Chapter 8: The Muscular System Overview
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Types of Muscle Tissue
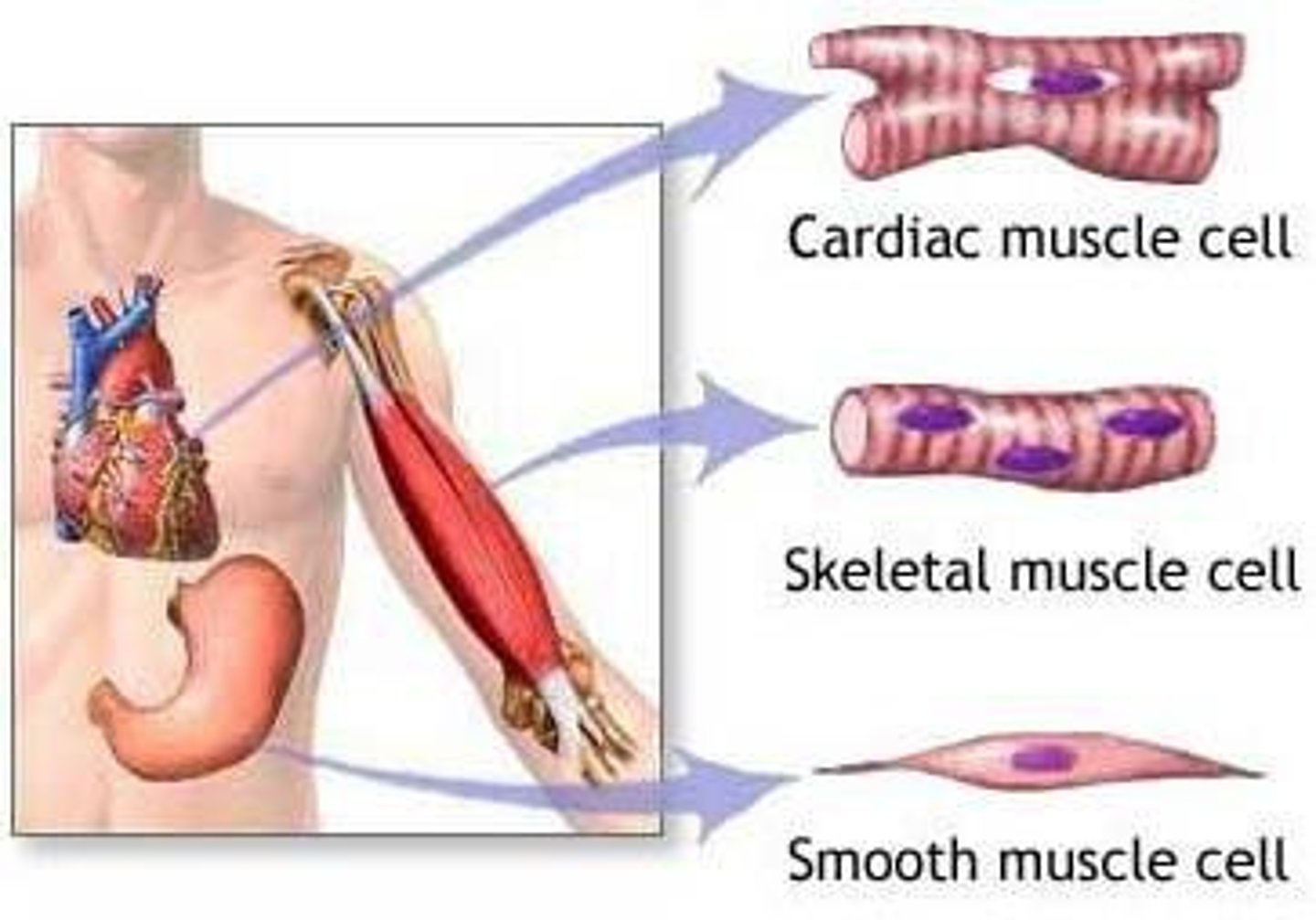
There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: Cardiac Muscle, Skeletal Muscle, and Smooth Muscle, differing in location, microscopic structures, and conscious control of contraction.
