L2: Noncovalent Interactions
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Intramolecular Force
Hold together the atoms making up a molecule. Strong interaction within the molecule.
Examples of Intramolecular Forces
Covalent bonds and ionic bonds
Intermolecular Force
Attraction or repulsion between neighboring particles (atoms, molecules or ions). Weaker than intramolecular force
Examples of Intermolecular Forces
ion-dipole, dipole-dipole interaction, hydrogen-bonding, van der Waals forces
substrate is to enzyme what receptor is to _______
ligand
what do ligands transmit
signals
Which bonds range from 150-400 kJ and are most biologically important
covalent
Biologically important noncovalent bonds are roughly
10 to 100 times weaker
noncovalent bonds being weaker allows
them to be continually broken and re-formed
interplay depends on
rapid exchanges of molecular partners
various noncovalent interactions are individually weak, but when many are present
their energies can sum to a total that is often several hundreds of kilojoules. This amount of energy is sufficient to provide stability to macromolecular structures
The variation in the dependence of bond energy on distance predicts that charge–charge interactions
are stronger over much longer distances than are van der Waals
interactions
All noncovalent interactions are _______ in nature;
electrostatic
The simplest electrostatic interactions are those between
a pair of charged particles, referred to as
ionic bonds
The attraction of the oppositely charged ions is
governed by ______. The law applies in a ________
Coulomb’s Law; vacuum
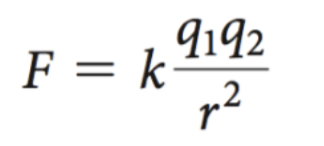
In a cell, charges are ____ in solution by the medium that exists between the charges
screened
The _______ of a medium is represented
by ε, the dielectric constant (water has a high
dielectric constant, 80) giving rise to the
equation:
screening effect
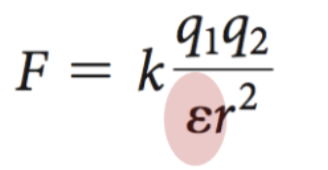
the vector sum, mu, represents
the net dipole moment
Benzene has neither a net charge nor a permanent dipole moment, but a nearby charge can induce a redistribution of electrons, producing an
induced dipole
Planar molecules like benzene have a strong tendency to stack because
fluctuations in the electron clouds of the stacked rings give rise to
mutually attractive induced dipoles (van der Waals interactions)
stacked benzene rings do not
Interpenetrate
At first the longer-range attraction dominates,
but then the repulsive energy increases so rapidly that it acts as a barrier
The repulsive energy barrier defines the distance of closest approach (rv) and
and the van der Waals radii