Lecture 17
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
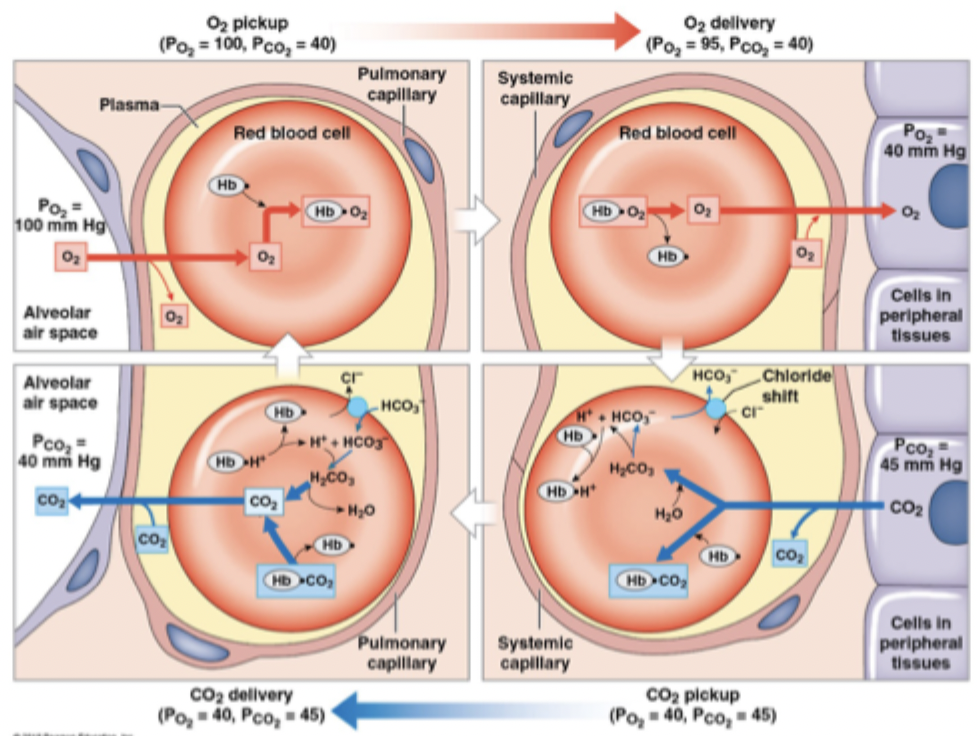
what 2 forms is O2 transported in
dissolved O2
combined with haemoglobin
dissolved O2
for each mmHg PO2 only 0.03ml og O2 is dissolved
so arterial blood with PO2 ~100mmHg contains only 3ml dissolved O2/litre (0.3ml of O2 dissolved per 100ml of blood)
so dissolved O2 is very inefficient for transport as we need about 250ml O2/min
haemoglobin
protein complex woth 4 subunits and a haem group attached to each subunit
red from iron of haem
lack of iron → form of anaemia, affects O2 binding/carrying capacity
structure of the haem
each haem can bind to one O2 molecule
4 haem and globin = Hb
O2 forms an easily reversible combination with Hb to give oxyhaemoglobin
binding depends on PO2
oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve
with increased partial pressure of oxygen, there is an increased amount of haemoglobin bound to oxygen
haemoglobin saturation in arterial blood is around 100% at around 100mmHg
in venous blood there is around 75-85% of Hb saturated at around 40mmHg
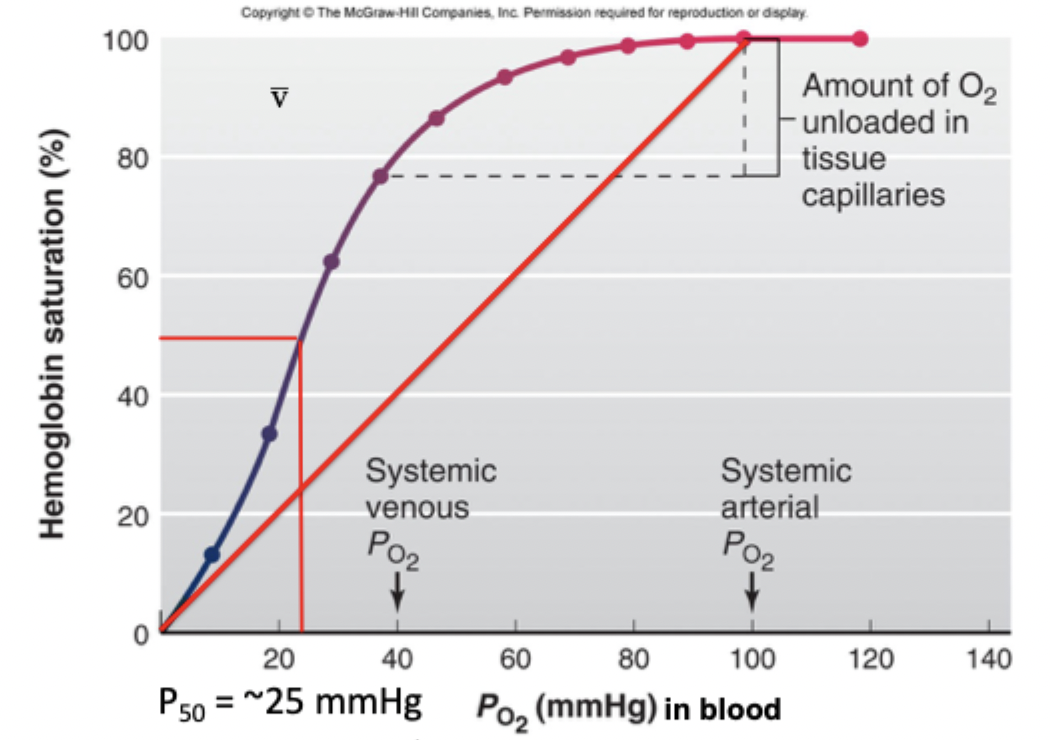
P50
the partial pressure of oxygen at which 50% of haemoglobin is bound to oxygen - pretty low
shape of oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve
sigmoidal, not linear
advantages of a sigmoidal oxygen haemoglobin curve
upper flat part of the curve - moderate changes in PO2 around the normal value (~100mmHg) have only small effects on the % saturation and therefore the amount of O2 carried by arterial blood i.e. some reserve capacity