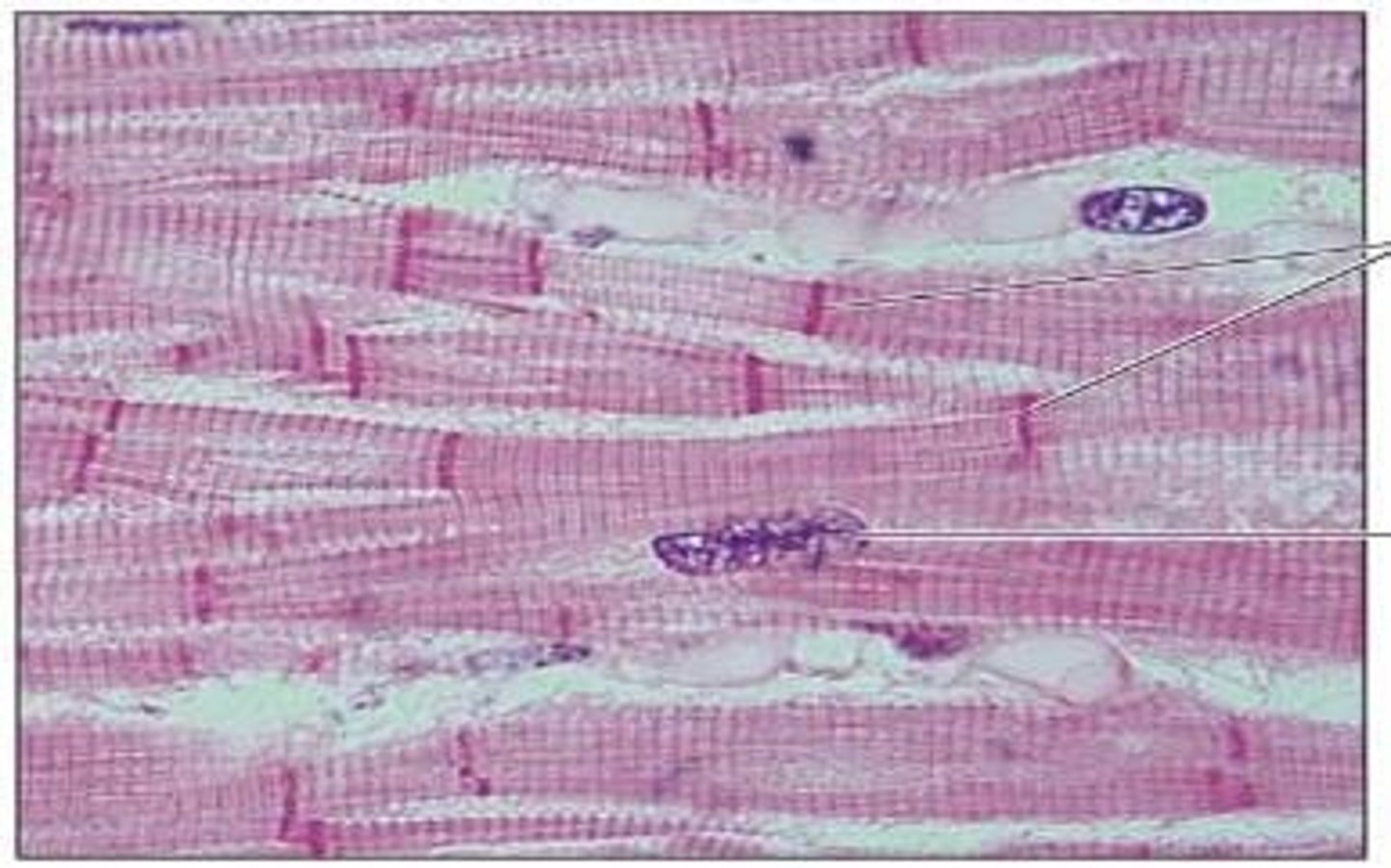
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary, striated muscle that forms the muscular wall of the heart (myocardium) and produces regular contractions known as heartbeats.
