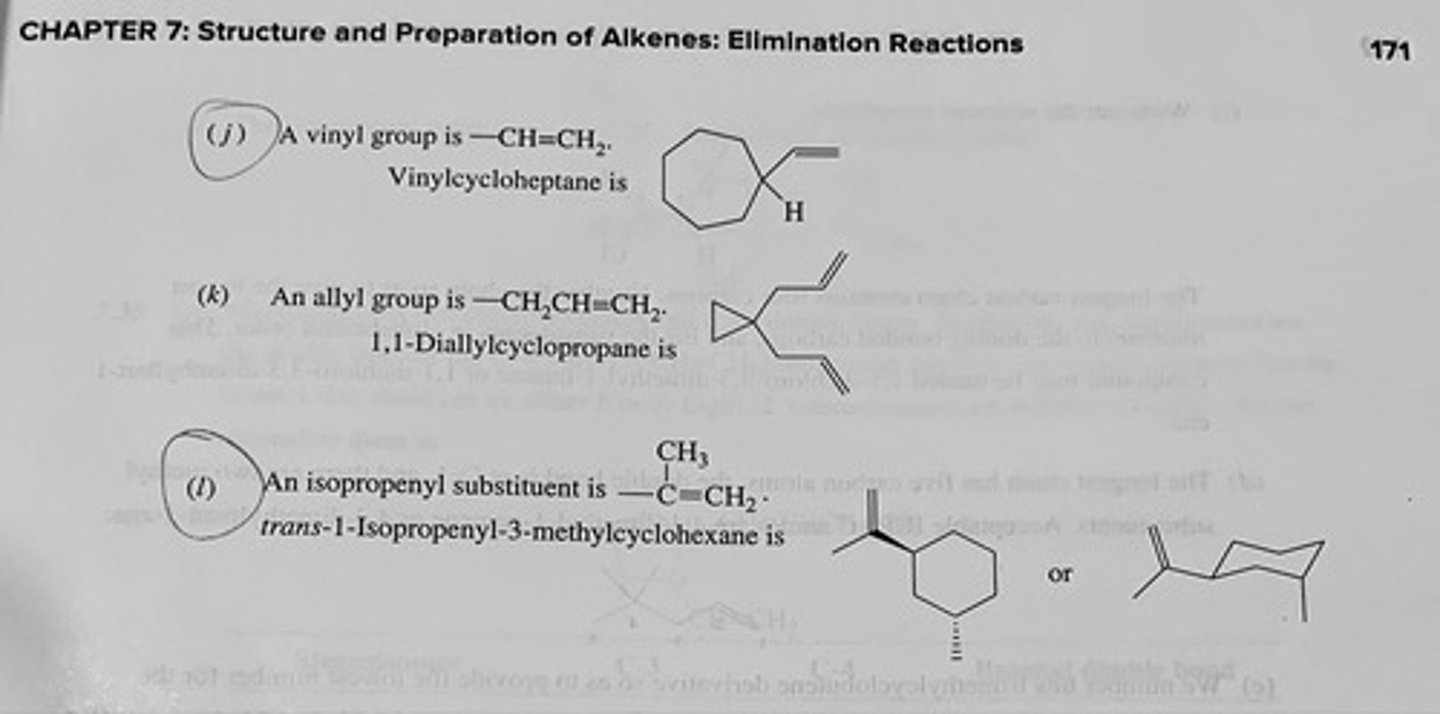
Write structural formulas for each of the following:
(j) Vinylcycloheptane
(k) 1,1-Diallylcyclopropane
(l) trans-1-Isopropenyl-3-methylcyclohexane
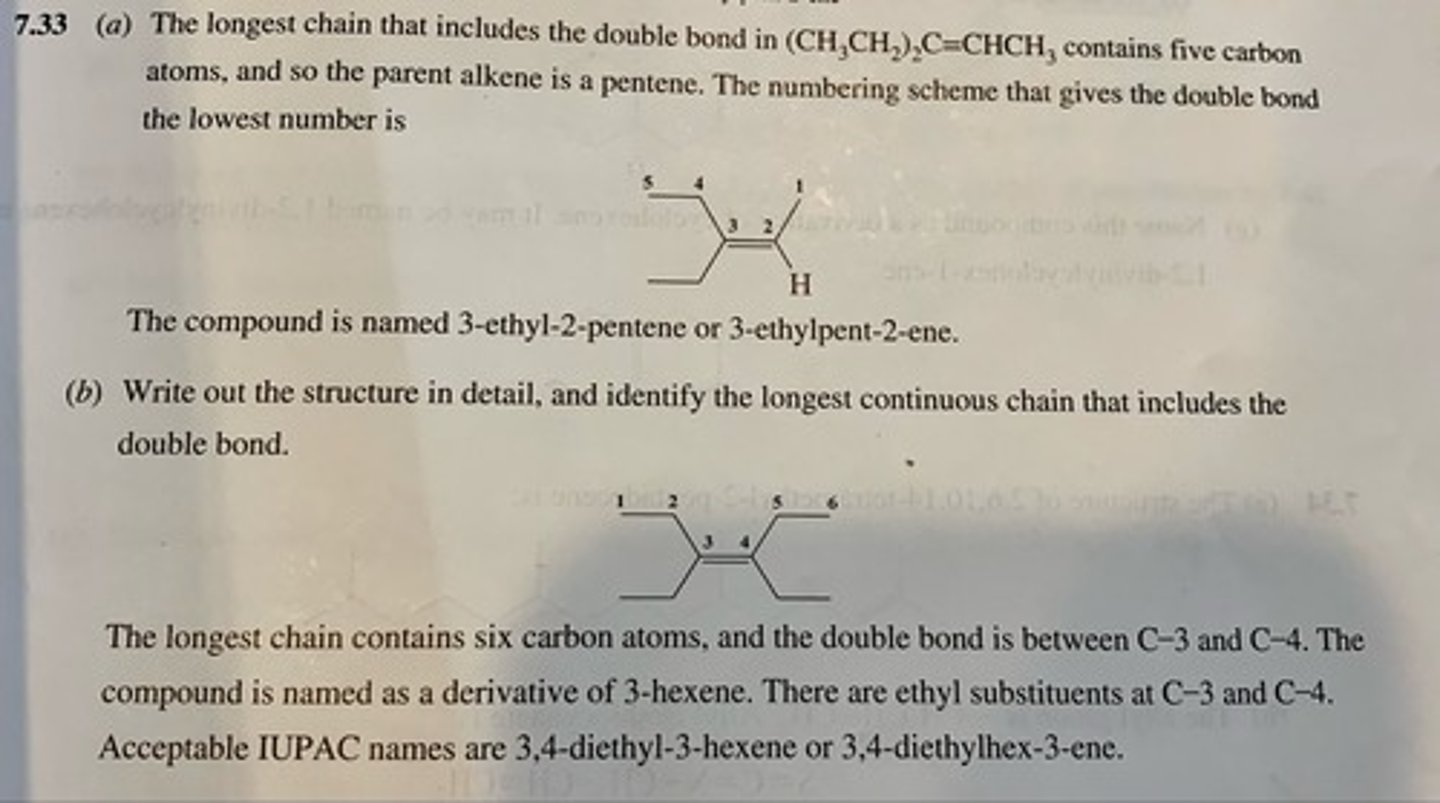
Give an IUPAC name for each of the following compounds:
(a) (CH3CH2)2C═CHCH3
(b) (CH3CH2)2C═C(CH2CH3)2
(a) 3-ethyl-2-pentene
(b) 3,4-diethyl-3-hexene
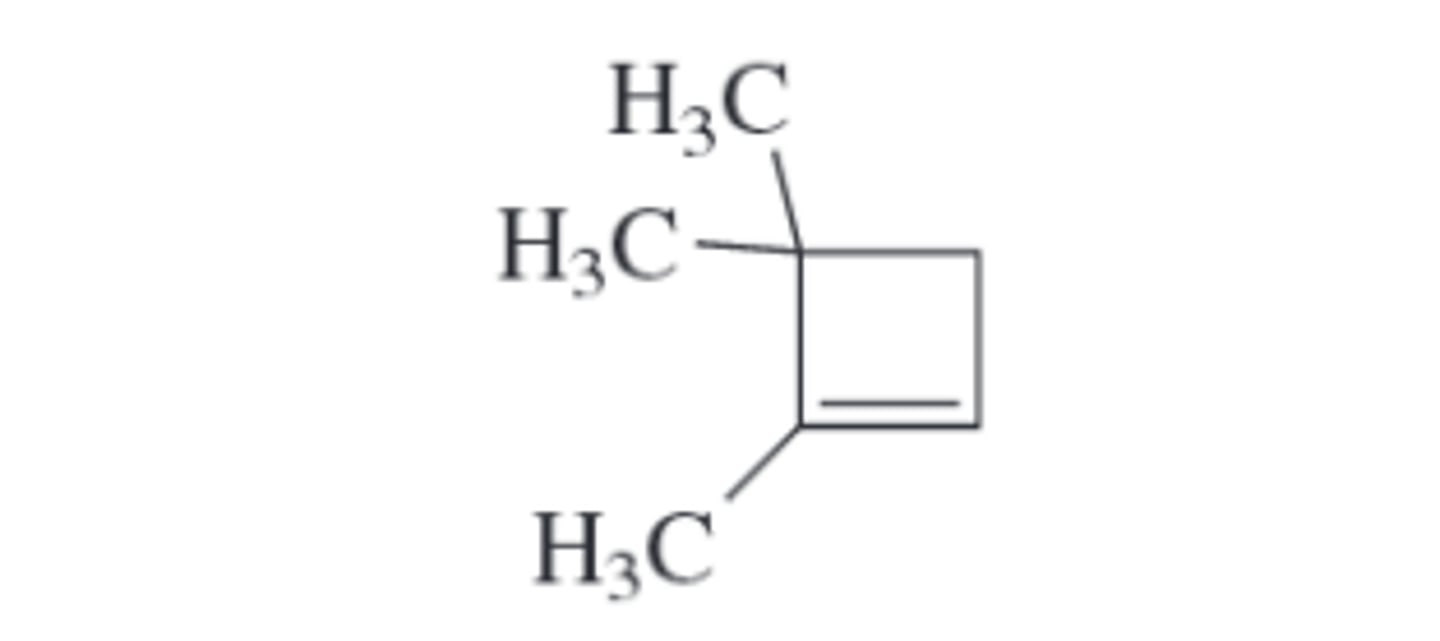
Give an IUPAC name for each of the following compounds: (see pic)
1,4,4trimethylcyclobutene
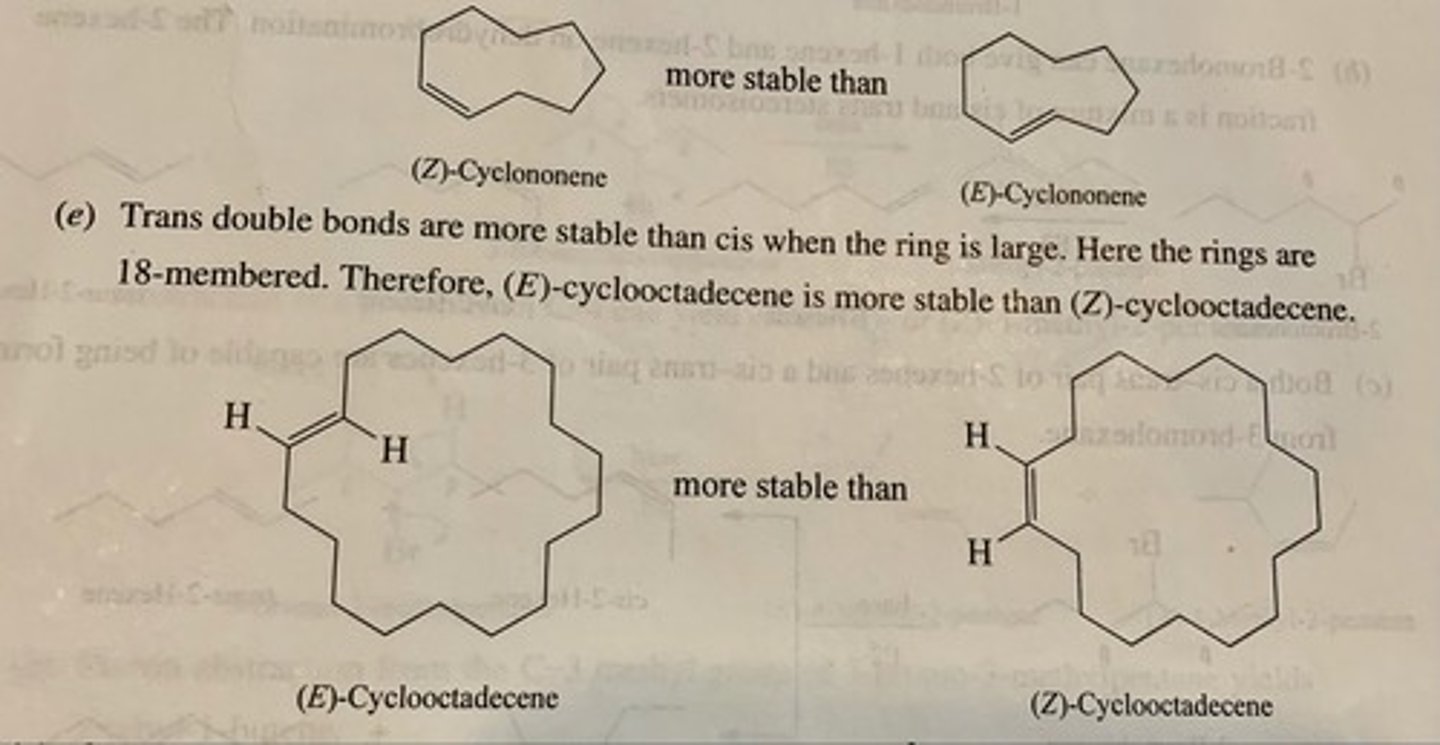
Which one is more stable and why? (see pic)
(a) (Z)-cyclonoene or (E)-cyclononene
(b) (E)-Cyclooctadecene or (Z)-Cyclooctadecene
(a) (Z)-cyclononene because when the ring is smaller than 11, trans double bonds are more stable
(b) (E)-cyclooctadecene because when the ring is larger than 11, the cis double bond is the most stable
Place a double bond in the carbon skeleton shown so as to represent (Z)−3−methylcyclodecene. (see pic)
(bond on the inside)
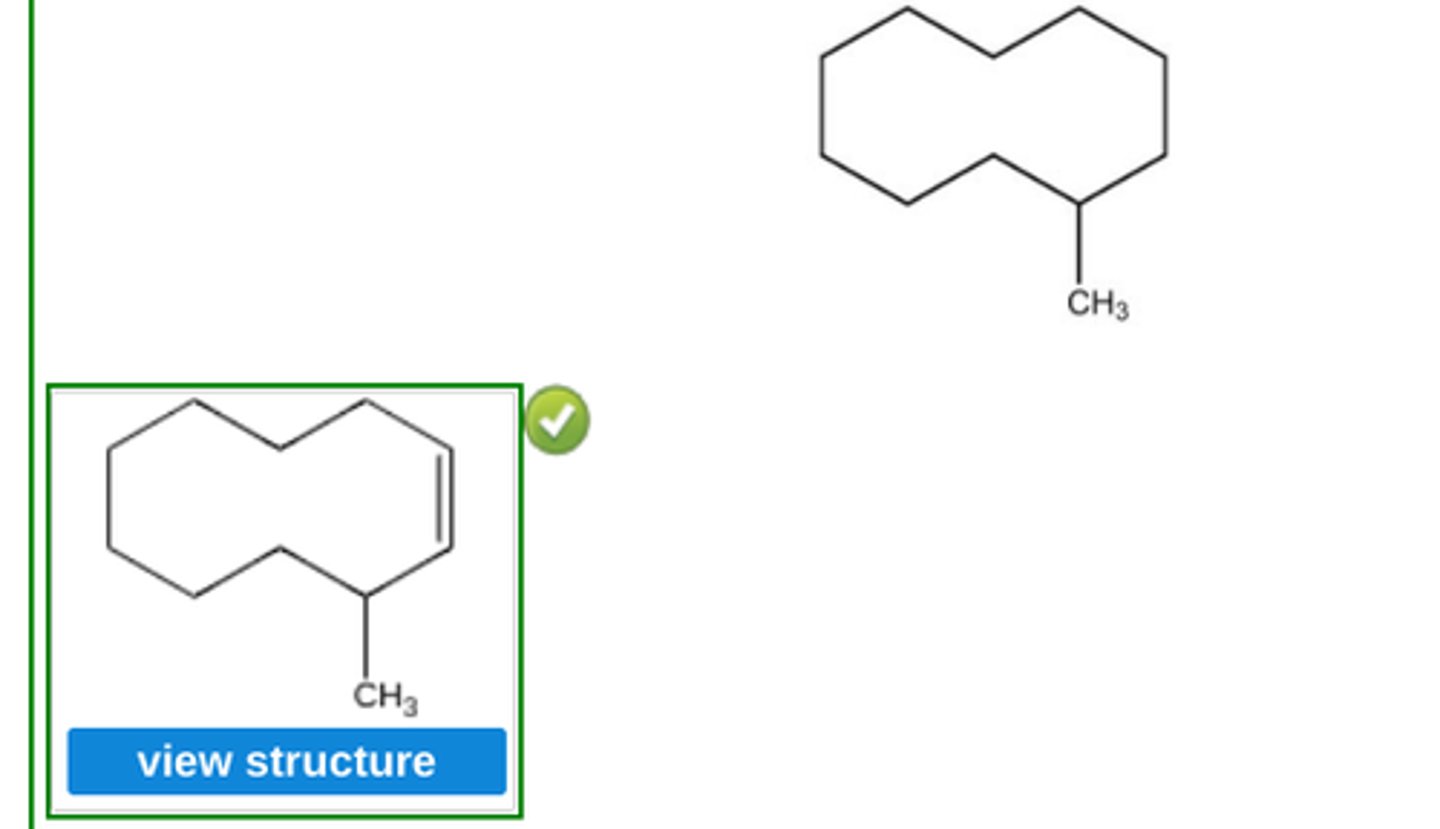
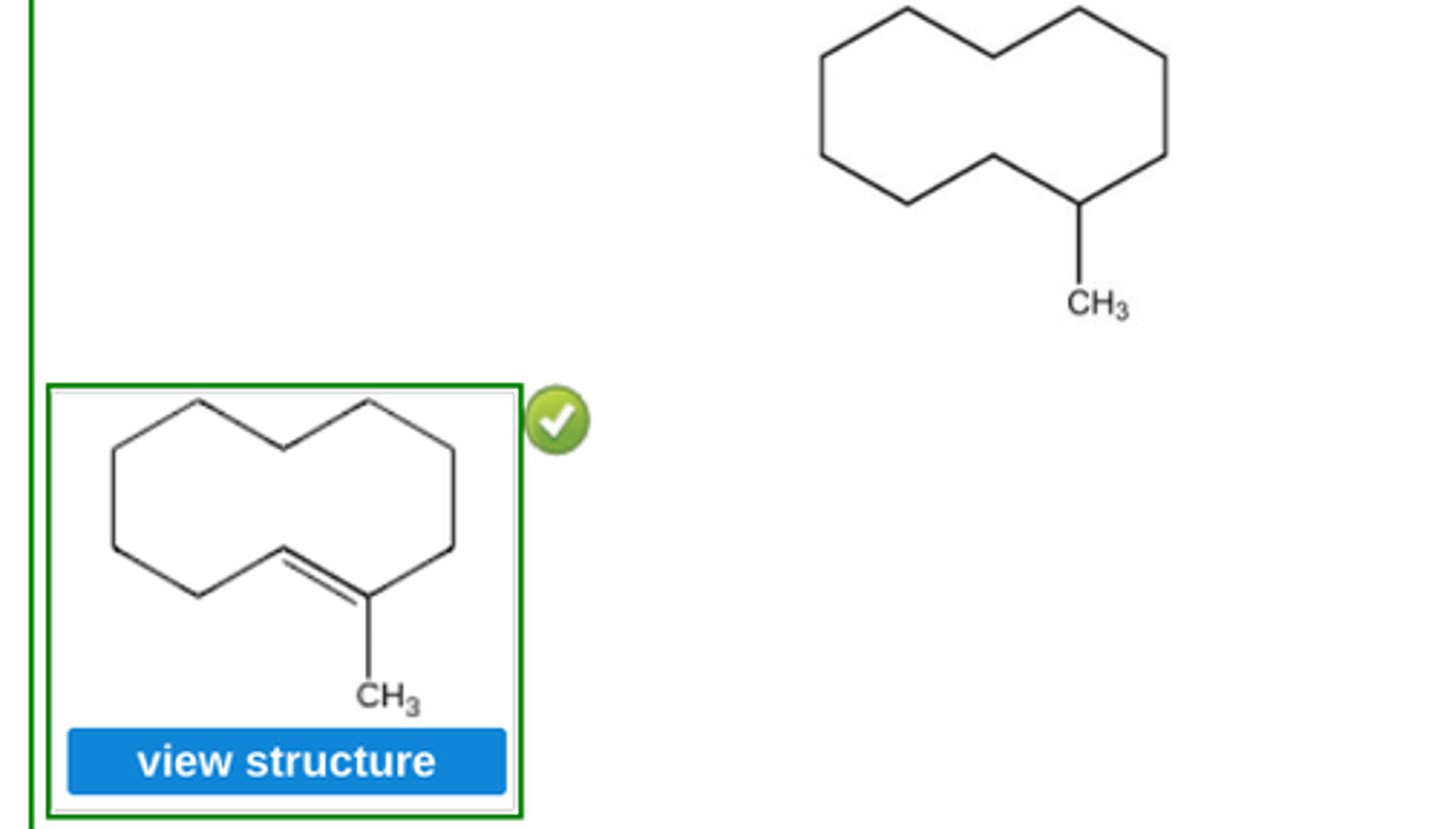
Place a double bond in the carbon skeleton shown so as to represent (E)−1−methylcyclodecene. (see pic)
(bonds on exterior)
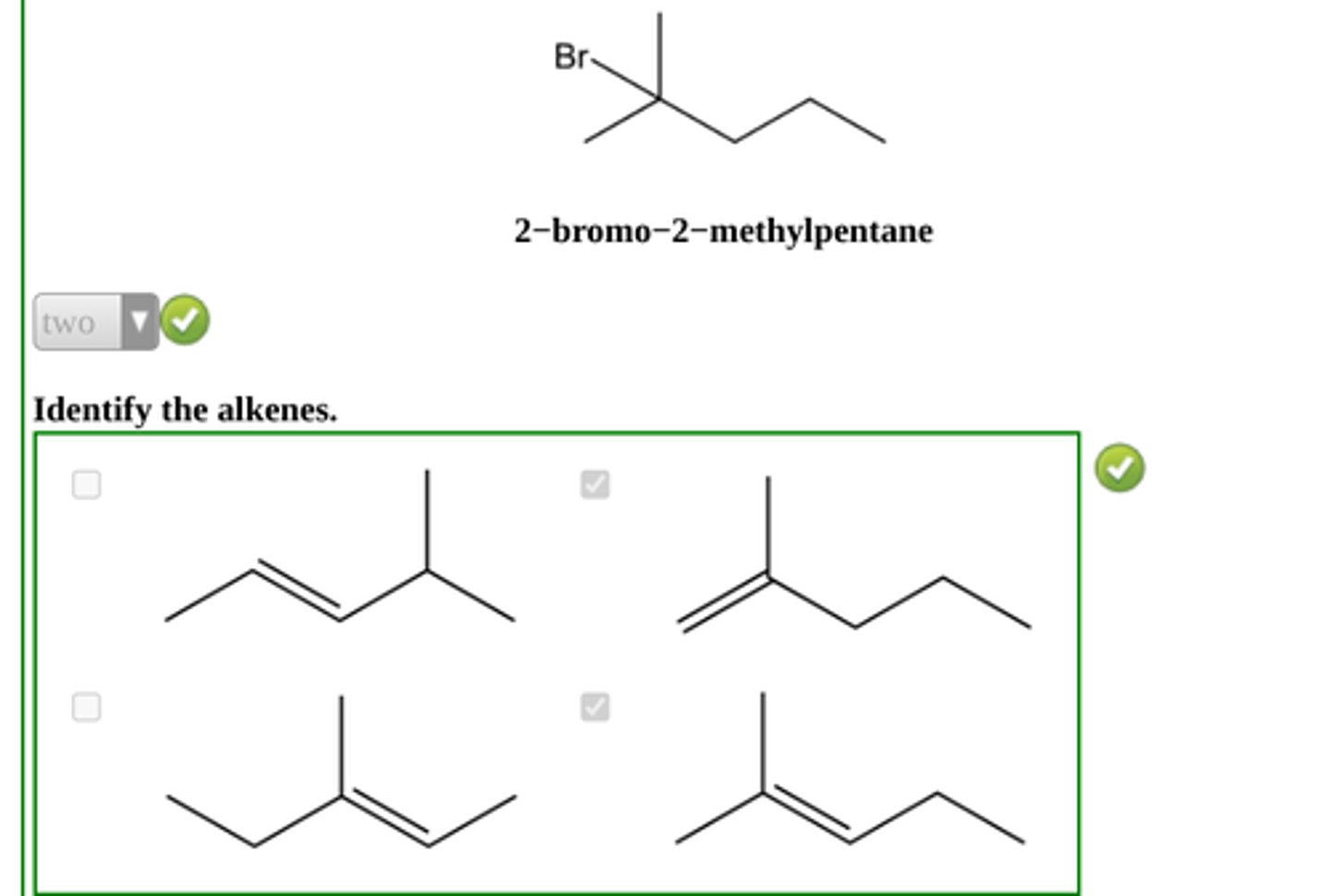
How many alkenes would you expect to be formed from the following alkyl bromide under conditions of E2 elimination?
