612 Benign bone lesions, Benign bone disorders
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
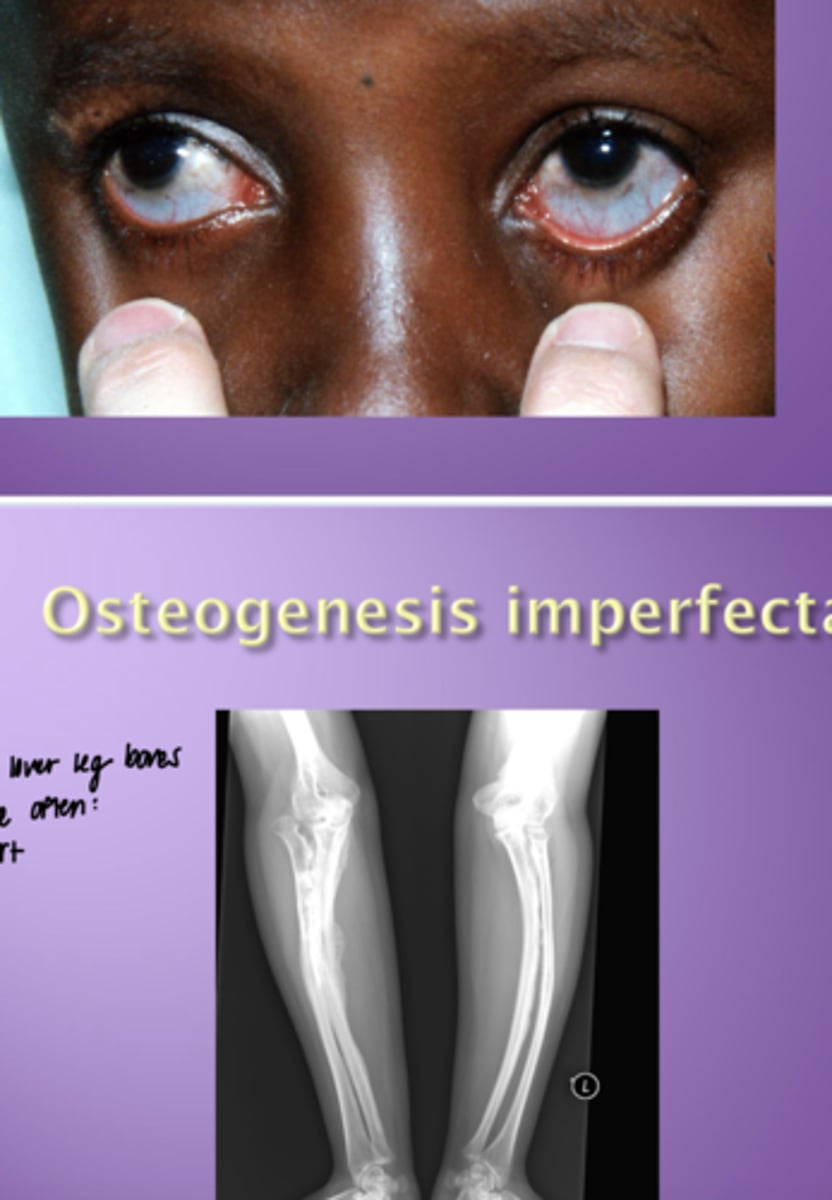
Osteogenesis imperfecta
- characteristics
- Blue sclera
- Bowed leg bones (pts often short)
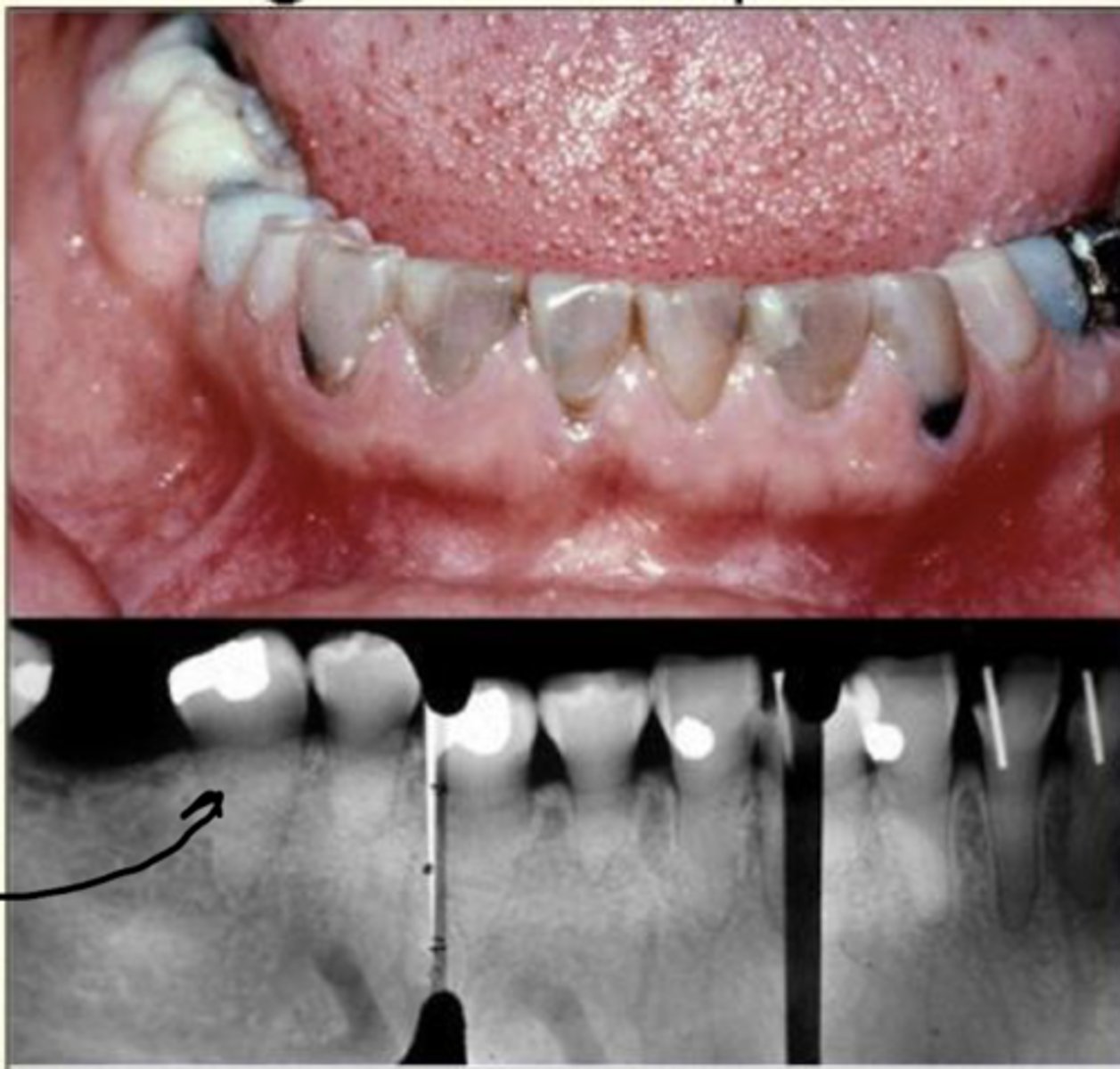
Dentinogenesis imperfecta
- Discolored teeth (yellow/brown/grey)
