4. Exam Review
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Define ABO discrepancies
unexpected rxns in forward, reverse, or both ABO typing
ABO discrepancies causes
misidentification
Technical: tech, reagents, equipment
incorrect entry
If there is a discrepancy, what is the first thing you should do
repeat test
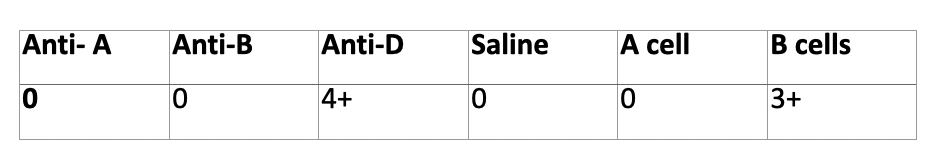
discrepancy?
A subgroup
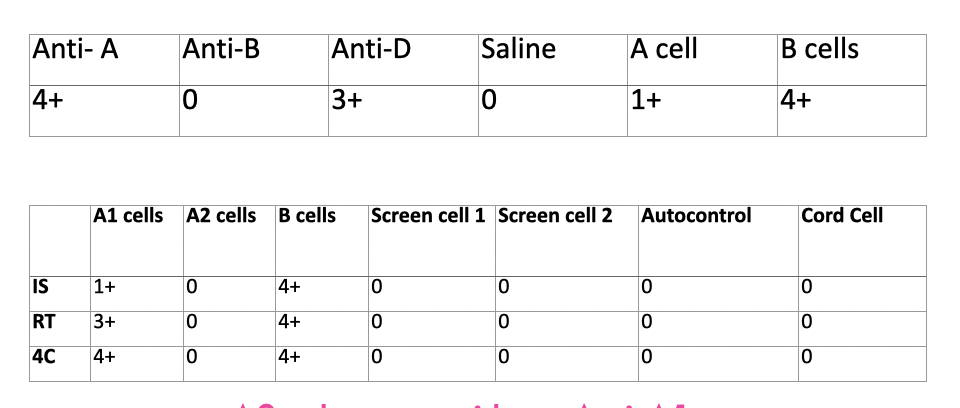
discrepancy?
A2 subgroup with anti-A1
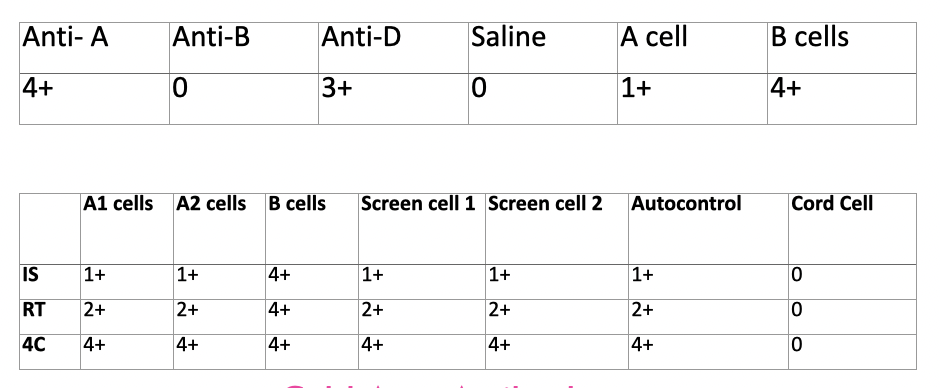
discrepancy?
cold auto antibody
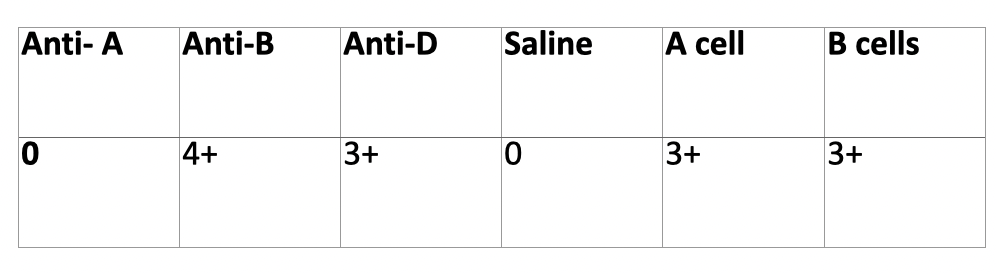
Patient has anti-M, discrepancy?