2-bromo-2-methylpentane
2
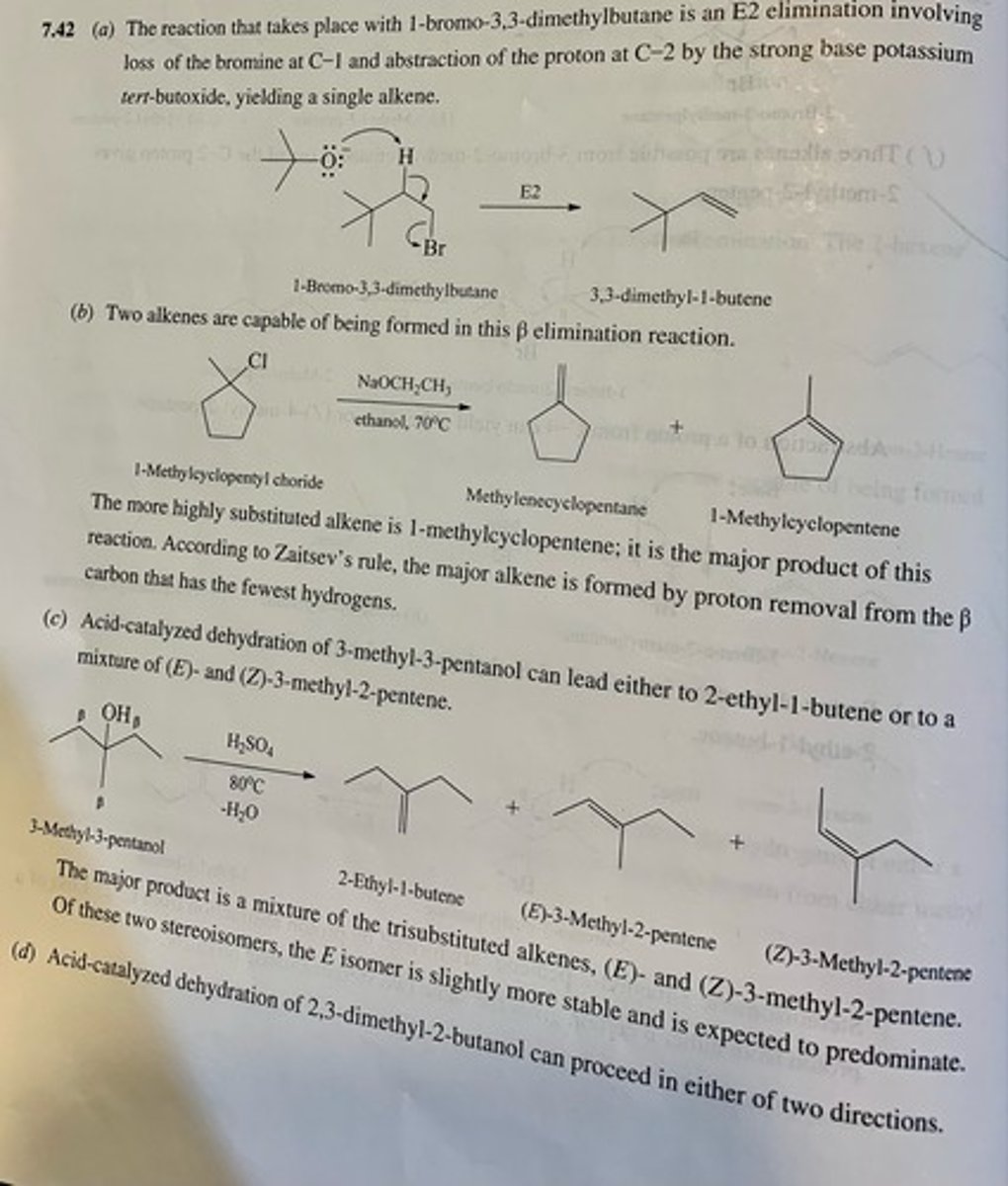
Write structural formulas for all the alkene products that could reasonably be formed from each of the following compounds under the indicated reaction conditions.
(a) 1-Bromo-3,3-dimethylbutane (potassium tert-butoxide, tert-butyl alcohol, 100°C)
(b) 1-Methylcyclopentyl chloride (sodium ethoxide, ethanol, 70°C)
(c) 3-Methyl-3-pentanol (sulfuric acid, 80°C)
Write structural formulas for all the alkene products that could reasonably be formed from each of the following compounds under the indicated reaction conditions. (see pic)
(d) 2,3-Dimethyl-2-butanol (phosphoric acid, 120°C)
(e) 3-Iodo-2,4-dimethylpentane (sodium ethoxide, ethanol, 70°C)

Predict the major organic product of each of the following reactions. (see pic)
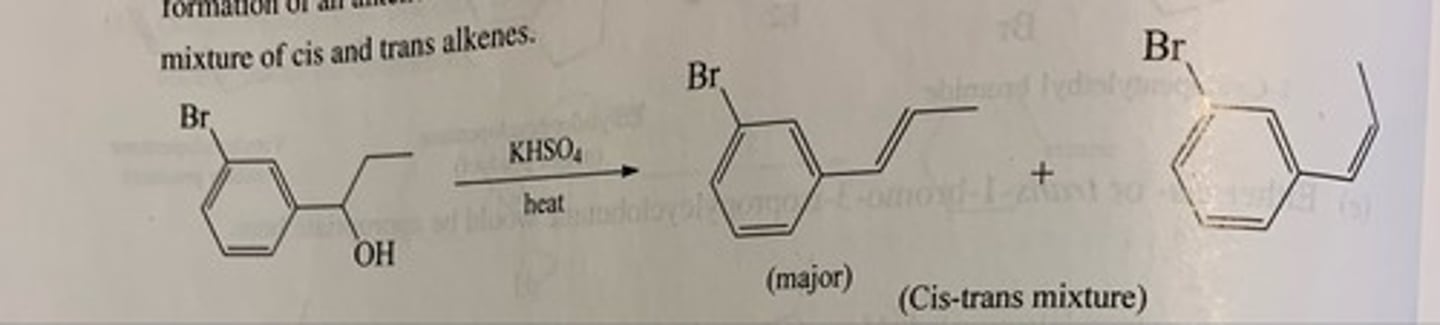
Predict the major organic product of each of the following reactions. (see pic)
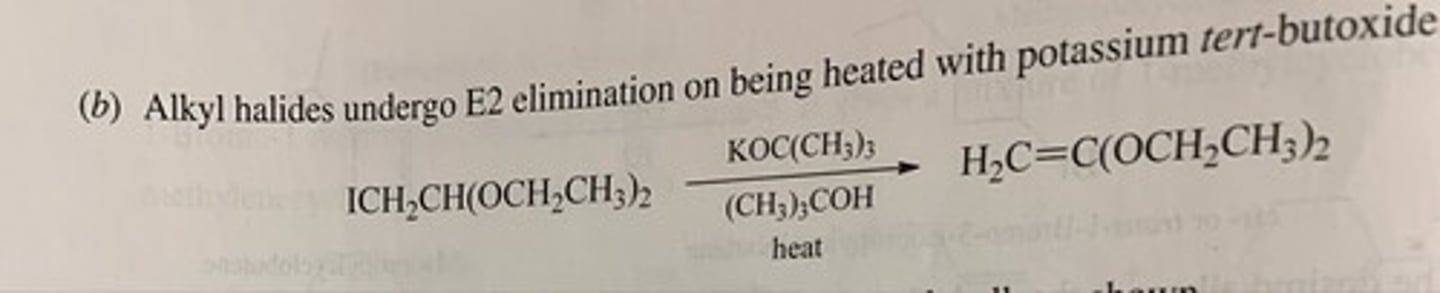
Predict the major organic product of each of the following reactions. (see pic)
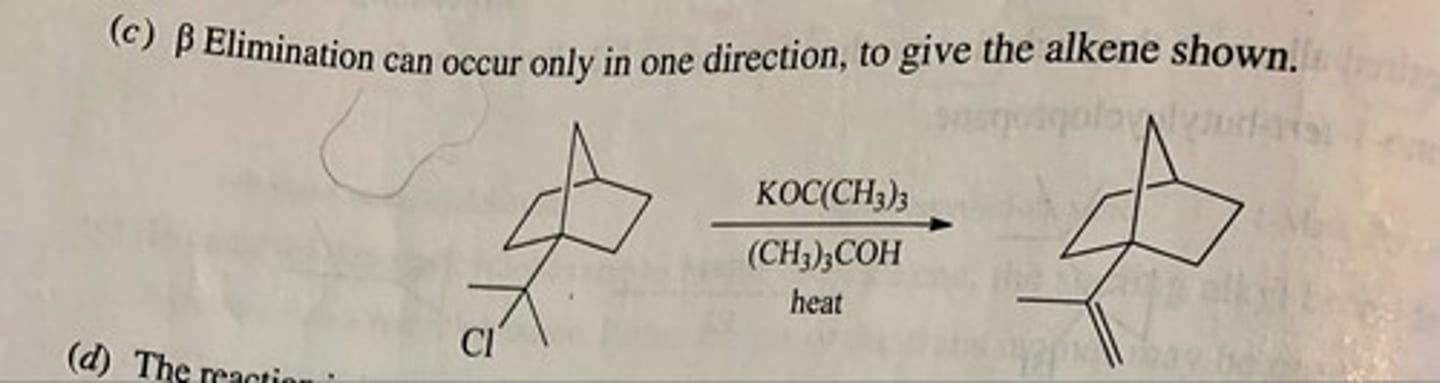
Predict the major organic product of each of the following reactions. (see pic)
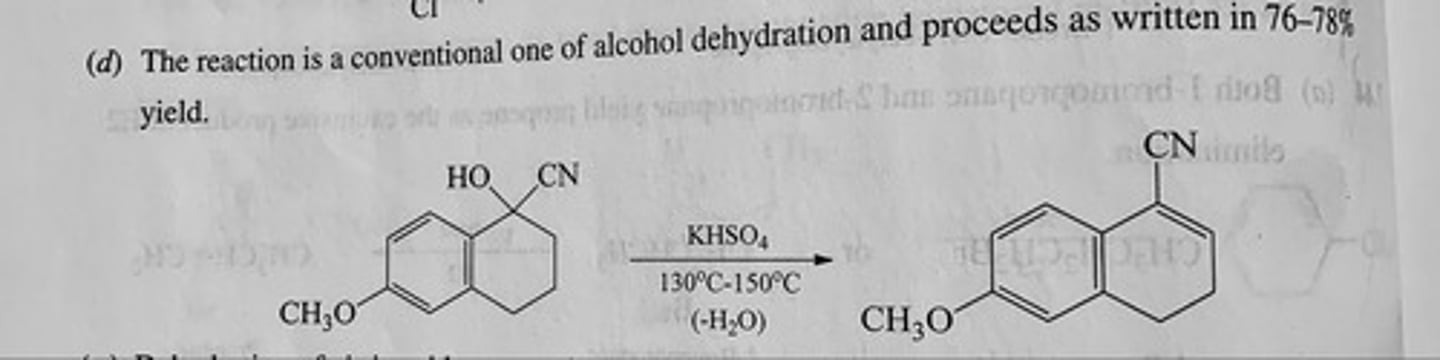
Predict the major organic product of each of the following reactions. (see pic)
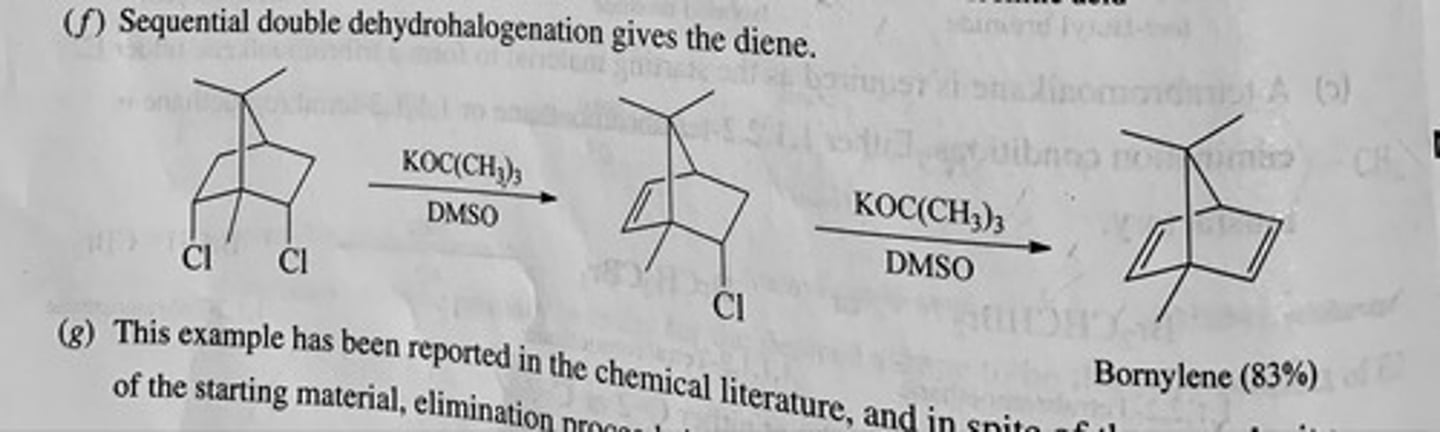
How many alkenes yield:
(a) 2,2,3,4,4-pentamethylpentane on catalytic hydrogenation?
(b) How many yield 2,3-dimethylbutane?
(c) How many yield methylcyclobutane?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
Write the structure of the major organic product formed in the reaction of 1-pentene with each of the following:
(a) Hydrogen chloride
(b) Dilute sulfuric acid
(c) Diborane in diglyme, followed by basic hydrogen peroxide
(d) Bromine in carbon tetrachloride
(e) Bromine in water
(f) Peroxyacetic acid
(g) Ozone
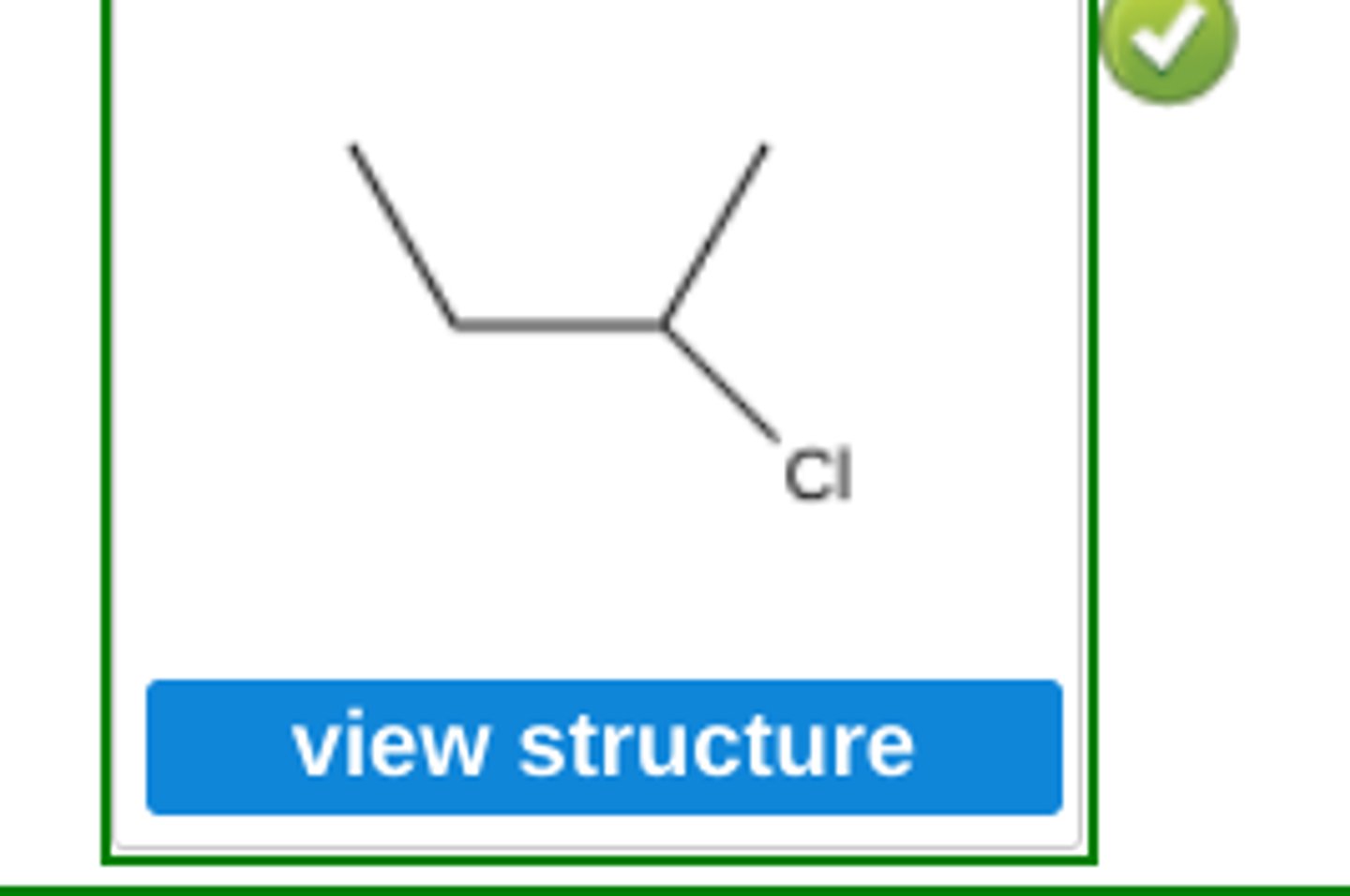
(a) 2-chloropentane
(b) 2-pentanol
(c) 1-pentanol
(d) 1,2-Dibromopentane
(e) 1-Bromo-2-pentanol
(f) 1,2-Epoxypentane
(g) Ozonide

Write the structure of the major organic product of ozonide with H2O/ ZN (see pic)
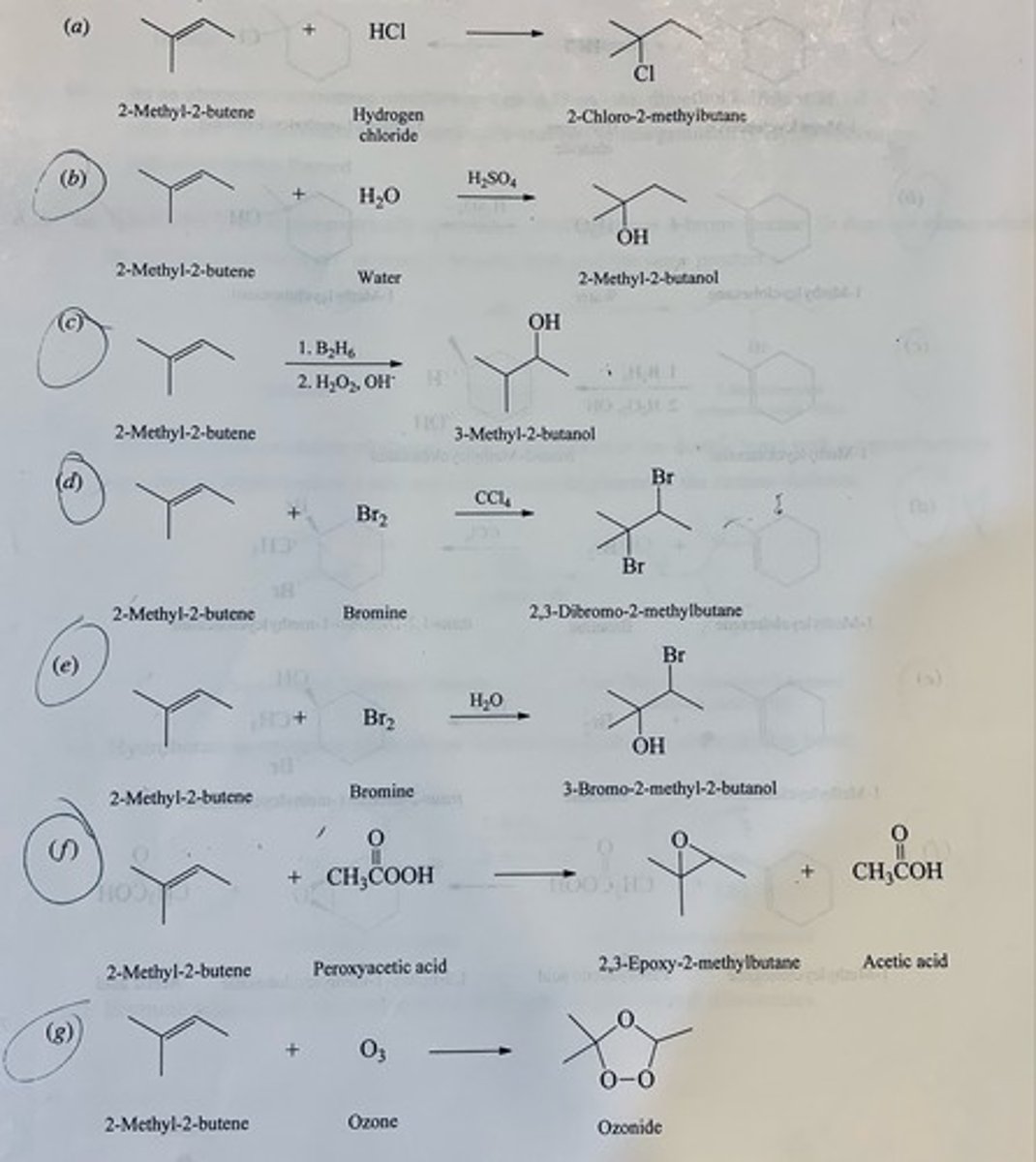
Write the structure of the major organic product formed in the reaction of 2-methyl-2-butene with each of the following:
(a) Hydrogen chloride
(b) Dilute sulfuric acid
(c) Diborane in diglyme, followed by basic hydrogen peroxide
(d) Bromine in carbon tetrachloride
(e) Bromine in water
(f) Peroxyacetic acid
(g) Ozone
(a) 2-Chloro-2-methylbutane
(b) 2-Methyl-2-butanol
(c) 3-methyl-2-butanol
(d) 2,3-Dibromo-2-methylbutane
(e) 3-Bromo-2-methyl-2-butanol
(f) 2,3-Epoxy-2-methylbutane
(g) Ozonide
Write the structure of the major organic product formed in the reaction of 1-methylcyclohexene with each of the following:
(a) Hydrogen chloride
(b) Dilute sulfuric acid
(c) Diborane in diglyme, followed by basic hydrogen peroxide