- Lack of enamel, exposed dentin
- Bulbous crowns
- Obliterated pulp chamber
- Short roots
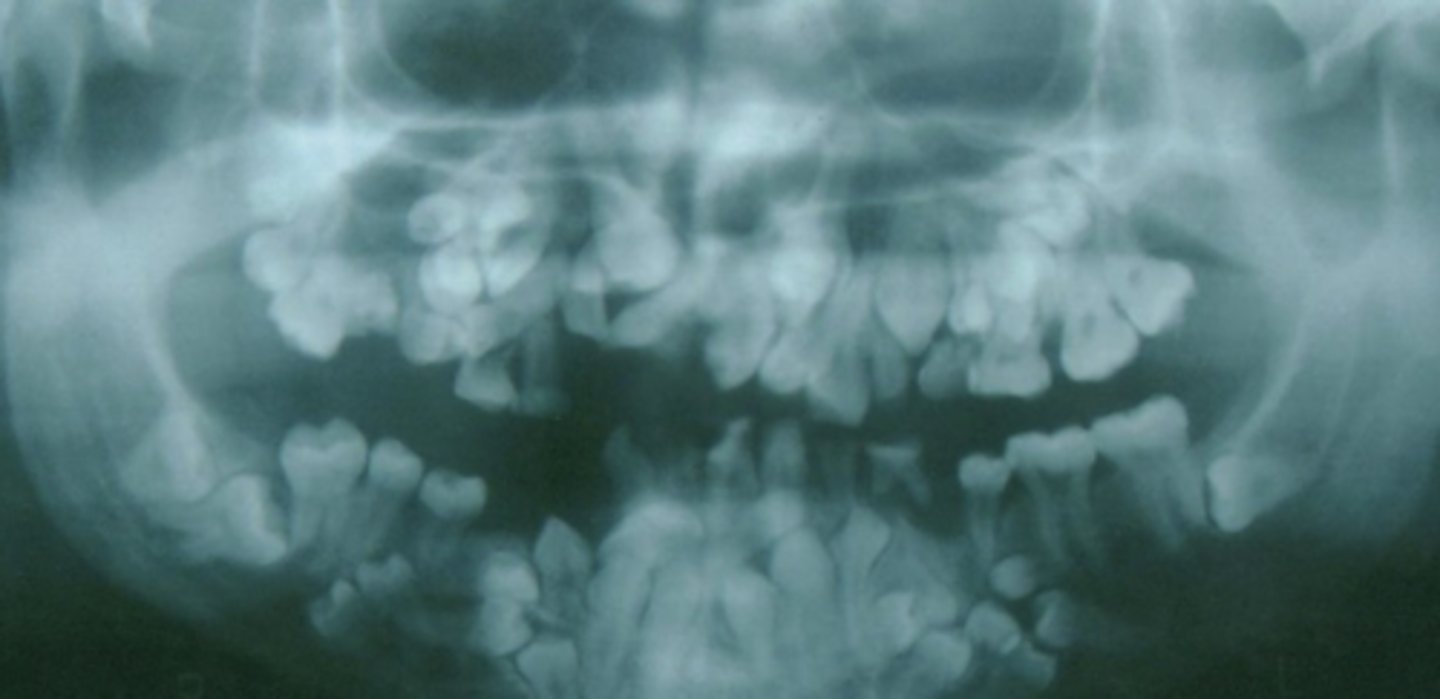
Cleidocranial dysplasia
- Lack of clavicles
- Many supernumerary, impacted teeth
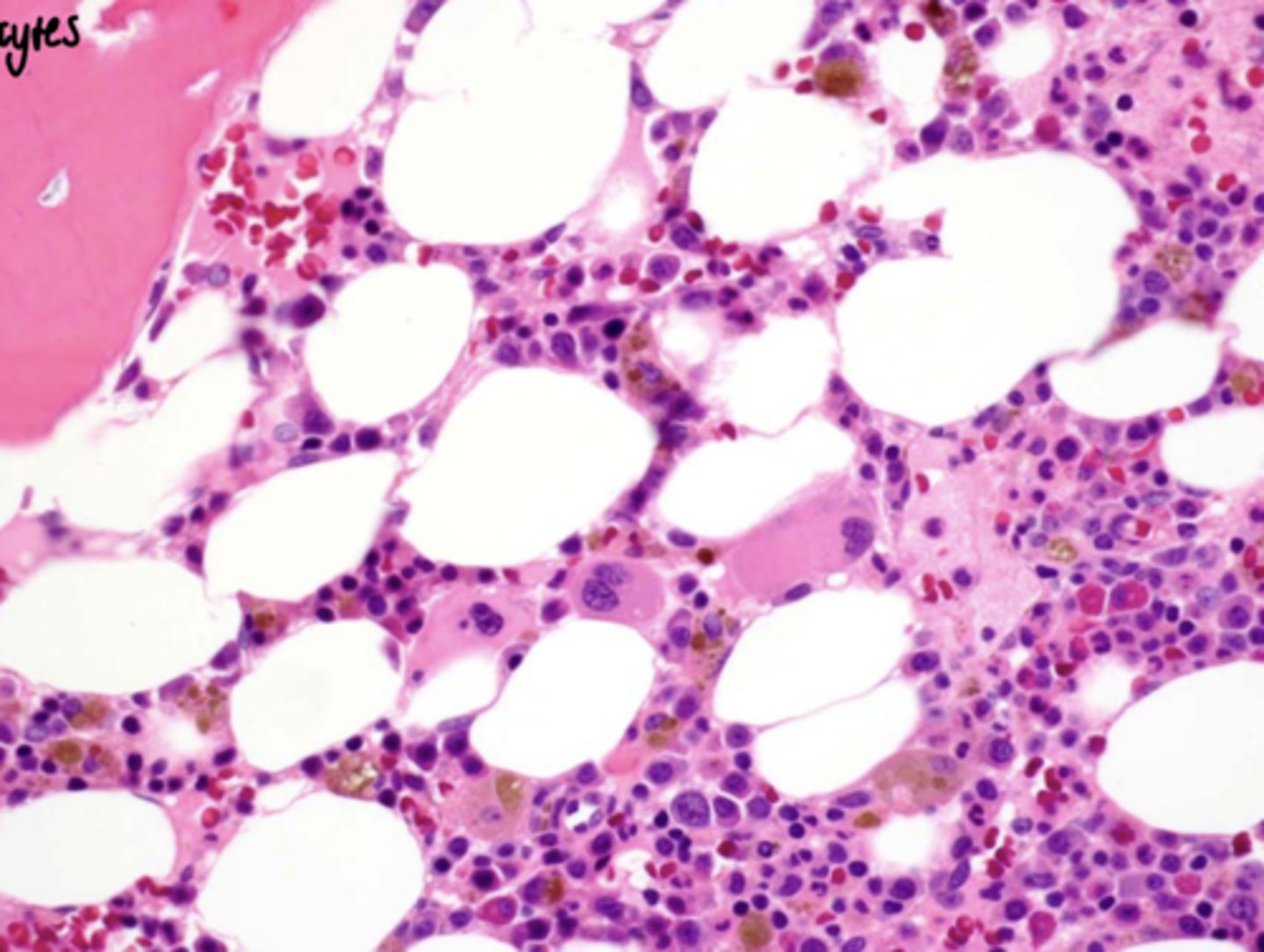
Focal osteoporotic bone marrow defect
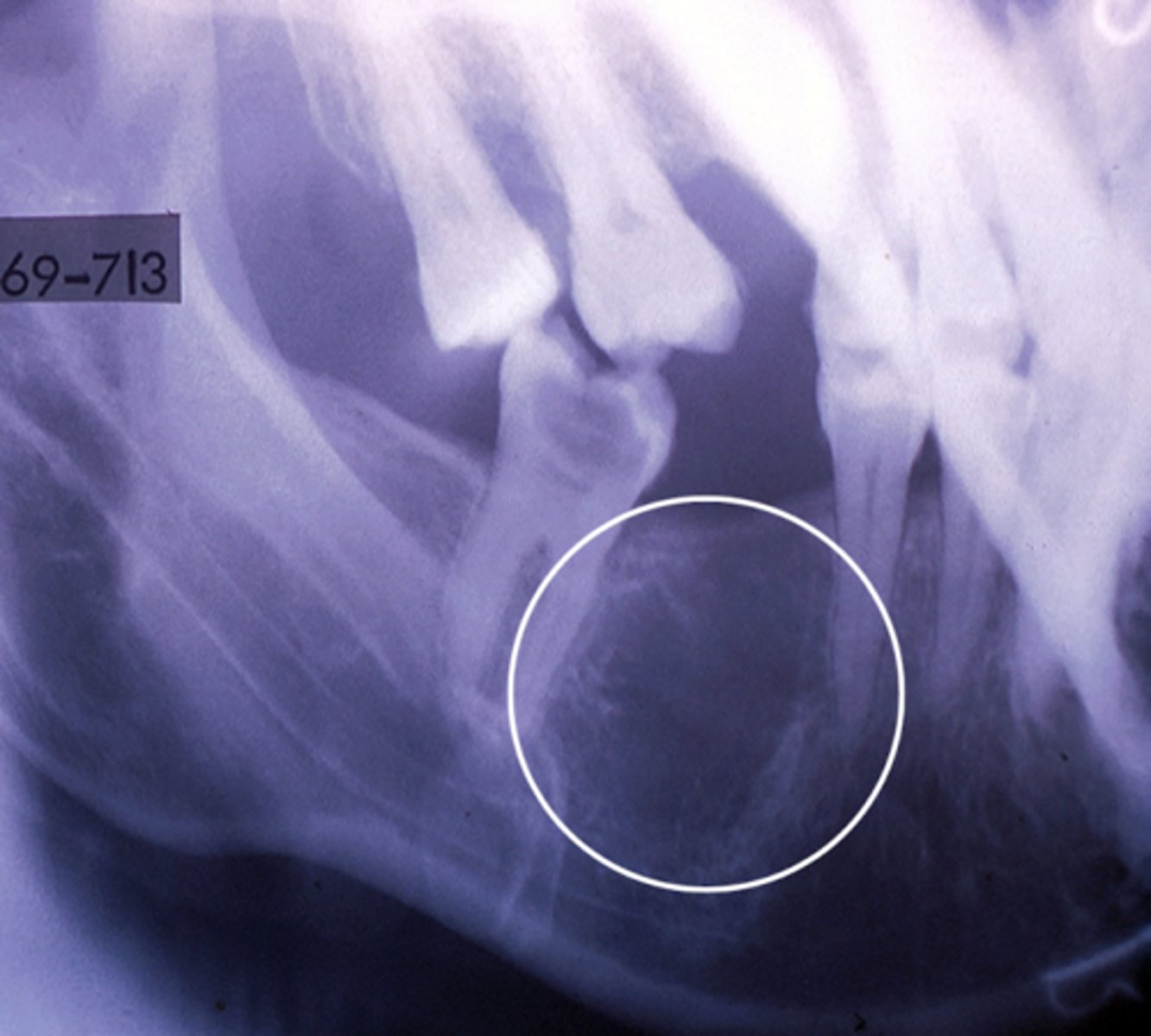