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary, unstriated muscle located in the walls of hollow organs such as blood vessels, digestive tract, airways, and bladder.
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary, striated muscle attached to bones, with muscle fibers in the form of long cylinders running parallel to each other and being multinucleated.
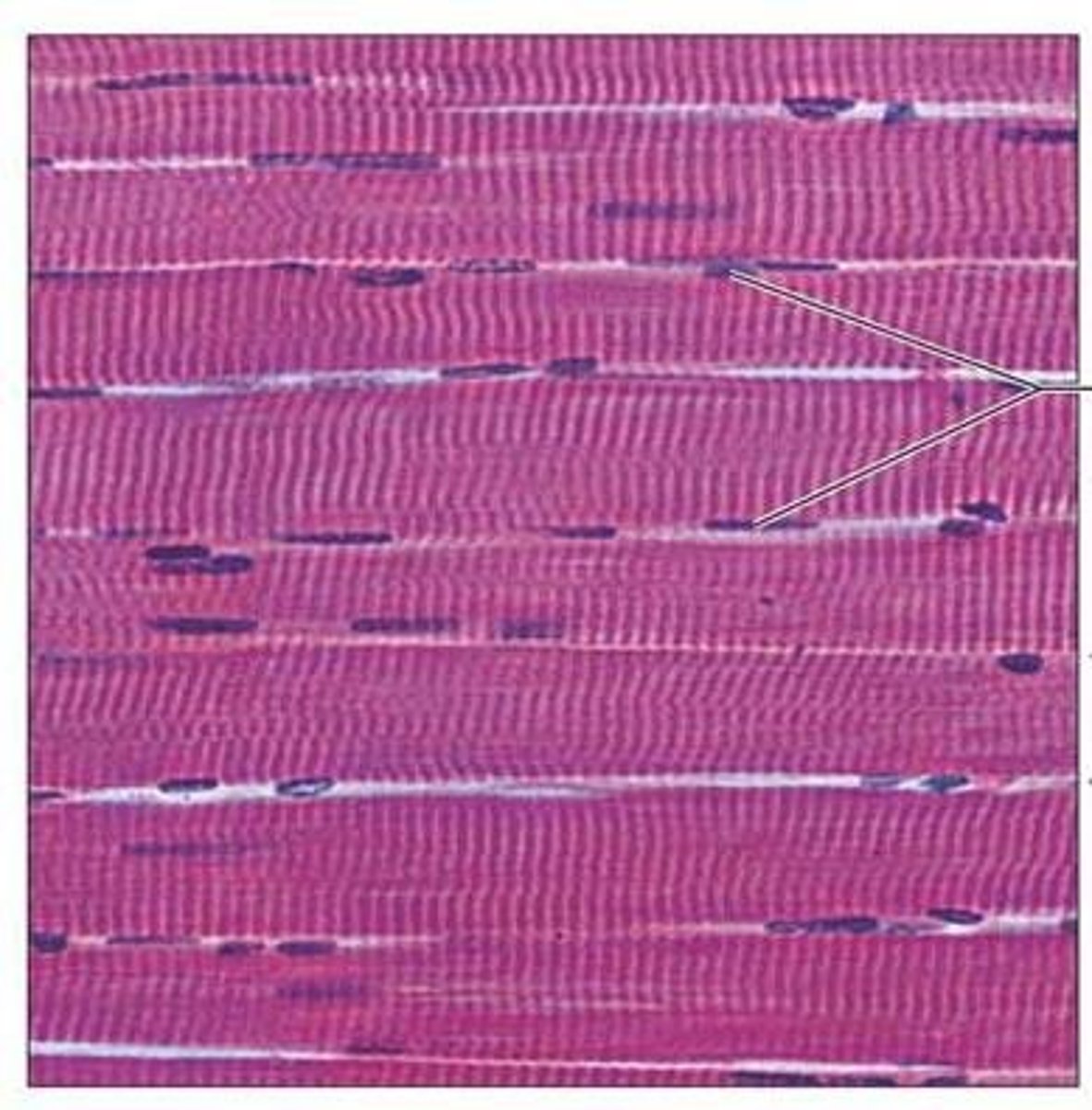
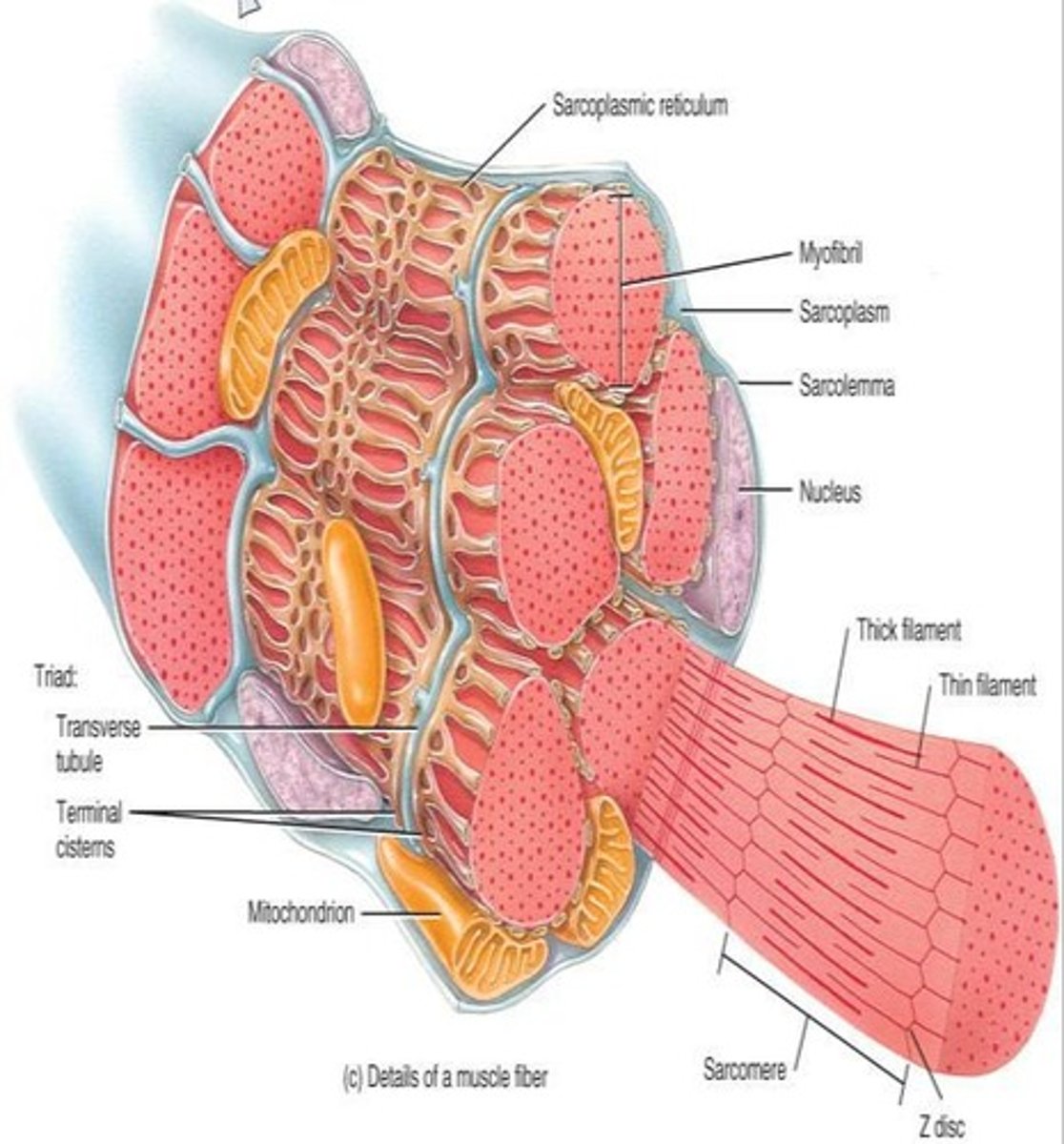
Histology of a Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Muscle fibers are long, cylindrical, and multinucleated; the sarcolemma is the cell membrane, and the sarcoplasm is filled with myofibrils and mitochondria.