(d) Bromine in carbon tetrachloride
(e) Bromine in water
(f) Peroxyacetic acid
(g) Ozone
(a) 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane
(b) 1-methylcyclohexanol
(c) trans-2-Methylcyclohexanol
(d) trans-1,2-Dibromo-1-methylcyclohexane
(e) trans-2-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexanol
(f) 1,2-Epoxy-1-methylcyclohexane
(g) 1-methylcyclohexene
All the following reactions have been reported in the chemical literature. Give the structure of the principal organic product in each case:
3-Hexene + HBr =
3-Bromohexane
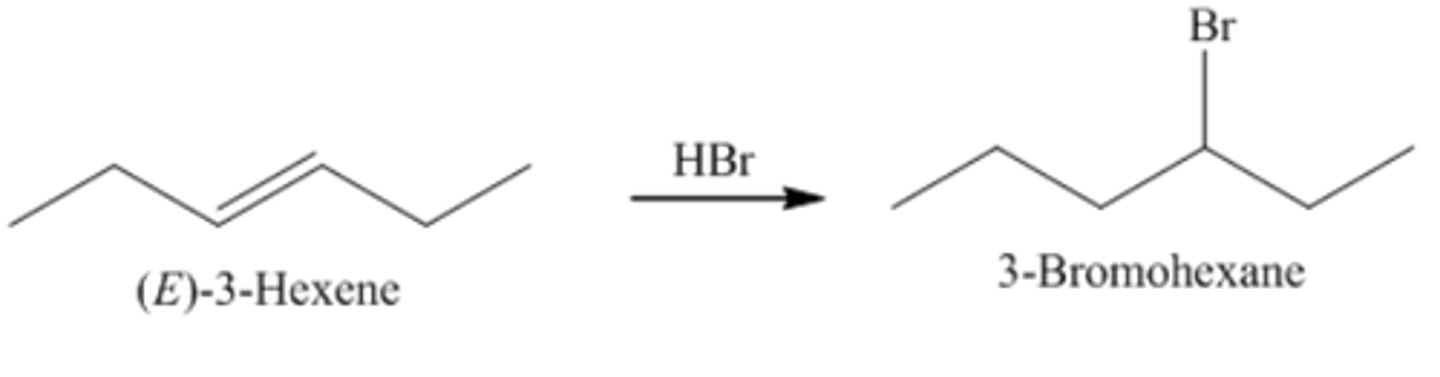
All the following reactions have been reported in the chemical literature. Give the structure of the principal organic product in each case:
2-tert-Butyl-3,3-dimethyl-1-butene + B2H6/H2O2OH
2-tert-Butyl-3,3-dimethyl-1-butanol
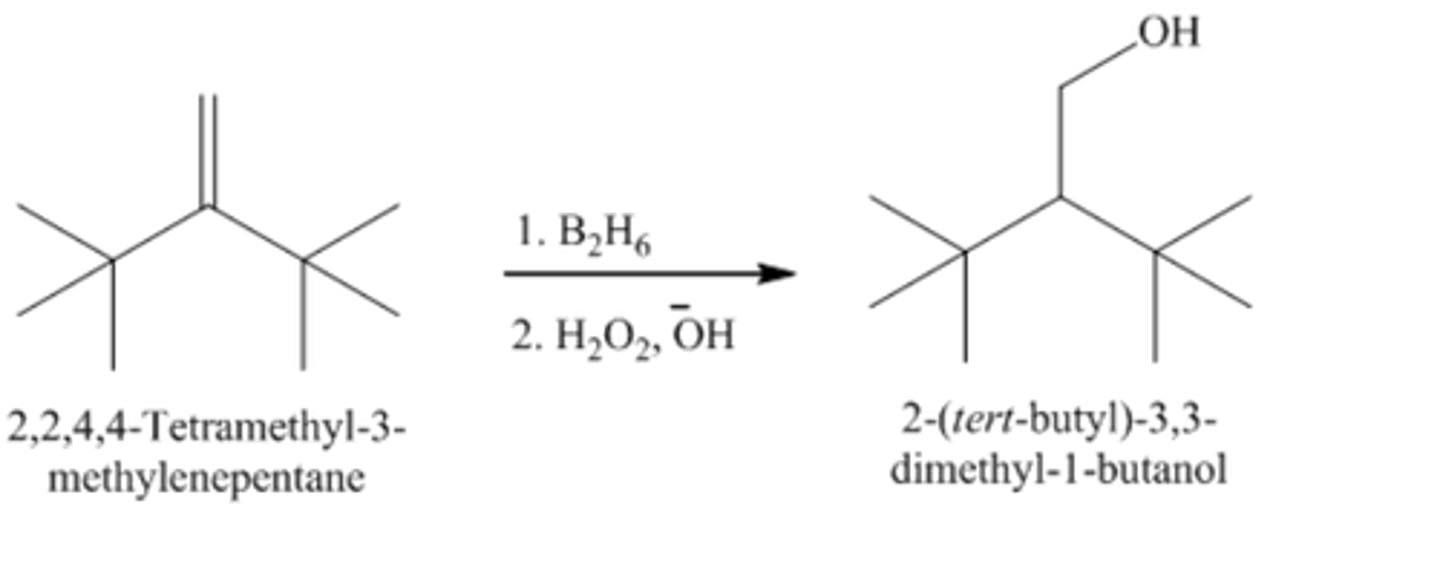
All the following reactions have been reported in the chemical literature. Give the structure of the principal organic product in each case:
1,2-Dimethylcyclohexane + B2H6/H2O2OH
cis-1,2-Dimethylcyclohexanol
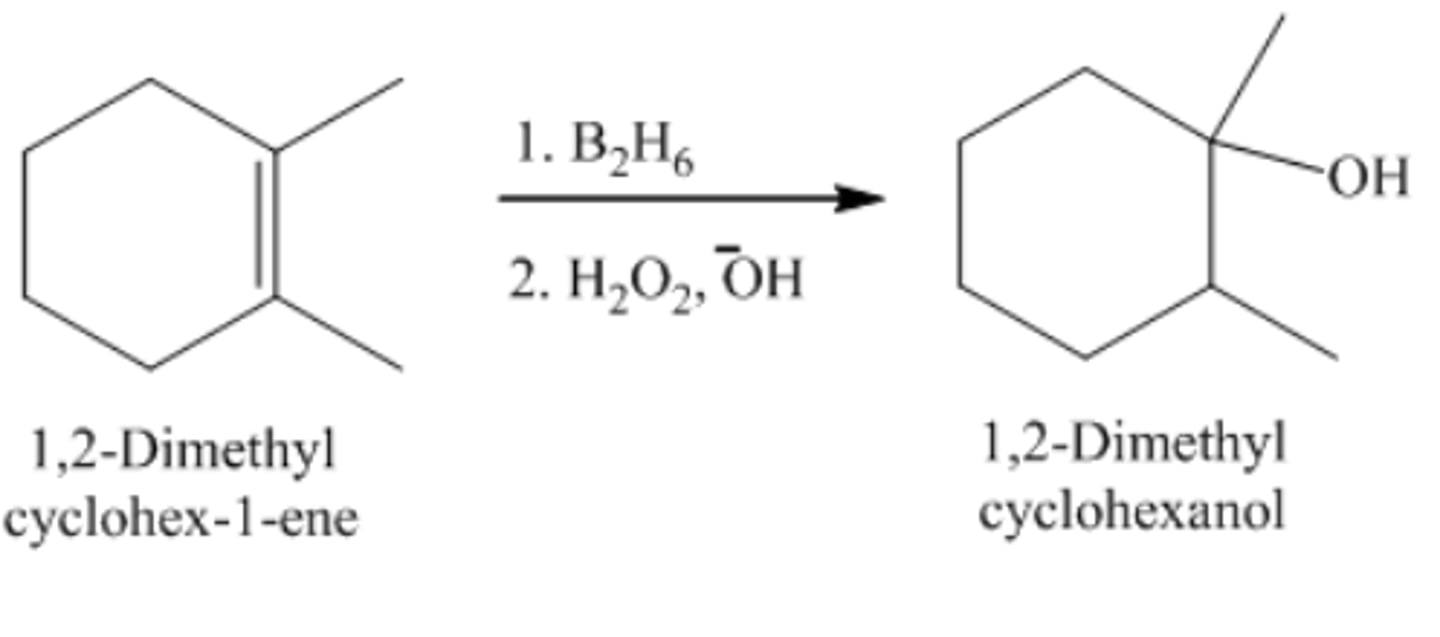
All the following reactions have been reported in the chemical literature. Give the structure of the principal organic product in each case:
2-methyl-1-pentene+ Br2/CHCl3
1,2-Dibromo-2-methylpentane
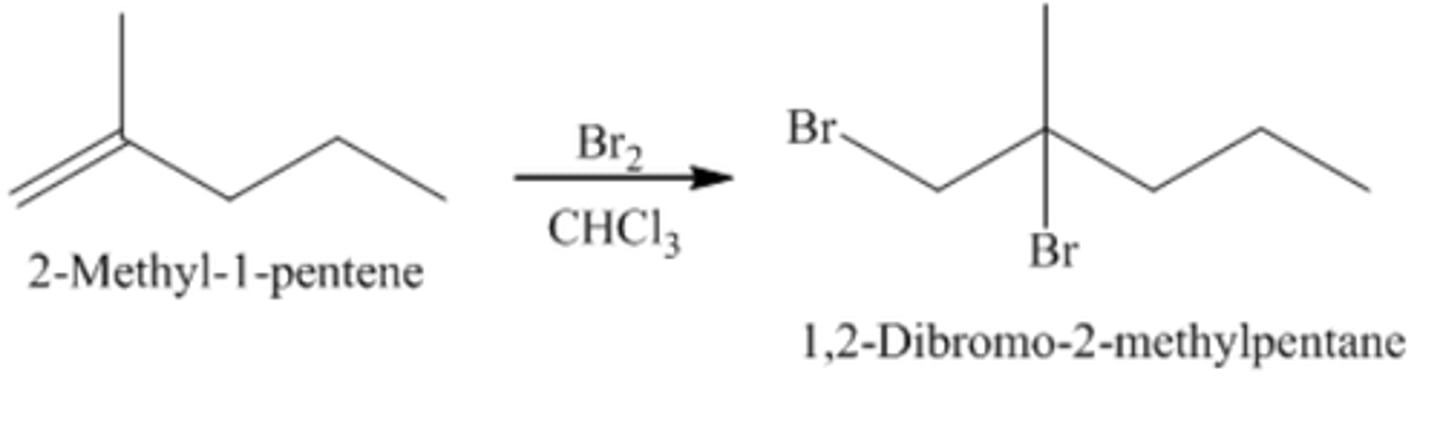
All the following reactions have been reported in the chemical literature. Give the structure of the principal organic product in each case:
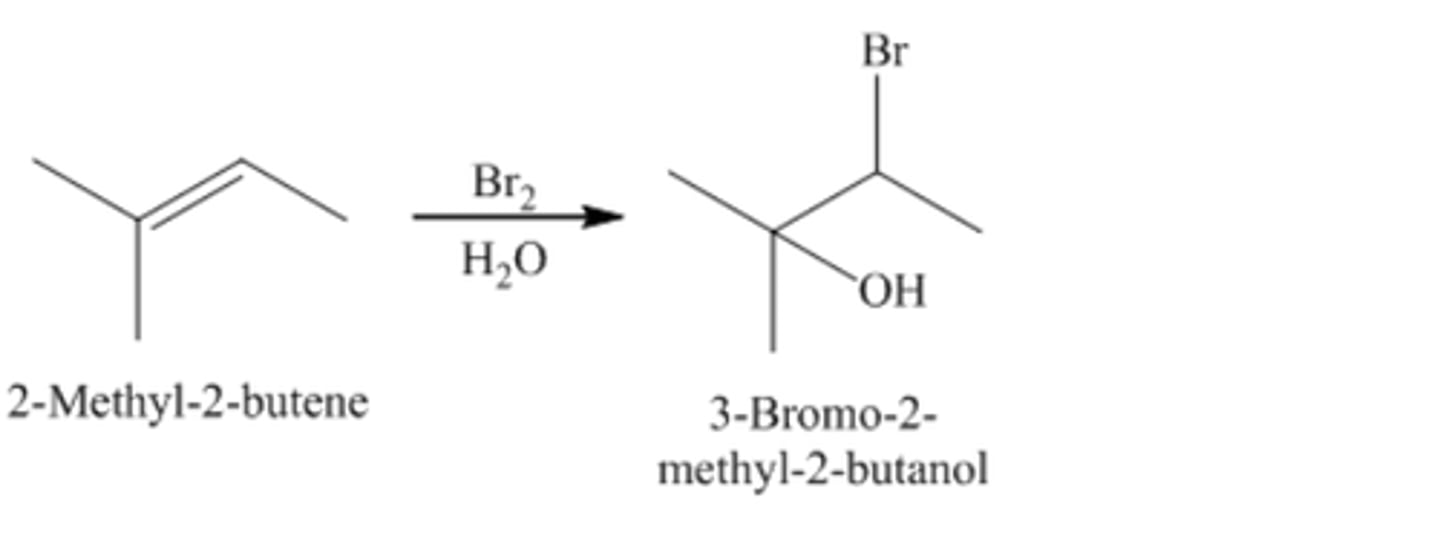
2-methyl-2-butene +Br2/H2O
3-Bromo-2-methyl-2-butanol
All the following reactions have been reported in the chemical literature. Give the structure of the principal organic product in each case:
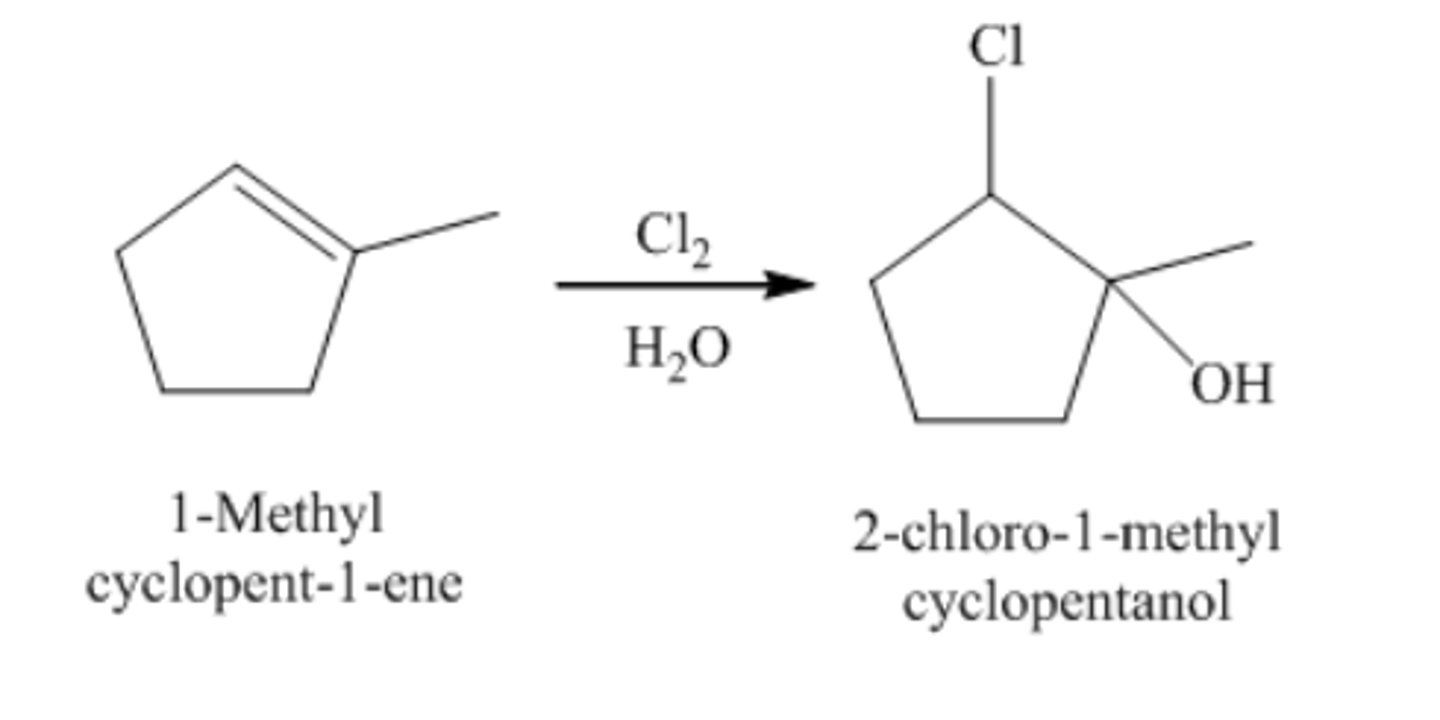
1-methylcyclopentene + Cl2/H2O
trans-2-chloro-1-methylcyclopentanol
All the following reactions have been reported in the chemical literature. Give the structure of the principal organic product in each case:
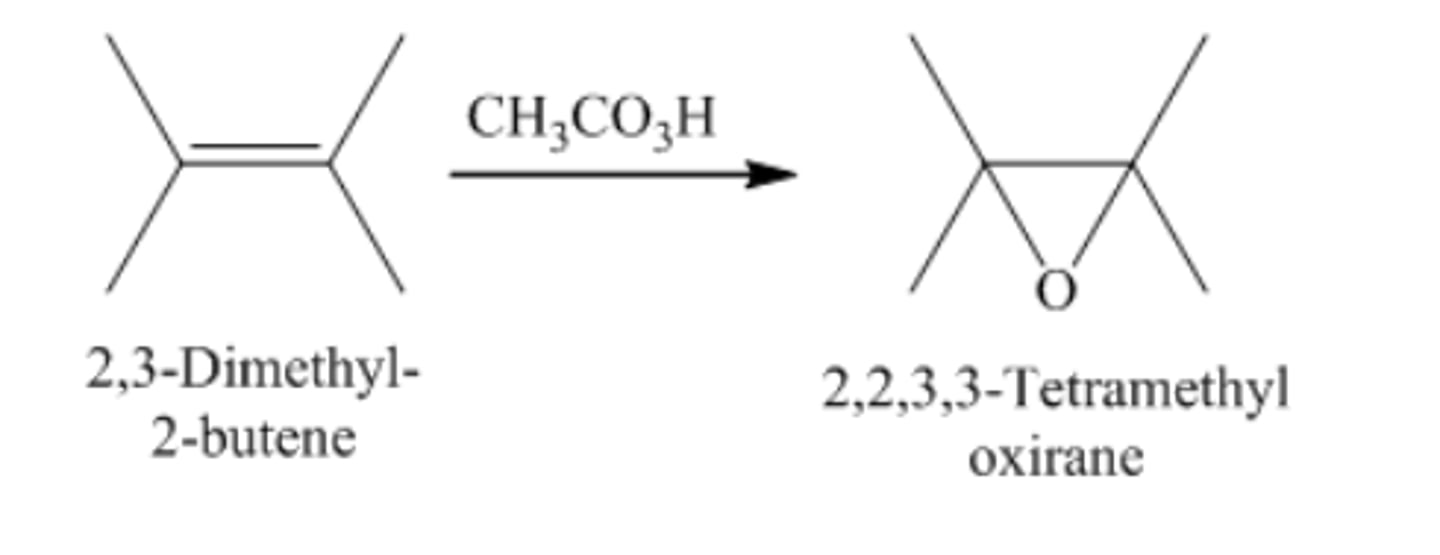
2,3-Dimethyl-2-butene + peroxyacetic acid
2,3-Epoxy-2,3-dimethylbutane + acetic acid
Use Markovnikov's rule to predict the major organic product formed in the reaction of hydrogen chloride with
cis−2−butene.
Use Markovnikov's rule to predict the major organic product formed in the reaction of hydrogen chloride with the following compound:
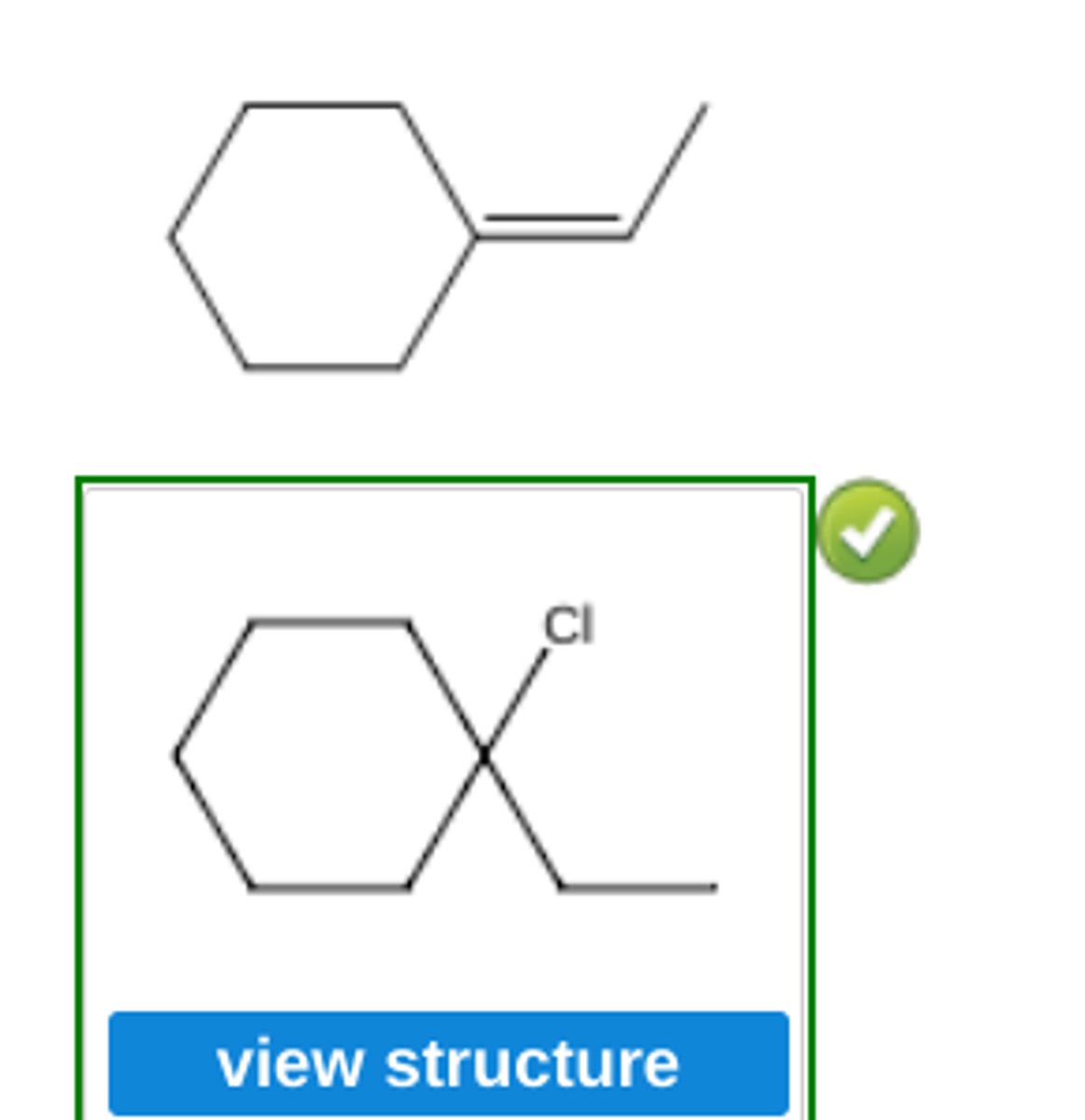
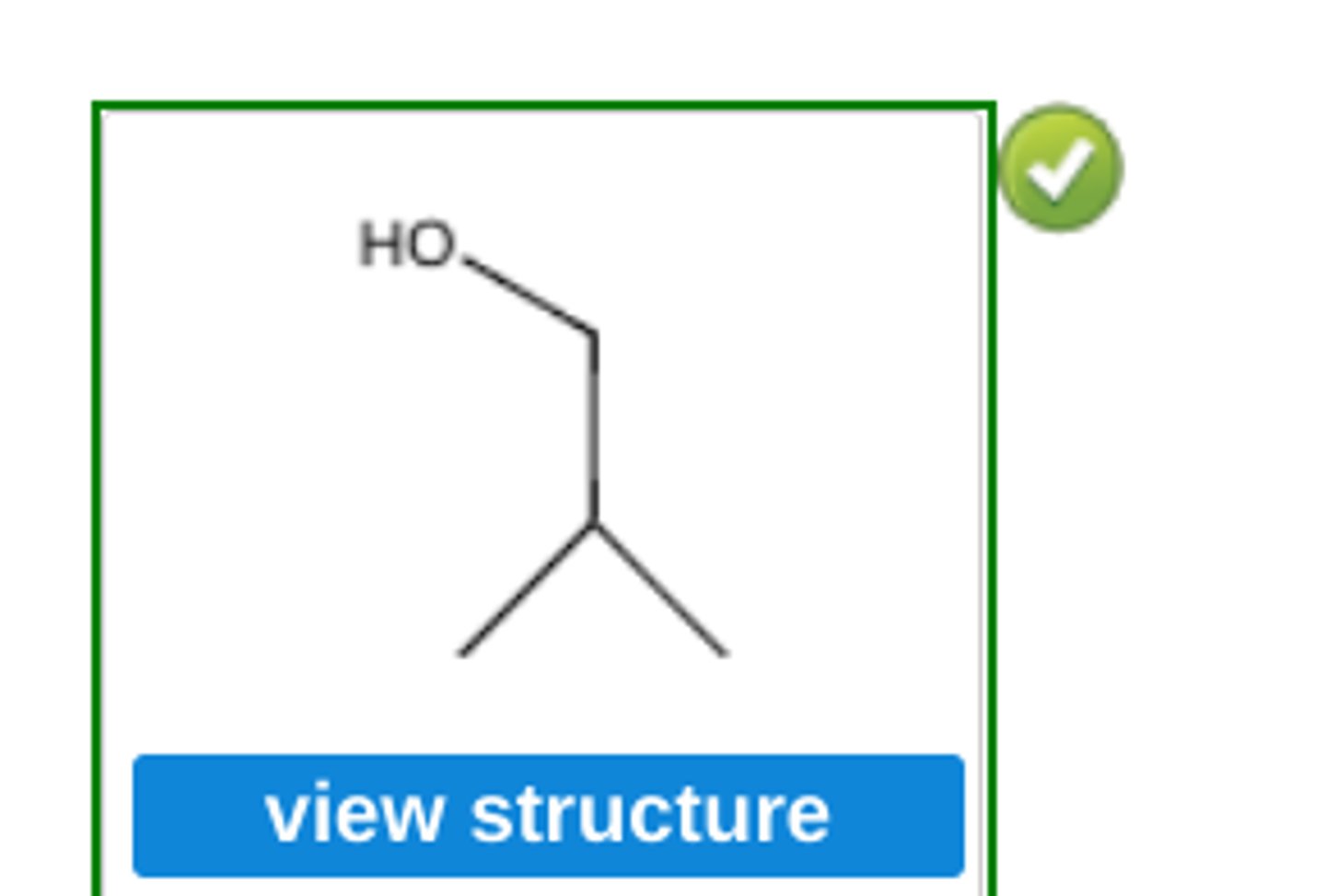
Write the structure of the major organic product obtained by hydroboration-oxidation of 2−methylpropene.
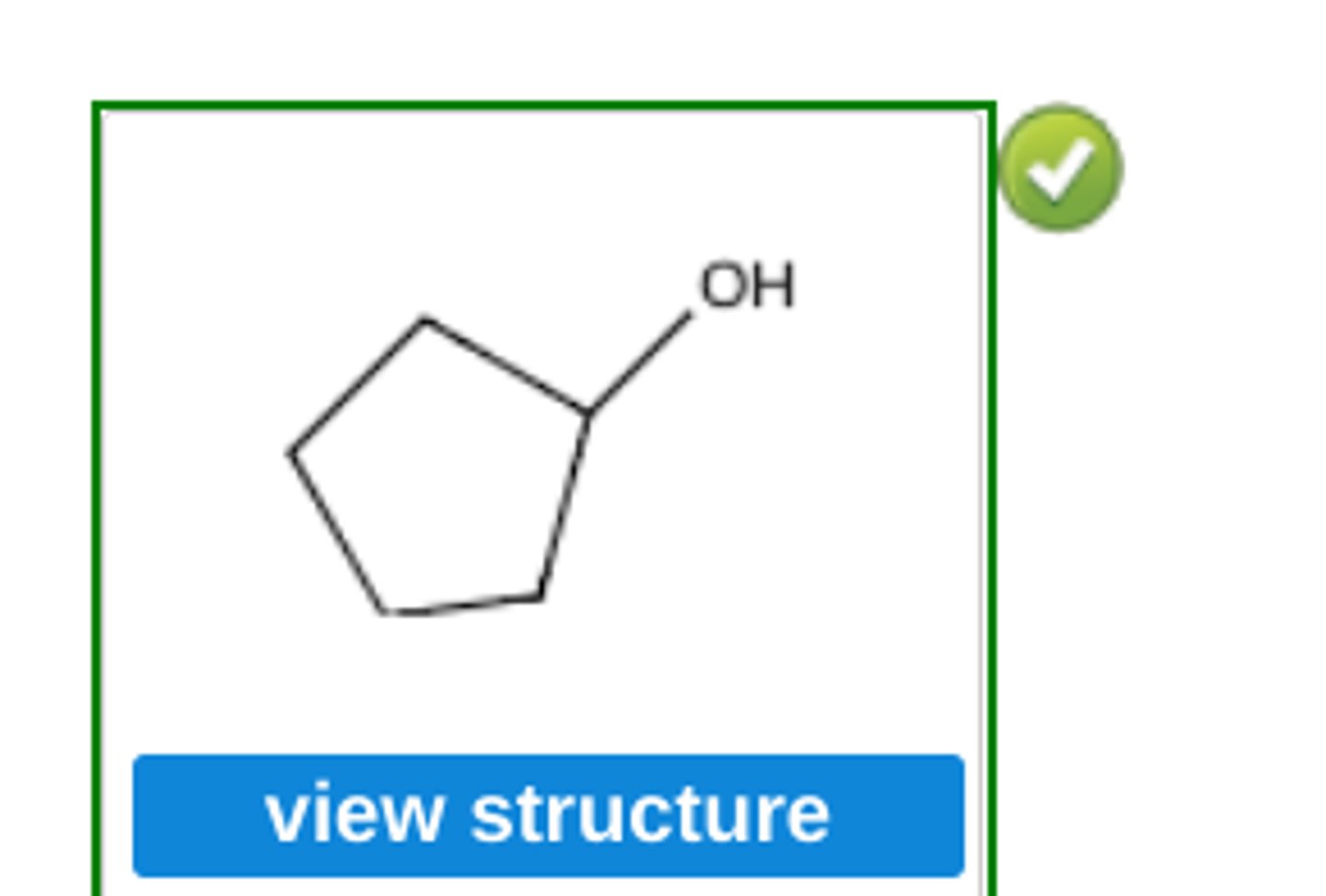
Write the structure of the major organic product obtained by hydroboration-oxidation of cyclopentene.
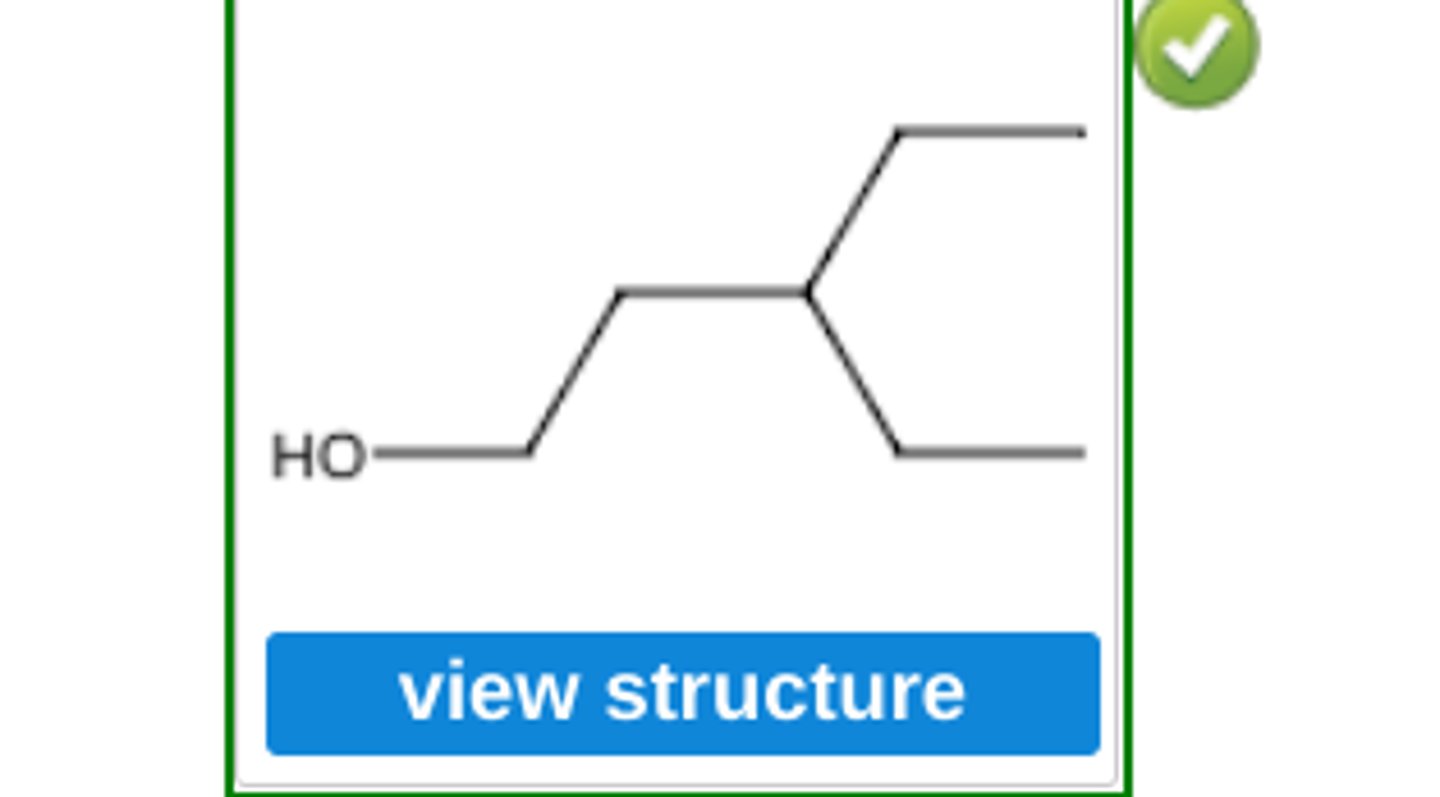
Write the structure of the major organic product obtained by hydroboration-oxidation of 3−ethyl−1−pentene.