Focal osteoporotic bone marrow defect - histology
When biopsied, see bone marrow:
- Usually hematopoeitic BM
- Huge cells in bone marrow: Megakaryocytes
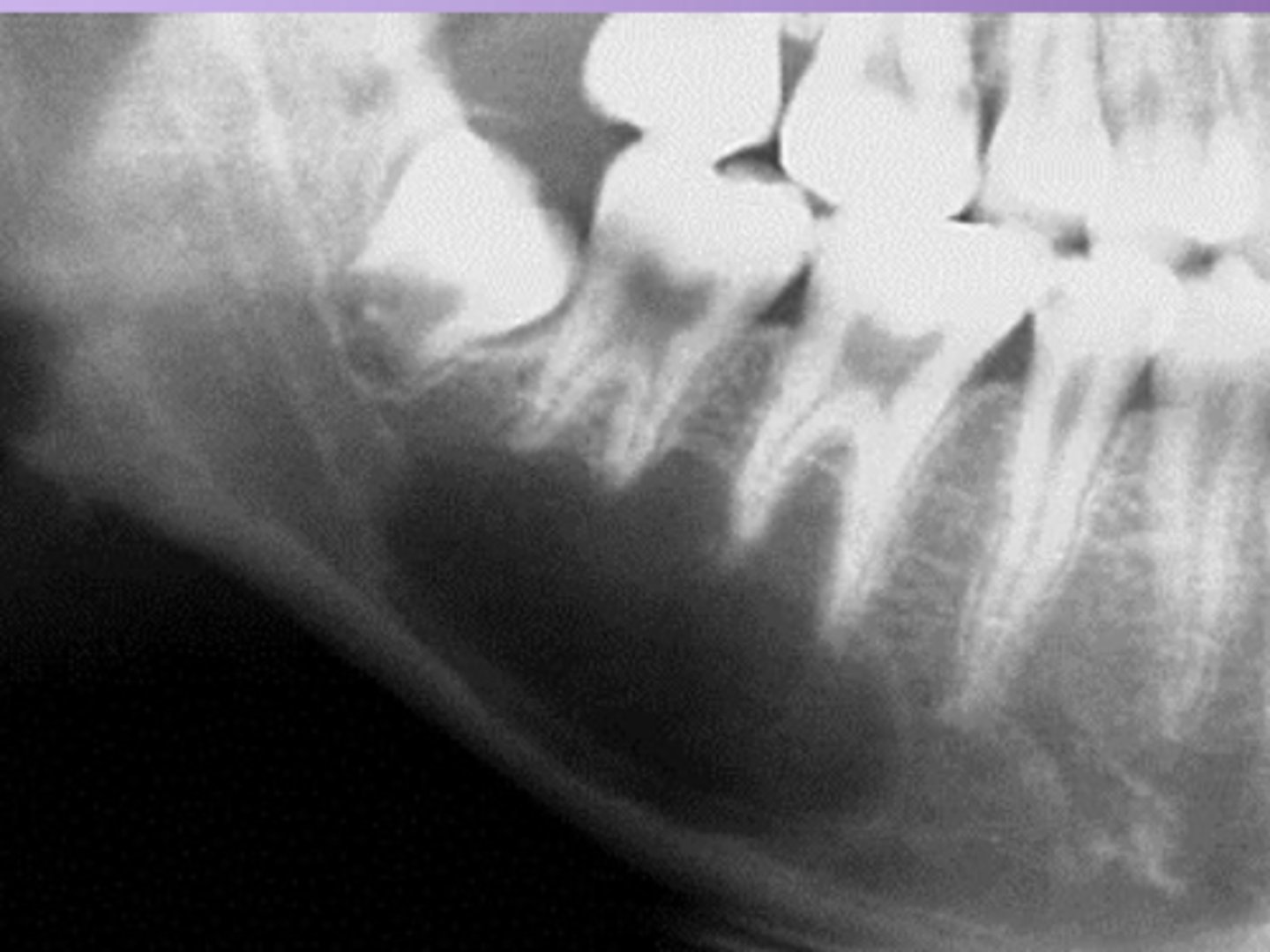
Traumatic bone cyst
= Well defined RL, scalloping
- #1: test teeth
- #2: biopsy
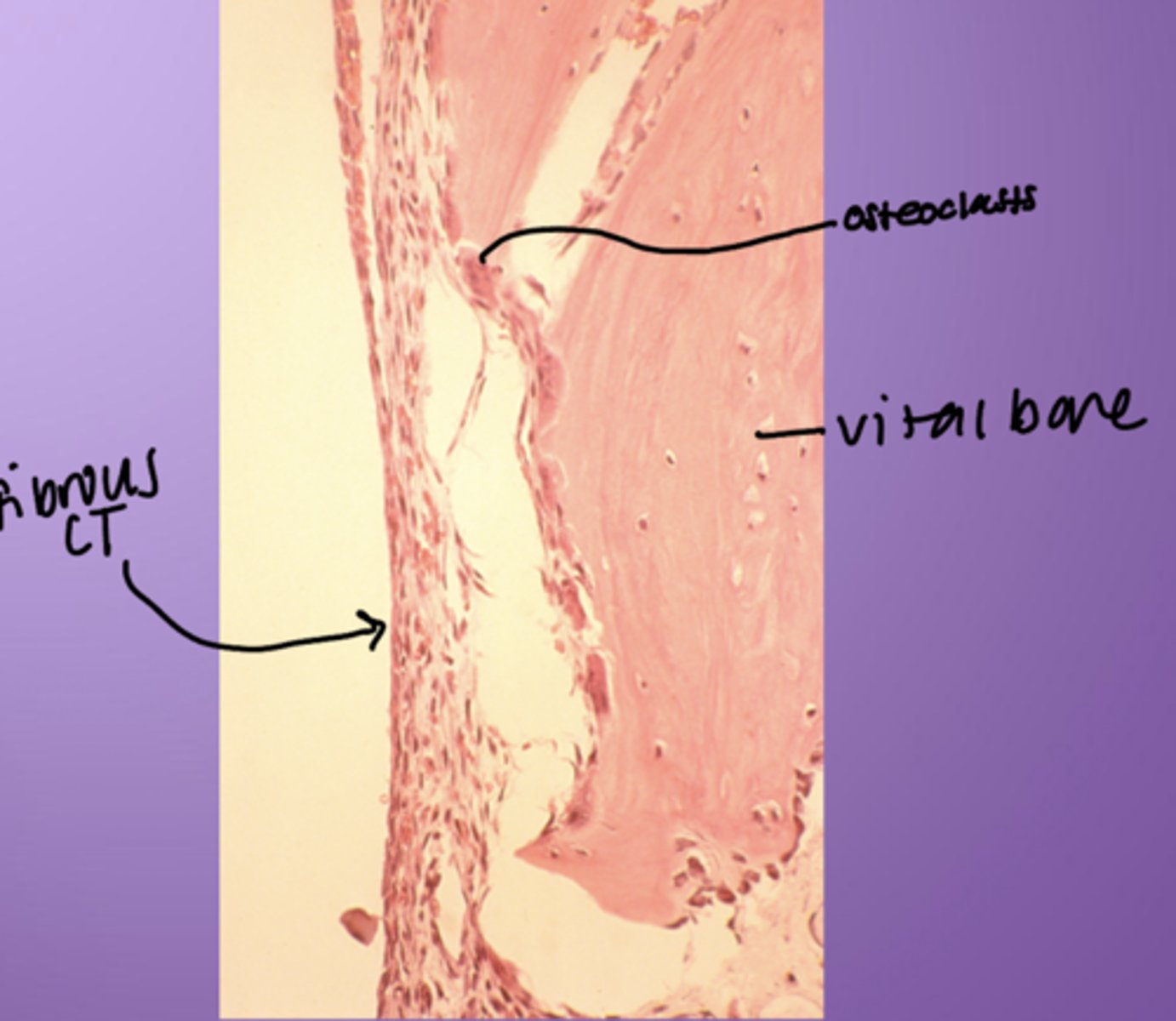
Traumatic bone cyst - histology
