Theme 1, Module 3 & 4 Review Lecture
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
S- Strain (polysaccharide capsule)
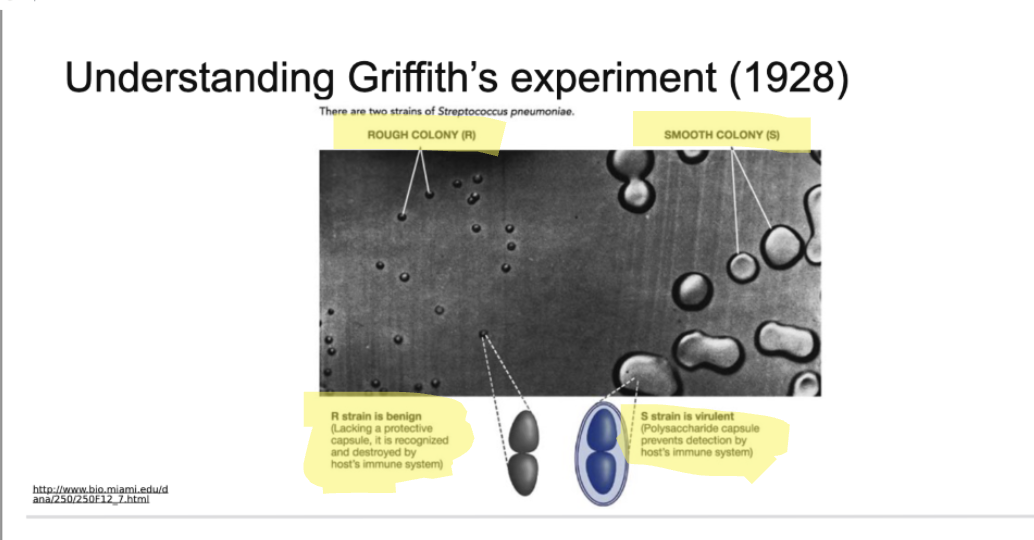
S- Strain (polysaccharide capsule) has the ability in its DNA to code for a sugar coating on all the colonies that s strain bacteria form
Bacteria grow in clumps or colonies and when they're grow in as colonies, they can make what's called a biofilm, like a sugar coating that is nice protective environment to grow and divide
This makes them invisible ot the immune system
R-Strain does not have the ability to code for the proteins that make this sugar coat so the colonies look rougher
Since they can't make the sugar coat the immune system can recognize the bacteria and recognize they don’t belong and attach them
Immune system can tag the bacteria, so there's a follow up in a muliti cell type of attach or the cells can engull the bacteria and then destory it internally or the white cells can release toxins
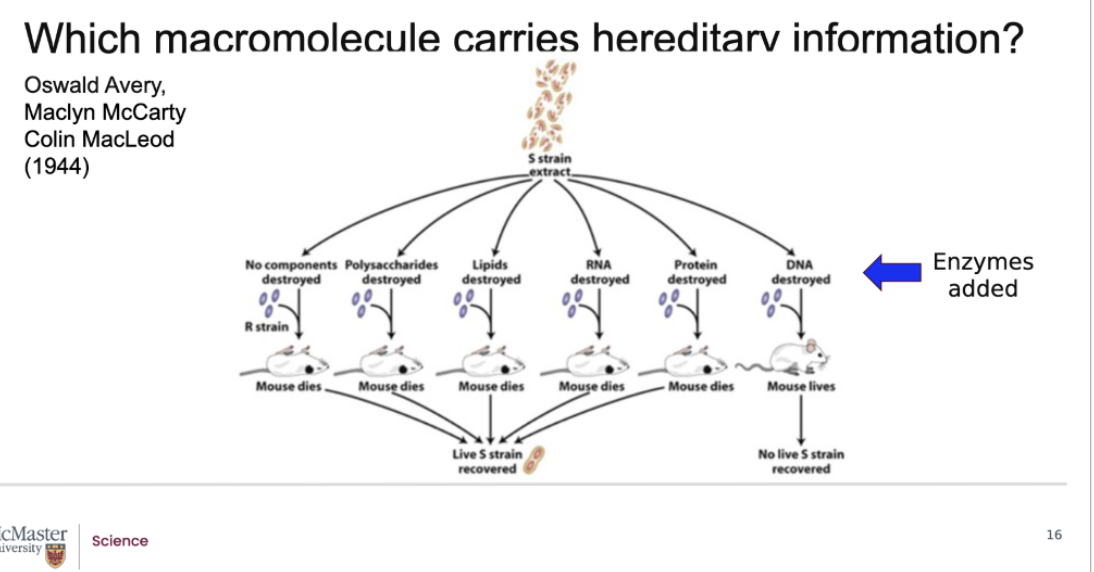
What do these first 5 results tell you? What does the laster strain tell you?
