Chapter 15: Therapies
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
psychotherapy vs biomedical therapy
• Psychotherapy: an interactive experience with a trained professional, working on understanding and changing behavior, thinking, relationships, and emotions
• Biomedical therapy: the use of medications and other procedures acting directly on the body to reduce the symptoms of mental disorders
Psychologist vs. Psychiatrist
The biggest difference is that a psychiatrist can prescribe medicine and has a medical degree
clinical psychologist
A psychologist that specializes in mental disorders
Ethical Guidelines in Therapy
Beneficence and Nonmaleficence: Do good and avoid harm in your work with clients.
Fidelity and Responsibility: Maintain trust and be accountable in your professional relationships.
Integrity: Be honest and truthful in all professional interactions.
Justice: Treat everyone fairly and equitably, regardless of their circumstances.
Respect for People's Rights and Dignity: Value the autonomy and worth of individuals.
Positive Psychology
Positive psychology seeks to identify factors that lead to well-being, resilience, positive emotions and psychological health. Expressing gratitude, a positive subjective experience, increases subjective well-being. People who exercise their signature strengths or virtues report higher levels of positive objective experiences such as happiness and subjective well-being. The 6 categories of virtues are:
Wisdom
Courage
Humanity
Justice
Temperance
Transcendence
Psychoanalytic vs. psychodynamic approach
Both are grounded in Freud's idea that the unconscious and unconscious conflicts are driving human behavior. The psychodynamic approach is faster and more direct and is what is practiced today. Traditional psychotherapy would be too expensive and time consuming for most people.
