W4 pre: Introduction to neuropeptides as regulators of physiological processes and whole-animal behaviour
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are neuropeptides?
peptides synthesised and released by neurons as intracellular signalling molecules
How large are neuropeptides?
3 - 40 residues
Where are neuropeptides derived from?
larger precursor proteins
Where are neuropeptides released from?
large dense core vesicles
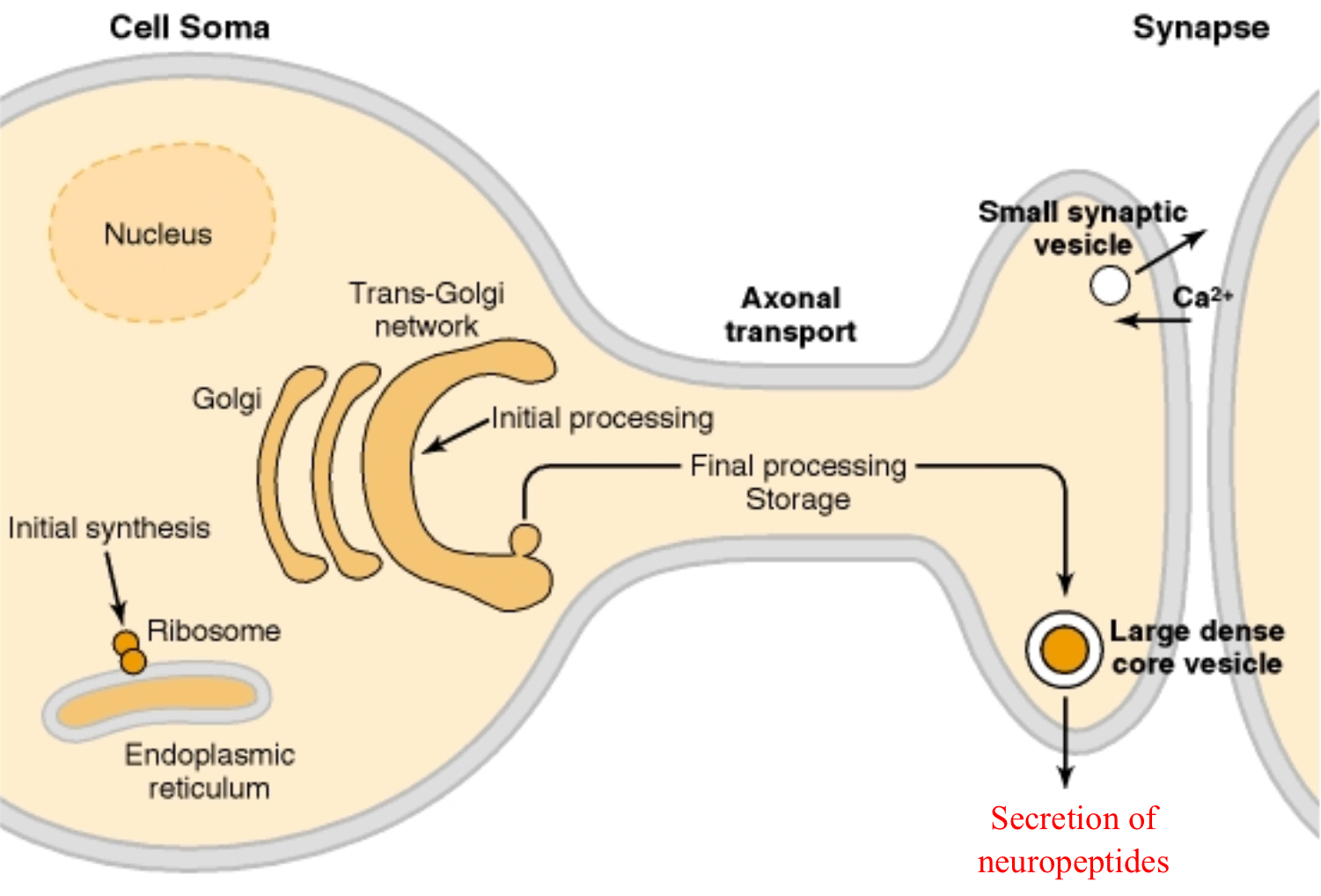
What is release of neuropeptides triggered by?
long lasting but low frequency bouts of action potentials
Compared to neurotransmitters, how quickly do neuropeptides work and what distances do they they cover?
more slowly
larger distances
What are neuropeptides involved in?
mediating neuronal control/regulation of wide range physiological and behavioural processes (feeding/reproduction)
What kind of receptors do neuropeptides typically bind to?
G-protein coupled receptors
What can neuropeptides be evolutionarily traced back to?
common ancestor of the Bilatera
How are neuropeptides derived from precursor proteins?
cleavage by endopeptidases at dibasic or nonobasic sites
Give an example of an endopeptidase and describe its action
prohormone convertases (PC1 & PC2) cleave precursors at the C terminus of peptide bonds at dibasic (Lysine-Arganine) or monobasic (Arg) sites
Where does cleavage of neuropeptides from precursor proteins occur?
golgi apparatus

Describe the cleavage process of neuropeptide enkephalin from its precursor protein (2 points)
prohormone convertase cleaves precursor at dibasic cleavage sites (lys-arg & lys-lys)
carboxypeptidase E removes the basic residues that make up the cleavage site

List 3 post-translational modifications of neuropeptides
C-terminal amidation & N-terminal pyroglutamate
sulphation of tyrosine residues
addition of disulphide bridges between cysteine residues
Discuss C-terminal amidation & N-terminal pyroglutamation (2 points)
conversion of C-terminal glycine residue into an amide group
conversion of N-terminal glutamine into pyroglutamate
Give an example of a
neuropeptide that undergoes C-terminal amidation & N-terminal pyroglutamation
thyrotropin releasing hormone
What is the benefit of C-terminal amidation & N-terminal pyroglutamation?
protects neuropeptide from from degradation by peptidases, increasing their half life when secreted
What peptidase is resisted by the addition of a C-terminal amide group?
carboxypeptidases
What peptidase is resisted by the addition of a N-terminal pyroglutamate group?
aminopeptidases
In which 2 neuropeptides do sulphation of tyrosine residues occur in and what’s its benefit?
cholecytokinin
gastrin
essential for their bioactivity
In which 2 neuropeptides do addition of disulphide bridges between cysteine residues occur in?
vasopressin
oxytocin
List 3 physiological levels that neuropeptides act on
molecular/cellular
neuronal circuit / systems
behavioural/emotional