They took fred neufeld's model where they're taking Fred Griffith's experiment, where you're taking the S strained extract that you blew up and combining it with our strain bacteria to inject into the mouse, but you're now changing. The condition so that in every sample you're injecting, you've destroyed one macromolecule.
They added enzyme that would only destroy one type of macromolecule on the Strain and put the live R strain
What do these first 5 results tell you?
They DON'T tell you anything about DNA
They just tell you all these macromolecules do not transform those R strain bacteria so they can't be the hereditary material
What does the last strain tell you?
Since DNA was destroyed, and the mice lives that was the hereditary macromolecule
what makes an amino acid hydrophobic?
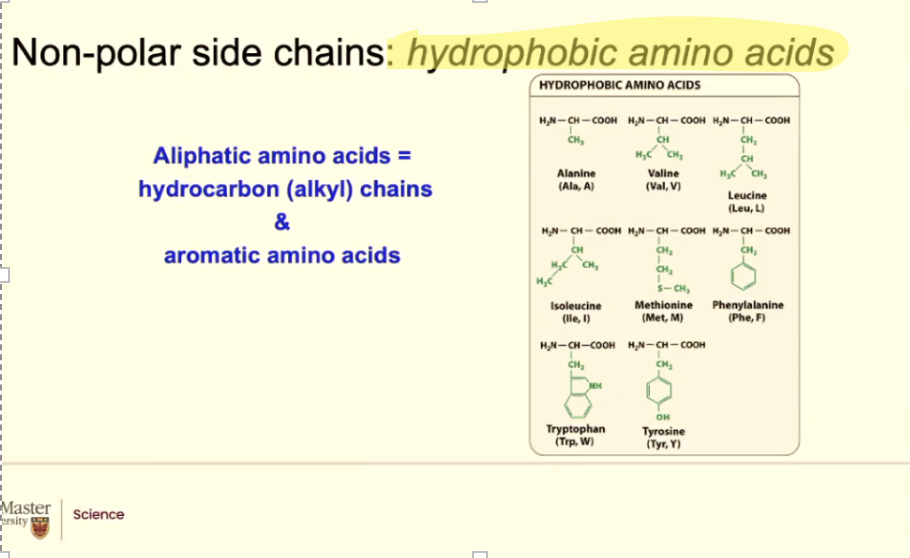
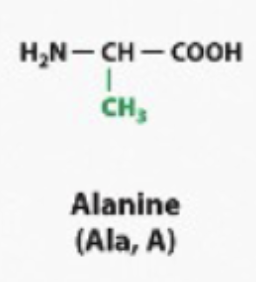
Any amino acid where the R group looks like a Hydrocarbon. Or it looks like it has like CH2, CH2, CH3. Bound bound together like a fatty acid tail. They will behave like a hydrocarbon, like a fatty acetate. They will be hydrophobic (non-polar)
