AP Gov - Chapter 12: The Executive Branch and the Presidency
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
22nd Amendment
Ratified in 1951, this amendment limits its presidents to two terms of office

25th Amendment
Ratified in 1967, this amendment permits the vice president to become acting president if the vice president and the president's cabinet determine that the president is disabled, and it outlines how a recuperated president can reclaim the job
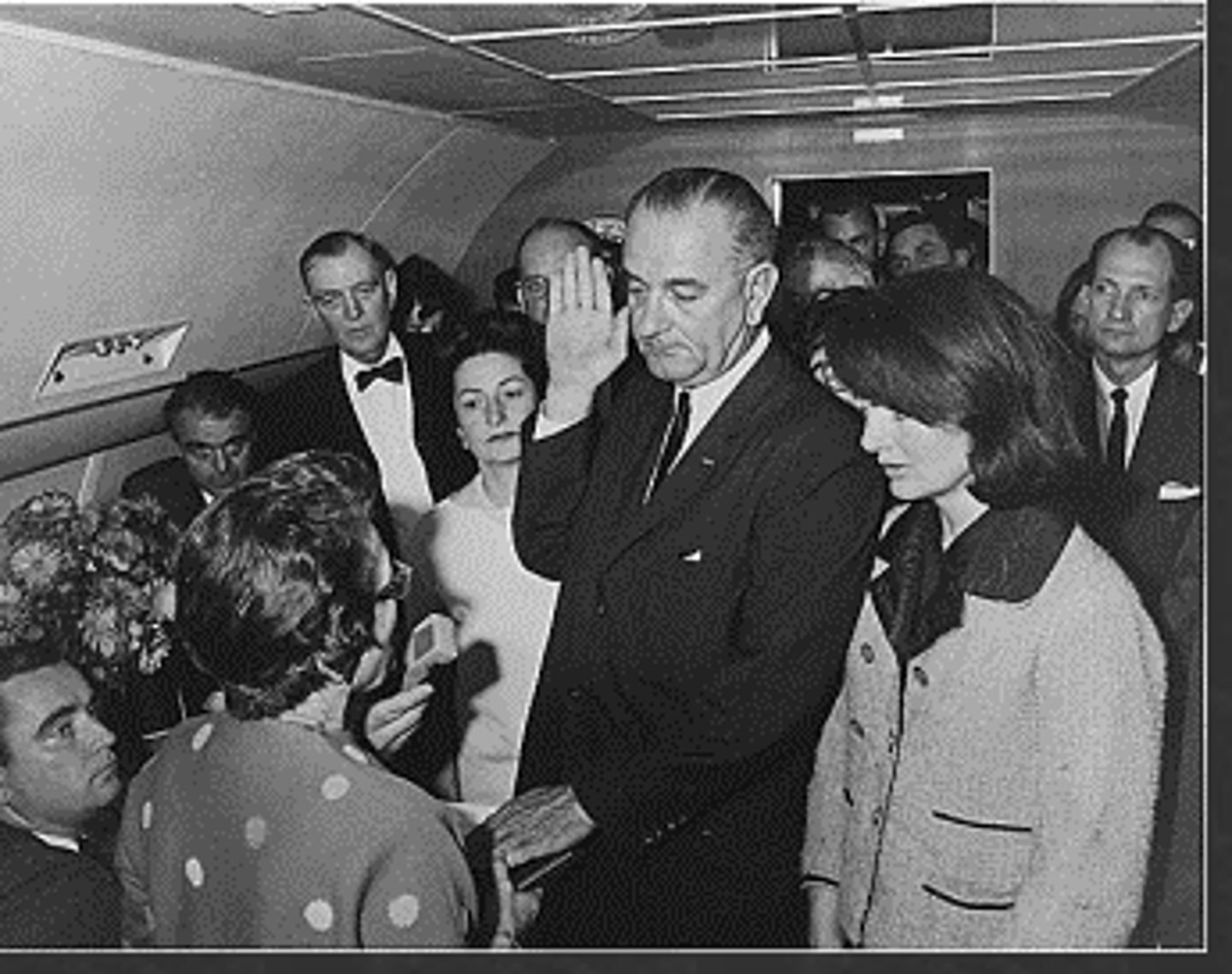