Free association
spontaneous report of all mental images, thoughts, feelings as a way of revealing unconscious conflicts
Resistance
patient's unconscious attempt to block revelation of unconscious material; usually sign that patient is close to revealing painful memories
Transference
process where emotions originally associated with a significant person are unconsciously transferred to the therapist
Dream analysis
Manifest content: the dream itself
Latent content: the interpretation of the dream (hidden meaning)
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
Participants view an image and create a story as to how the people are related, what is happening, or what happens next. Psychologists "read into" a person's unconscious by examining elements of the emotions presented in the patient's response to the TAT.
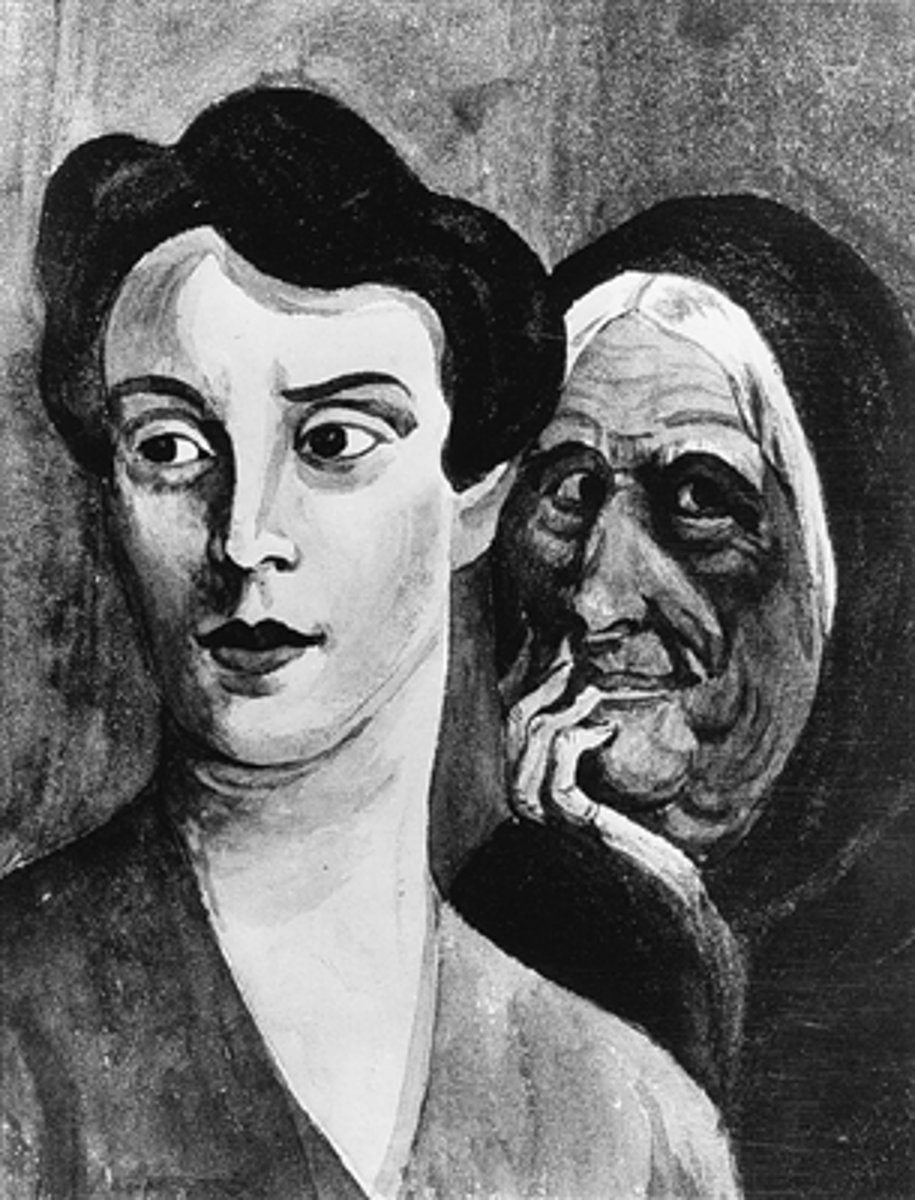
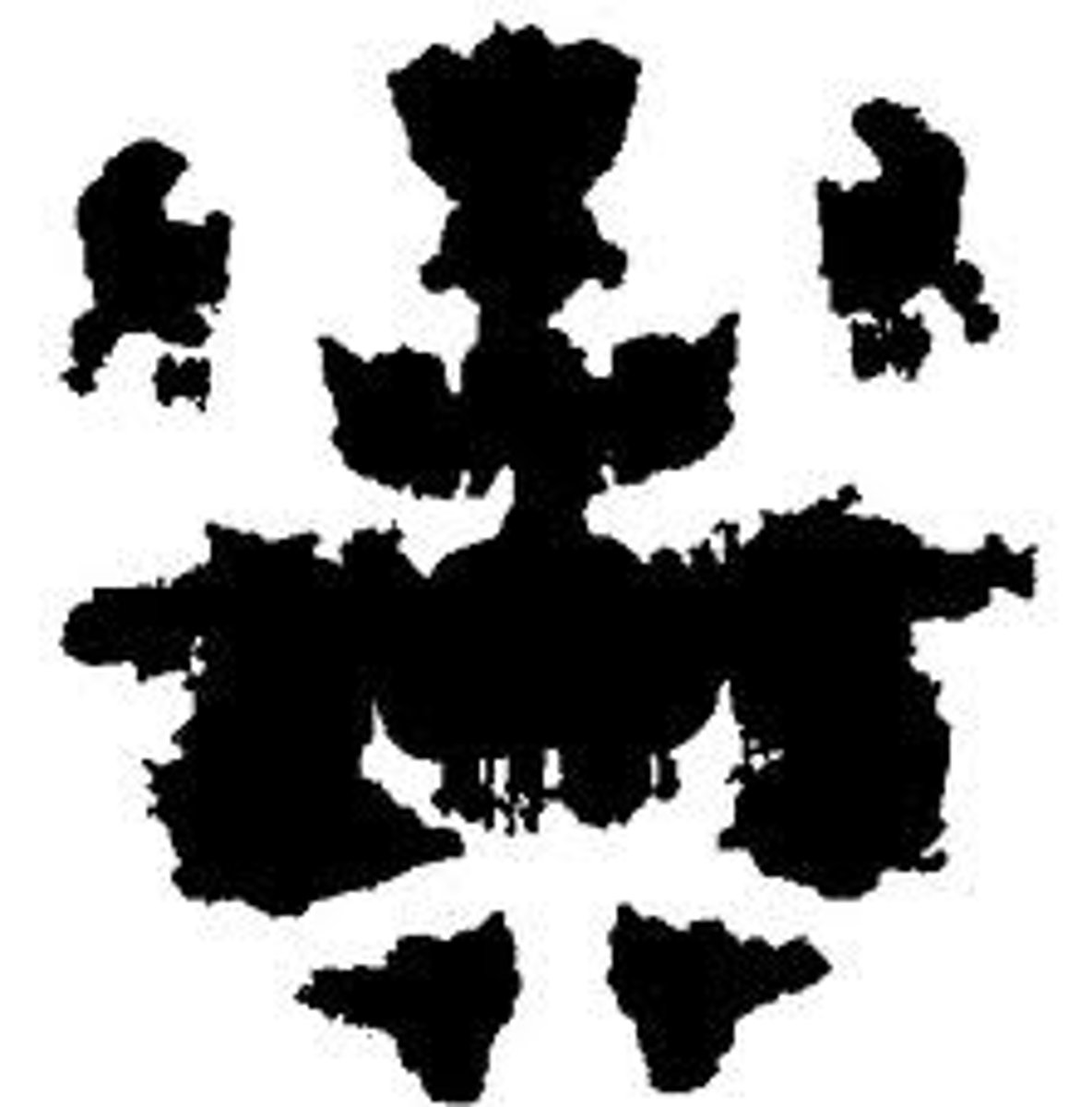
Rorschach inkblot test
Patients view a series of inkblots and say what they see in the image. Psychologists "read into" the patient's unconscious based on the pattern in emotions, what people see (whether or not it's plausible or even fits the shape of the image), if people look to minor details or the big picture, etc.

Client centered therapy (aka person centered therapy)
-Therapy is non-directive—therapist does not interpret thoughts, make suggestions,or pass judgment
-Therapy focuses on client's subjective perception of self and environment
-Does not speak of "illness" or "cure"
-"patients" are referred to as "clients" to help reduce the stigma of seeking therapy and remove the implication of people being "sick"
-Active listening is a typical technique
Humanistic qualities of a good therapist (Carl Rogers)
Genuineness, Empathy, Unconditional Positive Regard
unconditional positive regard