steep part of curve at lower PO2 - helps with loading of Hb in lungs and unloading of O2 to the tissues. so small changes in PO2 result in large changes in small amount of O2 bound to Hb 2
O2 carrying capacity
how much O2 COULD the blood carry - max amount
normal blood has about 150g of Hb per litre
one gram of Hb can combine with 1.34 ml O2
so O2 capacity = 200ml/litre of blood
O2 content
how much O2 is the blood actually carrying
O2 content = O2 capacity x saturation (+dissolved)
O2 content of blood (Ml O2/litre blood) = [1.34 x Hb x Sat/100] + 0.03 x PaO2
O2 content of arterial blood
assumes 150g of Hb/L, PaO2 100mmHg, SaO2 98%
using equation to find O2 content = [1.34 × 150 × 98/100] + 0.03 × 100
~200 ml O2/litre blood (arterial O2 content)
O2 content of venous blood
assuming 150g of Hb/litre, PvO2 40mmHg, SvO2 74%
using equation to fin O2 content = [1.34 × 150 × 74/100] +0.03 × 40
so O2 content of venous blood ~150 ml O2/litre blood
arterial - venous O2 difference
a-v difference = amount of O2 extracted by tissues
arterial content = 200ml O2/litre blood
venous content = 150ml O2/litre blood
so a-v difference = (200-150) = 50ml O2/litre blood i.e. 50ml O2 was extracted from each litre of blood by the tissues and used in metabolism
total O2 extracted by tissues
how many litres/min flow to tissues? - determined by cardiac output
if CO = 5L/min then total O2 extracted by tissues = 250ml/min (VO2)