Arrange the compounds 2−methyl−1−butene, 2−methyl−2−butene, and 3−methyl−1−butene in order of decreasing reactivity toward bromine. (see pic)
B>A>C
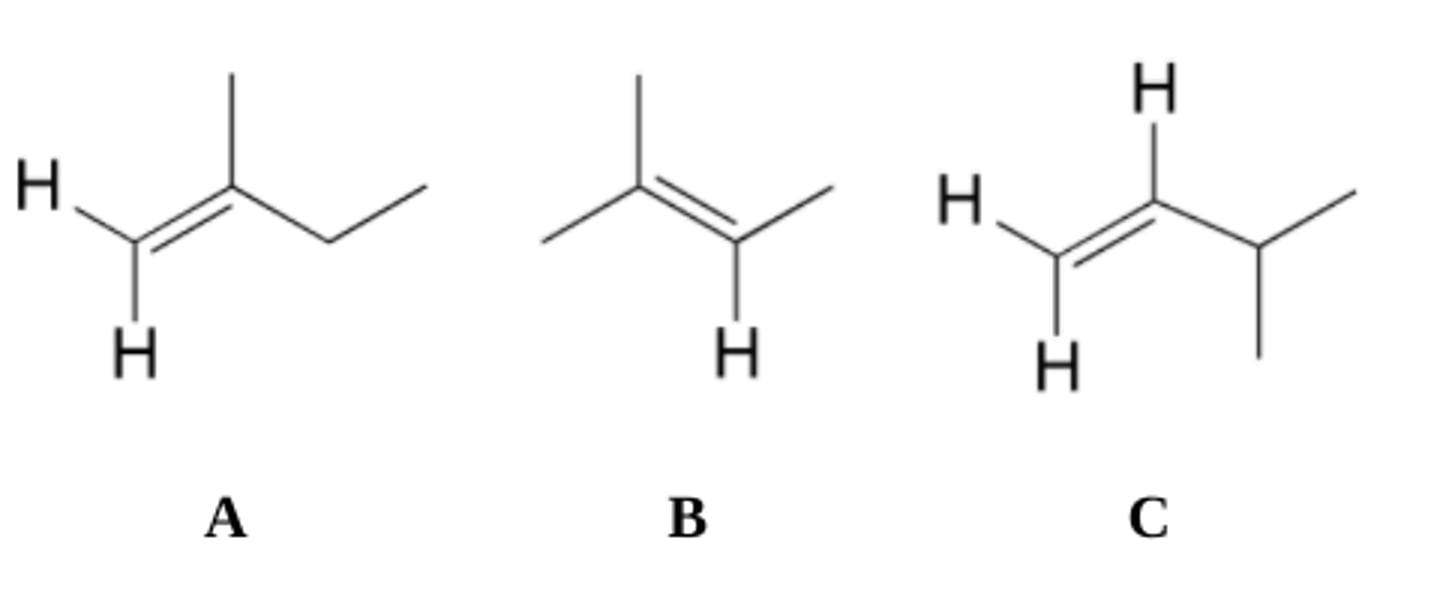
What two stereoisomeric alkanes are formed on catalytic hydrogenation of (E)-3-methyl-2-hexene? What are the relative amounts of each?
They are both equal
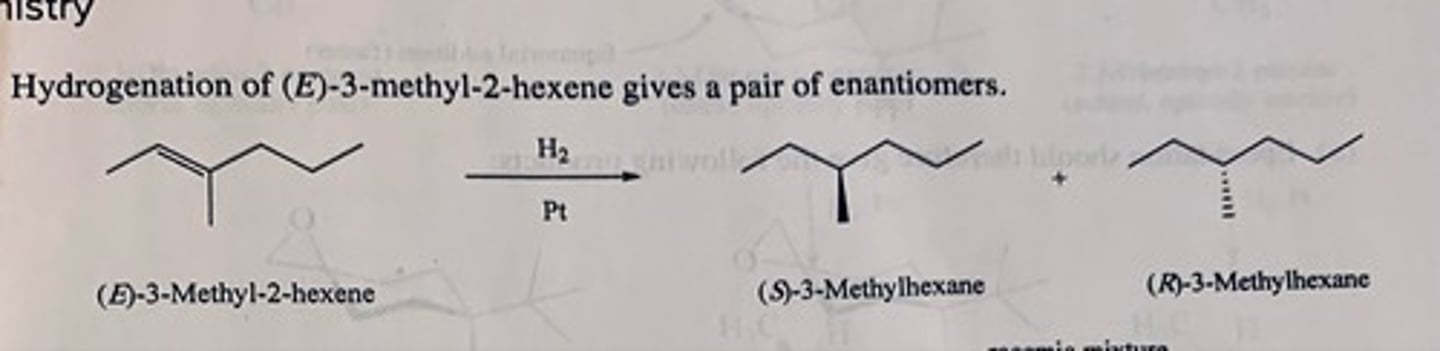
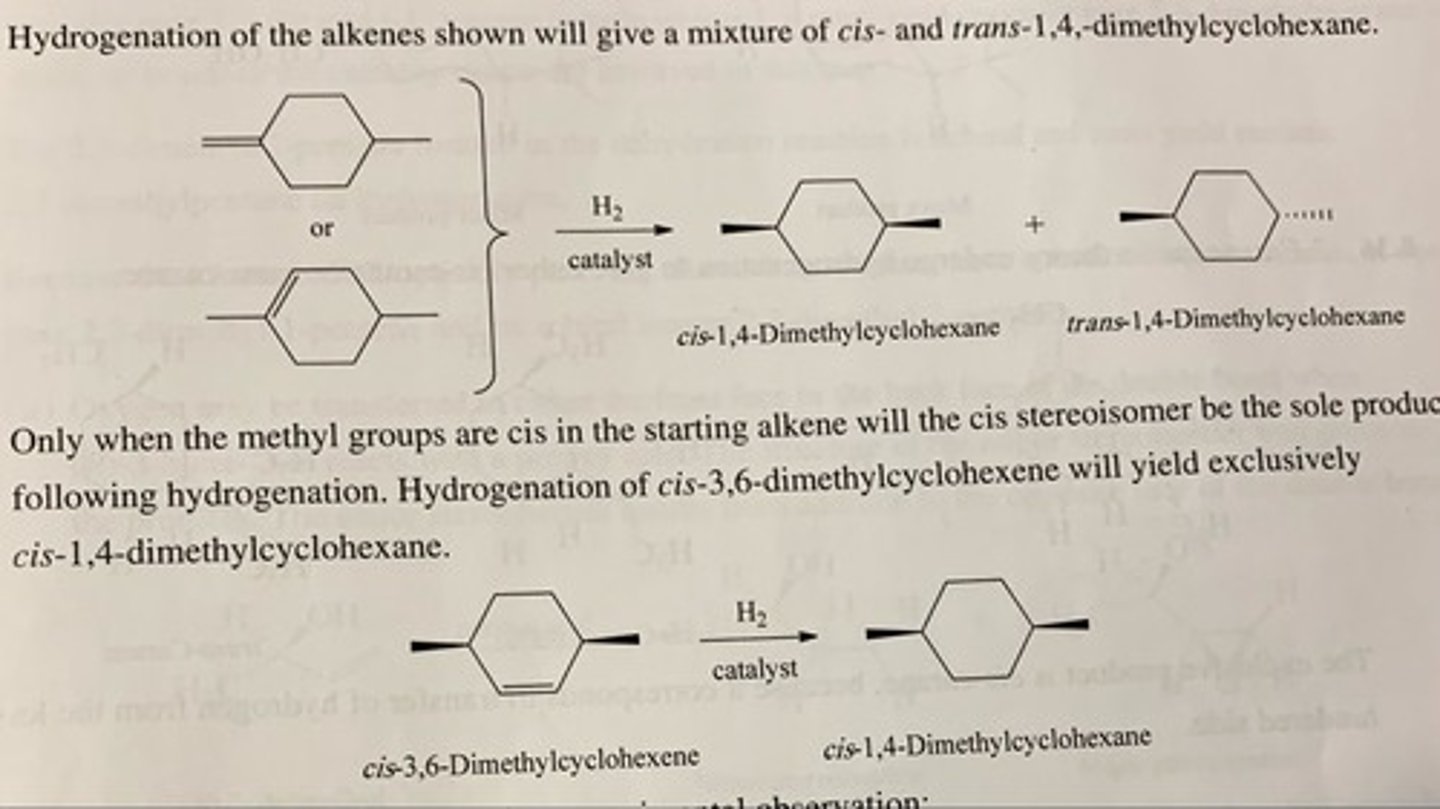
Two alkenes undergo hydrogenation to yield a mixture of cis- and trans-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane. Which two are these? A third, however, gives only cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane. What compound is this? (see pic)
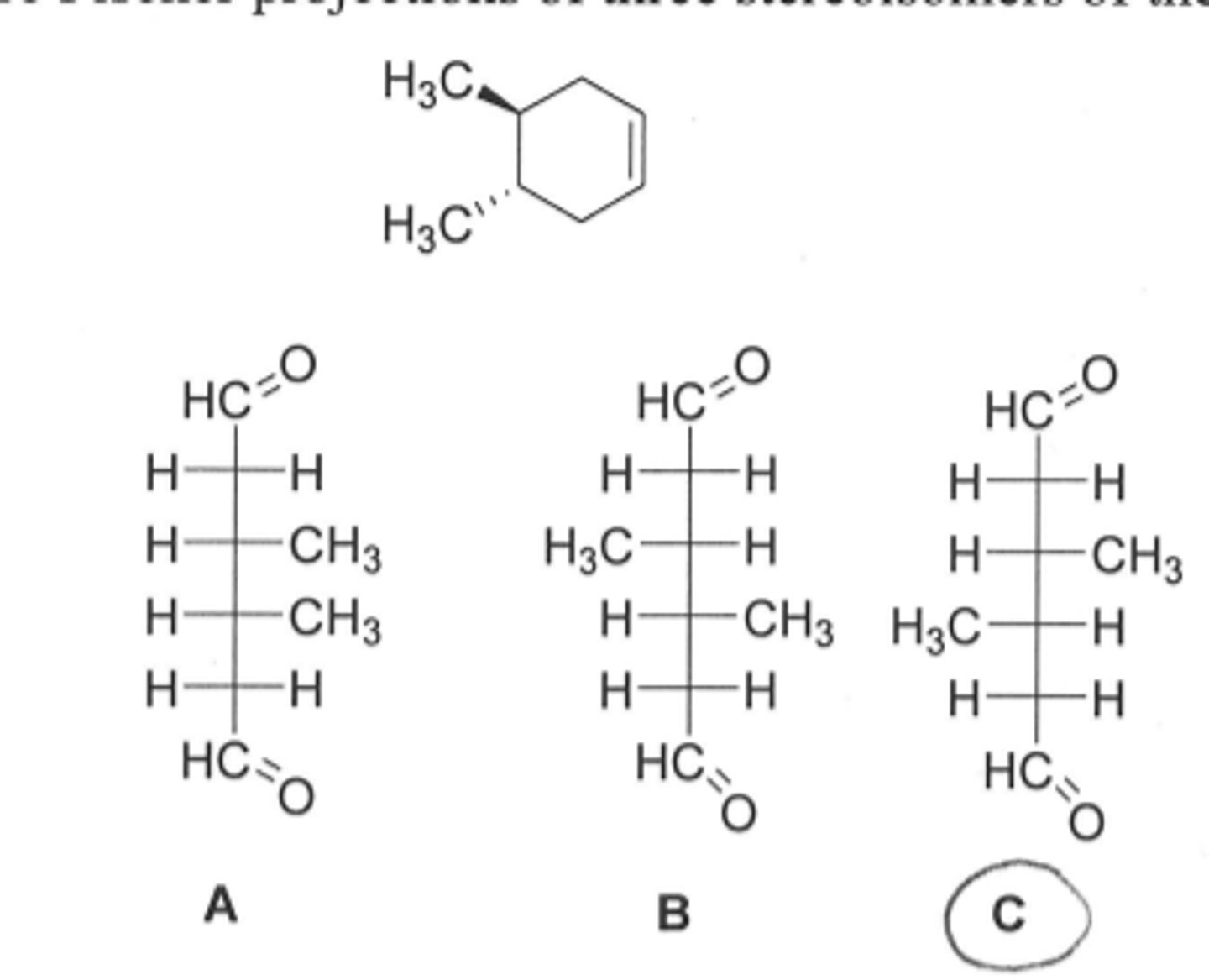
What is the product of ozonolysis of trans-4,5-dimethylcyclohexene with the shown configurations (see pic)
C
Which process is not possible for a carbocation?
(a) addition of a nucleophile
(b) rearrangement to a more stable carbocation
(c) addition of a proton to form an alkane
(d) loss of a B-hydrogen to form an alkene
C addition of a proton to form an alkane
Specify reagents suitable for converting 3-ethyl-2-pentene to each of the following:
(a) 2,3-Dibromo-3-ethylpentane
(b) 3-Chloro-3-ethylpentane
(c) 3-Ethyl-3-pentanol
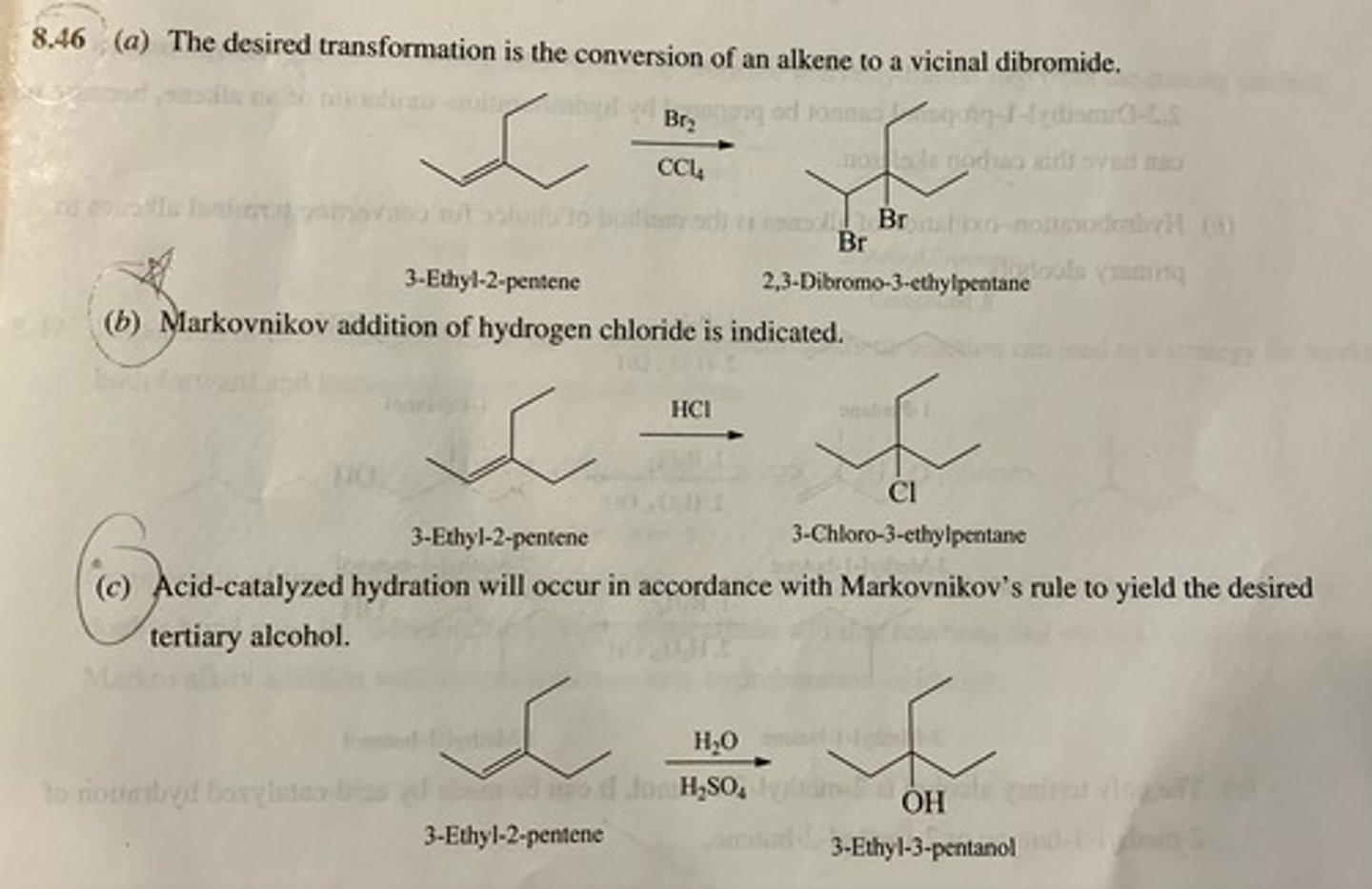
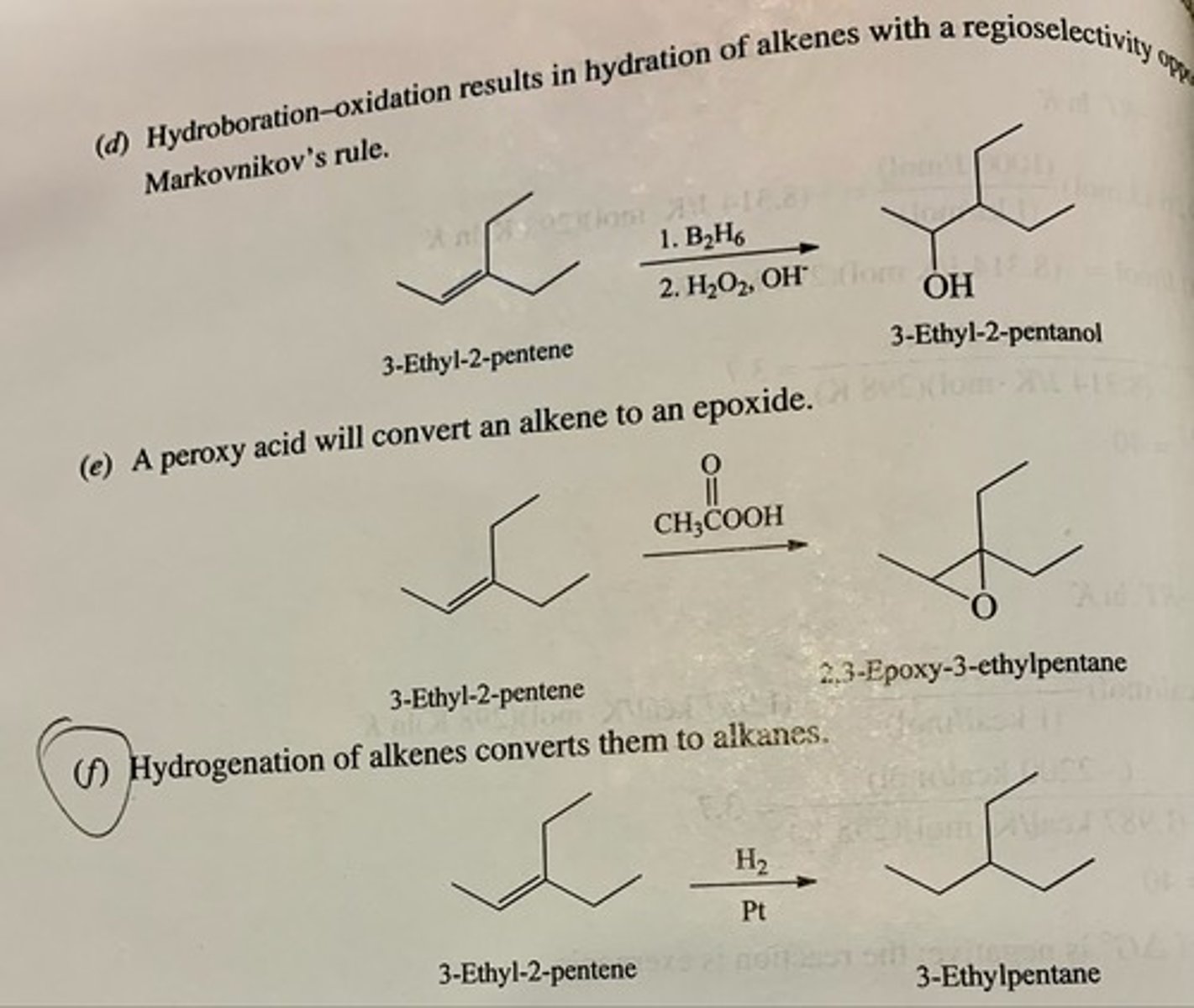
Specify reagents suitable for converting 3-ethyl-2-pentene to each of the following:
(d) 3-Ethyl-2-pentanol
(e) 2,3-Epoxy-3-ethylpentane
(f) 3-Ethylpentane
Apply retrosynthetic analysis to guide the preparation of each of the following compounds from the indicated starting material, then write out the synthesis showing the necessary reagents.
(a) 1-Propanol from 2-propanol
(b) 1,2-Dibromopropane from 2-bromopropane
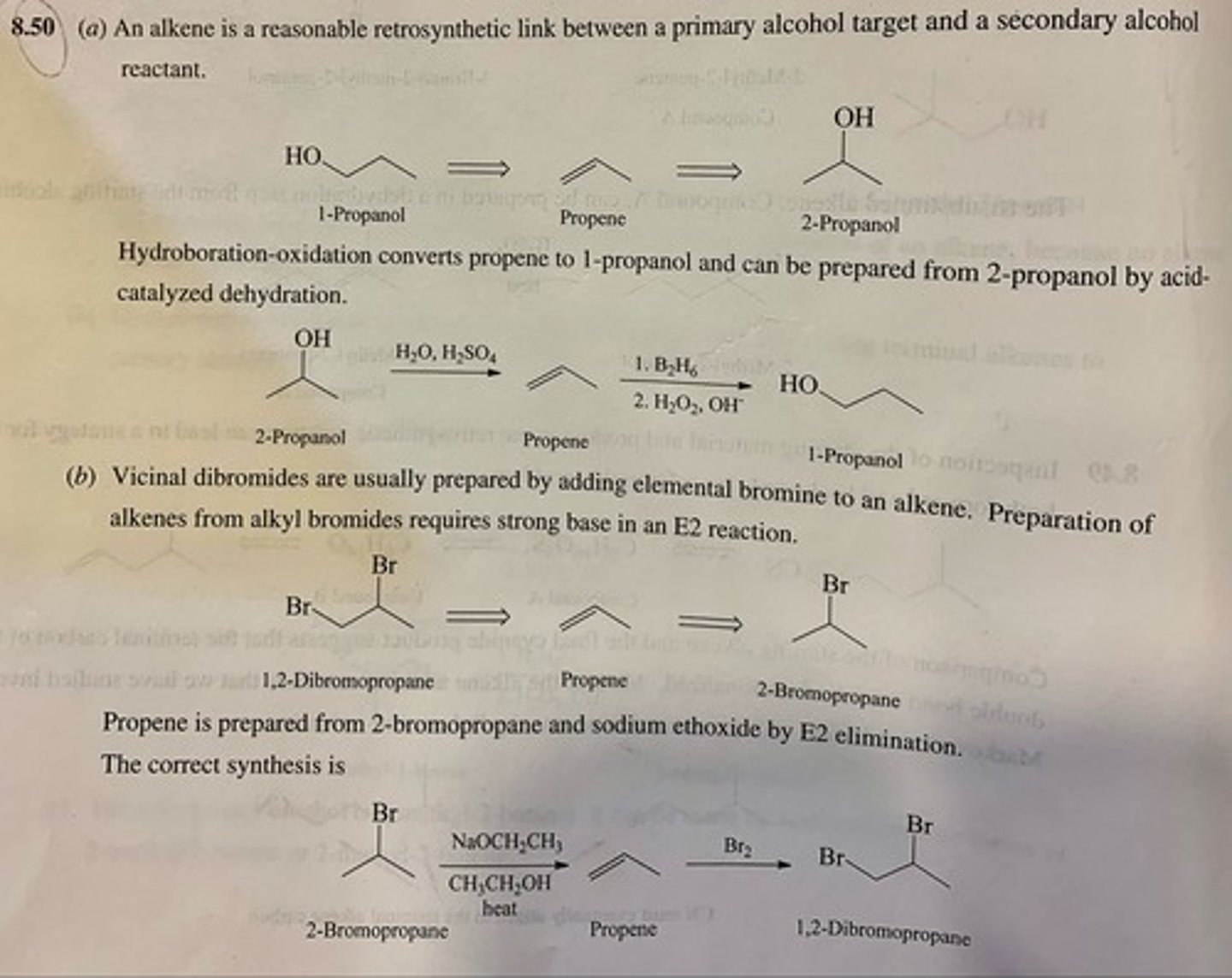
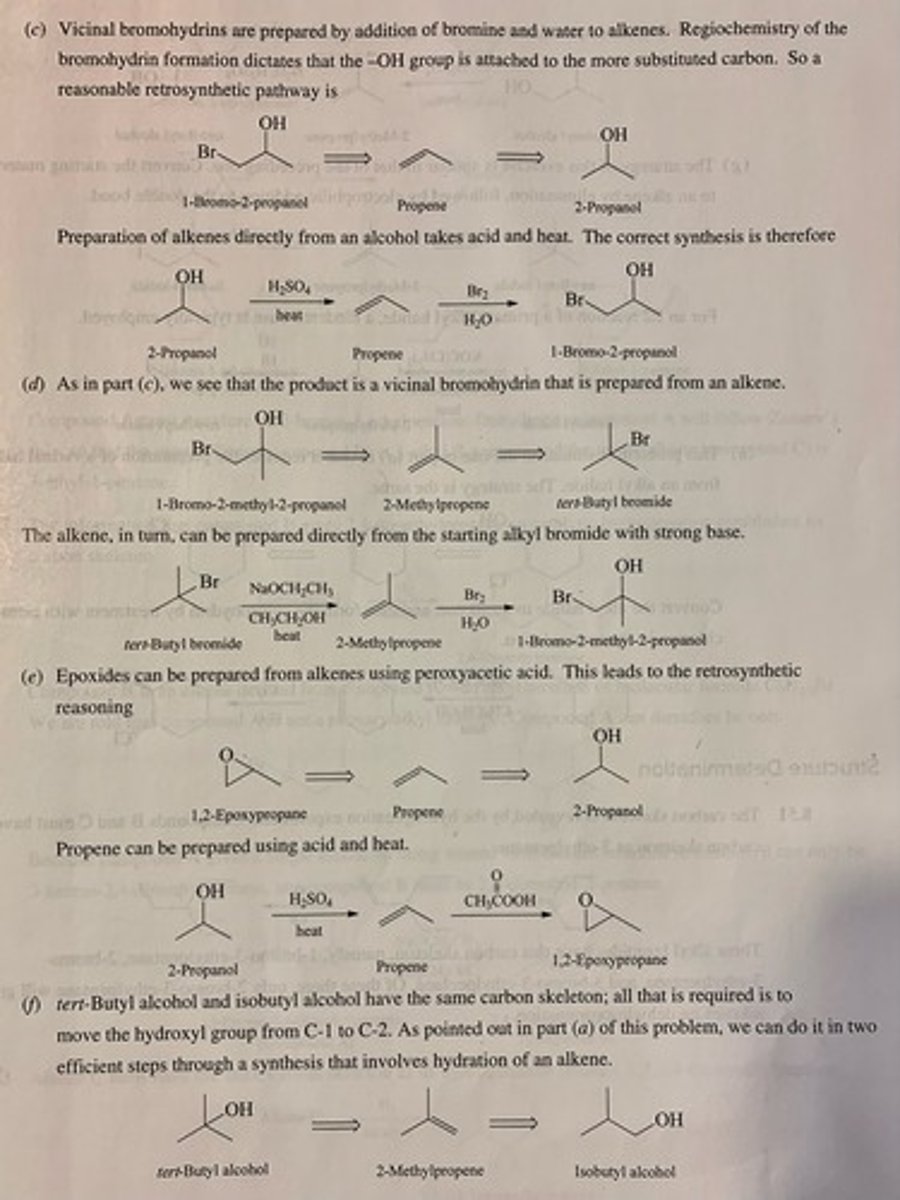
Apply retrosynthetic analysis to guide the preparation of each of the following compounds from the indicated starting material, then write out the synthesis showing the necessary reagents.