- Osteoclasts
- Vital bone
- Fibrous CT
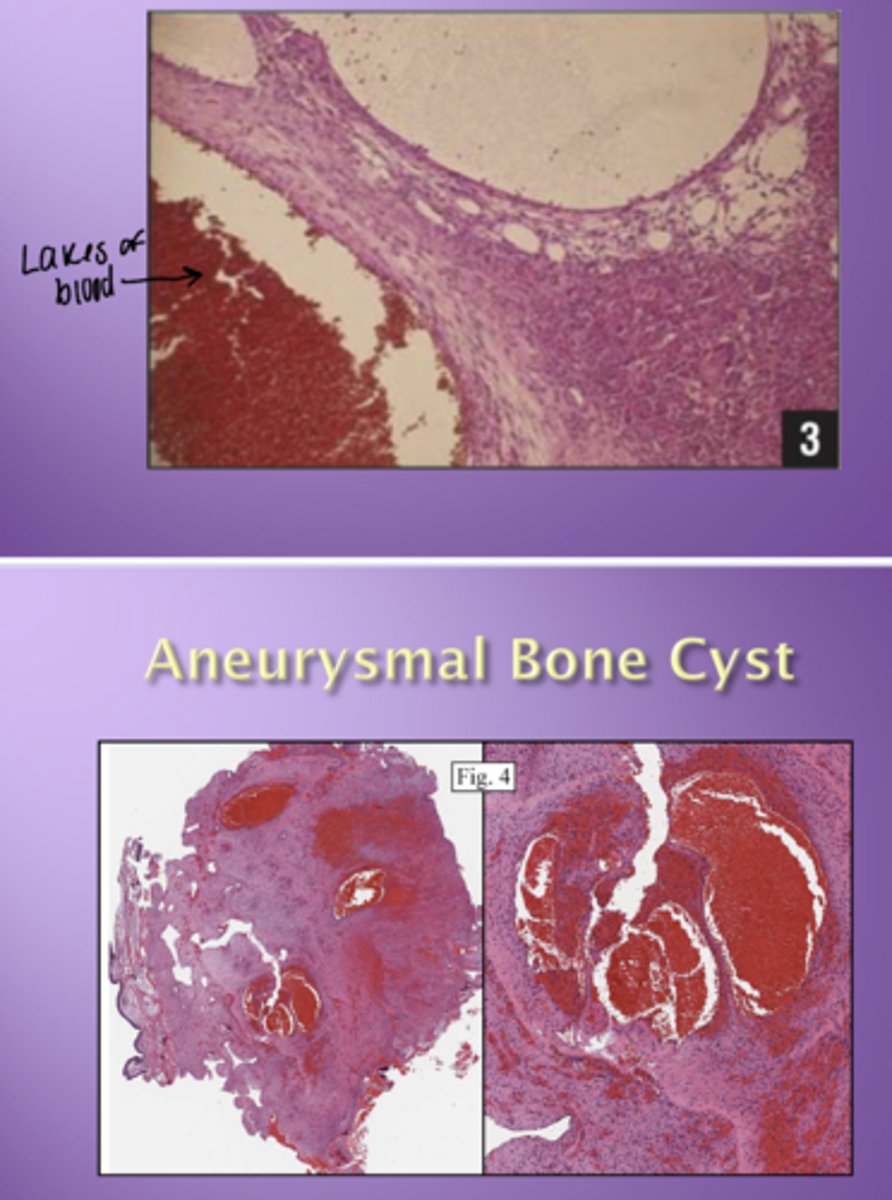
Aneurysmal bone cyst
= "Blow out fracture"
- Bone is thinning
- Contains multinucleated giant cells

Aneurysmal bone cyst - histology
Lakes of blood
- No endothelium around spaces
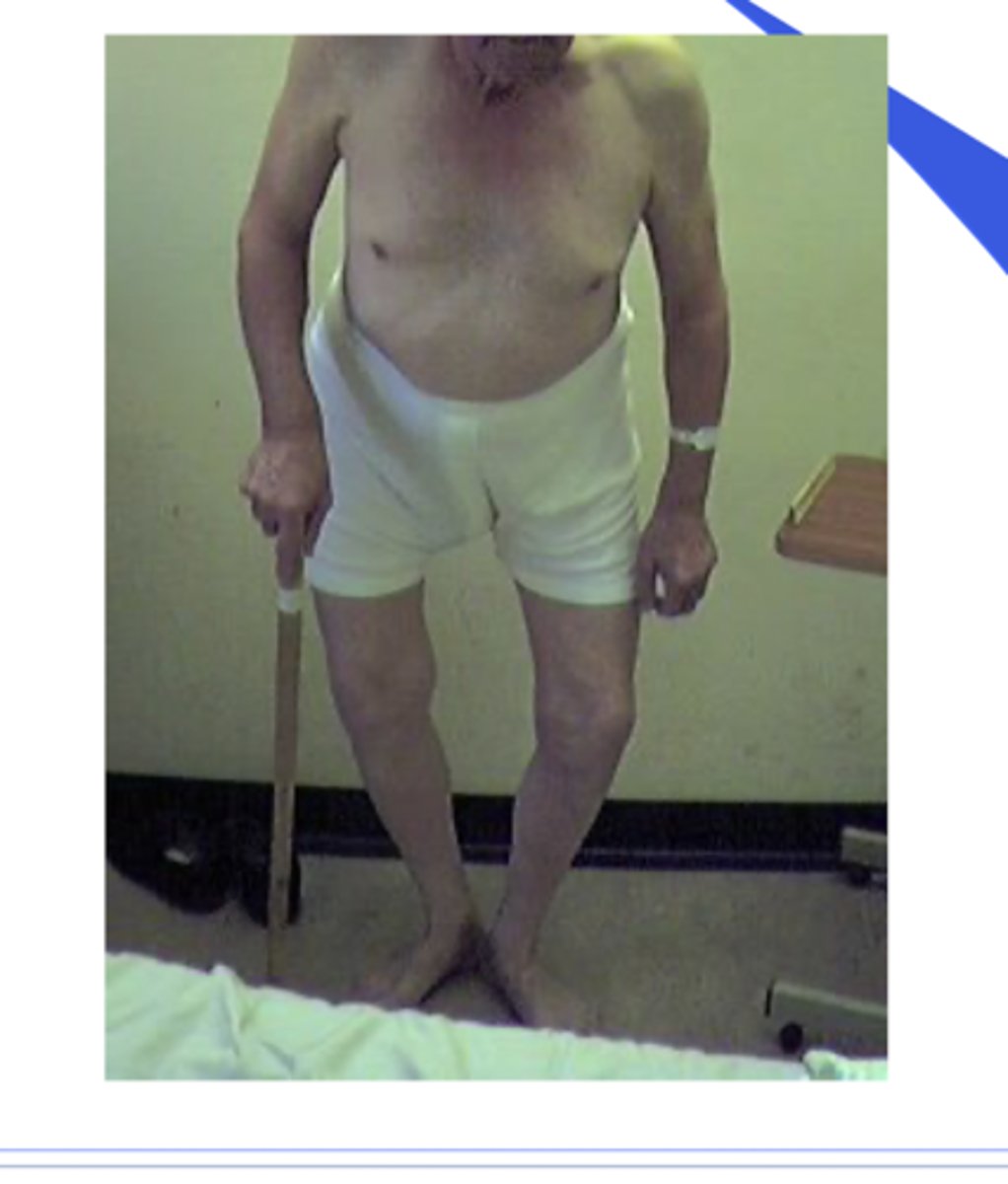
Paget's disease of bone
- characteristics?