oxygen extraction during exercise
more oxygen is extracted and used by the tissues when exercising
the a-v O2 difference will increase
e.g. normal is 50 and exercise could be 150
saturation curve has the capcity to provide this extra O2 extraction - because the Hb will only be 35% saturated to unloads at lower PO2 than at rest
but if low Hb (i.e. anaemia) then will cause problems
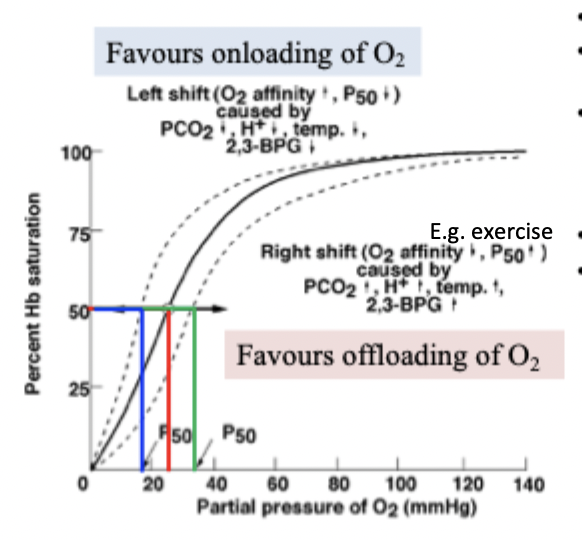
bohr effect overall - right and left shift
right shift = release
left shift = loading
right shift of O2-Hb curve
increased P50 and decreased O2 affinity
favours the release of O2 from Hb to tissues (offloading)
natural right shift occurs as blood flows through the capillaries of the tissues (high metabolic demand - high CO2 and H+) to facilitate O2 release
increased 2,3-BPG, increased H+, increased temperature
release
left shift of O2-Hb dissociation curve
decreased P50 and increased O2 affinity
favours the binding of O2 to Hb (onloading)
natural elft shift occurs as blood flows through the lung capillaries (less CO2 and H+)
facilitates the uptake of O2 from the alveoli into the blood
decreased 2,3-BPG, decreased H+, decreased temperature
loading
RBC 2,3-DPG
by-product of glycolysis
RBCs contain no mitochondria so rely on glycolysis
2l3-DPG increases with intense exercise, altitude, and due to devere lung diseases of anaemia
helps deliver O2 to tissues (due to rightward shift of Hb saturation curve which allows more O2 to be released from Hb at a particular PO2 - increase unloading)