What would fix it?
Interference in the back type from the cold reacting Anti-M. Fix with A cell and B cell negative for M antigen.
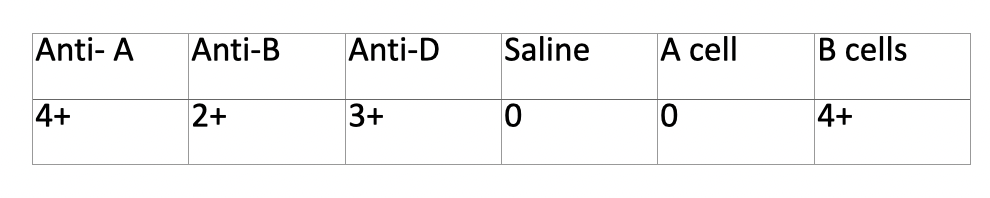
Acquired B – rectum or colon
If you see a mixed field in a patients blood type, what would you expect
That the patient has been recently transfused.
What antibodies are clinically significant for causing HDFN? Which one is most common?
Most common Anti-D
Anti-D, Anti-C, Anti-c, Anti-E, Anti-e, Anti-K, Anti Jka, Anti-Jkb, Anti-Fya, Anti-Fyb, Anti-S, Anti-s, Anti-U
How do we monitor prenatal antibody activity?
Titer
Rh Immune Globulin (RhIg) is given to who?
Rh negative pregnant women
How can we test blood type of a fetus in utero?
Blood draw from amniocentesis
When selecting blood for an intrauterine transfusion, what attributes should it have?
O neg, Antigen negative for moms antibodies, CMV neg, irradiated, fresh , <5 days, Hgb S neg
Fetal bleed screens are done on Rh______ moms who give birth to Rh _____ babies.
negative; positive
What is a fetal screen (rosette test)?
A test that screens for fetal cells in moms circulation. Anti D reagent in kit attaches to Rh positive fetal cells, once incubated and washed indicator cells are added to show agglutination of fetal cells in moms blood. They look like rosettes
What test is a follow up for a positive fetal bleed screen?
Kleihauer Betke or Fetal Flow
Within how many hours should a woman be given RhIg after delivery?
72 hrs
Which antibody is stronger a passive Anti-D from RhIg administration or a real Anti-D?
Real Anti-D
Is HDFN caused by ABO incompatibility clinically significant? How is it usually treated?
Usually not clinically significant, can occur in first pregnancies. Treated with phototherapy.
Kleihauer-Betke stain results on a postpartum mother indicate that there has been a fetal maternal bleed; 1.5% of the cells counted are fetal cells. Assuming the woman has a blood volume of 5000mL, please calculate the proper RhIg dosage.
0.015 x 5000mL = 75mL 75mL/30mL = 2.5 round up to 3 and add a dose
4 vials
The results of a Kleihauer-Betke stain indicate that a fetal maternal bleed of 60 mL whole blood has occurred. How many vials of RhIg is required?