Myofilaments
Structures that make up myofibrils within muscle fibers, essential for muscle contraction.
Myoglobin
Membranous sacs in muscle fibers that store oxygen.
Glycogen
A substance that can be broken down to release glucose when needed for energy.
Creatine Phosphate
A unique substance to muscle cells that can release energy when bonds are broken, used when ATP is depleted.
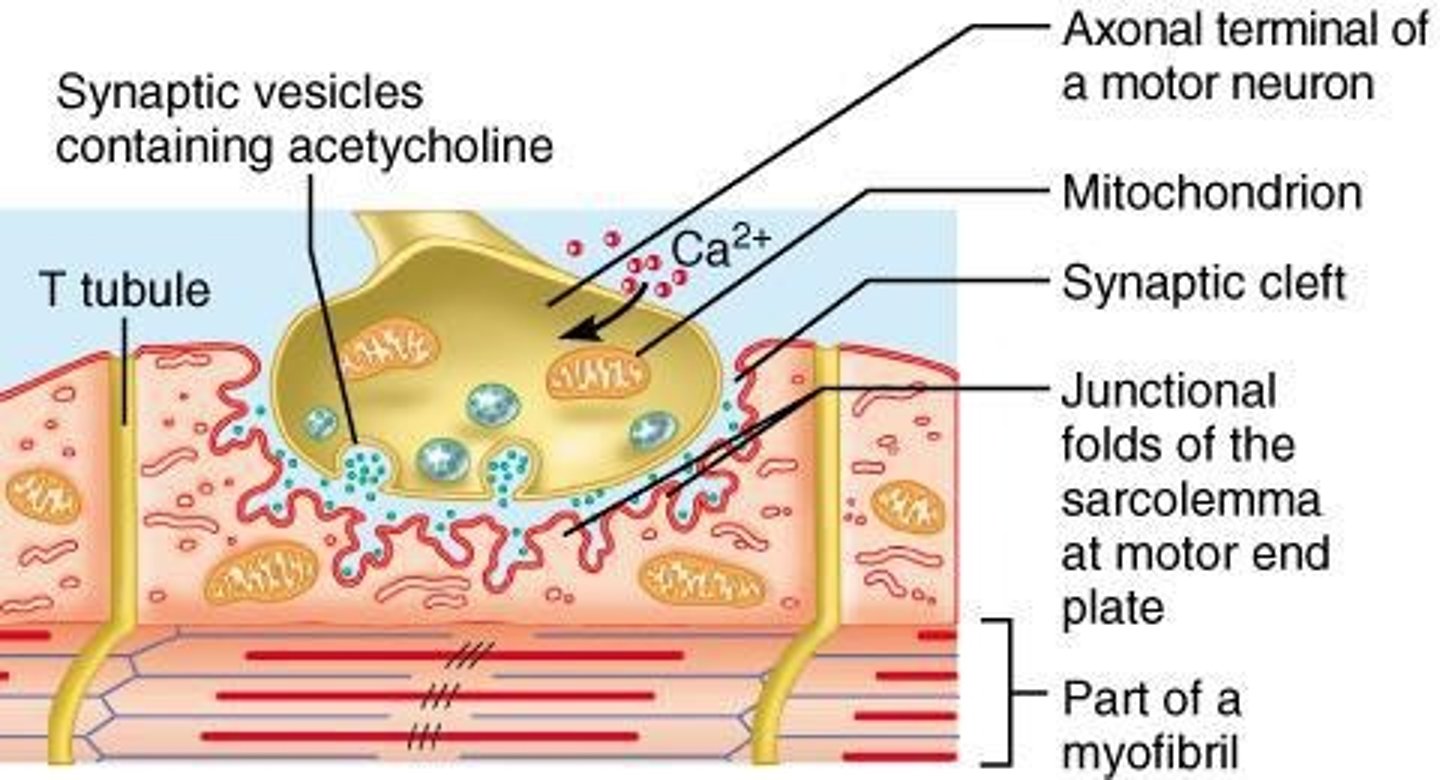
Neuromuscular Junction
The site where the axon of a motor nerve communicates with a muscle fiber, essential for muscle contraction.