a caring, accepting, nonjudgmental attitude, which Carl Rogers believed would help clients to develop self-awareness and self-acceptance
Counter Conditioning (Mary Cover Jones)
-Mary Cover Jones, one of Watson's students became interested in how to eliminate fear using the principles of conditioning in reaction to the "Little Albert" experiment.
-Jones developed a system called "counterconditioning" to treat a patient named Peter who was afraid of furry objects.
-Peter was given his favorite snack to eat while a rabbit was at a safe and non threatening distance in a cage
-Over the course of nearly two months the rabbit was slowly inched closer to Peter.
-Peter was eventually unafraid of the rabbit and then generalized that new counterconditioned response to other furry objects or animals.
Systematic Desensitization (John Wolpe)
Uses three steps:
1. Patient is taught progressive relaxation techniques
2. Development of anxiety hierarchy (see next slide for an example)
3. Patient navigates their anxiety hierarchy while using the relaxation techniques (this would be done mostly under the supervision of the therapist)
Flooding
coming in direct and constant contact with the feared stimulus. Flooding eliminates the anxiety hierarchy and directly addresses the feared stimulus. The idea is that people can only have a heightened sense of anxiety for so long and that repeated exposure might diminish the anxiety response.
ex. A person with a fear of germs may have to hold money and not wash their hands. The person would then have to deal with the anxiety the comes.
aversion therapy
treatment that uses punishment to decrease the frequency of undesirable behaviors
ex. putting a bitter substance on fingernails to stop biting them
Token Economy
-Based on operant conditioning where people are given a "token" that can be used towards a desirable reward.
