Chapter 8 a): Molecular Biology- Genetic Material and DNA structure
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are the 4 characteristics of genetic material?
Replication
Storage of info
Expression of that info
Variation by mutation
Prior to the discovery of DNA what was believed to be genetic material and why?
Proteins. They were thought to carry genetic information due to their complexity and abundance in cells.
What did the Fredrick Griffith experiment conclude?
Griffith's experiment concluded that a substance from heat-killed virulent bacteria could transform non-virulent bacteria into a virulent form, indicating the existence of a "transforming principle."
What combination killed the mice in Fredrick Griffith experiment?
A combination of
heat-killed virulent bacteria (S)
Alive non-virulent bacteria (R).
Why was the S virus able to kill the mice but the R was not?
The S strain has a polysaccharide coat that protects bacteria from the host’s defense system
The R strain lacks this coat and will be destroyed by the host defense.
Who identified DNA to be the material and how?
Oswald Avery, et al. They purified DNA from S bacteria and transferred it to R bacteria which converted R bacteria to be virulent.
What did the Hershey Chase experiment conclude?
When these radiolabeled viruses were used to infect bacteria, the virus DNA, not the proteins, entered the host bacterial cells.
This demonstrated that DNA is the genetic material responsible for heredity.
The virus attacks the host bacterium and inserts its _____ into the host, where it _______ and takes over the host cell machinery, and produces many more T2 ______.
DNA; replicates; viruses
Nucleotide is composed of….
a nitrogenous base, a sugar (pentose), and a phosphate group.
Nucleic acids are ______consisting of many _______monomers, including DNA (_______acid) and RNA (_______acid)
polymers; nucleotide; deoxyribonucleic; ribonucleic
Purines are ______ & _________
adenine; guanine
Pyrimidines are ______ & _______ & _______
cytosine; thymine; uracil
What is a nucleoside?
A nucleoside is a compound formed from a nitrogenous base and a sugar, without any phosphate group. It serves as a building block for nucleotides, which make up nucleic acids.
In RNA _____ is replaced by _______
thymine; uracil
What forms nucleic acids?
Polymerization of mononucleotides
The linkage between two mononucleotides consists of a ______ group linked to two sugars forming a _________bond.
phosphate; phosphodiester
DNA sequence is read from…..
5' to 3' end.
What are Chargraf’s rules?
Amount of adenine= thymine
Amount of cytosine= guanine
Reflecting base pairing in the double helix structure.
Who proposed DNA is a double helix structure?
James Watson and Francis Crick.
DNA molecule consists of 2 strands that are ______
antiparallel- run in opposite directions.
The backbone of strand is sugar-phosphate linked end to end through ______________
phosphodiester bonds.
Nitrogenous bases connect the strands in the middle through ___________. The bases in two strands are _________to each other via _____ pairing.
hydrogen bonds; complementary; base
RNA is generally a _____ ______ polynucleotide although in some cases it may fold upon itself to form internal ____ pairing.
single-stranded; base
Sugar molecule in RNA is ______ instead of _______ .
ribose; deoxyribose
What are the 3 types of RNA?
mRNA (Messenger RNA)
tRNA (Transfer RNA)
rRNA (Ribosomal RNA)
What is the function of MRNA?
A transcript of the gene carries information (as a sequence of codons) for the synthesis of proteins.
It serves as a template for translation, guiding the assembly of amino acids to form proteins.
What is the function of tRNA?
An RNA molecule that functions as an interpreter between nucleic acid and protein language by picking up specific amino acids and recognizing the appropriate codons in the mRNA
To ensure correct protein synthesis by matching amino acids to mRNA codons.
What is the function of rRNA?
A component of the ribosome, rRNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by facilitating the binding of tRNA and mRNA during translation.
The most abundant type of RNA, which together with proteins forms the structure of ribosomes
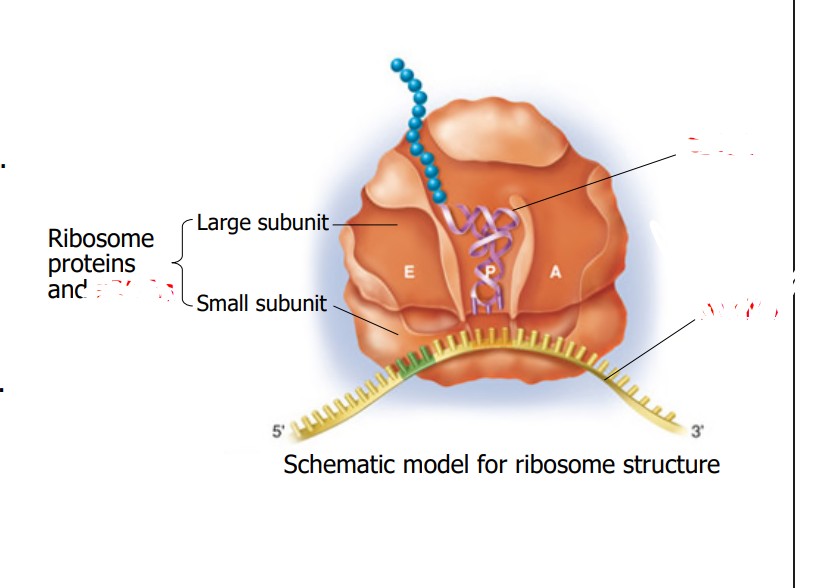
What is the purple part?
tRNA
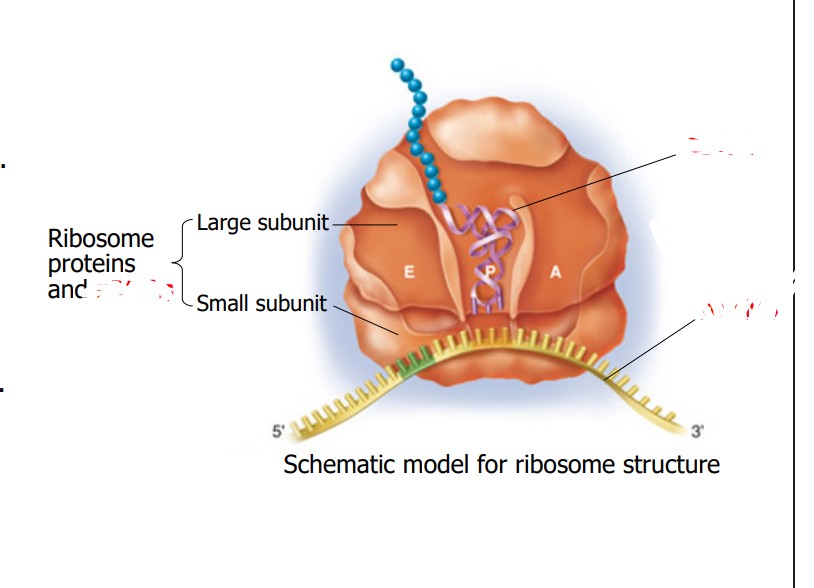
What is the yellow part?
mRNA
Where are rRNA’S found?
rRNA is found in the ribosomes of all living cells, both in the cytoplasm and on the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
How is the genetic information coded in the DNA molecule?
The information must lie on the linear sequence of nitrogenous bases; i.e. the arrangement of bases.
How is the information passed on from one cell to the next (i.e. during mitosis)?
It must be because of the complementary base pairing of nitrogenous bases, that one strand serves as a template to form a new strand (DNA replication).
How does the genetic material function?
It must be that the DNA passes on its information (transcription) where is this used in cell function