Carbohydrates and Lipids B 1.1
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Macromolecules
Molecules formed by a very large number of atoms, with relative molecular mass over 10,000 amu
Condensation reactions
Link monomers to polymers, water is usually released
Glycosidic bonds
Bonds made by condensation reactions in carbohydrates
Use of carbohydrates
Short term energy storage
Starch
Stores energy in plants
Glycogen
Stores energy in humans
Glycoproteins
Composed of polypeptides with carbohydrates attached
ABO Glycoproteins
Effects blood transfusions — marks what blood type (O is universal donor)
Lipids
dissolve in non-polar solvents
Hydrophobic
Triglyceride
Combines three fatty acids with one glycerol (linked through condensation reaction/dehydration reaction)
Ester bond
Bond that is the result of the condensation reaction between 3 fatty acids and glycerol
Phospholipids
Have 2 fatty acids linked to a glycerol (hydrophobic)
Saturated fatty acid
All carbon bonds are single bonds → solids
Unsaturated fats
Broad name for mon and poly unsaturated fatty acids
Monounsaturated fatty acid
Carbon has one double bond → oil
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
Carbon has 1+ double bonds → oil
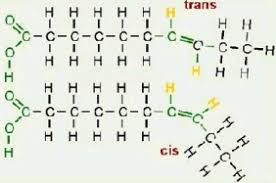
Cis-fatty acids
Hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the two double bonded C
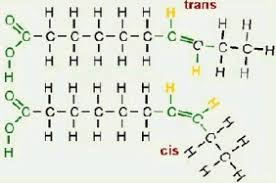
Trans-fatty acids
Hydrogen atoms are on opposite sides of the the two double bonded C
Use of triglycerides
Long term storage
Phosphate head
Hydrophilic part of the phospholipid bilayer
Hydrocarbon tail
Hydrophobic part of the phospholipid bilayer
Steroids
A type if lipid, usually in rings
Metabolism
Sum of all reactions that occur in an organism, catalyzed by enzymes
Intracellular metabolism
Occurs within cells
Extracellular metabolism
Occurs outside of cells (ex. Digestion)
Anabolic pathways
Build up simple molecules into complex molecules, requires ATP (remember Ana brought the group together)
Catabolic pathways
Break down complex structures into simpler ones, release ATP, occurs by hydrolysis (remember Cat tore the group apart)
Hydrolysis
Breaking bonds by adding water