60 mL/2000 mL = 0.03 x 5000 mL = 150 mL/30mL = 5 and add a dose
6 vials
Special Techniques
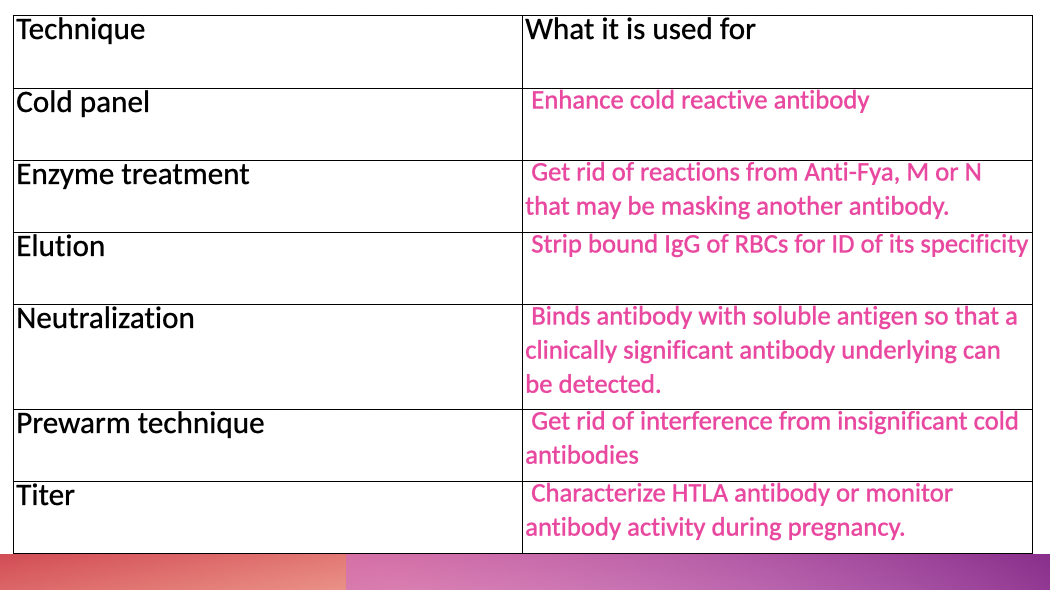
What indicates the endpoint of a titer?
The last 1+ reaction.
What blood group antigens are enhanced by enzymes?
Kidd, Rh (C,c, E,e), Lewis, I/I, P1
What blood group antigens are destroyed by enzymes (e.x ficin, trypsin)?
Duffy, M, N, S is variable
Other Blood Group characteristics
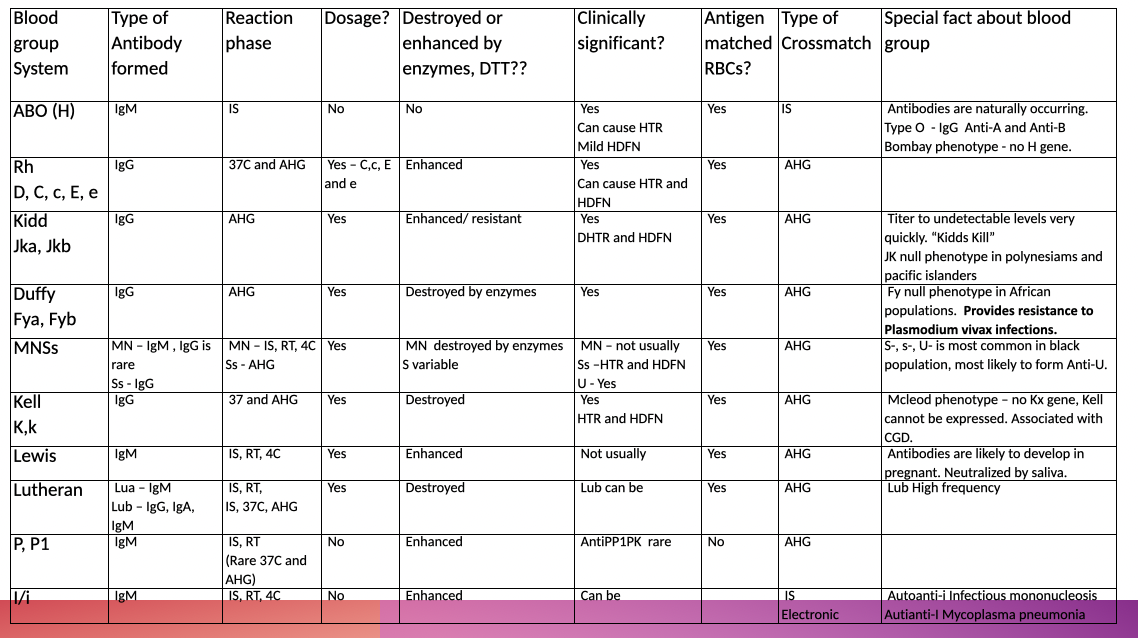
ZZAP =
DTT +papain & ficin (enzymes)
ZZAP enhances
Rh, Kidd, Lewis, P, I
ZZAP (i.e. WARM) destroys
KELL
Duffy, MN, S, Lu
What antibodies are most common?