anaemia
saturation curve stays the same
O2 content is reduced - e.g. [Hb] = 76 → 100ml)2/L
exercose problems from a-v difference e.g. can’t remove 150ml/L when only have 100
carbon monoxide
has high affinity to Hb - 250 times the affinity of O2 for Hb
small amounts of CO can tie up large proportion of Hb in the blood, making it unavailable for O2 carriage - so less O2 content
shifts curve to the left - more difficult to unload O2 to tissues
smoking → arterial CO increases
oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve
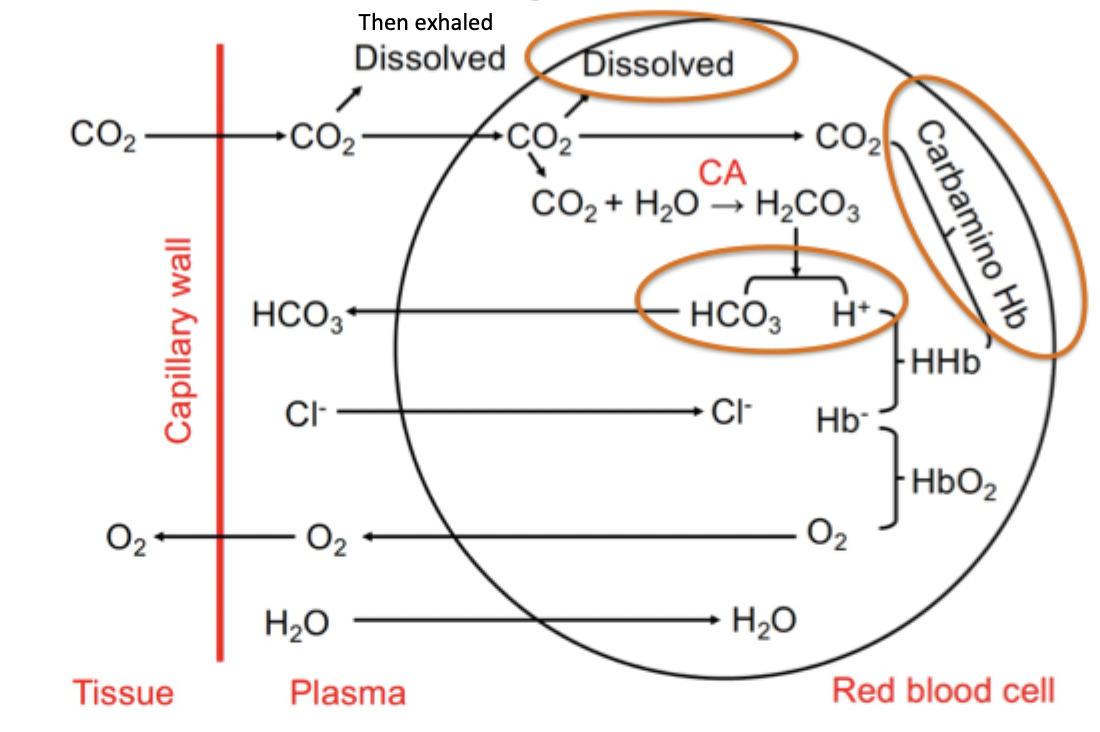
what 3 forms is CO2 transported in
dissolved in plasma - 20 times more soluble than O2 (10%)
as bicarbonate (70%)
combined with proteins as carbamino compounds (20%)
CO2 uptake and O2 liberation in systemic capillaries
CO2 in capillaries either exhaled as dissolved CO2, or goes into RBC where it can be dissolved, to turn into carbamino Hb or bicarbonate which can be transported out of the RBCs to the lungs
Cl- also moves into the cell
haldane effect
deoxygenation of blood increases CO2 transport
Hb affinity for CO2 increases when it is not bound to oxygen
RBC vs tissues gas exchange
RBC:
haldane - Hb oxygenation facilitates CO2 unloading
bohr - decreased CO2 facilitates O2 loading
tissue:
bohr - increased CO2 facilitates O2 unloading
haldane - unoxygenated Hb facilitates CO2 loading
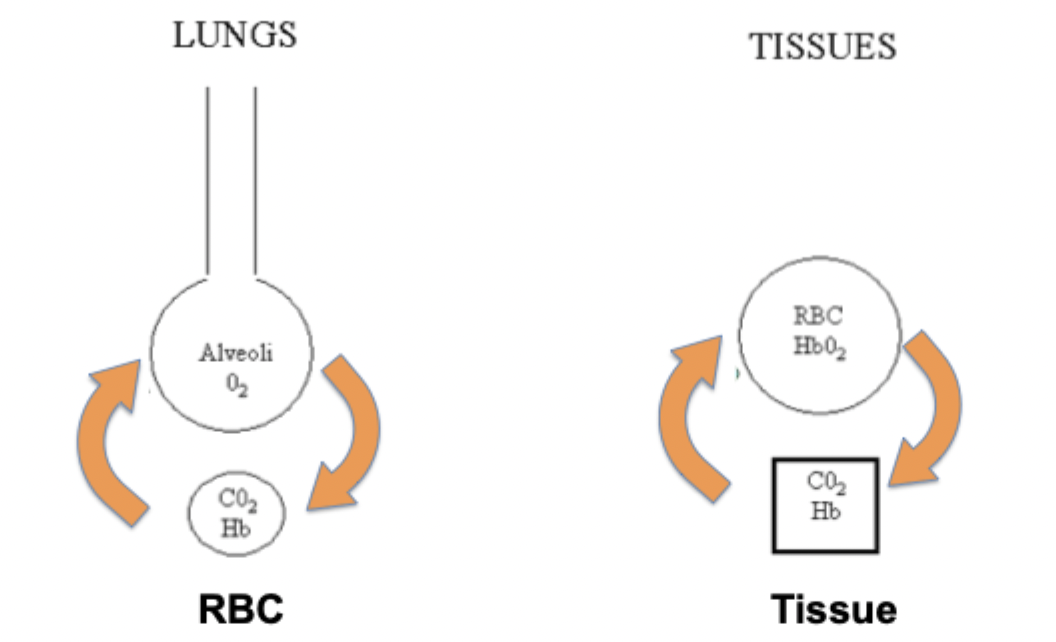
transport of O2 and CO2 in lungs and peripheral tissues