- Heavy brow
- Upper skull
- Upper midface in nose region
- Enlarged mandible
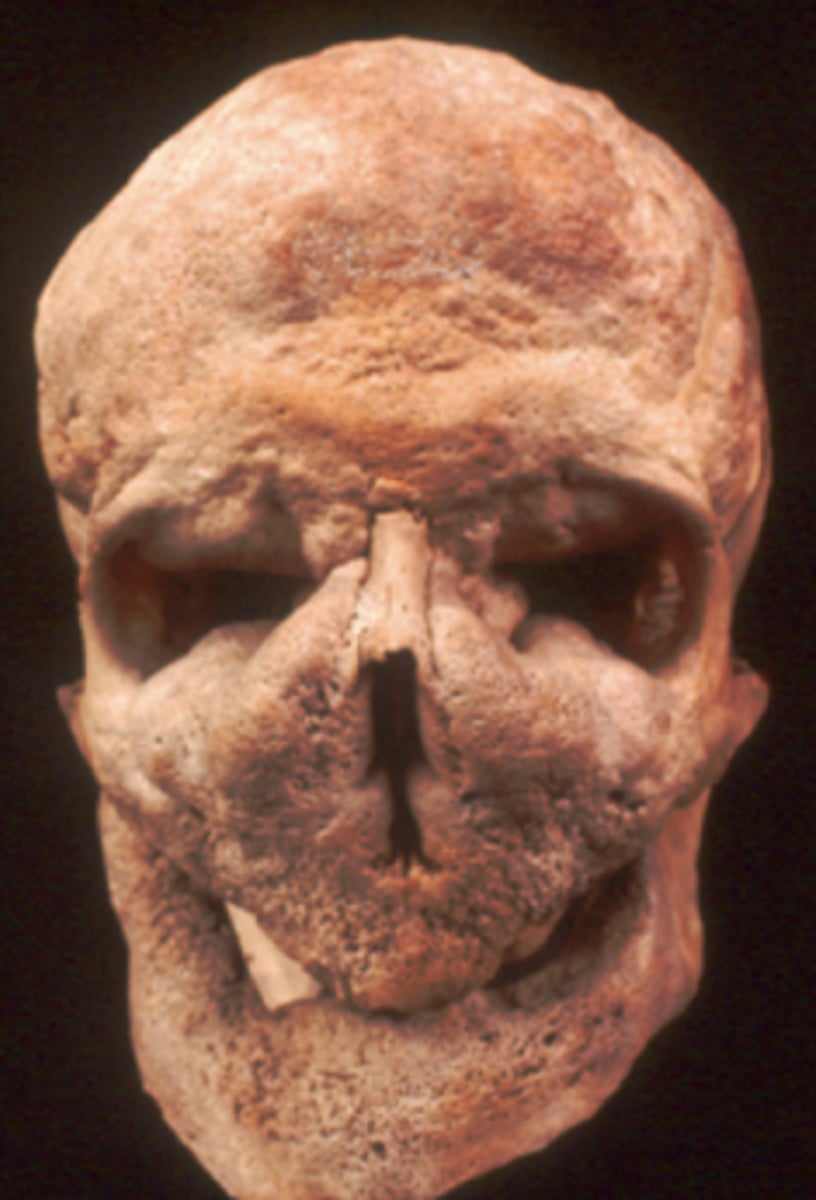
Paget's disease of bone =
Osteitis Deformans
- Abnormal collagen creating abnormal bone
- bowing of legs
- Hat and dentures may no longer fit
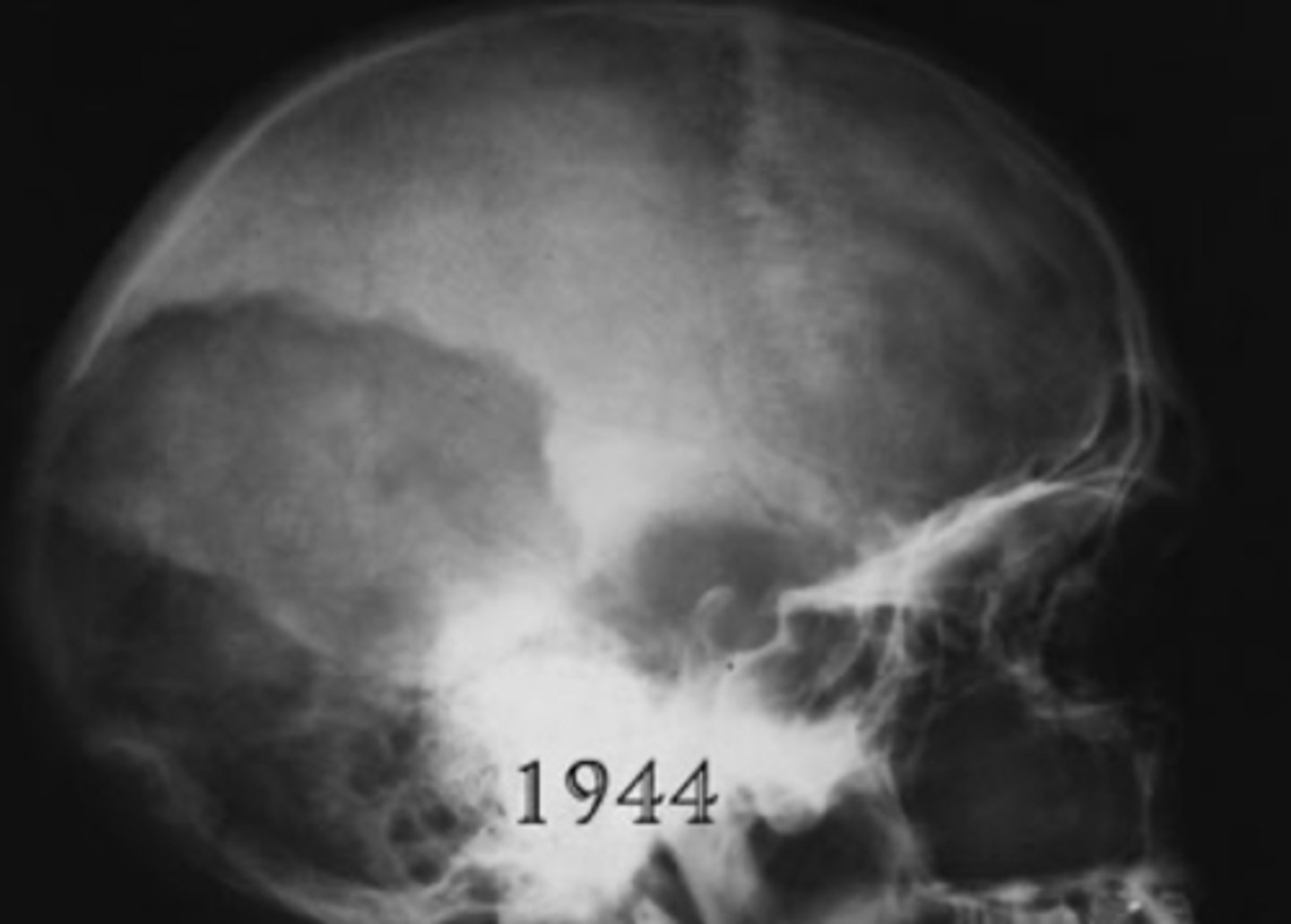
Pagets disease of bone - radiographic appearance
Cotton woll appearance = appositional bone growth
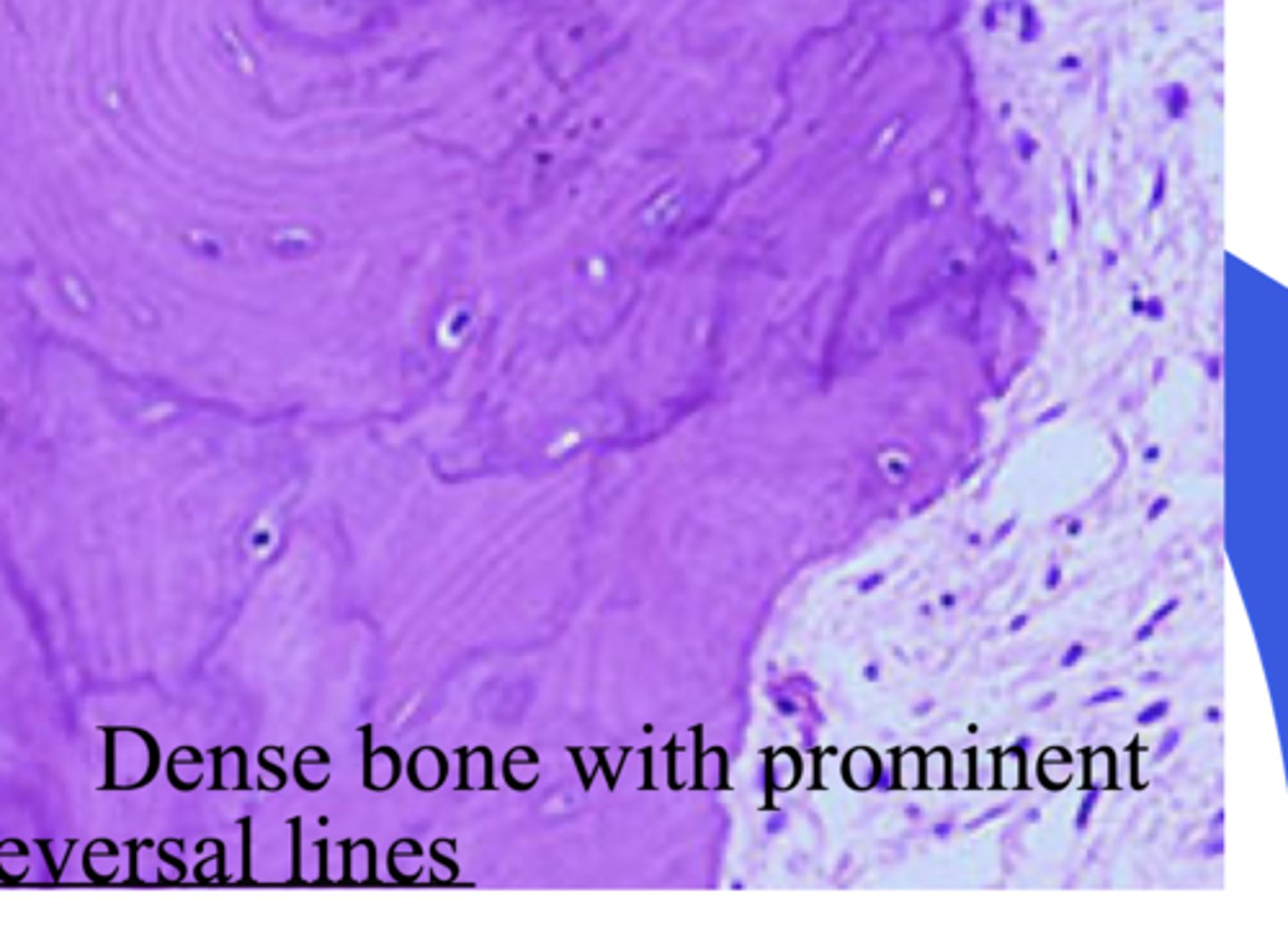
Paget's disease - histology
- Reversal lines
Leontiasis ossea
= Lion face
- Pagets
- Smashed in look centrally in face