(c) 1-Bromo-2-propanol from 2-propanol
(d) 1-Bromo-2-methyl-2-propanol from tert-butyl bromidePage 325
(e) 1,2-Epoxypropane from 2-propanol
(f) tert-Butyl alcohol from isobutyl alcohol
(g) tert-Butyl iodide from isobutyl iodide
(h) trans-2-Chlorocyclohexanol from cyclohexyl chloride
Write the structure of the major organic product formed in the reaction of the ozonide with zinc and water. (see pic)
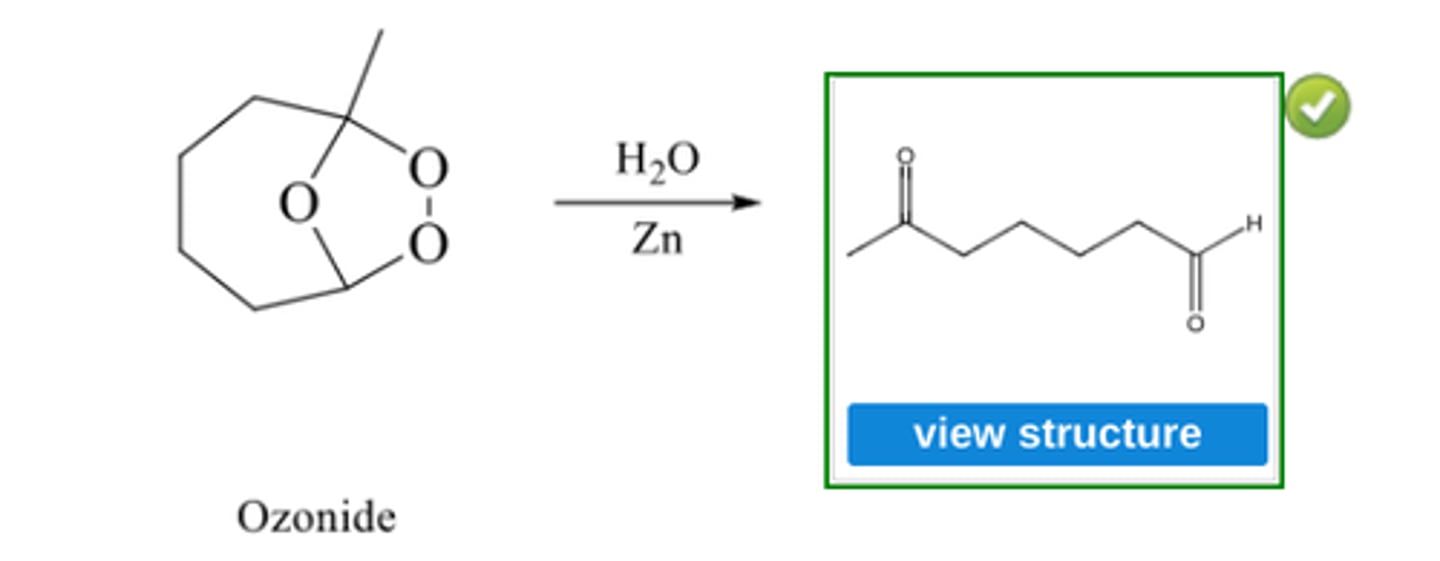
Write the structure of the major organic products formed when the following ozonide is treated with zinc and water. (see pic)
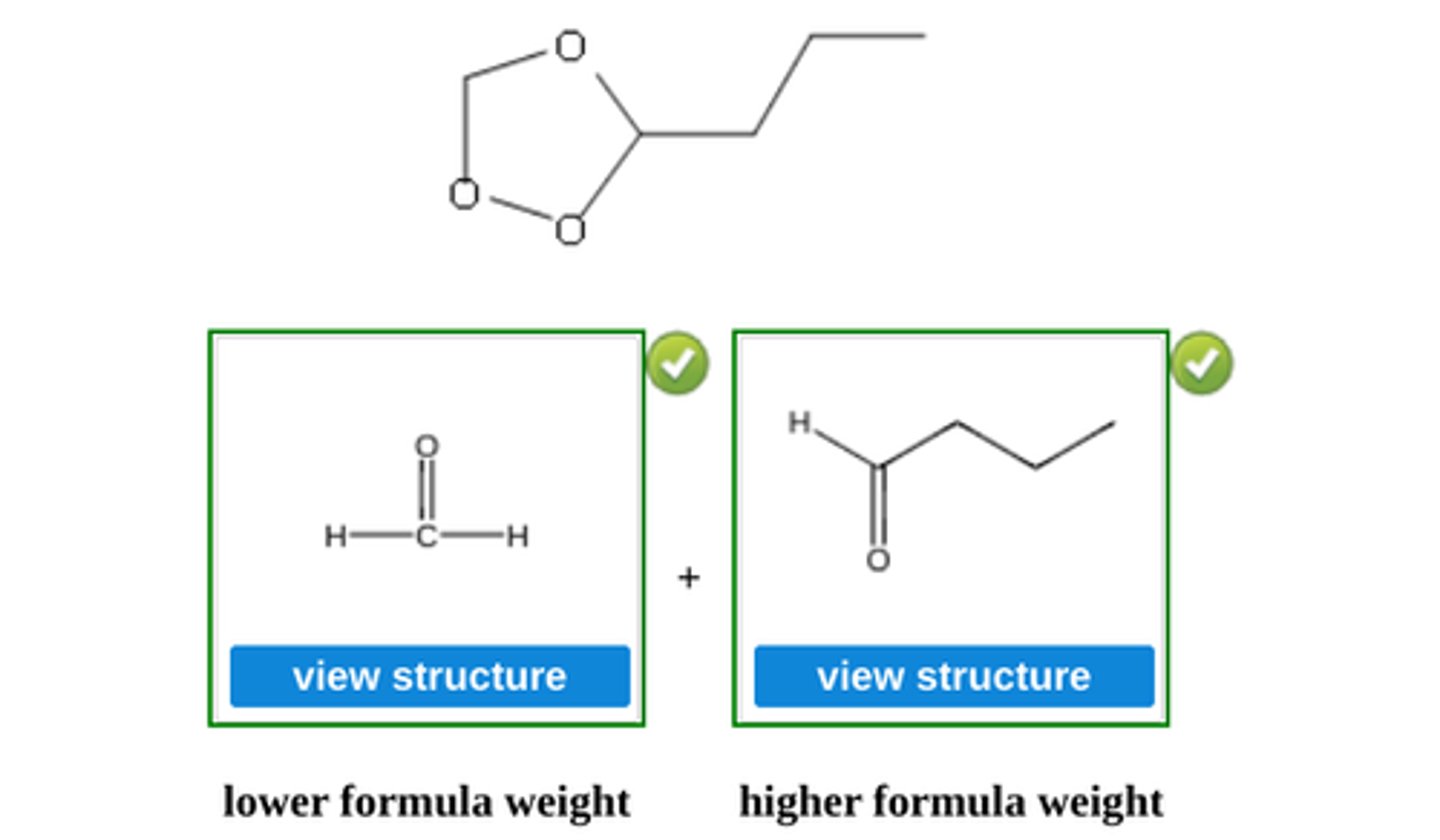
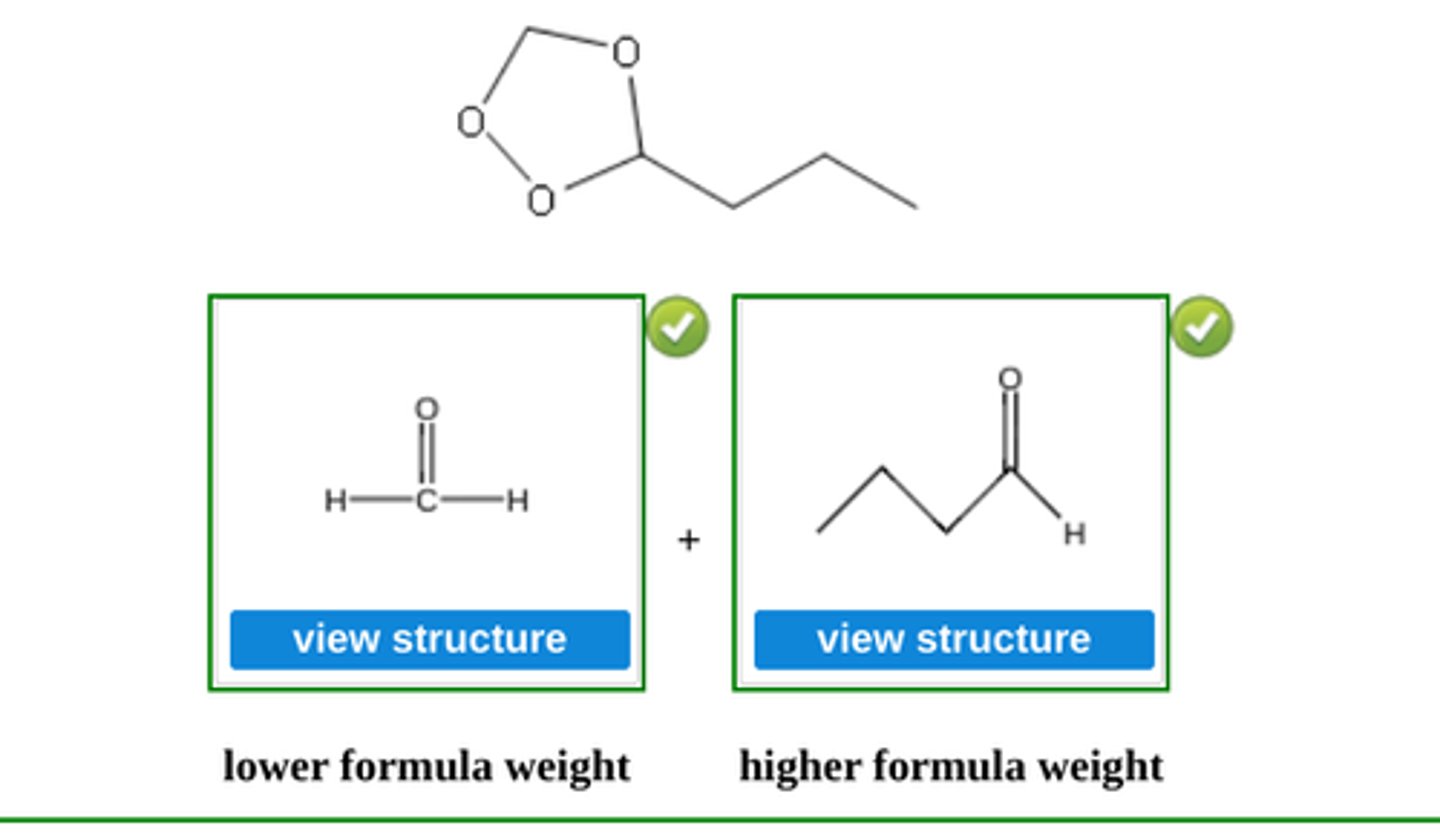
Write the structure of the major organic products formed when the following ozonide is treated with dimethyl sulfide, (CH3)2S. (see pic)
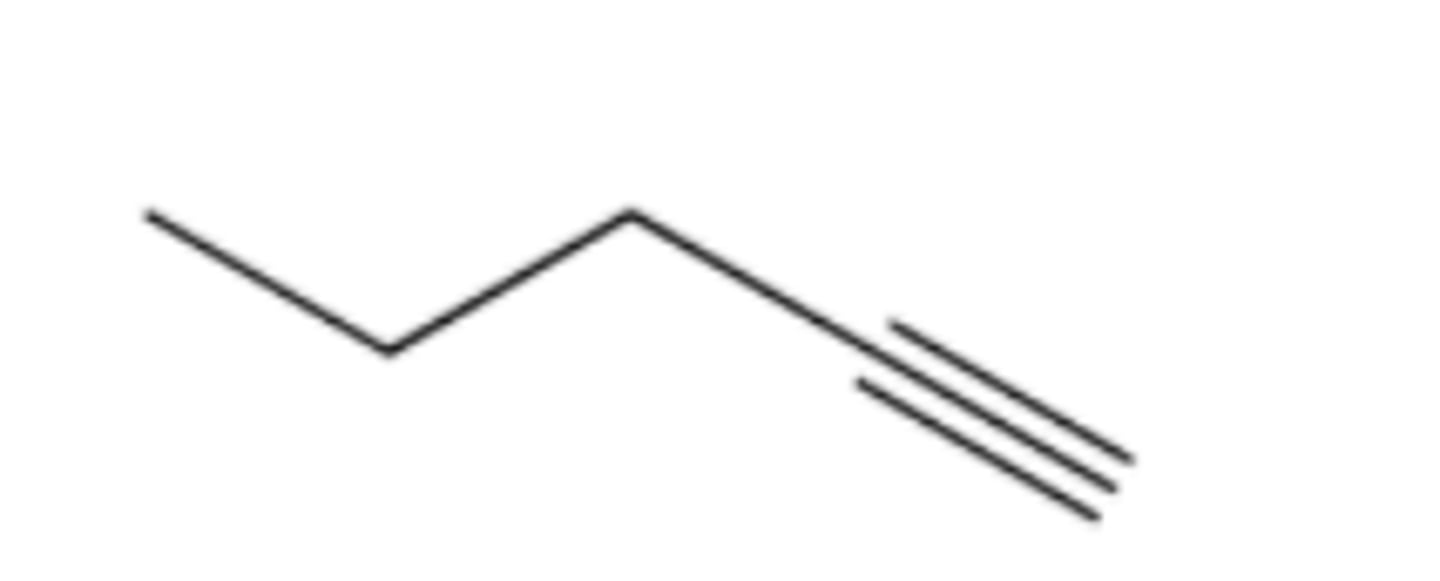
Provide the IUPAC name for each of the following alkynes: (see pic)
1-pentyne
Provide the IUPAC name for each of the following alkynes: (see pic)
2-pentyne
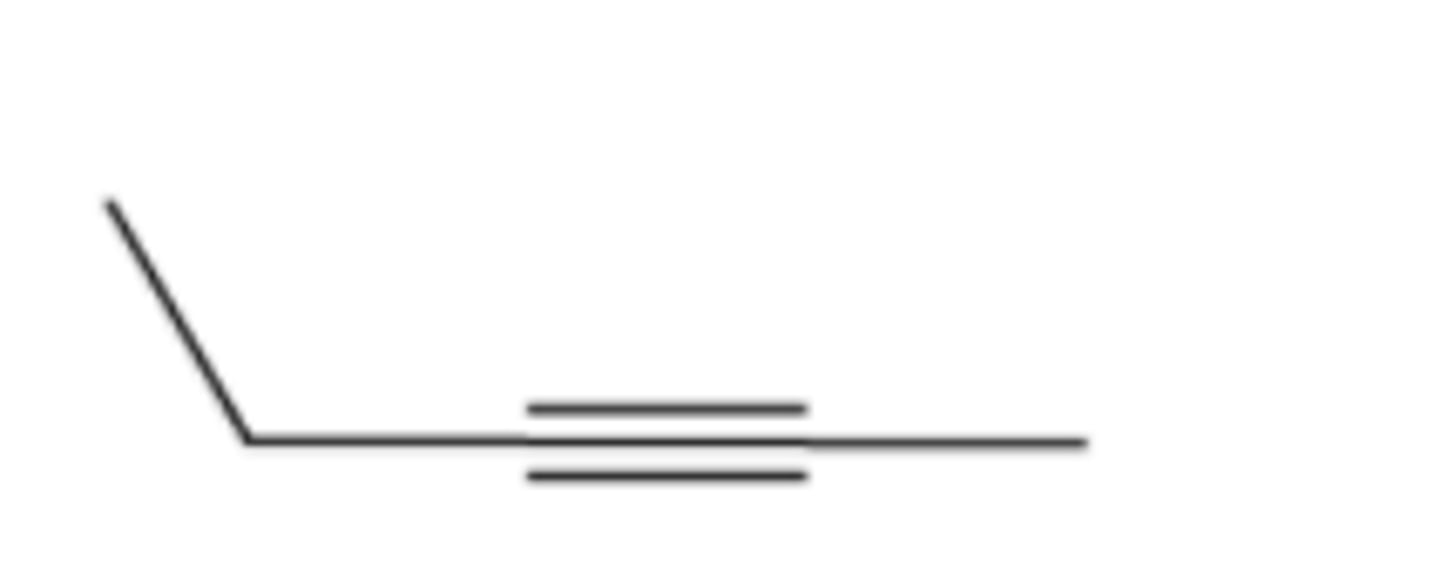
Provide the IUPAC name for each of the following alkynes: (see pic)
4,5-dimethyl-2-hexyne
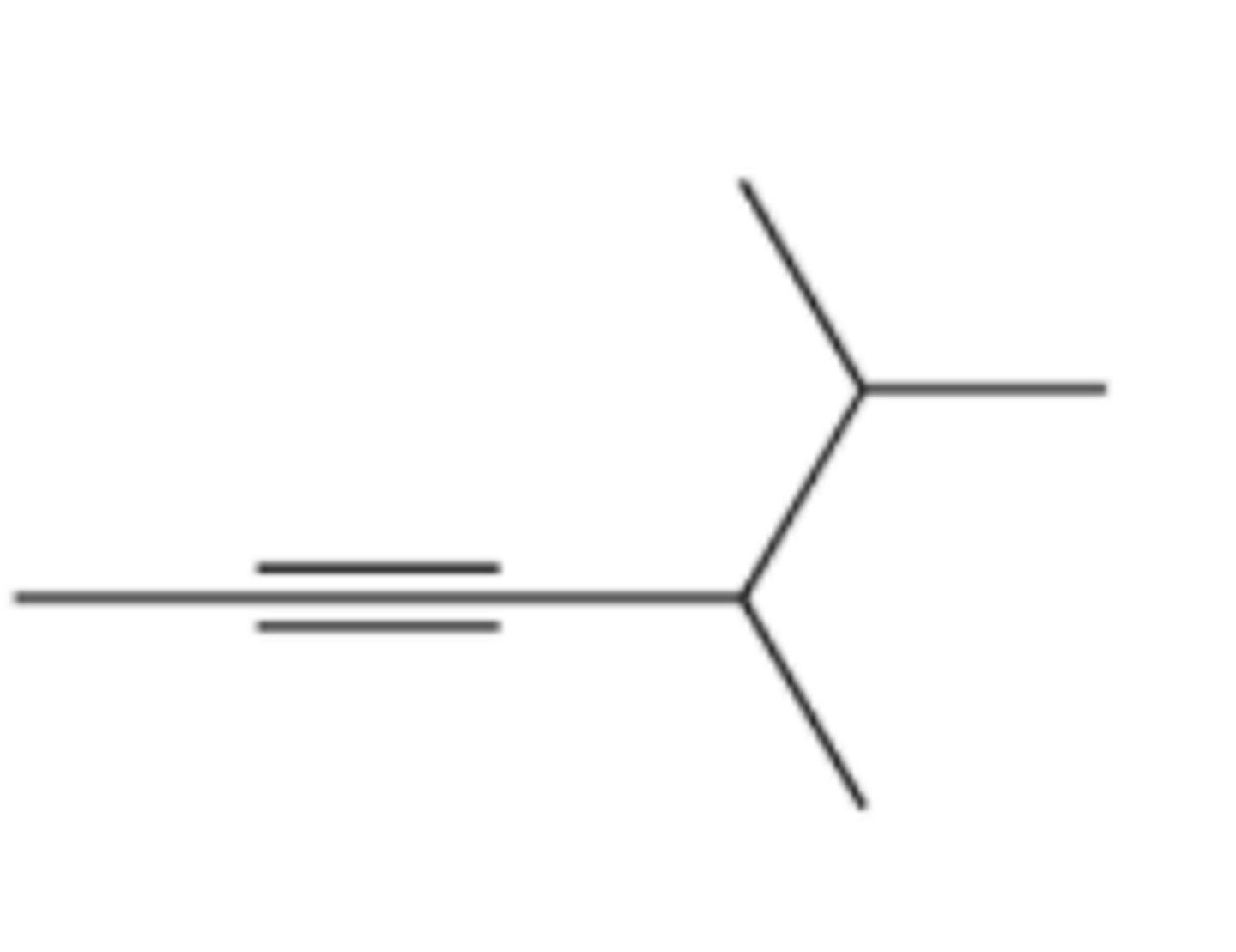
Provide the IUPAC name for each of the following alkynes: (see pic)
cyclotridecyne
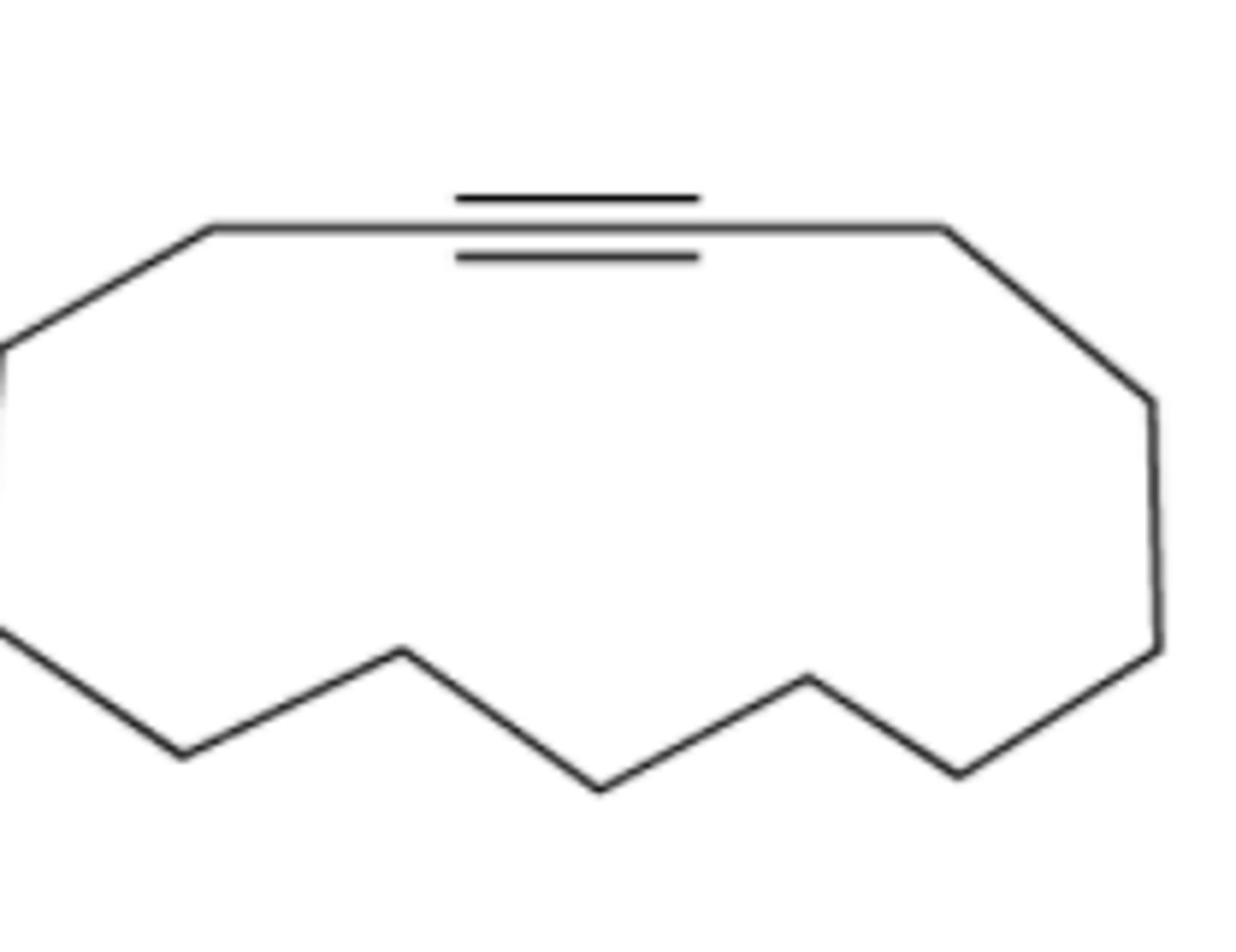
Provide the IUPAC name for each of the following alkynes: (see pic)
(f) 4-butyl-2-nonyne
(g) 2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-3-hexyne
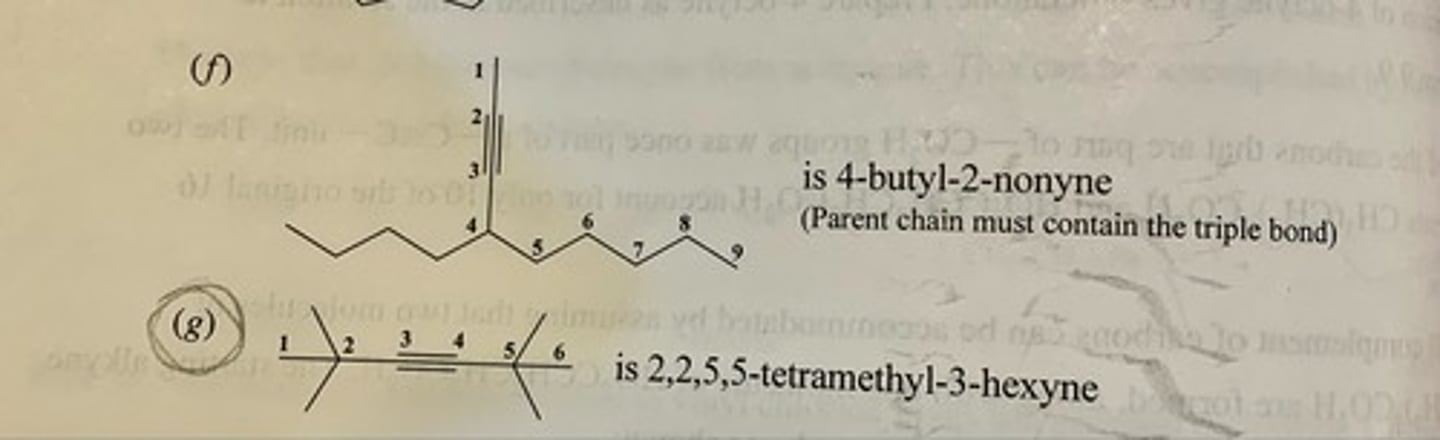
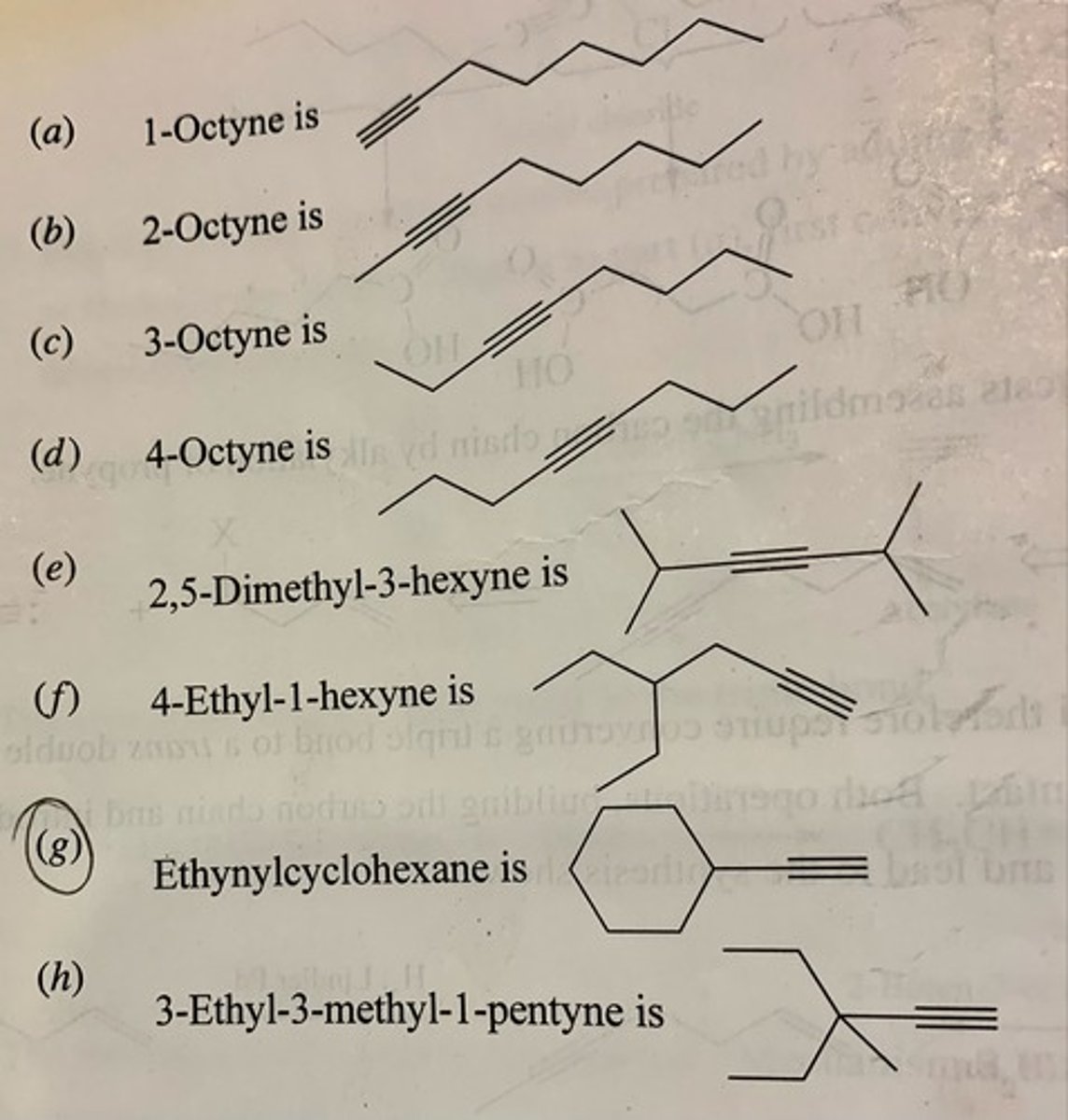
Write a structural formula for each of the following:
(a) 1-Octyne
(b) 2-Octyne
(c) 3-Octyne
(d) 4-Octyne
(e) 2,5-Dimethyl-3-hexyne
(f) 4-Ethyl-1-hexyne
(g) Ethynylcyclohexane
(h) 3-Ethyl-3-methyl-1-pentyne
which alkene has the highest heat of hydrogen
(a) 1-pentene
(b) trans-2-pentene
(c) cis-2-pentene
(d) 2-methyl-2-butene
(a) 1-pentene
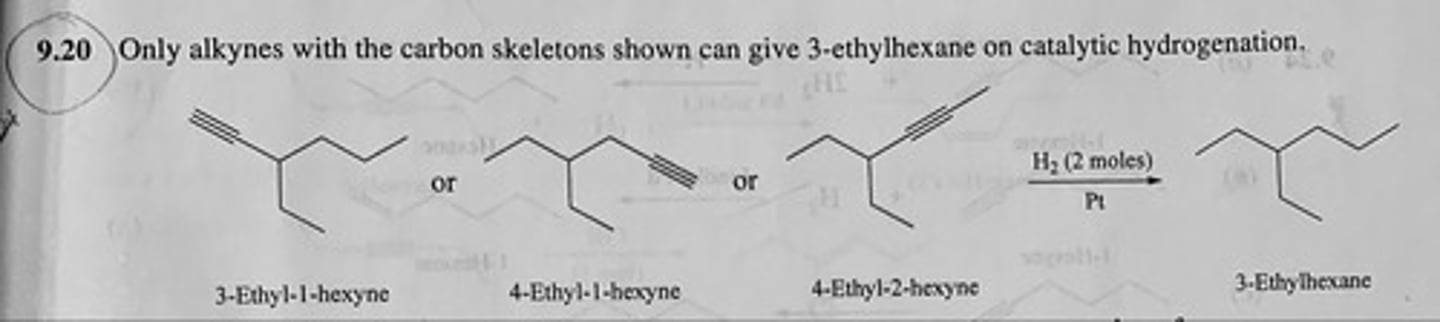
Write structural formulas for all the alkynes of molecular formula C8H14 that yield 3-ethylhexane on catalytic hydrogenation.