ALSO BENZENE (hydorphobic)
Tyrosine is mostly hydrophobic but it has a hydroxyl group that can form hydorgn bonds
BOTH HYDOPHOIC OR HYDEOPHILIC
hydrophobic
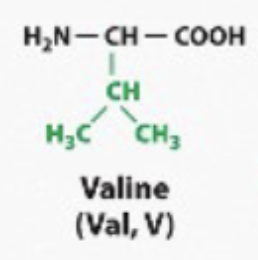
hydrophobic
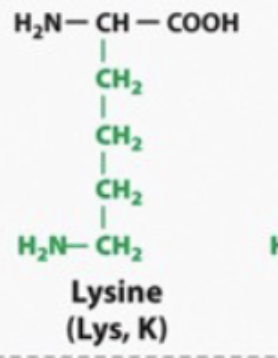
basic and hydrophilic
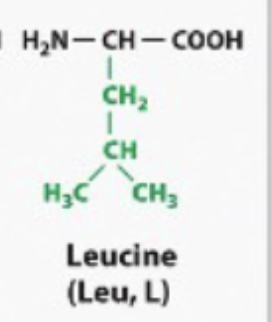
hydrophobic
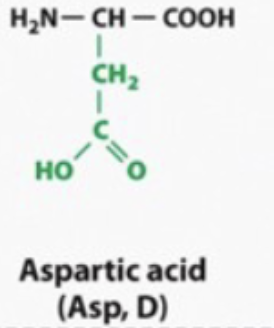
acidic and hyrophilic
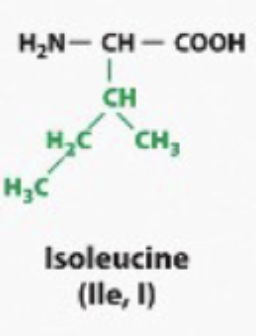
hydrophobic
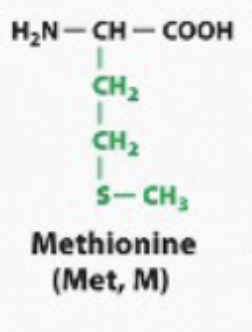
hydrophobic
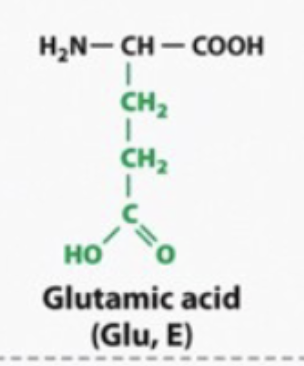
acidic
hyrophilic
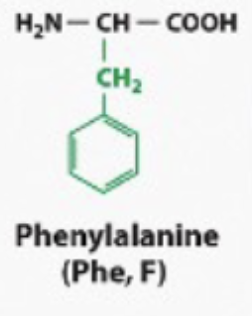
hydrophobic
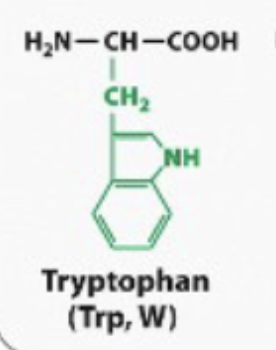
hydrophobic
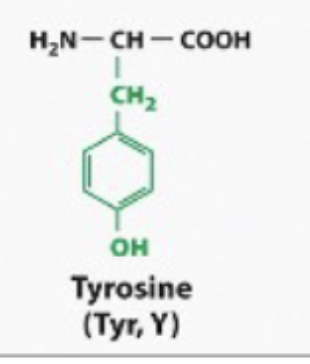
Tyrosine is mostly hydrophobic but it has a hydroxyl group that can form hydorgn bonds
BOTH HYDOPHOIC OR HYDEOPHILIC
What makes an amino acid hydrophilic amino acids?
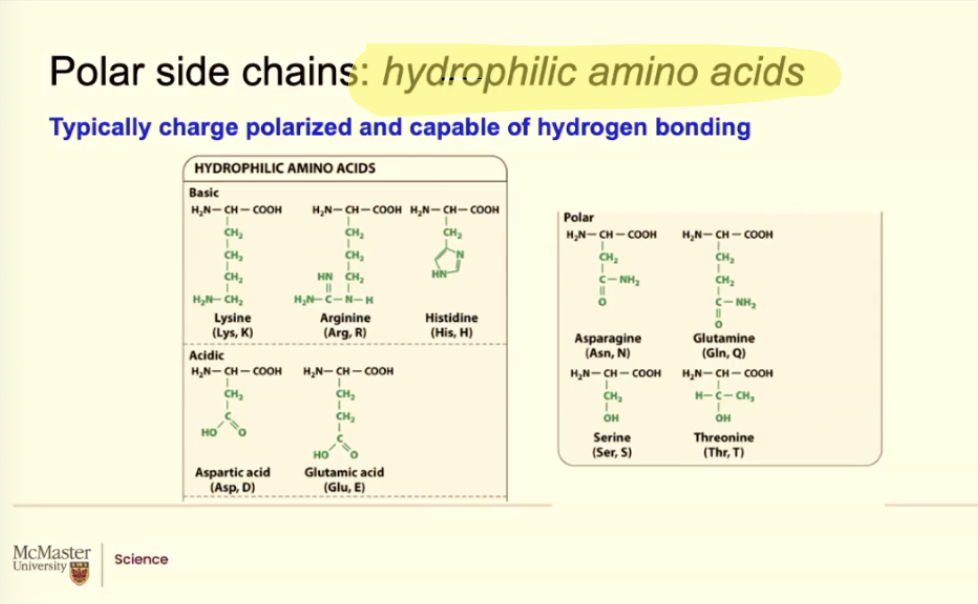
BASIC become positively charged /acidic in water
ACIDIC become negatively charges/ basic in water
Water has these dipole moments where the oxygen can be
slightly negative, the hydrogen can be slightly positive.