- Thick ribs and vertebrae
- ~2% of cases become osteosarcoma
Langerhans cell disease
= aka Histiocytosis
- Mostly RL lesions
Langerhans cell disease - cells
Birbeck granules
- tennis racquet shaped cells
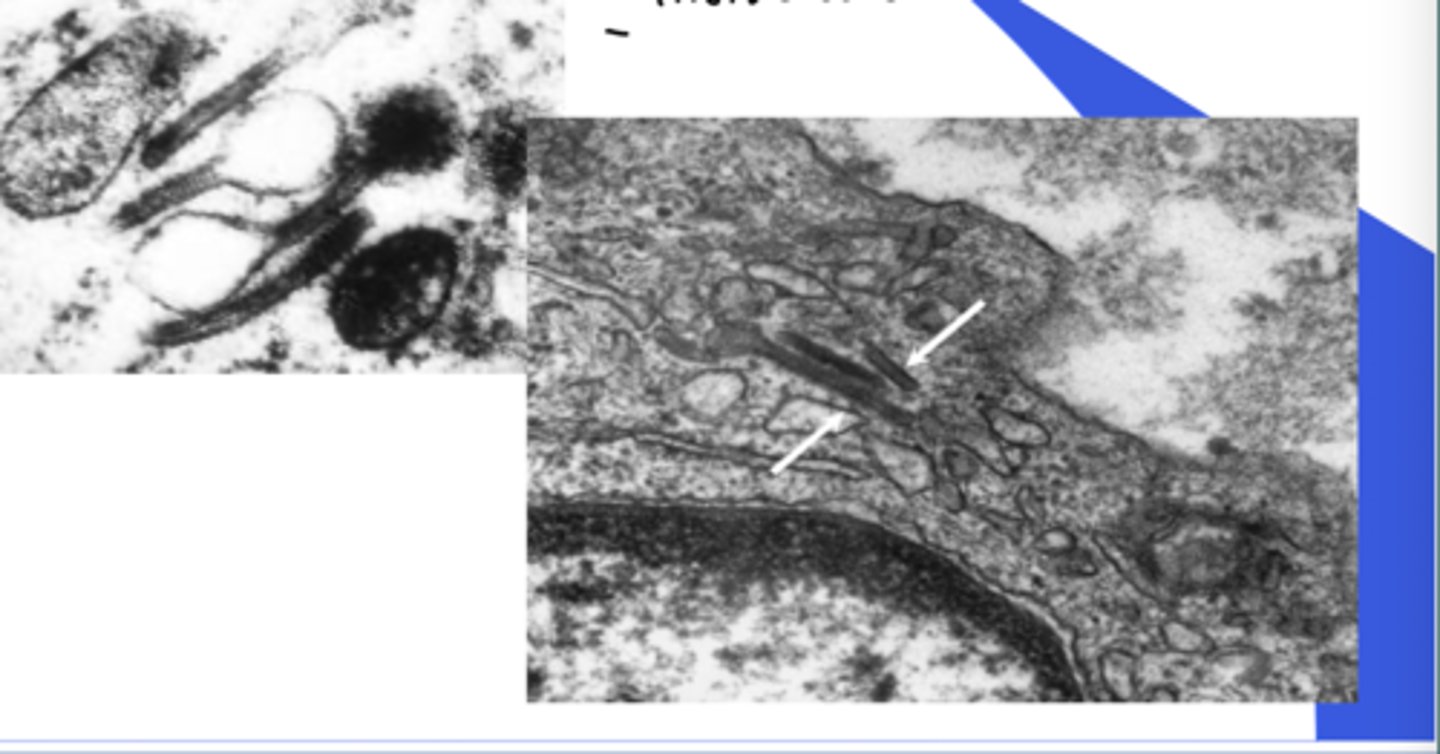
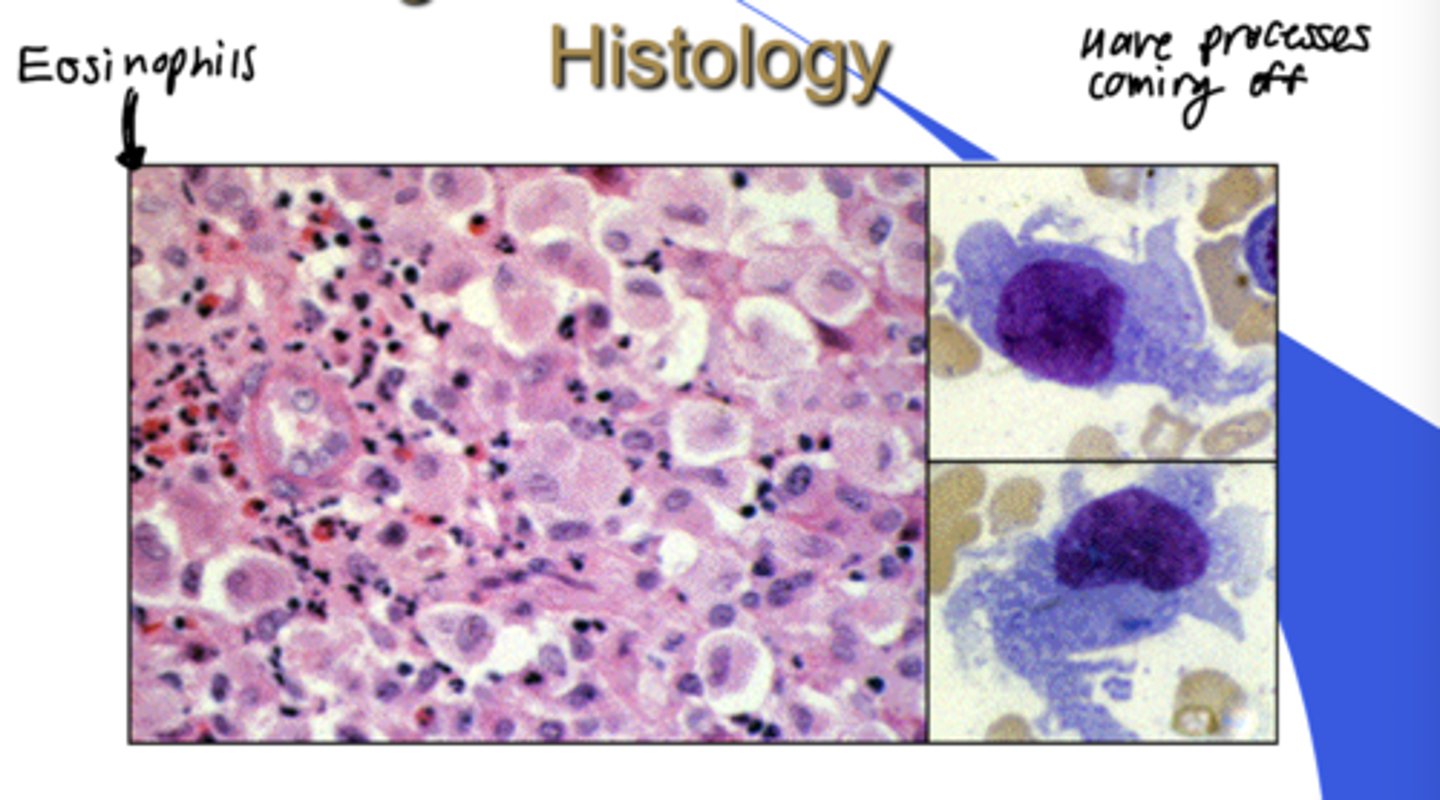
Langerhans cell disease - histology
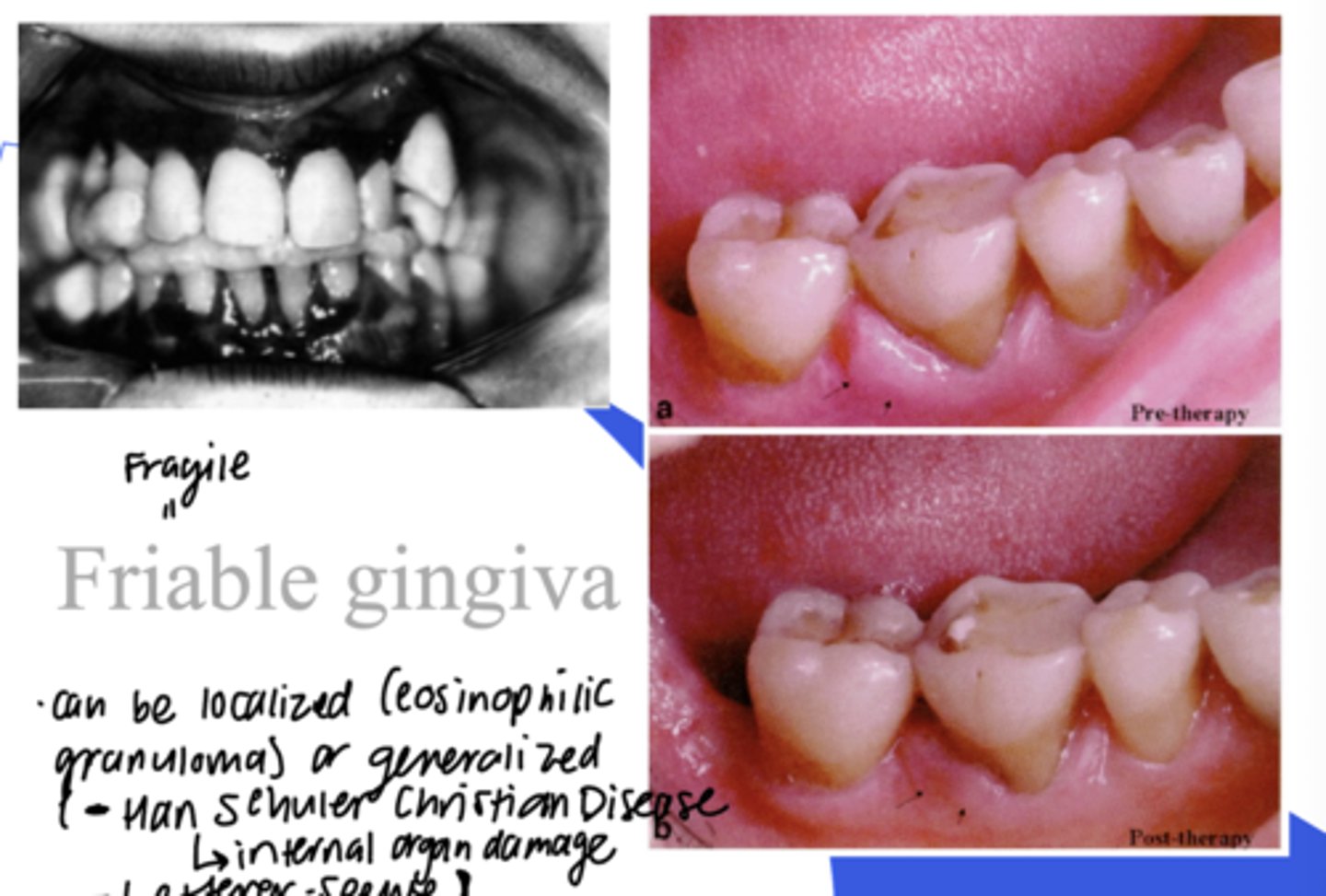
Friable gingiva
= Fragile gingiva
- Can be localized (eosinophilic granuloma) or generalized
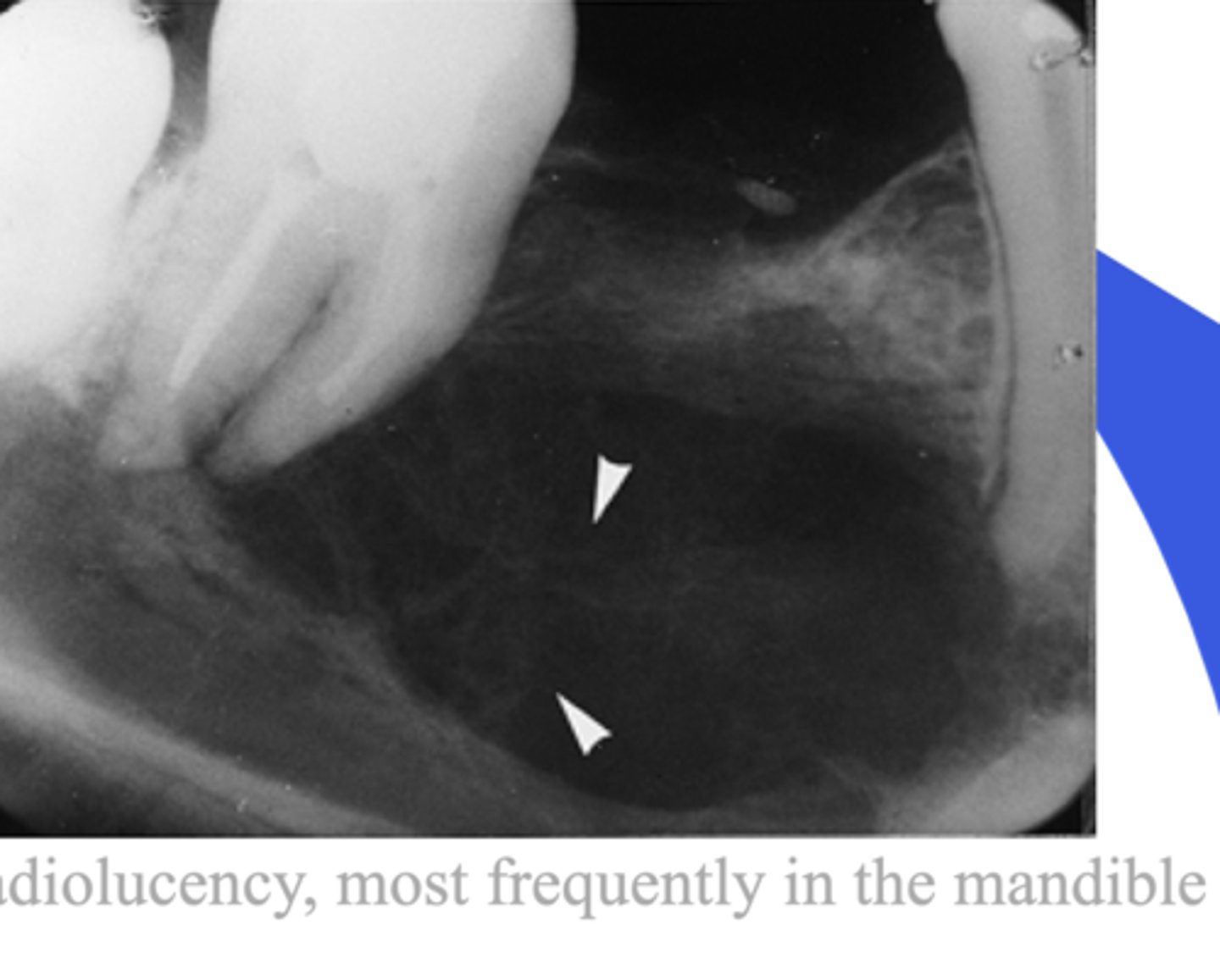
Central giant cell granuloma
- RL --> will keep growing if left alone