Motor Unit
A single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it stimulates.
T-tubules
Deep invaginations of the sarcolemma that allow depolarization of the membrane to quickly penetrate to the interior of the muscle cell.
Axon Terminal
The end of the axon of the motor neuron, containing synaptic vesicles filled with the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (Ach).
Sarcoplasm
The cytoplasm of a muscle fiber, filled with myofibrils and containing mitochondria for ATP production.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum in muscle fibers for calcium storage.
Muscle Fiber
The basic cellular unit of muscle tissue, long and cylindrical, capable of contraction.
Striated Muscle
Muscle tissue that has a striped appearance due to the arrangement of myofilaments.
Unstriated Muscle
Muscle tissue that does not have a striped appearance, typically found in smooth muscle.
Involuntary Muscle
Muscle that contracts without conscious control, such as cardiac and smooth muscle.
Voluntary Muscle
Muscle that is under conscious control, such as skeletal muscle.
Oxygen Debt
The amount of oxygen required to oxidize lactic acid and restore muscle cells to their resting state after exercise.
Muscle Contraction
The process by which muscle fibers shorten and generate force.
Sarcolemma
The cell membrane of a muscle fiber.
Synapse
Small gap (synaptic cleft) forming a point of communication between the axon terminal and the muscle fiber, through which acetylcholine diffuses.
Motor end plate
The region of the sarcolemma adjacent to the axon terminal, it forms multiple folds holding acetylcholine receptors.
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
Fluid outside of cells that provides a medium for the exchange of materials.
ACh
Acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter released by synaptic vesicles at the axon terminal.
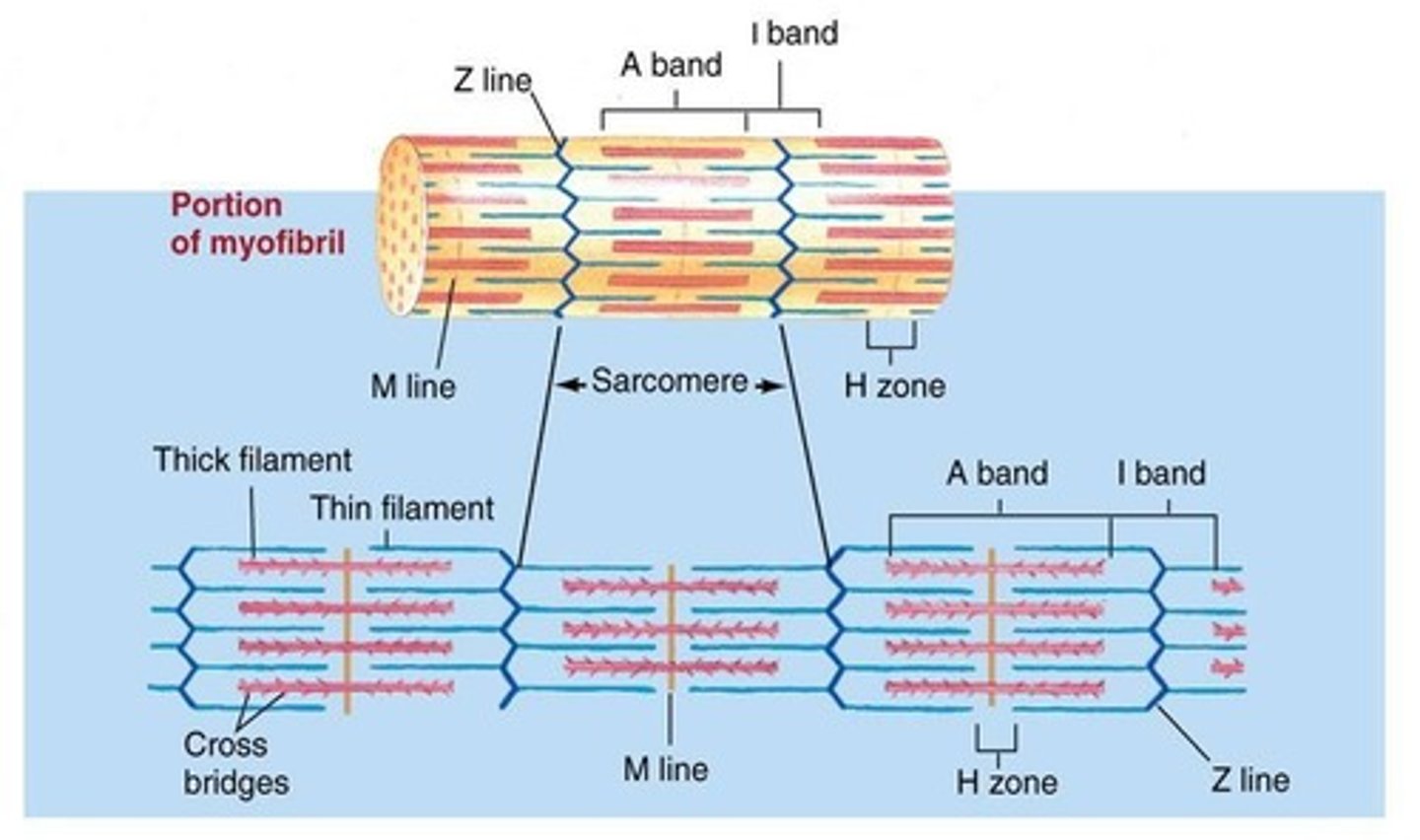
Thick filaments
Myosin filaments that are part of the muscle structure.
Thin filaments
Actin filaments that are part of the muscle structure.
A band
Represents the length of the myosin thick filaments, its length stays constant during contraction.
I band
Represents the region between adjacent myosin filaments, containing actin filaments not overlapped by myosin filaments.
H zone
A paler zone in the middle of the A band where the myosin filaments are not overlapped by the actin filaments.
