Atomic structure
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
The sample of chromium is analysed in a time of flight (TOF) mass spectrometer. Give two reasons why it is necessary to ionise the isotopes of chromium before they can be analysed in a TOF mass spectrometer. (2 marks)
Ions will interact with and be accelerated by an electric field
Ions create a current when hitting the detector
One of the methods of ionising samples in time of flight mass spectrometry is by electron impact. How is this ionisation done? (4 marks)
high energy electrons
from electron gun
fired at sample
knocks off one electron
A second method of ionising samples in time of flight mass spectrometry is by electrospray ionisation. How is this ionisation done? (4 marks)
sample dissolved in volatile solvent
injected through a fine hypodermic needle giving a fine mist / aerosol
tip of needle has high voltage
each particle gains a proton as it leaves the needle
A sample of germanium is analysed in a TOF mass spectrometer using electron impact ionisation. Give an equation, including state symbols, for the process that occurs during the ionisation of a germanium atom. (1 mark)
Ge(g) → Ge+(g) + e-
P is ionised by electrospray ionisation.
Give an equation to represent the ionisation of P in this process
P(g) + H+(g) → PH+(g)
The first ionisation energies of the elements in Period 2 change as the atomic number increases. Explain the pattern in the first ionisation energies of the elements from lithium to neon (6 marks)
Stage 1: General Trend (Li → Ne)
1st IE increases
More protons/increased nuclear charge
Electrons in same energy level, no extra shielding
Stronger attraction between nucleus and outer e- (ignore radius decreases)
Stage 2: Deviation Be → B
B lower than Be
Outer electron in 2p
Higher in energy than 2s
Stage 3: Deviation N → O
O lower than N
2 electrons in 2p are paired in orbital
Pairing causes repulsion
The products of the reaction were separated and analysed in a time of flight (TOF) mass spectrometer. Two peaks were observed at m/z = 104 and 118.
Outline how the TOF mass spectrometer is able to separate these two species to give two peaks. (4 marks)
Positive ions are accelerated by an electric field
To a constant kinetic energy
The positive ions with m/z of 104 have the same kinetic energy as those with m/z of 118 and move faster
Therefore, ions with m/z of 104 arrive at the detector first
Explain why the atomic radius decreases across Period 3, from sodium to chlorine. (2 marks)
The number of protons increases
Shielding is similar/same OR electrons are added to the same shell
In a TOF mass spectrometer, explain how:
ions are accelerated
ions are detected
the abundance of ions is determined
(3 marks)
Ions are accelerated by an electric field
Detected by gaining electrons
The current produced is proportional to ion abundance
What are the (short) electron configurations of chromium and copper?
Cr is [Ar] 3d5 4s1 (not [Ar] 3d4 4s2)
Cu is [Ar] 3d10 4s1 (not [Ar] 3d9 4s2)
This is because these configurations are energetically stable.
State, in terms of fundamental particles, why the isotopes 10B and 11B have similar chemical reactions. (1 mark)
Same number of outer electrons
Explain why the second ionisation energy of boron is higher than the first ionisation energy of boron. (1 mark)
Electron being removed from a positive ion (therefore needs more energy)
Explain why the value of the first ionisation energy of neon is higher than that of sodium. (2 marks)
In Ne the outer electron is lost from a 2p subshell, in Na it is lost from 3s
Less shielding by inner electrons in Ne
Sketch a graph to show the successive ionisation energies of sodium. (2 marks)
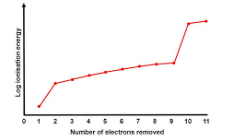
Explain, in terms of structure and bonding, why the melting point of magnesium is higher than the melting point of sodium. (2 marks)
Magnesium is a smaller ion compared to sodium
Mg2+ has a higher charge than Na+
(stronger electrostatic forces of attraction)
What is the electron configuration of V2+ in the ground state? (1 mark)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3
A student has a 10 cm3 sample of a 1.00 × 10-2 mol dm-3 methanoic acid solution. The student is asked to dilute the methanoic acid solution to a concentration of 2.00 × 10-4 mol dm-3 by adding distilled water.
Which volume of water should be added? (1 mark)
490 cm3
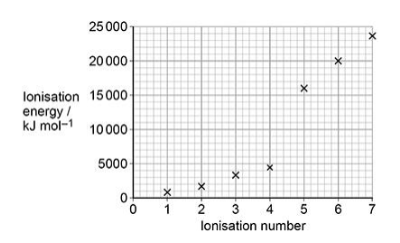
The first seven successive ionisation energies for element Z are shown.
What is element Z? (1 mark)
A Carbon
B Nitrogen
C Silicon
D Phosphorus
C Silicon
What is the (short) electron configuration of Cu2+? (1 mark)
[Ar]3d9
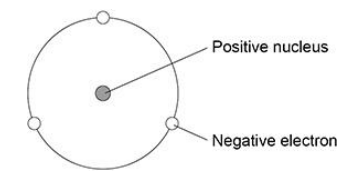
The figure is a model proposed by Rutherford to show the structure of an atom.
State two features of the current model that are not shown in the Rutherford model. (2 marks)
Current model includes neutrons and protons
Current model shows electrons in different energy levels