- Always check tooth vitality
- Beehive combe (multilocular)
- more common in younger pts
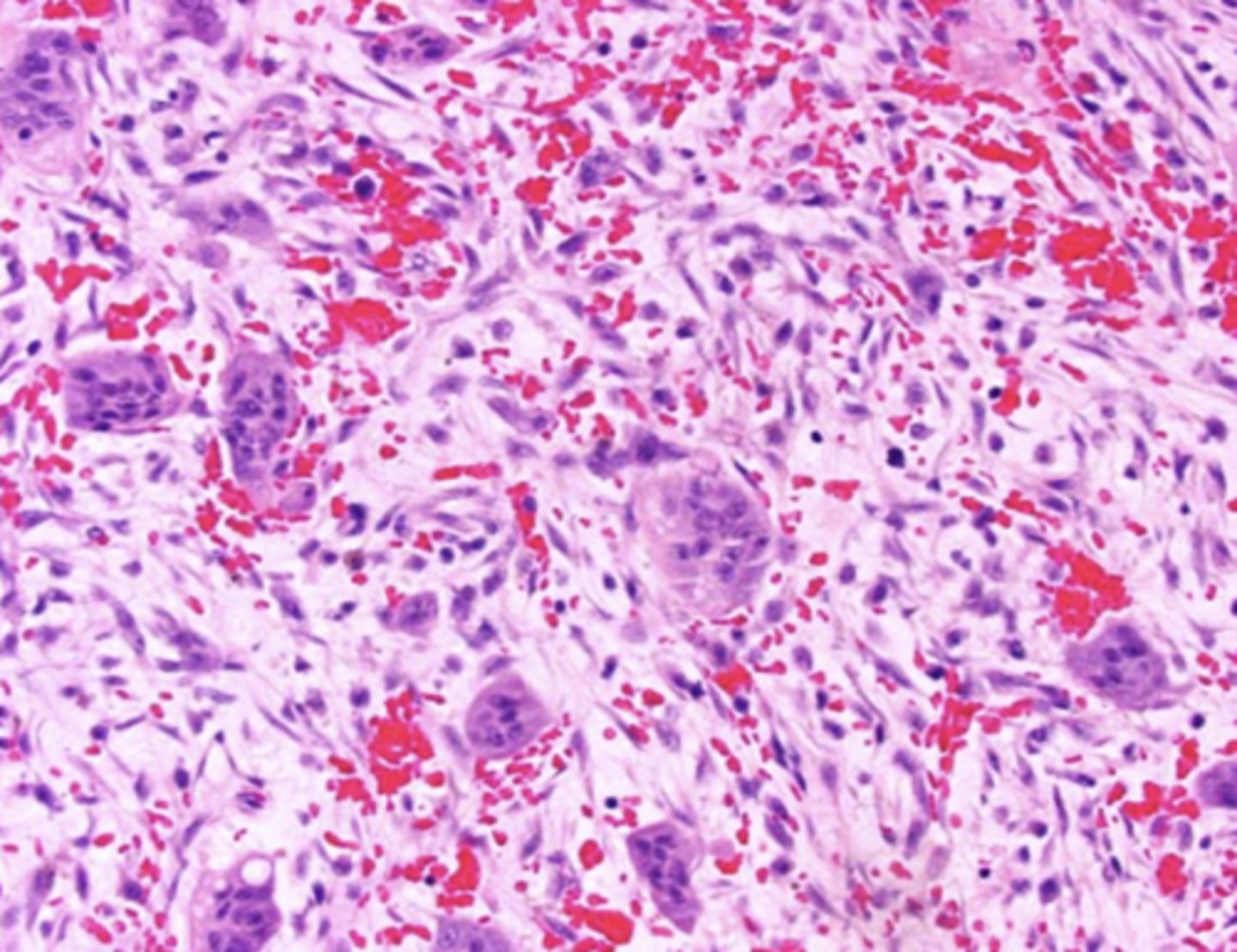
Central giant cell granuloma - histology
- Multinucleated giant cells
- Marcophages
- Areas of hemorrhage
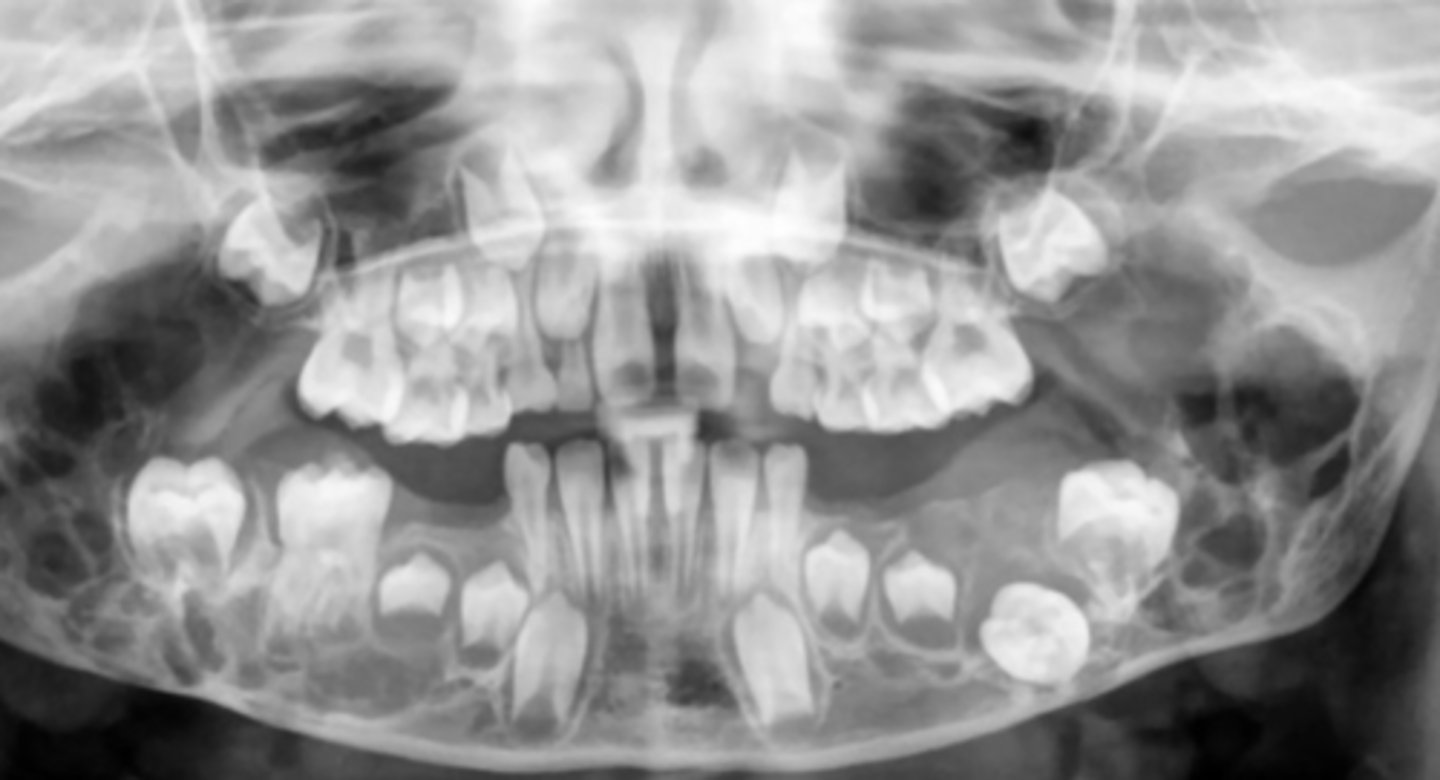
Cherubism
- characteristics
- what kind of inheritance pattern?
- Bilateral multilocular radiolucencies
- Autosomal dominant inheritance
- Classic facies, Proptotic eyes, Lengthening of ramus, Prominent condyle
- Usually resolve after puberty

Cherubism - histology