The alkane formed by hydrogenation of (S)-4-methyl-1-hexyne is optically active, but the one formed by hydrogenation of (S)-3-methyl-1-pentyne is not. Explain. Would you expect the products of hydrogenation of these two compounds in the presence of Lindlar palladium to be optically active?
The alkane formed by hydrogenation of (S)-3-methyl-1-pentyne is achiral and can not be optically active. The product of hydrogenation of (S)-4-methyl-1-hexyne is optically active because a chirality center is present in the starting material and is carried through to the product.
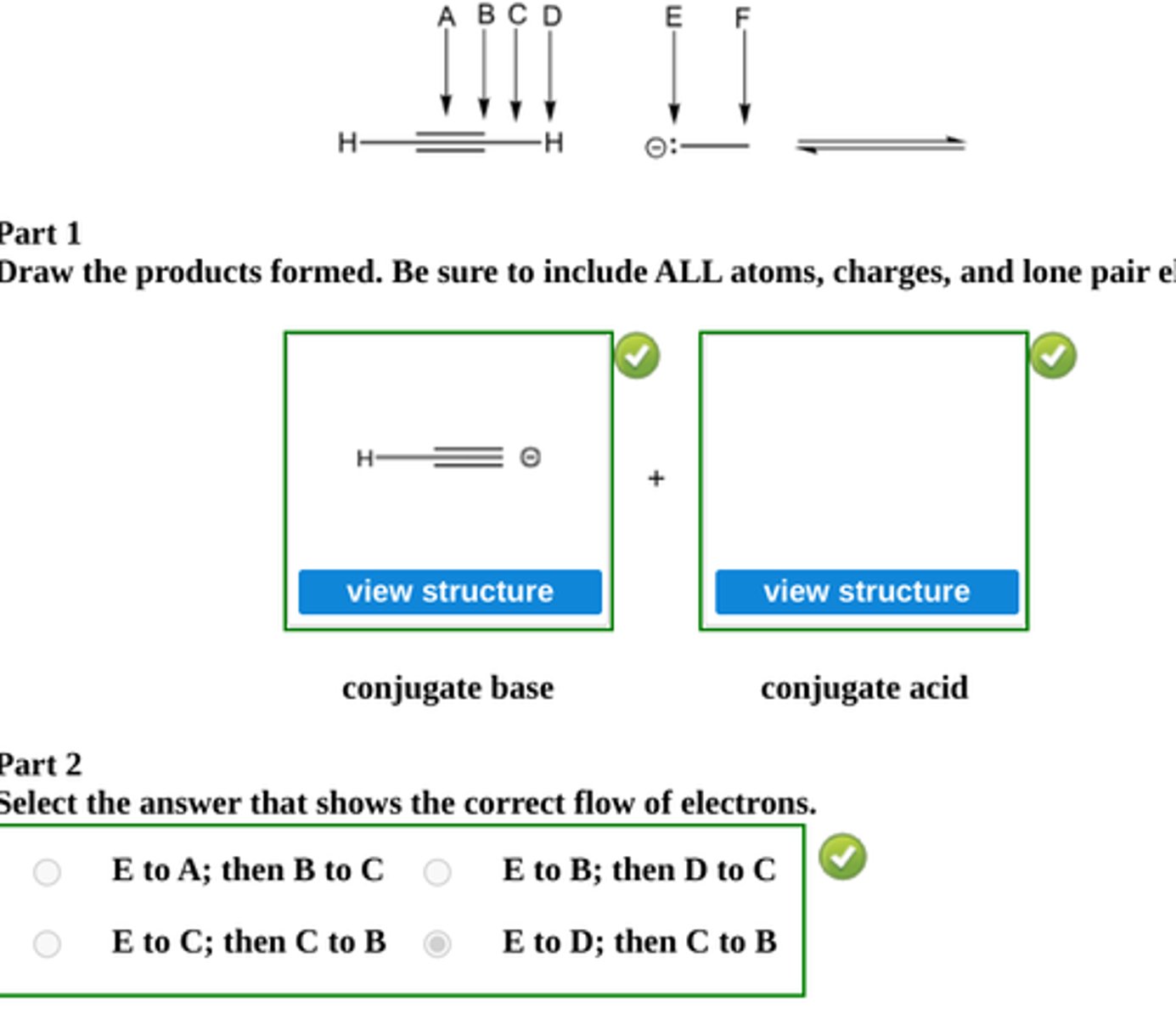
Draw the conjugate base and the conjugate acid formed by proton transfer between the indicated species below.
Then select a letter for electron flow, and state which direction equilibrium flows to. (see pic)
equilibrium lies to the right
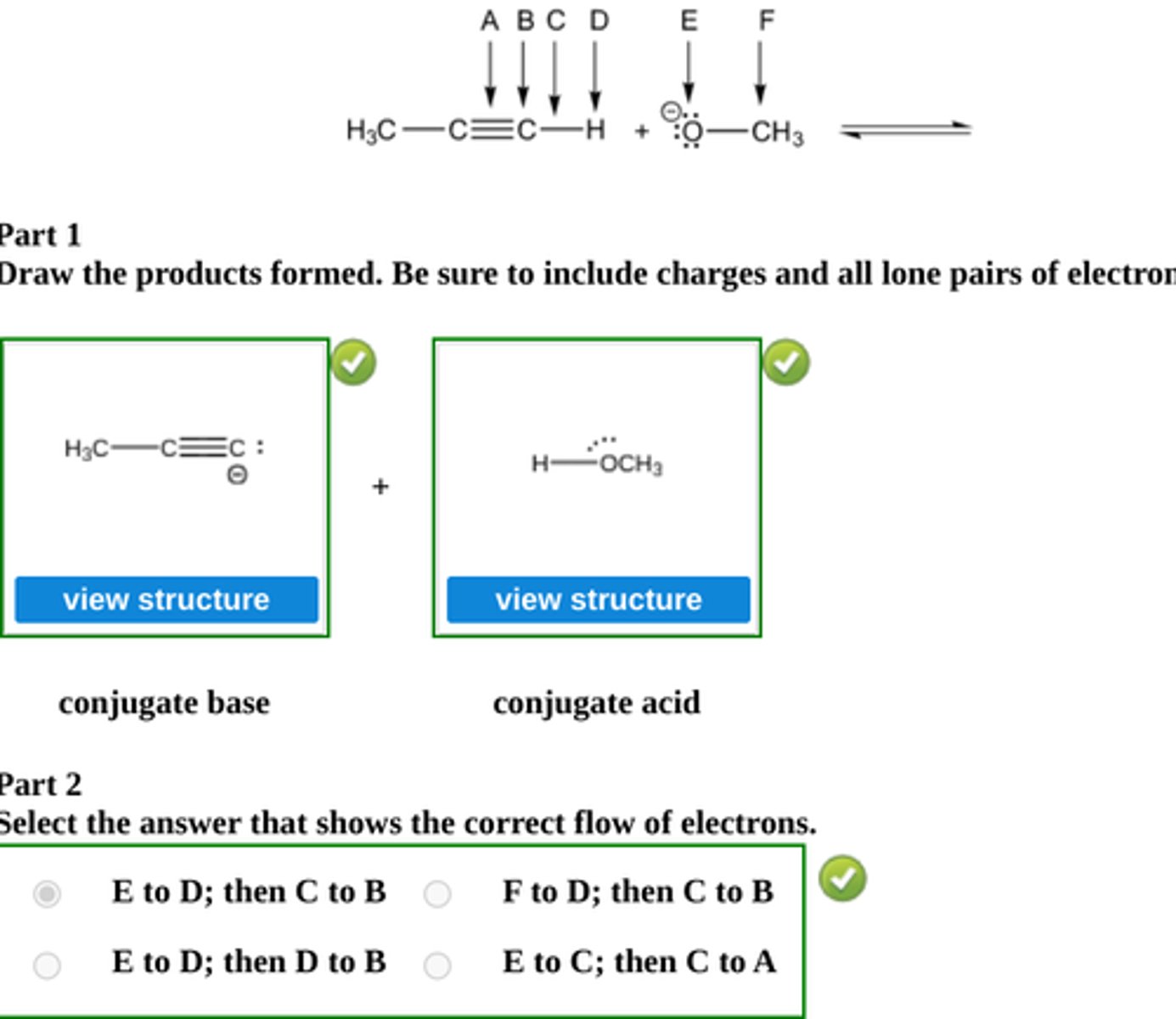
Draw the conjugate base and the conjugate acid formed by proton transfer between the indicated species below.
Then select a letter for electron flow, and state which direction equilibrium flows to. (see pic)
equilibrium lies to the left
Write the structure of the major organic product isolated from the reaction of 1-hexyne with:
(a) Hydrogen (2 mol), platinum
(b) Hydrogen (1 mol), Lindlar palladium
(c) Sodium amide in liquid ammonia
(d) Product in part (c) treated with 1-bromobutane
(e) Product in part (c) treated with tert-butyl bromide
(f) Hydrogen chloride (1 mol)
(g) Hydrogen chloride (2 mol)
(h) Chlorine (1 mol)
(i) Chlorine (2 mol)
(j) Aqueous sulfuric acid, mercury(II) sulfate
(a) Hexane
(b) 1-hexene
(c) sodium 1-hexynide
(d) 5-decyne
(e) 1-hexyne + 2-methylpropene
(f) 2-chloro-1-hexene
(g) 2,2-dichlorohexane
(h) (E)-1,2-Dichloro-1-hexene
(i) 1,1,2,2-tetrachlorohexane
(j) 2-hexanone
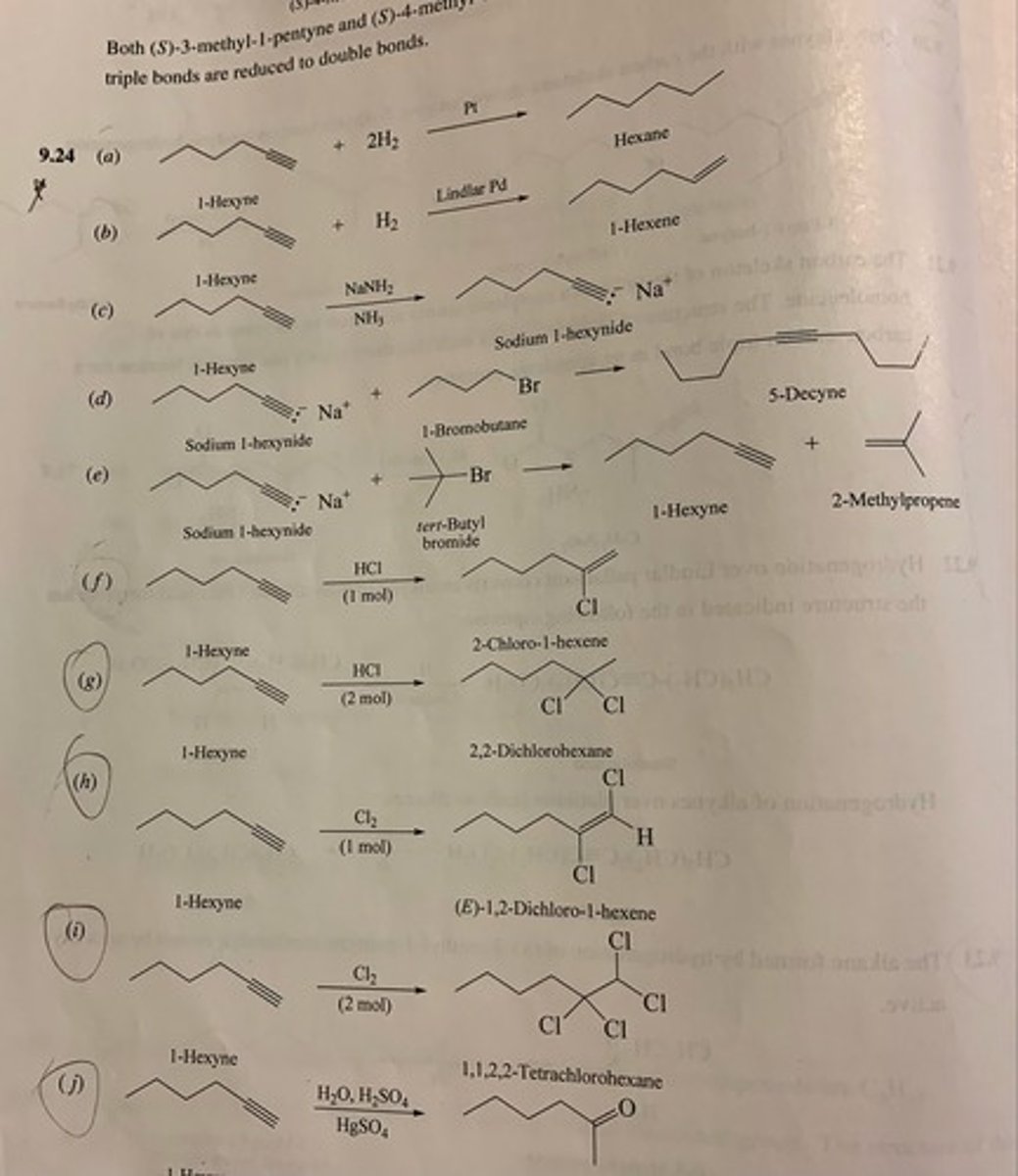
Write the structure of the major organic product isolated from the reaction of 1-hexyne with:
(k) Ozone followed by hydrolysis
(k) pentanoic acid + carbonic acid
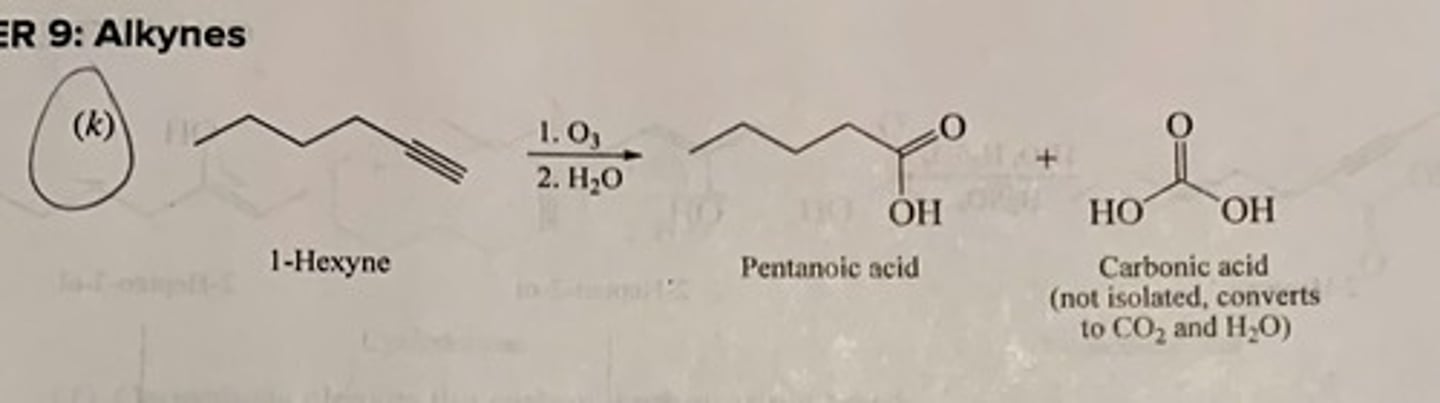
Write the structure of the major organic product isolated from the reaction of 3-hexyne with:
(a) Hydrogen (2 mol), platinum
(b) Hydrogen (1 mol), Lindlar palladium
(c) Hydrogen chloride (1 mol)
(d) Hydrogen chloride (2 mol)
(e) Chlorine (1 mol)
(f) Chlorine (2 mol)
(g) Aqueous sulfuric acid, mercury(II) sulfate
(h) Ozone followed by hydrolysis
(a) Hexane
(b) (Z)-3-hexene
(c) (Z)-3-chloro-3-hexene
(d) 3,3-dichlorohexane
(e) (E)-3,4-dichloro-3-hexene
(f) 3,3,4,4-tetrachlorohexane
(g) 3-hexanone
(h) propanoic acid
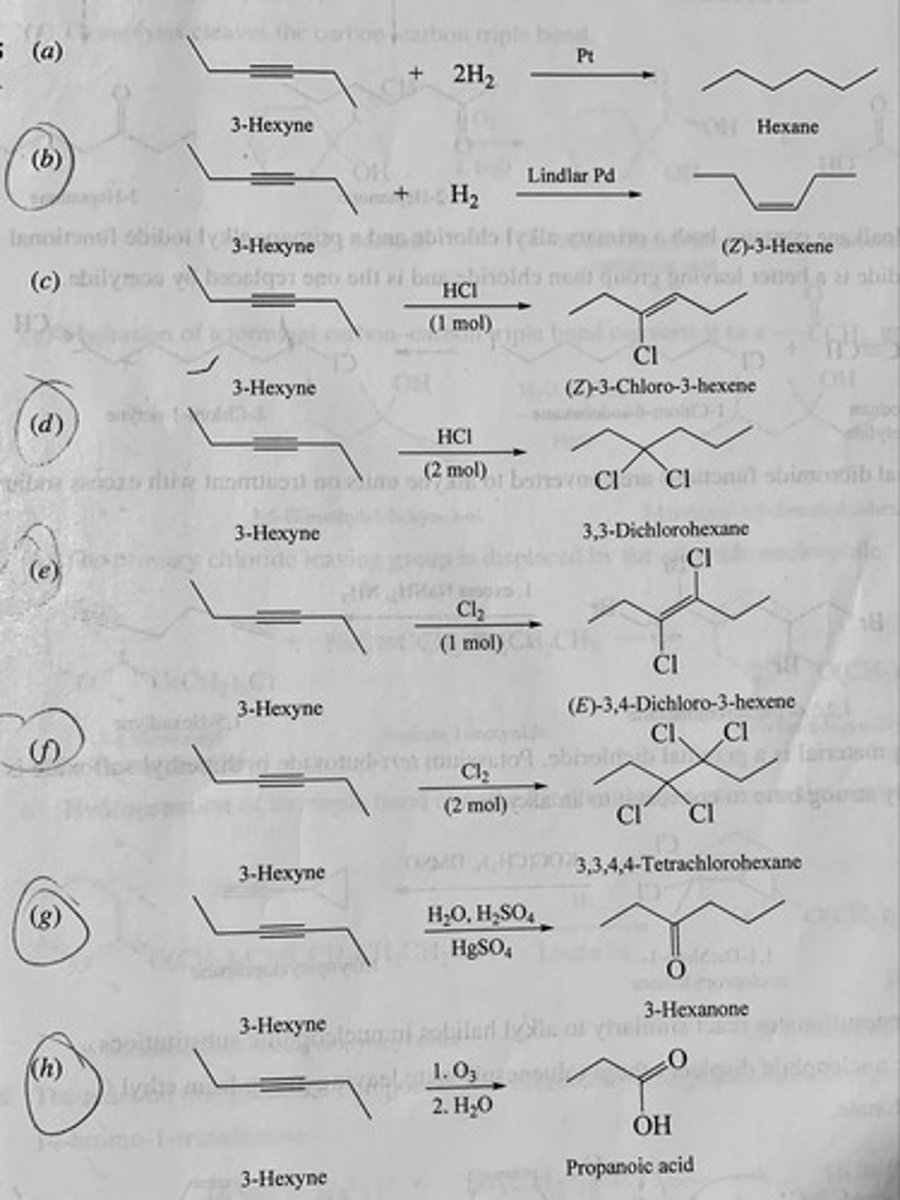
When 1,2-dibromodecane was treated with potassium hydroxide in aqueous ethanol, it yielded a mixture of three isomeric compounds of molecular formula C10H19Br. Each of these compounds was converted to 1-decyne on reaction with sodium amide in dimethyl sulfoxide. Identify these three compounds.