-Use for behavior modification in group settings (prisons, classrooms, hospitals)
ex. students get a gold star on a chart that they can trade in for a prize when they earn enough.
Difficult to implement and administer because the administrator must remember to award the tokens and must do so in a consistent manner.
Biofeedback
Biofeedback uses principles of conditioning to help clients regulate body systems (such as the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems) that contribute to feelings of anxiety or depression.
Rational Emotive Therapy (RET) (Albert Ellis)
ABC model
Activating Event
Beliefs
Consequences
Identification and elimination of core irrational beliefs.
Ex. A person that fears dating because they believe they are "hurting" a person that they break up with.
A: Breaking up
B: "I'm hurting the person"
C: Anxiety
Ellis would try to change the belief to reduce anxiety
Cognitive Therapy (CT) (Aaron Beck))
Problems due to negative cognitive bias that leads to distorted perceptions and interpretations of events.
The therapist helps to recognize the bias then test accuracy of these beliefs.
If a person in seeking Cognitive Therapy (CT) from Beck came in with the complaint that they got passed over for a promotion and they fail at everything in life, Beck would guide the client to recognize the unrealistic belief.
ex.
"Is it really true that you fail at everything"? "What things have you been successful at in life"?
cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
Integrates cognitive and behavioral techniques. Based on the assumption that thoughts, moods, and behaviors are interrelated.
ex. A person with a fear of germs has to handle money and not wash their hands. The person then attempts to change the irrational belief (thought) that something terrible is going to happen through cognitive restructuring. All of this would take place under the supervision and guidance of a therapist.
Cognitive Triad
Negative thoughts about oneself, the world, and the future
Dialectical Behavior Therapy
DBT focuses on helping people accept the reality of their lives and their behaviors, as well as helping them learn to change their lives, including their unhelpful behaviors. DBT skills aim to help enhance capabilities in day-to-day life. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is especially effective for people who have difficulty managing and regulating their emotions. Some skills a therapist would focus on include:
Mindfulness
Distress tolerance
Interpersonal effectiveness (This means understanding how to ask for what you want and need and setting boundaries while maintaining respect for yourself and others).
Emotion regulation
Typical Antipsychotics
A class of older drugs to treat schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders primarily by reducing excess levels of dopamine in the brain. Good at treating the positive symptoms but has side effects such as weight gain and sexual dysfunction in addition to things like tardive dyskinesia.
tardive dyskinesia
involuntary movements of the facial muscles, tongue, and limbs; side effect of typical antipsychotic medication.
atypical antipsychotics
Less side effects than typical antipsychotics and also treat the negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Benzodiazepines
antianxiety medication that works by increasing levels of GABA. May decrease alertness and coordination and is considered addictive. These drugs begin working immediately. ex. Valium and Xanax
Nonbenzodiazepines
May take up to two weeks to begin working to treat anxiety. Does not have the side effect of loss in coordination and they are not addictive.
ex. Buspar
Lithium
used to treat bipolar disorder
MAO Inhibitors
Antidepressant drug that when used, must be coupled with a diet that avoids aged and protein rich foods. ex. aged cheese and smoked meat must be avoided because the body can no longer process them
SSRIs
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin once the neurotransmitter has sent its message. This make more serotonin available in the synapse, which improves the person's mood. ex. Prozac, Paxil, Zoloft.
ECT
electroconvulsive therapy used to treat severe depression when medication does not work. A side effect is memory loss.
Psychosurgery
The lobotomy is a form of psychosurgery that was popular in the mid-20th century but is rarely, if ever, performed today. It involves severing the connections between the frontal lobes of the brain and other parts of the brain, typically the thalamus.
TMS
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in specific areas of the brain. It is an FDA-approved treatment for major depressive disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
A magnetic coil is placed over the patient's head, targeting the area of the brain involved in the condition being treated.
The coil generates magnetic pulses that penetrate the skull and stimulate nerve cells.
These pulses can alter brain activity and improve symptoms.