M line
Bisects the H zone in the muscle fiber.
Z line
Bisects the I band and marks the boundaries of a sarcomere.
Sarcomere
The functional unit of striated muscle contraction formed of a band of thick myosin filaments in the middle and thin actin filaments on each side.
Contractility
The ability of a muscle fiber to undergo shortening and to become thicker.
Myosin Filament
Thick protein filament formed of myosin molecules, each with a rod-like tail and two heads.
Actin Filaments
Thin protein filament formed of actin molecules joined end-to-end and arranged into two helical strands.
Tropomyosin
Filaments that spiral around the actin strands blocking the myosin binding sites.
Troponin
A regulatory protein which attaches to tropomyosin and has a binding site for calcium.
Calcium
Released in the sarcoplasm during muscle contraction.
Actin
A protein that forms thin filaments in muscle fibers.
Ca2+
The ion that plays a crucial role in muscle contraction by binding to troponin.
Myosin
A protein that forms thick filaments and binds to actin to facilitate muscle contraction.
Myosin cross bridge
The connection formed when myosin binds to actin during muscle contraction.
Contraction Cycle
The series of events that occur during muscle contraction, including ATP breakdown and cross bridge formation.
ATP
A molecule that provides energy for muscle contraction and is required for cross bridge detachment.
ADP
A product of ATP breakdown that is involved in the muscle contraction cycle.
Pi
Inorganic phosphate released during ATP breakdown that is involved in muscle contraction.
Power Stroke
The phase of muscle contraction where myosin changes shape and pulls actin toward the center of the sarcomere.
Relaxation
The process where calcium is pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum and tropomyosin-troponin complex recovers binding sites.
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
The process of producing ATP in the presence of oxygen, involving the metabolism of glucose and fatty acids.
Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
The process of producing ATP without oxygen, resulting in the conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic acid.
Lactic Acid
The product of anaerobic respiration that accumulates in muscles during strenuous exercise.