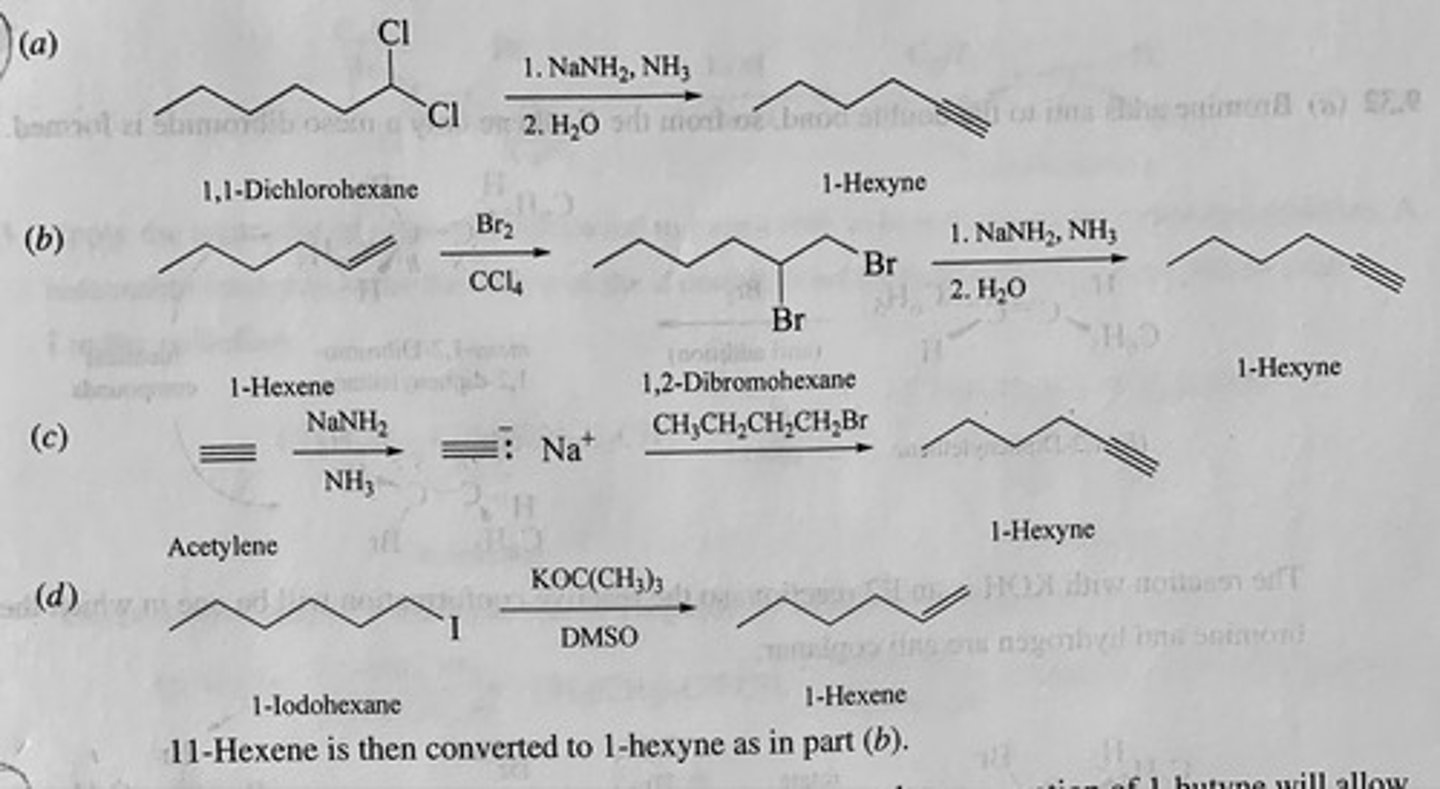
Show by writing appropriate chemical equations how each of the following compounds could be converted to 1-hexyne:
(a) 1,1-Dichlorohexane
(b) 1-Hexene
(c) Acetylene
(d) 1-Iodohexane
Show by writing appropriate chemical equations how each of the following compounds could be converted to 3-hexyne:
(a) 1-Butene
(b) 1,1-Dichlorobutane
(c) Acetylene

Draw the major organic product (see pic)
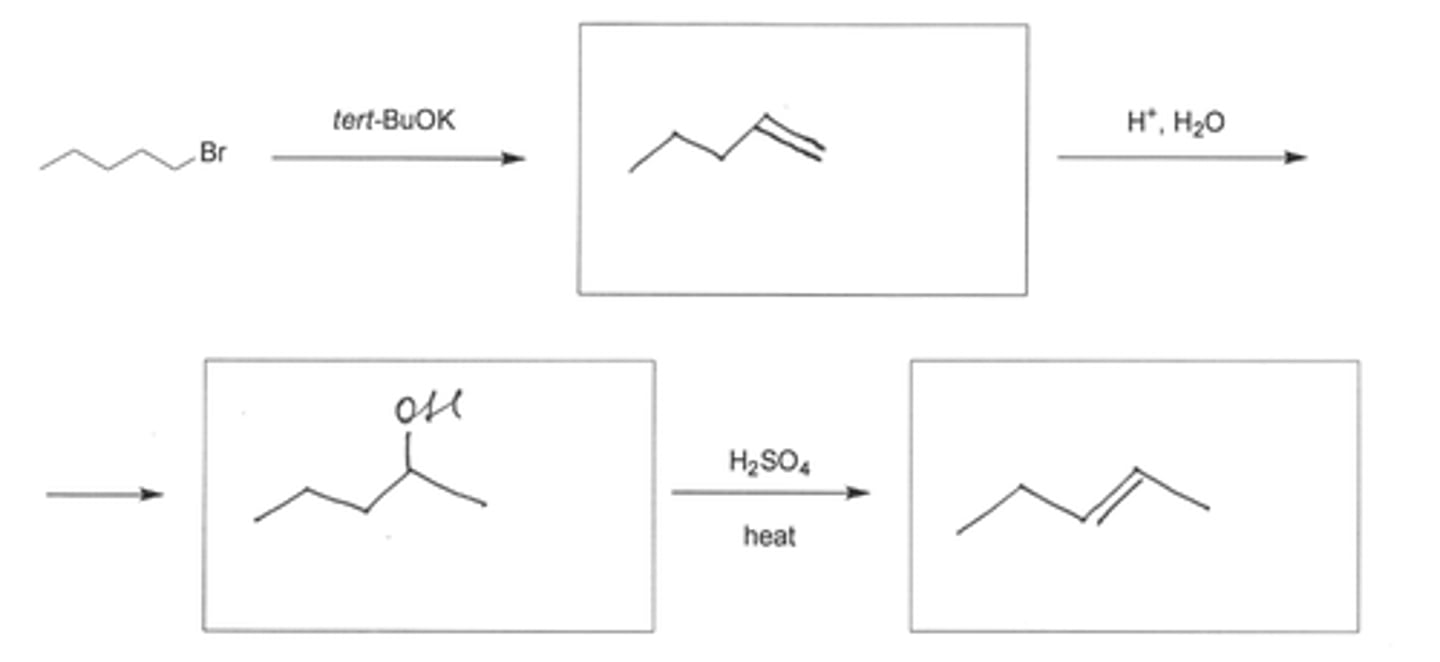
Draw the major organic product (see pic)
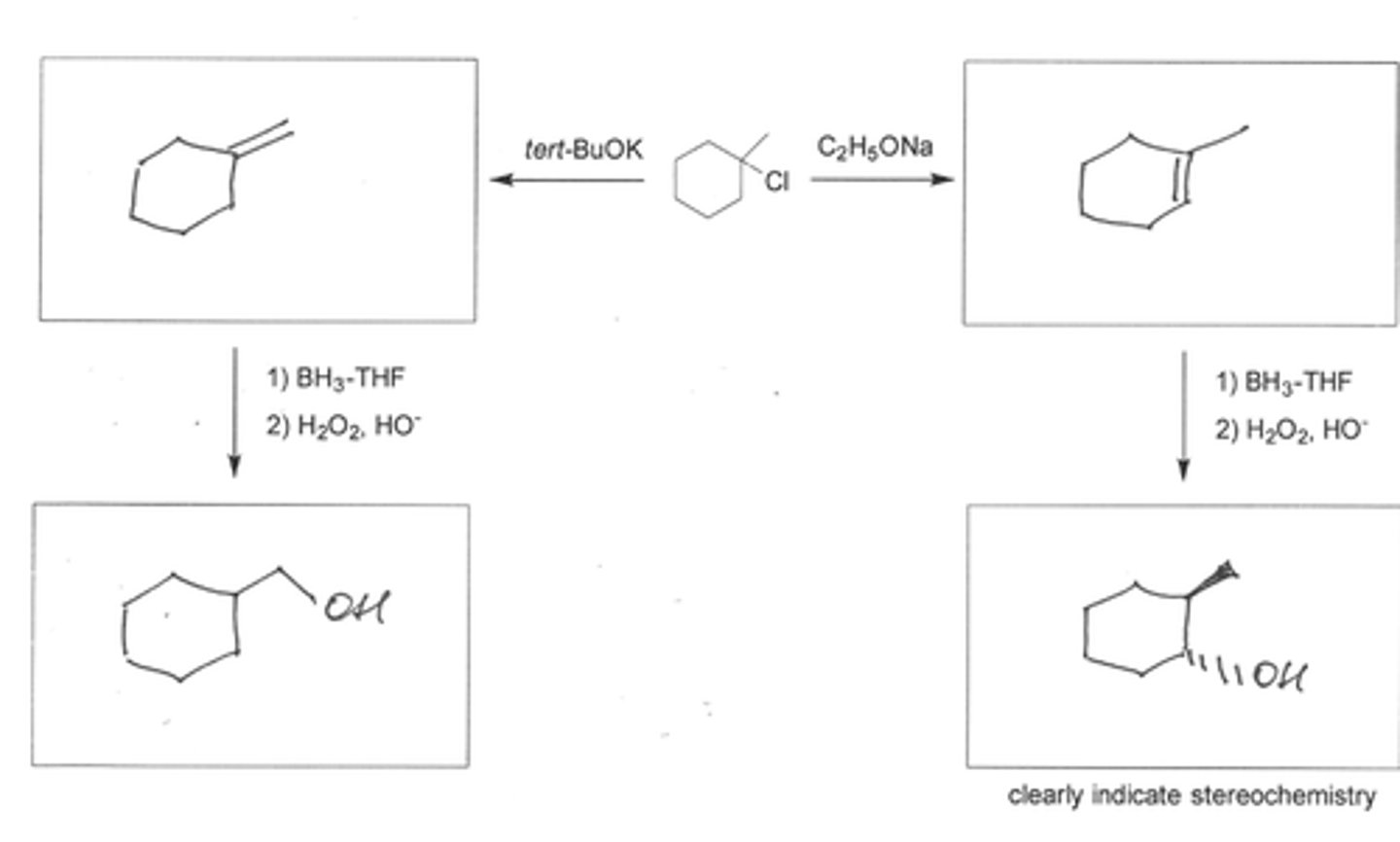
Draw the major organic product (see pic)
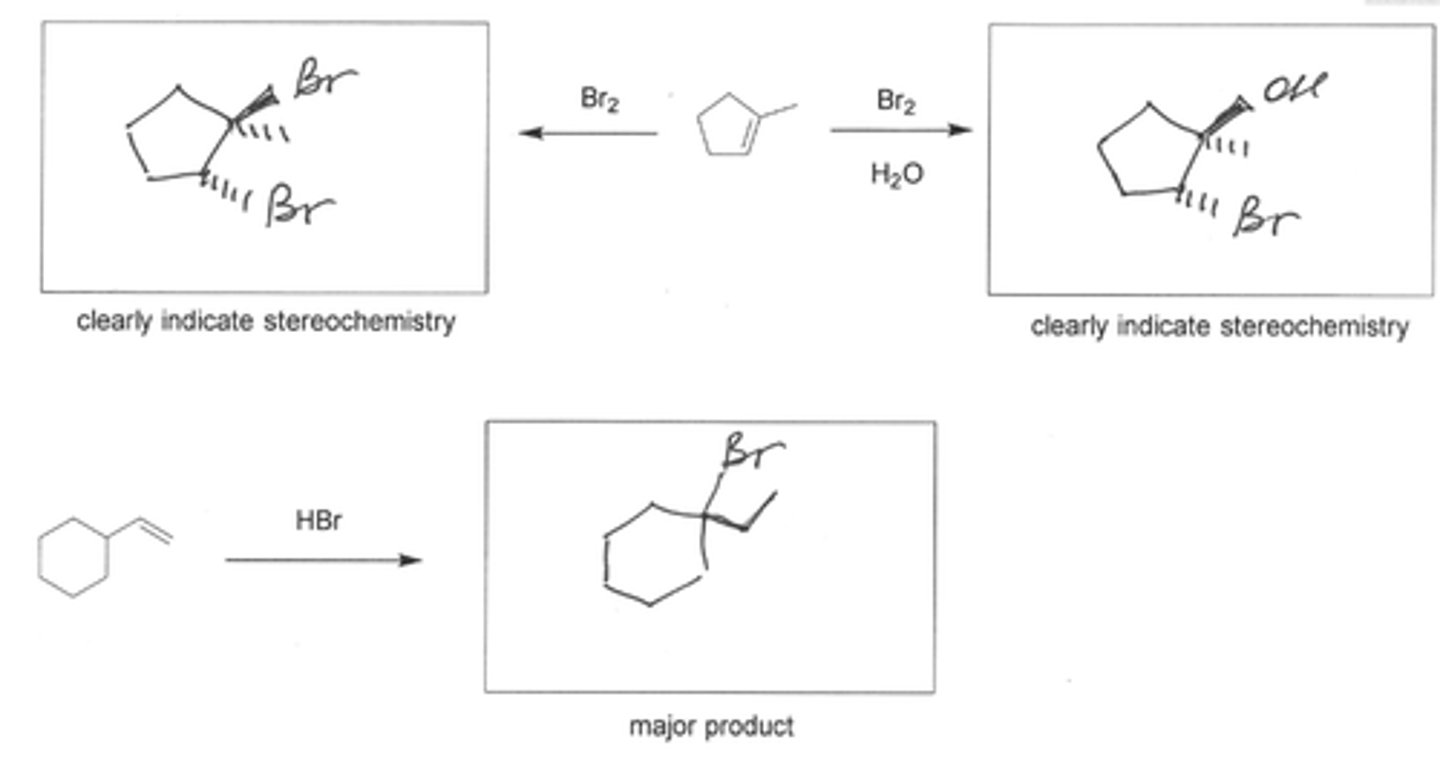
Do the stepwise detailed arrow pushing (see pic)
What is the correct order of decreasing acidity (see pic)
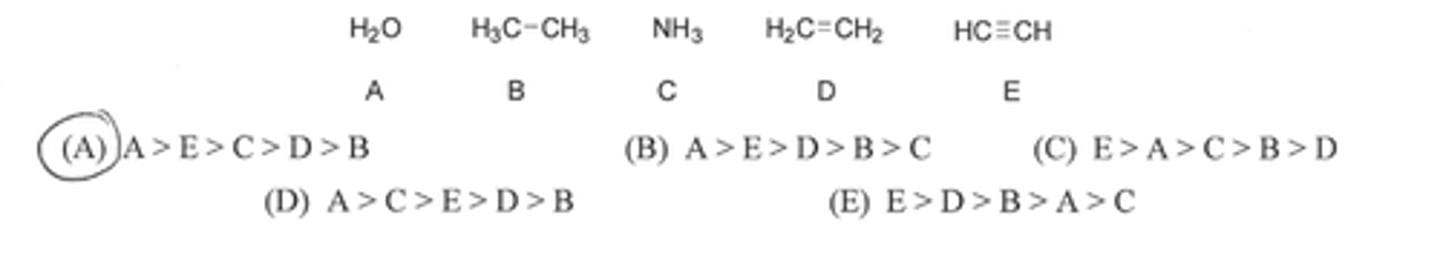
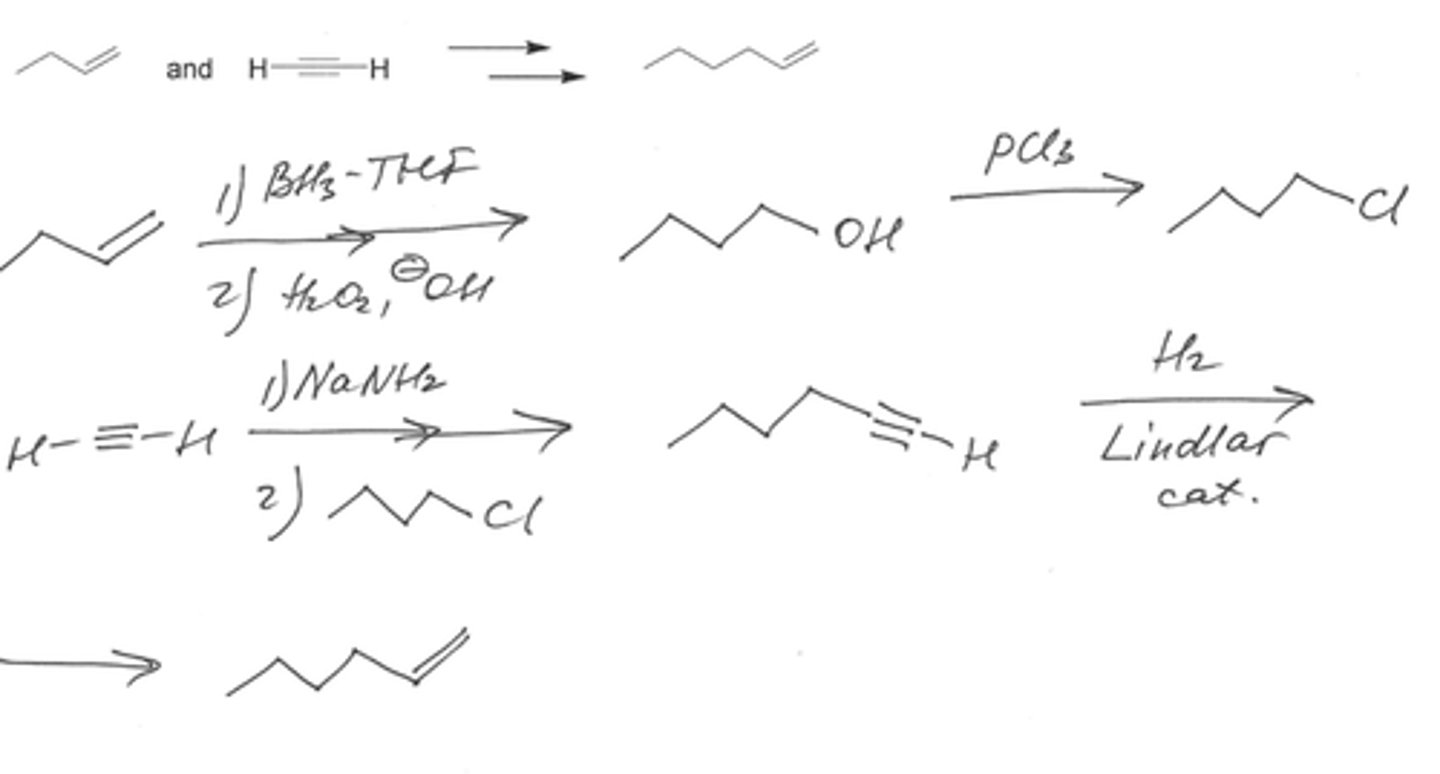
complete the synthesis (see pic)
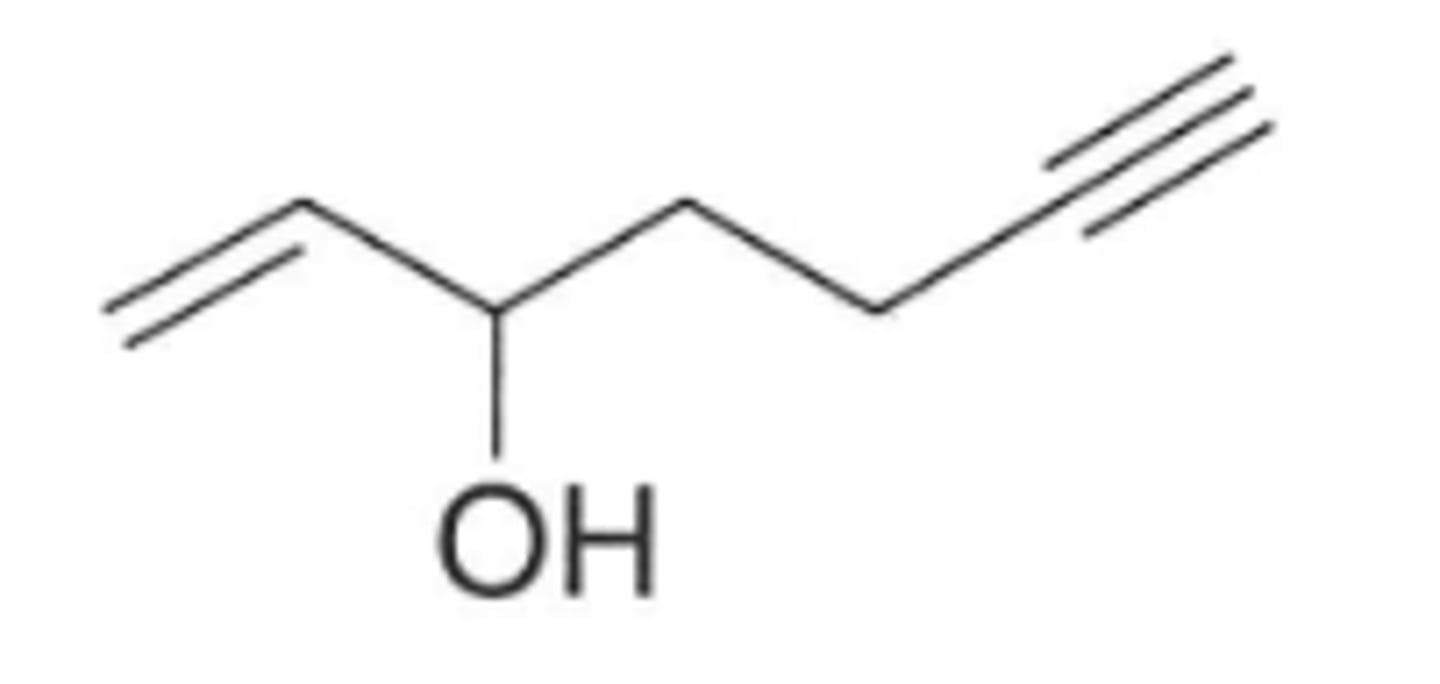
Give the IUPAC name for this structure (see pic)
Hept-1-en-6-yn-3-ol
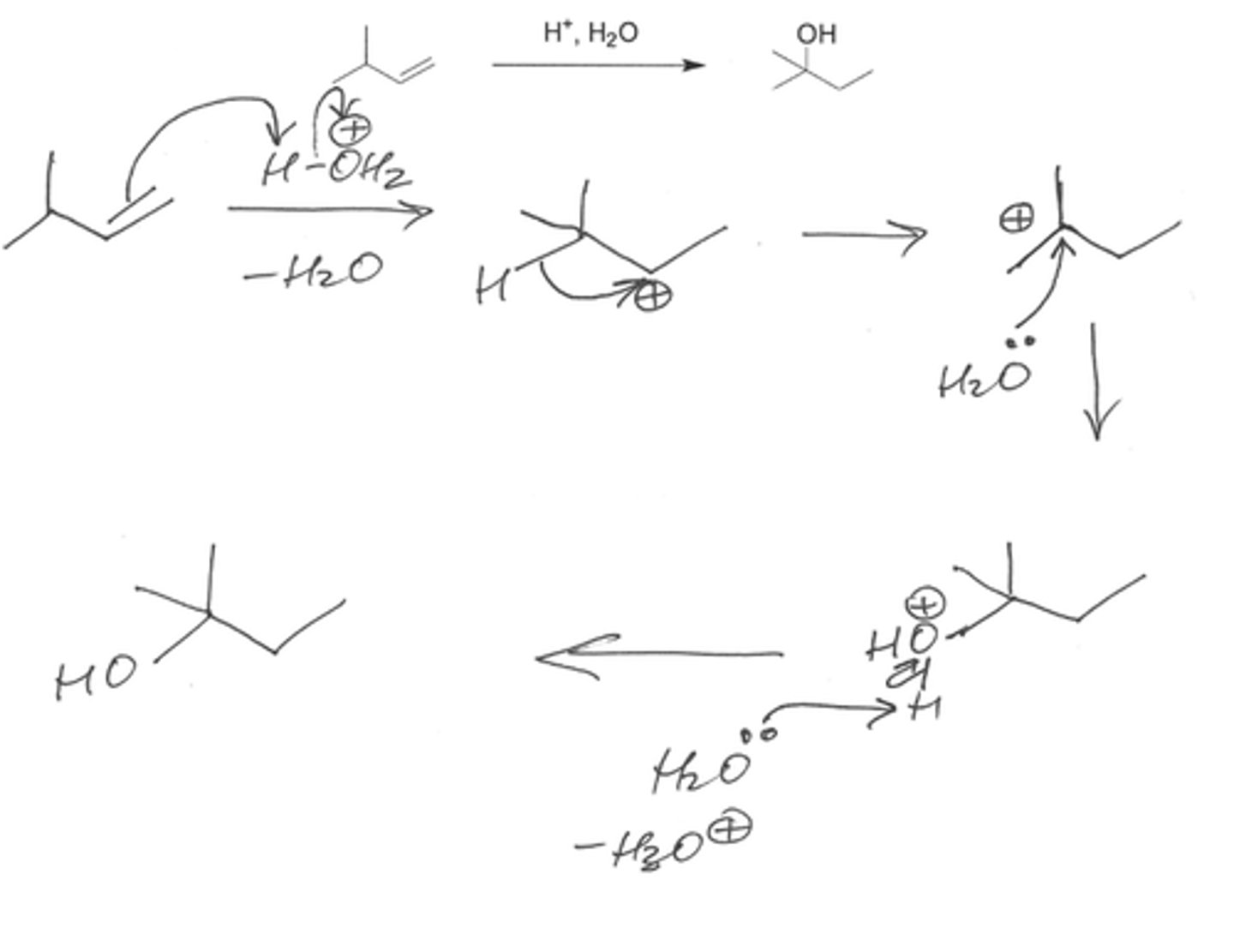
What is the slow rate determining step of the acid catalyzed dehydration of tert-butyl alcohol?
The loss of water from an oxonium ion to form a carbocation
What are the most likely mechanisms for the reaction of 3-iodohexane with sodium ethoxide?
Sn2 and E2
The higher acidity of acetelyne as compared to ethylene can be mainly attributed to what?