Because of that, when these amino acids are in aqueous
environment, they get charged, they can interact with water, so
they're hydrophilic,
its the same thing with asparagine and glutamine
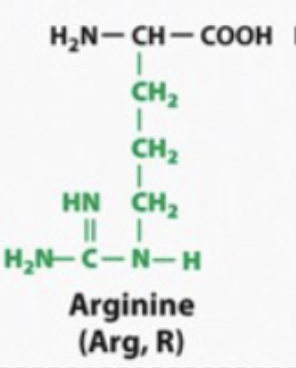
basic and hydrophilic
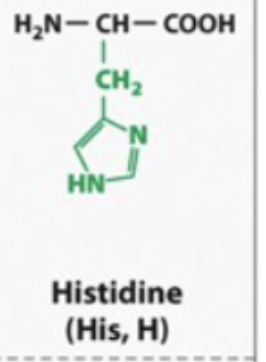
basic and hydrophilic
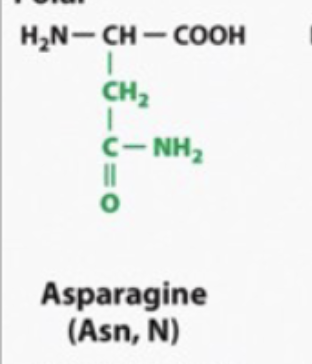
polar and hydrophilic
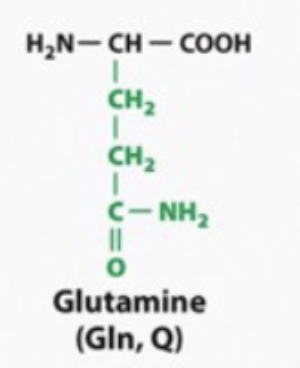
polar and hyrophilic
hydrophilic
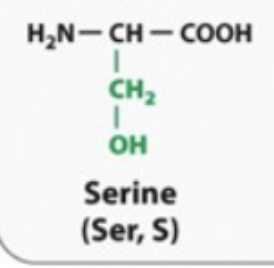
SERINE AND THERONINE ARE DIFFERENT
They have hydroxyl groups so they will make hydogen bonds
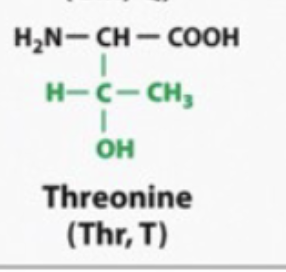
hydrophilic
SERINE AND THERONINE ARE DIFFERENT
They have hydroxyl groups so they will make hydogen bonds
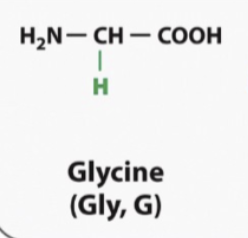
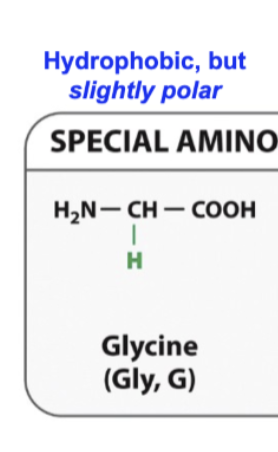
Glycine
Smallest amino acid
Might find in an area when a protein is folding with tight turns
At the same time because its CH2 its gonna be hydrophbic but the hydeogen bond or that hyfogen can interact with water or any hydroxyl group and make a hydrogen bond
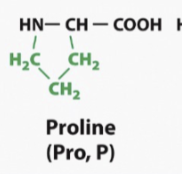
Proline
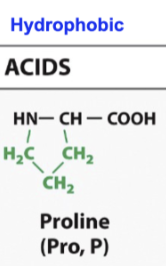
Cyclical molecule
What makes it special is when its in an aqueous environment, the R group actually makes a covalent bond with eh amino group, so it actually becomes bigger
So any time a protein is folding and there needs to be a bigger turn, proline might be found there as a wedge to a spacer to help make bigger turns like in a alpha helix or a beta sheet structure
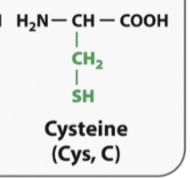
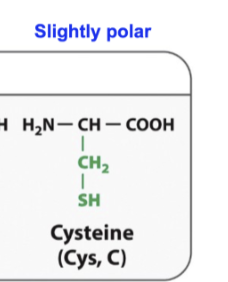
Cycstenine
SH behaves like a hydroxyl group
It can make hydrogen bonds
Cysteeins interact with each other, and the sulurs can make a covalent bond with each other and make proteins really stable
Ex: insulin
It its reall stable because cysteines keep it stable buy interacting with each other in different parts of the protein