Transport and water potential quiz
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mrs. Bose AP Bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Types of Transport
Passive Transport
Active Transport
Passive Transport
No energy needed
Particle movement from higher to lower concentration
Active Transport
Requires energy (ATP)
Particle movement from lower to higher concentration
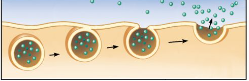
Endocytosis
A form of Active Transport where a cell takes in material by forming a vacuole around it
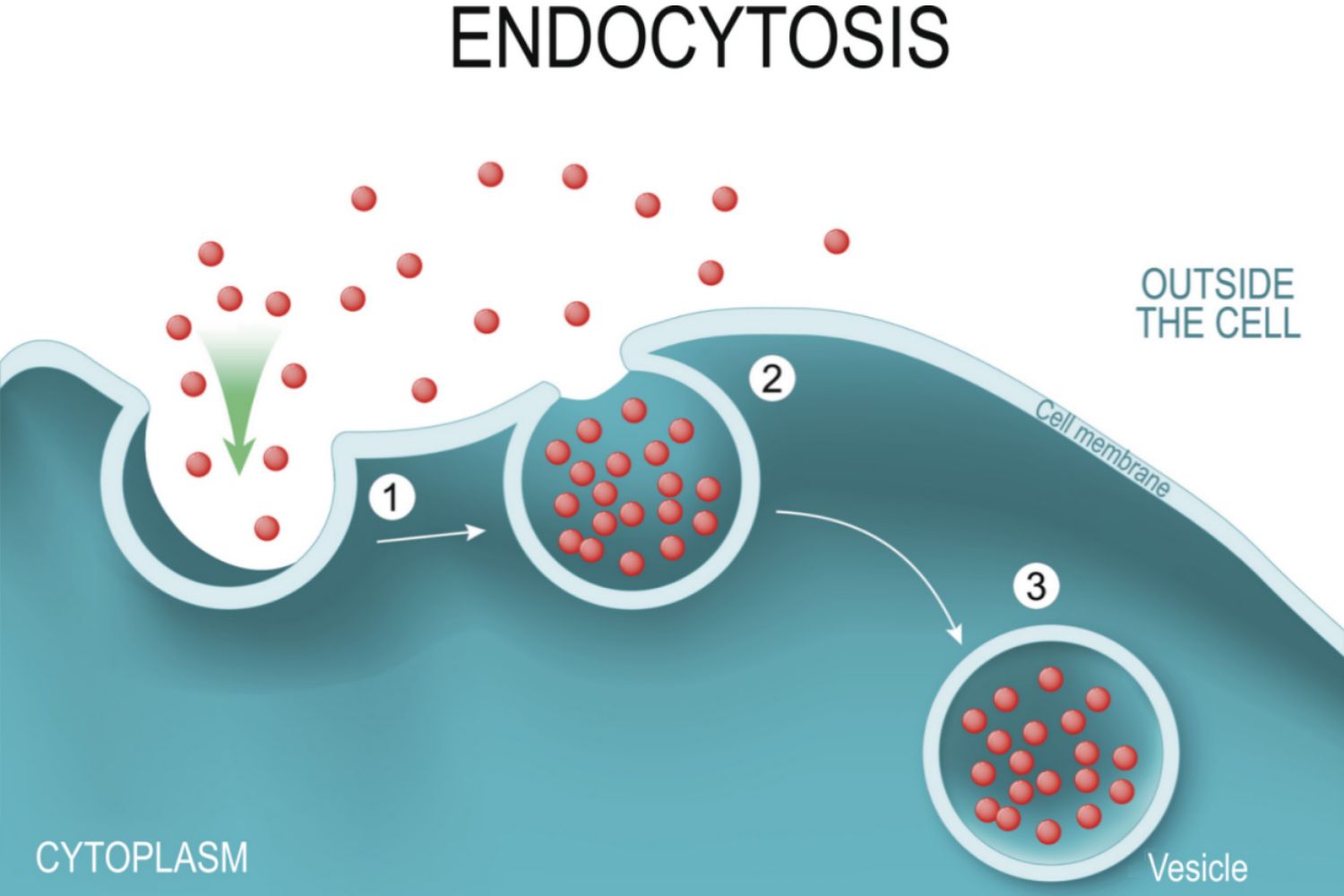
Types of Endocytosis
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
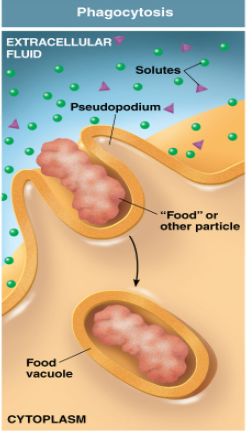
Phagocytosis
The cell membrane forms around another substance, “cell eating”
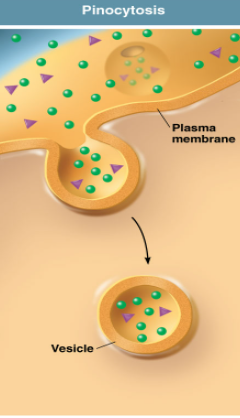
Pinocytosis
Cell takes in liquids surrounding it. Non specific
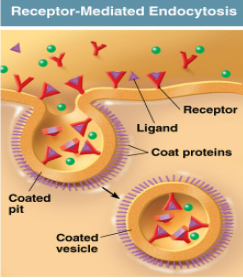
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Transports a specific molecule into the cell using vesicles, like cholesterol
Facilitated Diffusion
A form of passive transport that uses transport proteins
helps hydrophilic substances cross; no energy used
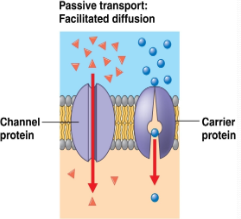
Types of Facilitated Diffusion
Carrier Proteins
Channel Proteins
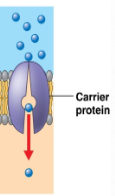
Carrier Proteins
Loosely bind/carry specific larger molecule across (ex. glucose)
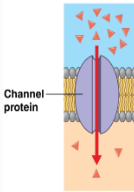
Channel Proteins
Provide hydrophilic channel/opening for ions and water to diffuse
Can be Gated
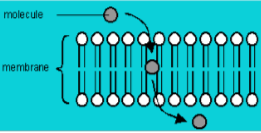
Simple Diffusion
no proteins or energy involved
Movement across the lipid bilayer
used for small or hydrophobic molecules
Osmosis
Form of Passive Transport, sometimes needs protein help (aquaporin)
movement of water from areas of more free water to areas of less free water
Aquaporin