The higher electronegativity of an sp carbon as compared to an sp2 carbon
The ratio of substitution to elimination is exactly the same (26% elimination) for 2-bromo-2-methylbutane and 2-iodo-2-methylbutane in 80% aqueous ethanol. By what mechanism does this probably occur by?
Sn1 and E1
Show by writing a suitable series of equations how you could prepare each of the following compounds from the designated starting materials and any necessary organic or inorganic reagents:
(a) 2,2-Dibromopropane from 1,1-dibromopropane
(b) 2,2-Dibromopropane from 1,2-dibromopropane
(c) 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloropropane from 1,2-dichloropropane
(a) NaNH2,NH3/H2O
(b) NaNH2,NH3/H2O and 2HBr
(c) NaNH2, NH3/H2O and 2Cl2
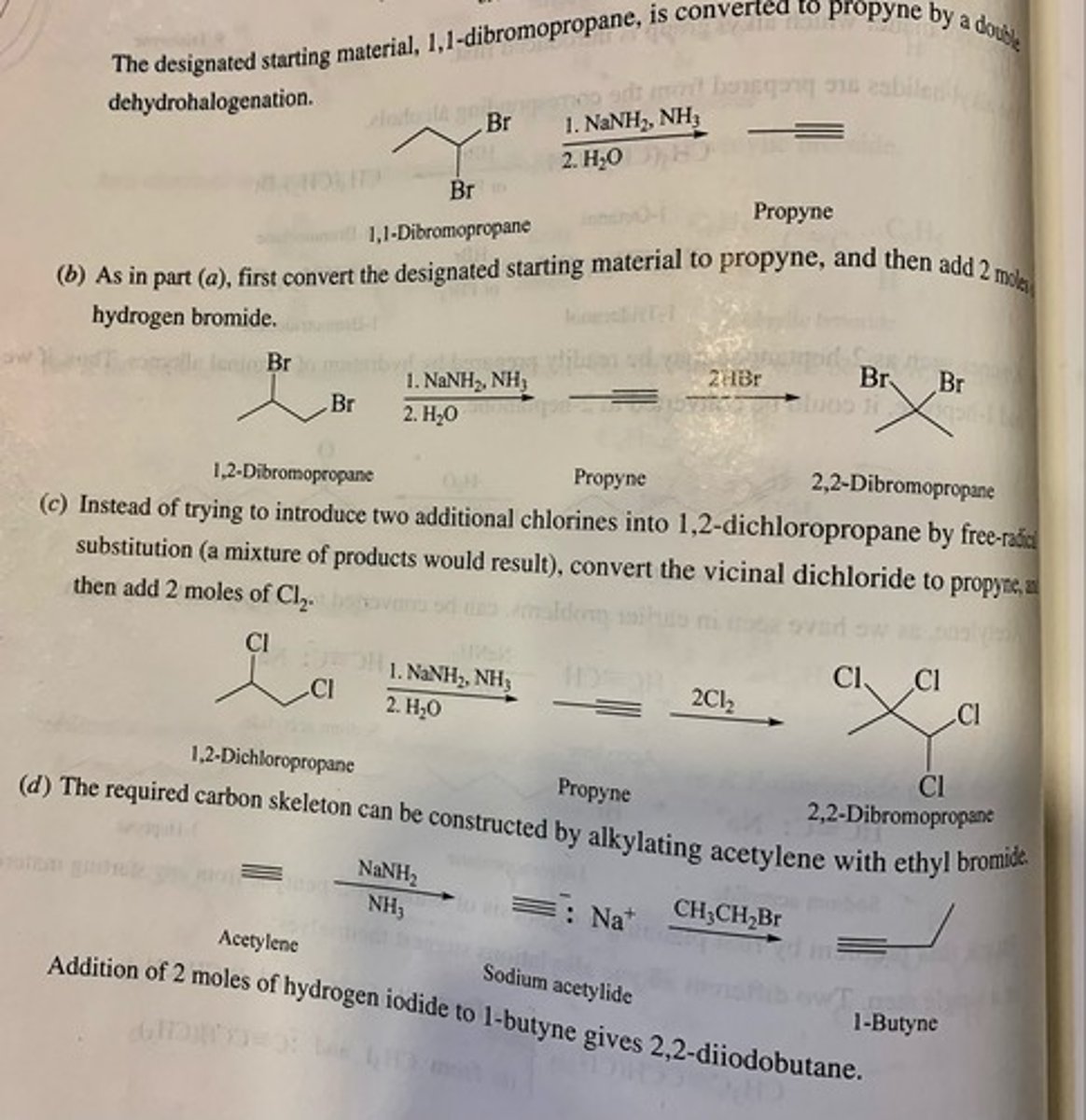
Give the IUPAC name for this structure (see pic)
How many isomeric alkenes with the formula C5H10, including stereoisomers, are possible?
6
What will be the major organic product formed upon heating 2-methylcyclopentanol with H2SO4?
1-methylcyclopentene
Rank the following alkenes in the order of increasing stability (from the least stable to the most stable):
(1) 1-hexene;
(2) trans-3-hexene;
(3) cis-3-hexene;
(4) 2-methyl-2-pentene
1,3,2,4
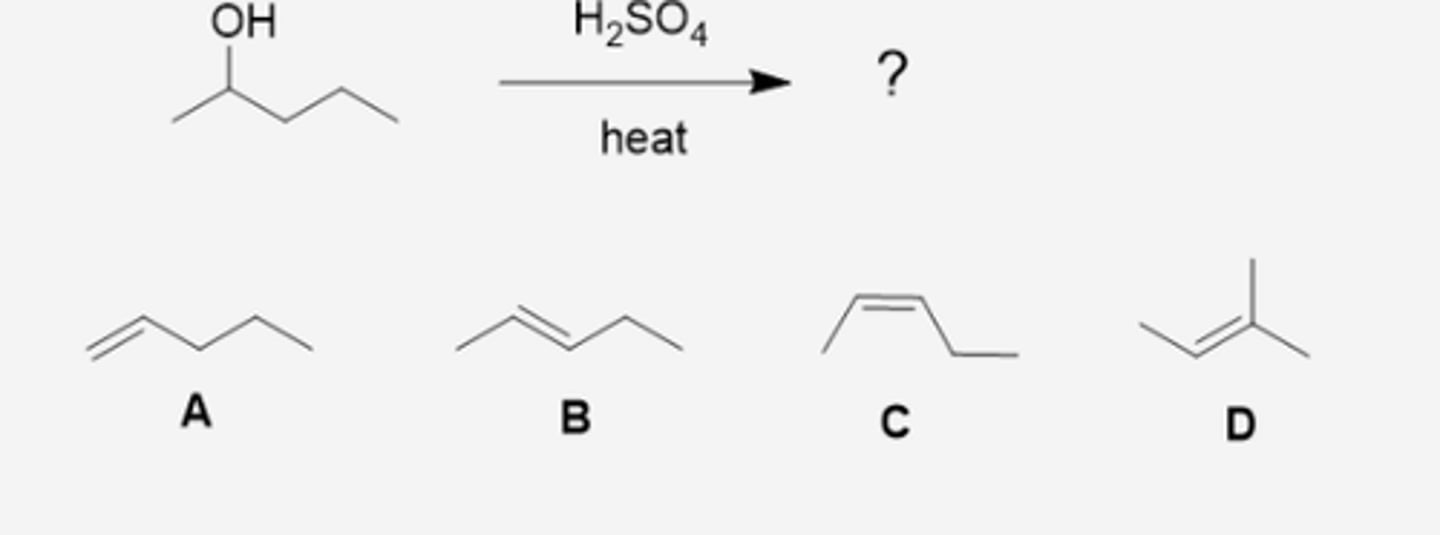
What will be the major organic product when 2-pentanol is heated with H2SO4? (see pic)
A
What is the slow, rate-determining step in the acid-catalyzed dehydration of tert-butyl alcohol?
Loss of water from the oxonium ion to form a carbocation.
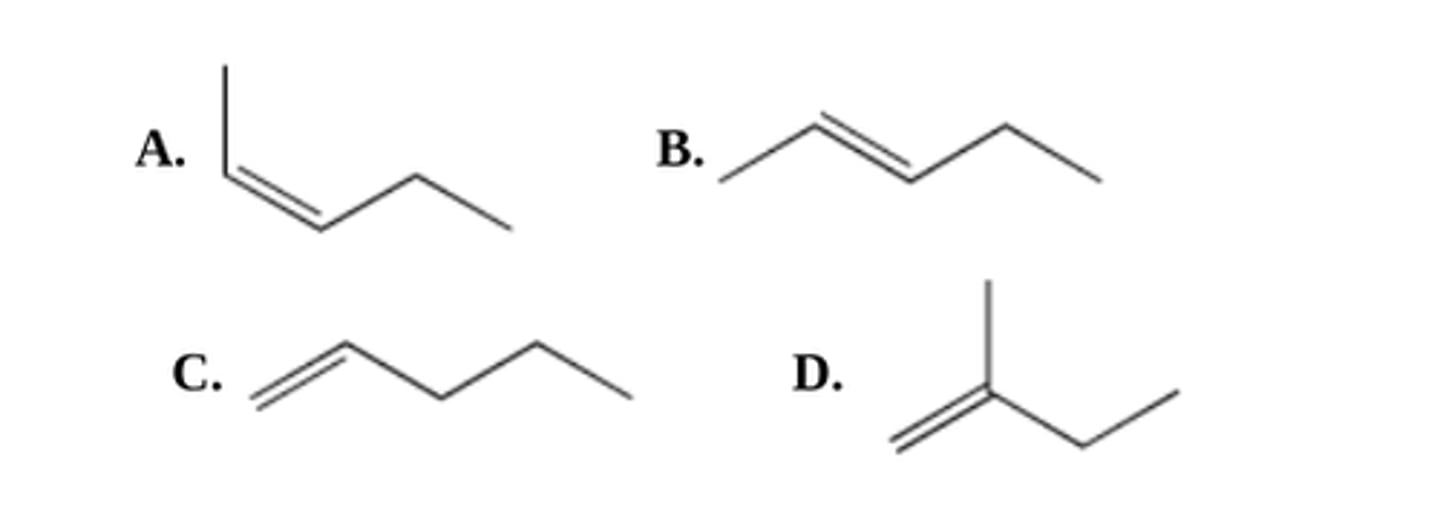
Which of these compounds would give a single E2 elimination product upon reaction with sodium ethoxide in ethanol? (see pic)
1 and 3
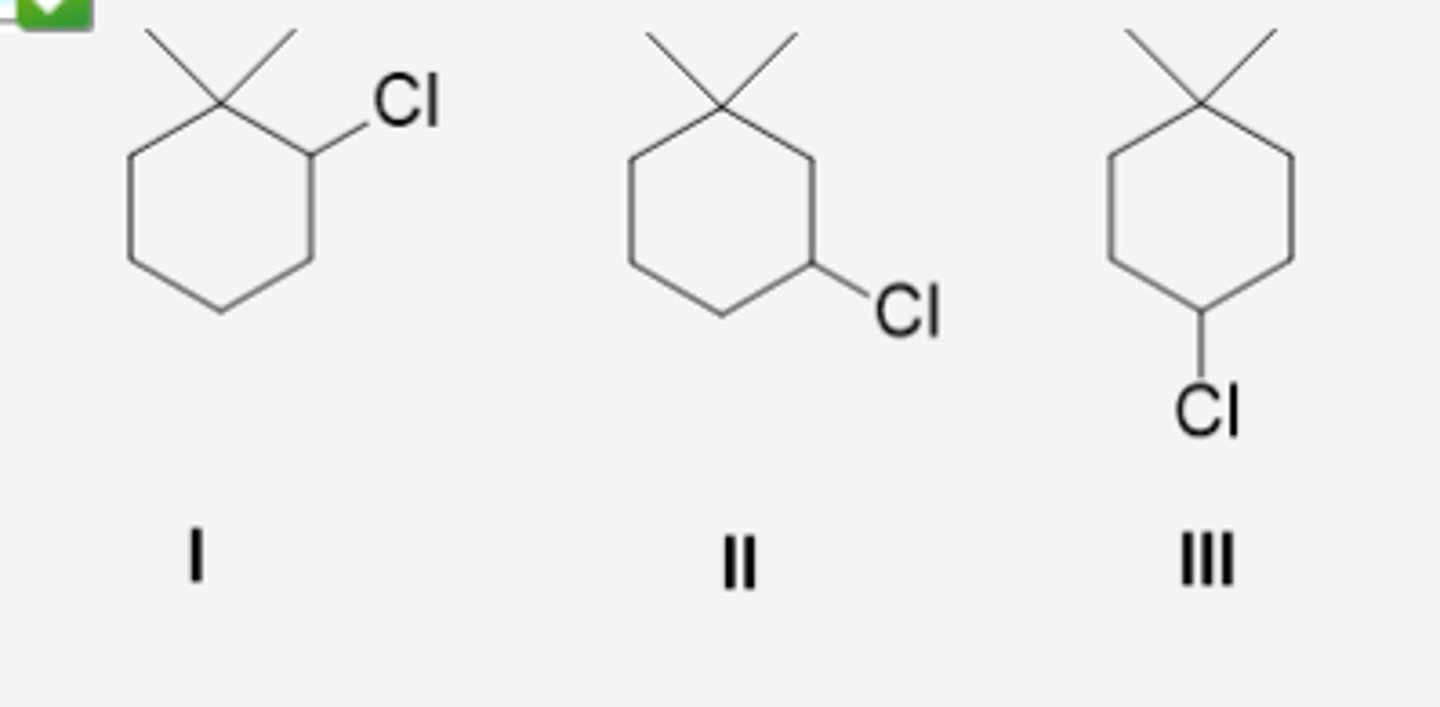
Which of the compounds below cannot undergo an E2 elimination reaction? (see pic)
only 1
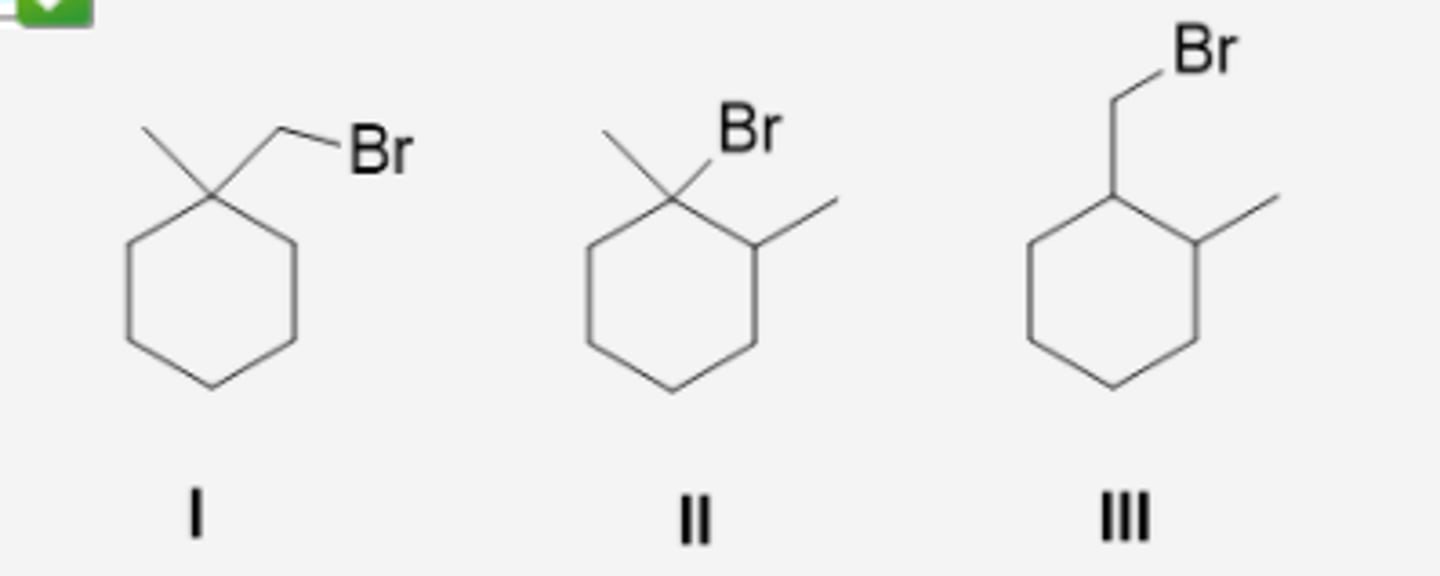
What would be the best method to accomplish this synthetic transformation? (see pic)
PBr3/tert-BuOK
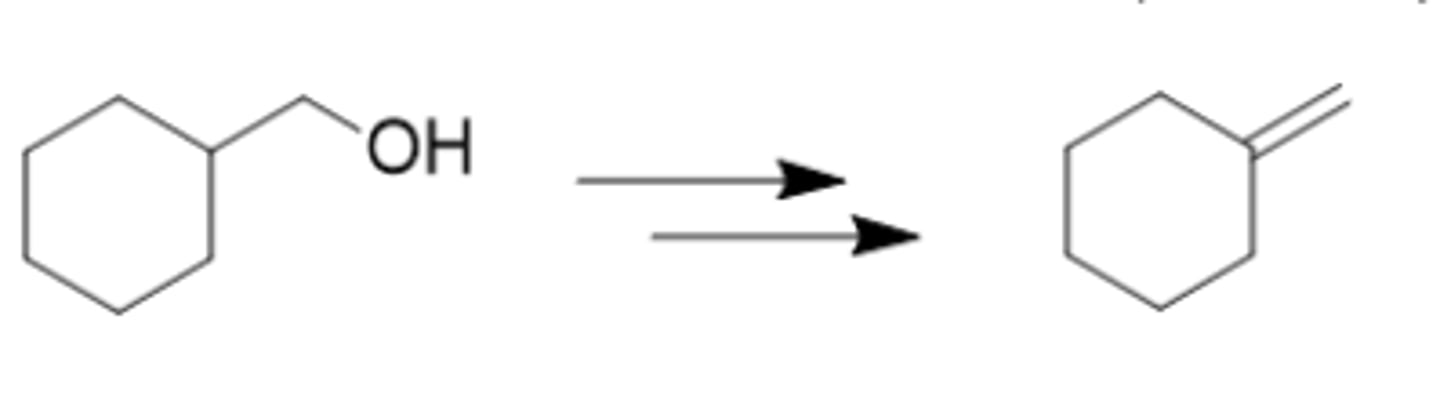
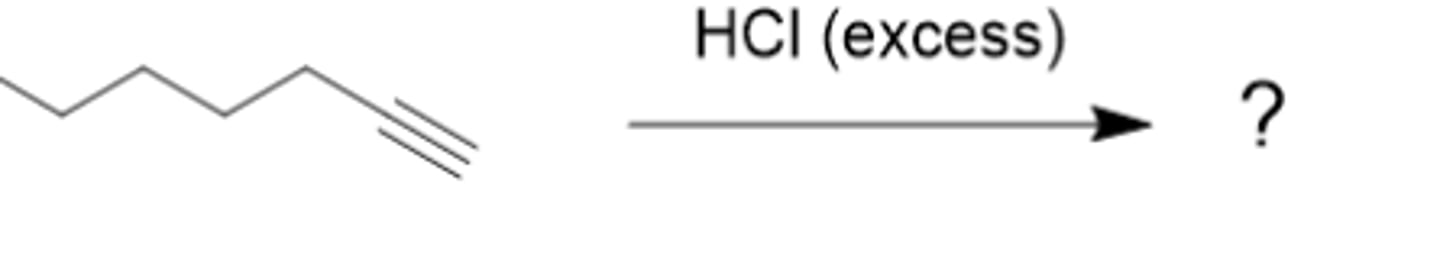
What is the major organic product in this reaction? Type its systematic IUPAC name. (see pic)
2-methyl-2-hexene
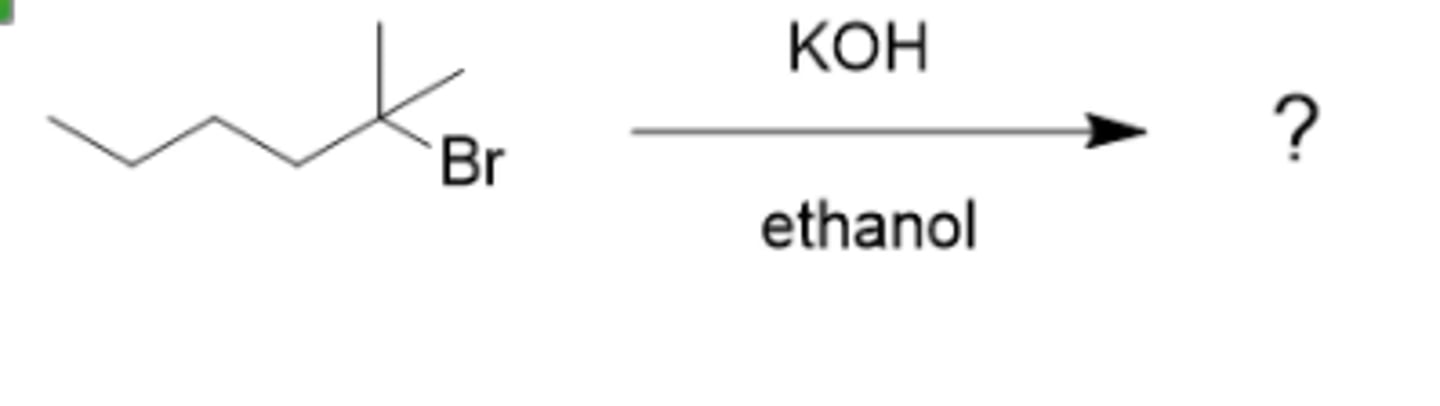
Predict the two most likely mechanisms for the reaction of 3-iodohexane with sodium ethoxide.
Sn2 and E2
Which process is not possible for a carbocation?
addition of a proton to form an alkane
What would be the best method for converting 2-methyl-2-heptene to 2-methyl-2-heptanol?
dilute H2SO4
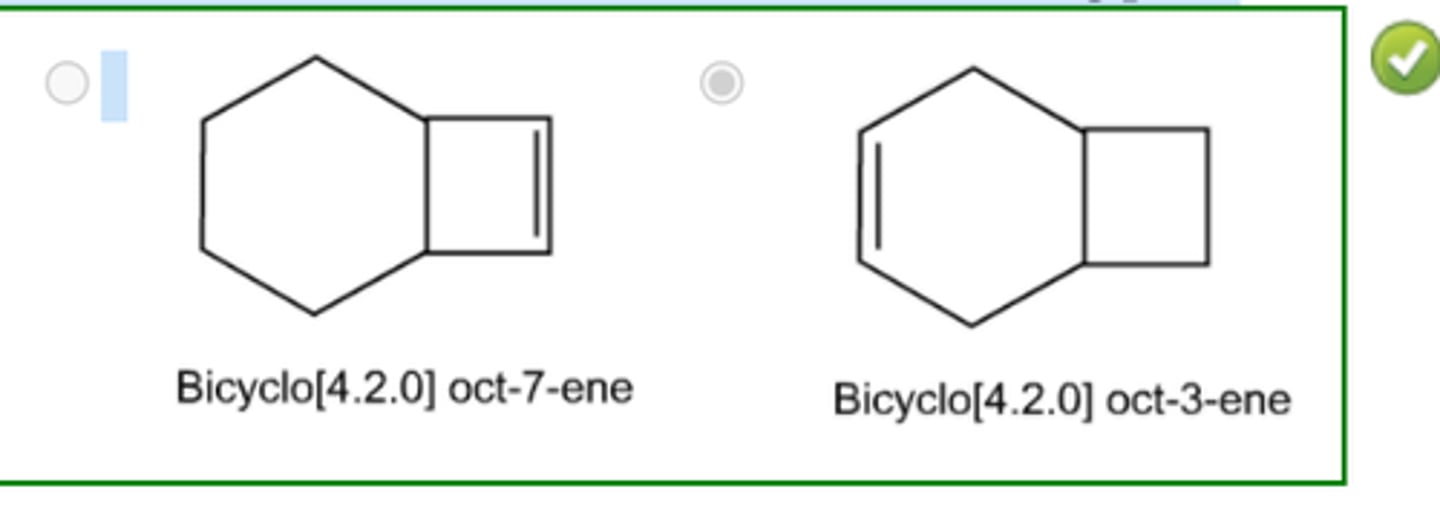
Which alcohol cannot be prepared using hydroboration-oxidation of an alkene? (see pic)
3
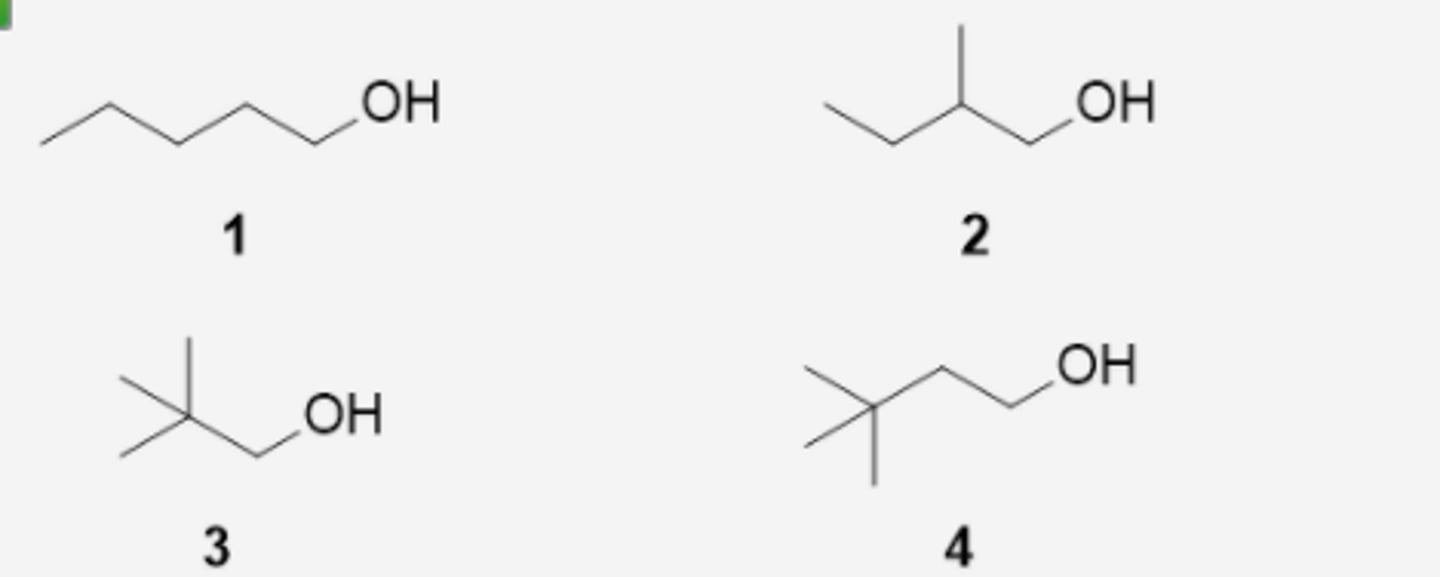
Which reaction sequence would be the best method to convert 3-pentanol to 2,3-dibromopentane?
1) H2SO4, heat; 2) Br2
What is the major organic product of this reaction? Type its systematic IUPAC name (see pic)
2,2-dichloroheptane