impeachment
The political equivalent of an indictment in criminal law, prescribed by the Constitution
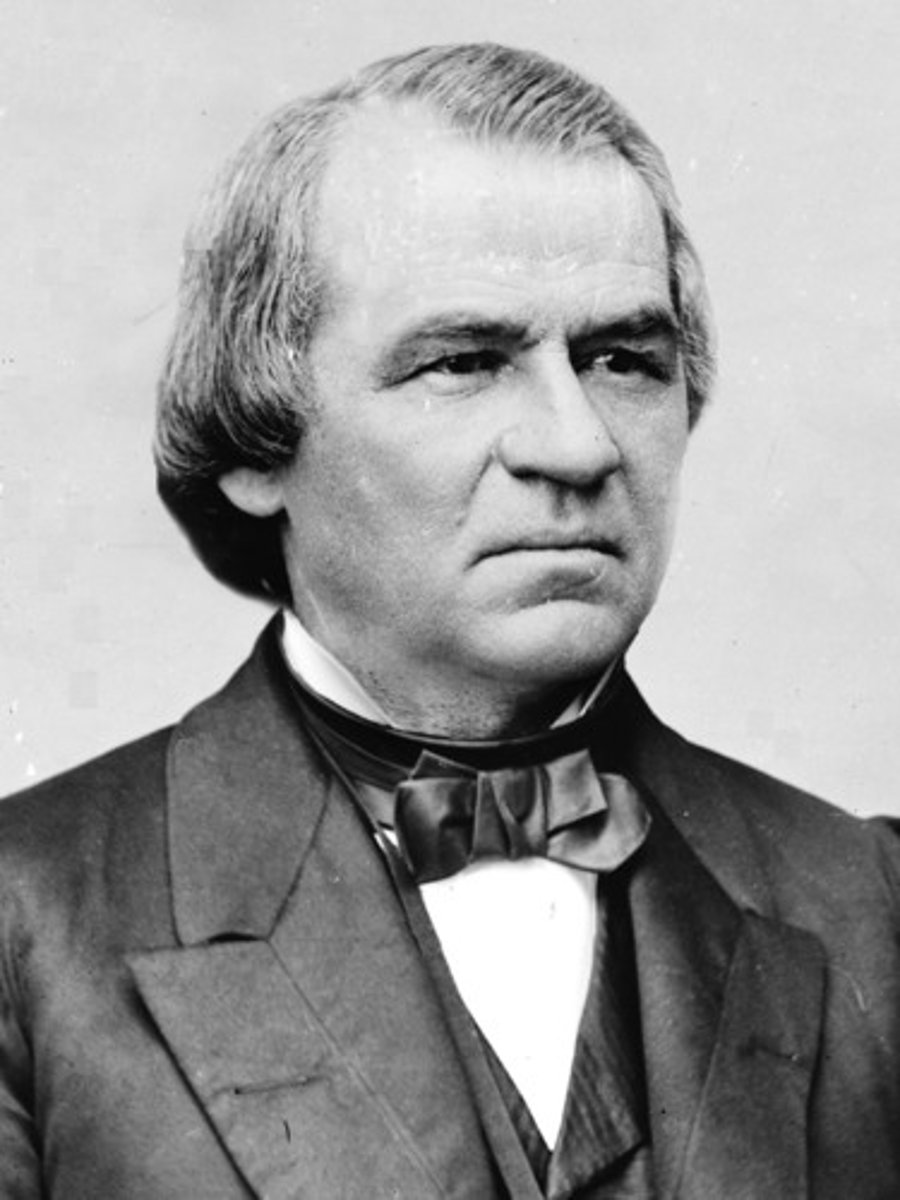

Watergate
The events and scandal surrounding a break-in at the Democratic National Committee headquarters in 1972 and the subsequent cover-up of White House involvement, leading to the eventual resignation of President Nixon under the threat of impeachment

Executive Order
Regulations originating with the executive branch which have the effect of law

Cabinet
A group of presidential advisers not mentioned in the Constitution, although every president has had one

Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
An office that prepares the president's budget and also advises presidents on proposals from departments and agencies and helps review their proposed regulations

Veto
The constitutional power of the president to send a bill back to Congress with reasons for rejecting it

Pocket Veto
A type of veto occurring when Congress adjourns within 10 days of submitting a bill to the president and the president simply lets the bill die by neither signing not vetoing it

Treaty
A formally concluded and ratified agreement between countries.

Executive Agreement
A formal agreement between the U.S. president and the leaders of other nations that does not require Senate approval. It only lasts that President's term(s).
State of the Union Address
The president's annual statement to Congress and the nation.

Presidential Line of Sucession
The order of the people who take over if the President is unable

Executive privilege
constitutional principle that permits the president and high-level executive branch officers to withhold information from Congress, the courts, and ultimately the public

Impoundment
an act by a President of the United States of not spending money that has been appropriated by the U.S. Congress.

Line item veto
the power of an executive or other elected executive to reject individual provisions of a bill. Presidents do not have this power.