channel protein that allows passage of water
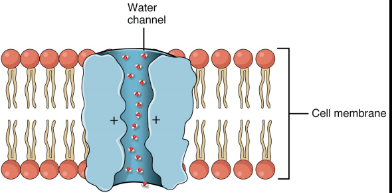
Cell Membrane Pumps
carrier proteins that transport small + charged substances against concentration gradient (low to high)
Types of Cell Membrane Pumps
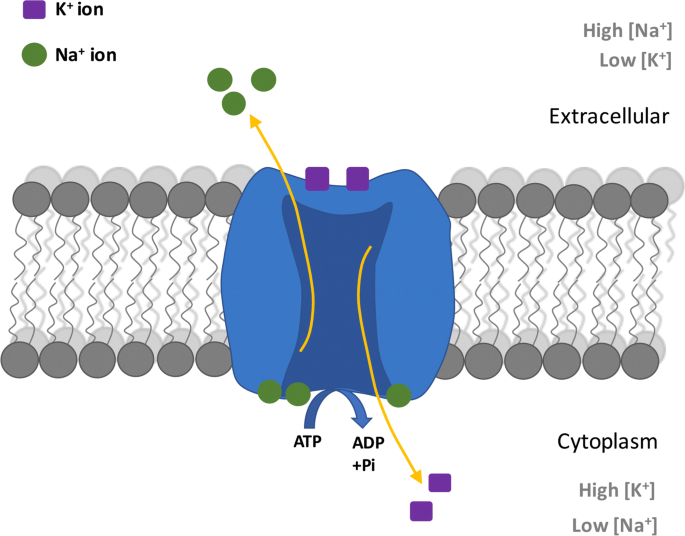
Na+/K+ pump
Proton (H+) Pump
Na+/K+ pump
Pumps 3 Na+ out, 2 K+ into cell, makes cell interior more negative
Process powered by ATP
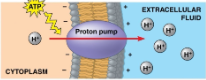
Proton (H+) Pump
Pushes protons across membrane
ex) mitochondria for ATP production
Stores energy to be used later via charge differences
Bulk Transport
Transport of large molecules
Independent of concentration gradient
Energy is required
ex) endocytosis and exocytosis
Exocytosis
When a vacuole membrane becomes a part of the cell membrane and the contents are released, Active Transport
ex) Proteins, hormones, neurotransmitters, waste
Diffusion
when energy is required to move materials through a cell membrane
Equilibrium
When the molecules of one substance are spread evenly throughout another substance to become balanced
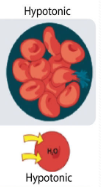
Hypotonic Solution
Less concentrated solution
More free water
Hypertonic Solution
More concentration
Less free water
Isotonic Solution
2 solutions have equal concentrations
How does water move?
hypotonic to hypertonic
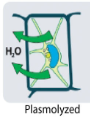
Plasmolysis
plant cell shrinking due to water loss
Crenation
animal cell shrinking due to water loss

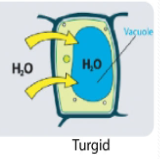
Turgor pressure
The force of water in the vacuole pressing against the cell wall, expands only until back pressure is exerted that limits further water intake
Keeps the cell healthy.
Cytolysis
animal cell bursting due to water gain
Cells in hypertonic solutions…
Lose water, get smaller
Cells in hypotonic solutions…
Gain water, get bigger