Same as CGCG
Cherubism - Radiographic
bilateral multilocular lucencies
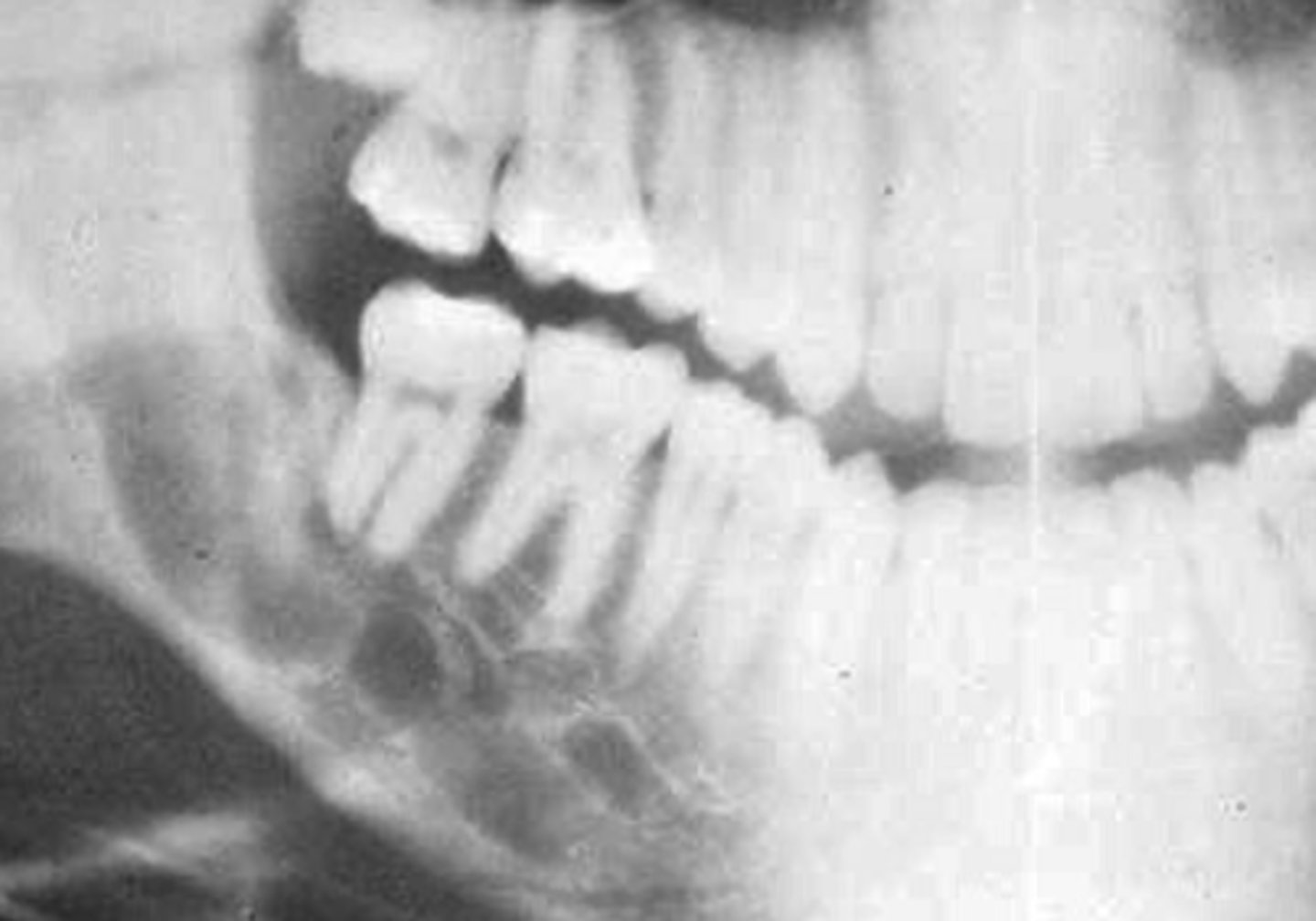
Central hemangioma
- Honeycomb (multilocular) appearace
If unilocular, use a stethescope nd listen for pulse - if it has pulse, leave alone bc may be AV malformation
Central hemangioma - guidelines (3)
- Check for bruits
- Do not extract teeth
- Perform angiogram
Osteogenesis imperfecta is associated with what dental disorder?
Dentinogensis imperfecta
Characteristics of OI
- discolored and weak teeth
- wear of enamel
- pupil dilation
- blue slcera