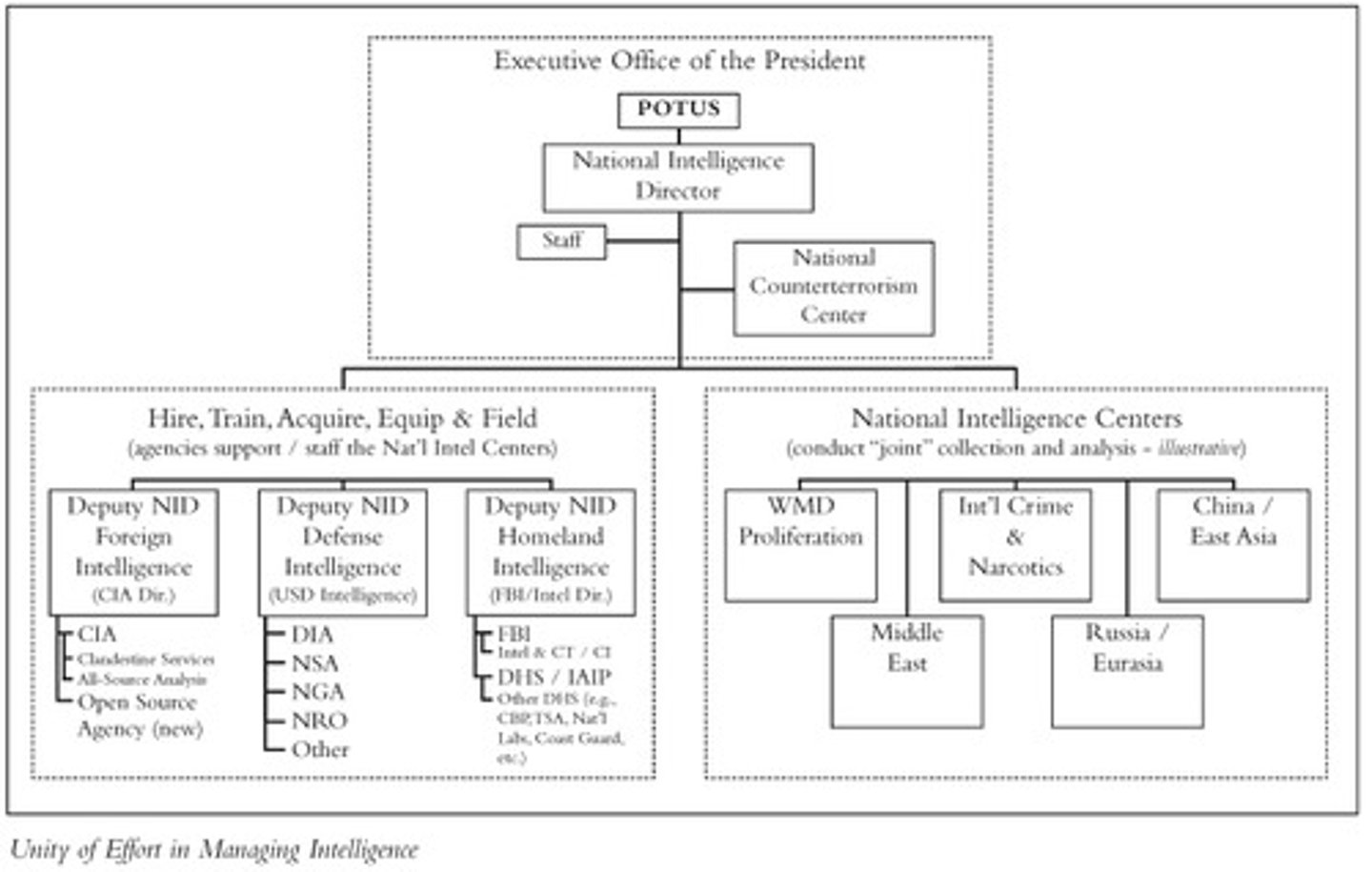
Executive Office of the President
Known as the EOP, the cluster of presidential staff agencies that help the president carry out his responsibilities; currently this office includes the Office of Management and Budget, the Council of Economic Advisors, the White House staff and several other units
Chief Diplomat
Role of the President as he represents the country in foreign affairs and conducts the US foreign relations.

Chief of State
Role of the President as he serves as the ceremonial head in a non political role. Receives other heads of state and checks over credentials of foreign ambassadors.

Lame Duck
When an elected official or group continues to hold political office during the period between the election and the inauguration of a successor.

Requirements to be President
35 years old
14 years a citizen of America
Natural born citizen

Signing Statement
A document issued by the president when signing a bill into law explaining his interpretation of the law which often differs from the interpretation of congress, in an attempt to influence how the law will be implemented.

Vesting Clause
the president's constitutional authority to control most executive functions

Power of appointment
President's power to name members of his cabinet, ambassadors, federal judges etc.

Bully Pulpit
The president's use of his prestige and visibility to guide or enthuse the American public also the ability to use the office of the presidency to promote a particular program and/or to influence Congress to accept legislative proposals

Economic sanctions
Boycotts, embargoes, and other economic measures that one country uses to pressure another country into changing its policies.

Chief of Staff
the person who oversees the operations of all White House staff and controls access to the president

Lame duck
an outgoing official serving out the remainder of a term, after retiring or being defeated for reelection

Take Care Clause
The constitutional requirement (in Article II, Section 3) that presidents take care that the laws are faithfully executed, even if they disagree with the purpose of those laws.