Anti-D, Anti-E, Anti-K
Which antibodies are not clinically significant?
Anti-M, Anti-N, Anti-Lea, Anti-Leb, Anti-Lua, Anti-P1
Who is most likely to have an Anti-U? Is it clinically significant?
Black population, yes it is clinically significant
What antibodies are enhanced by cold?
Anti-M, Anti-N, Anti-Lea, Anti-Leb, Anti-Lua, Anti-P1
What population is likely to develop a Lewis antibody?
Pregnant
Lewis and Secretor genes
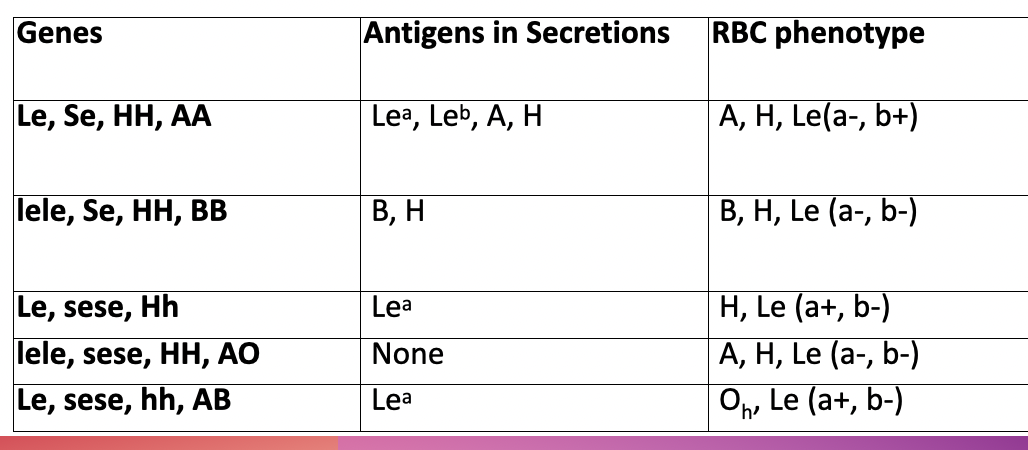
Antigen and neutralizing agent
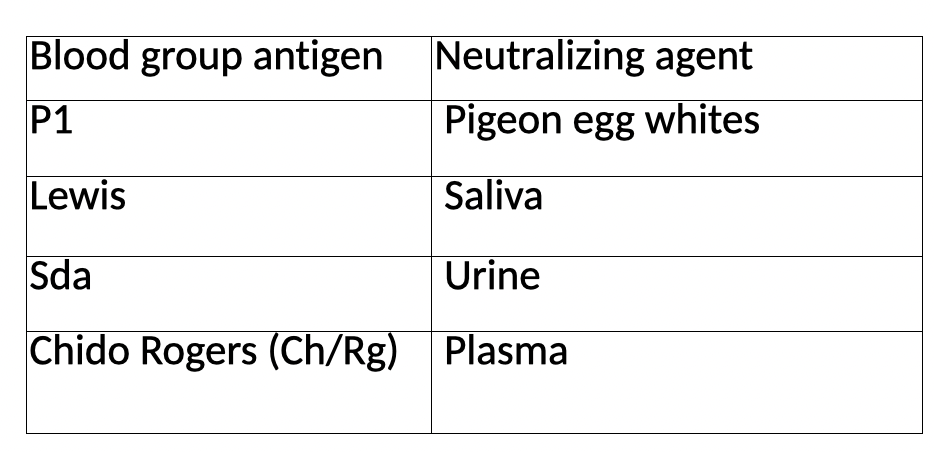
Using Rh antigen frequencies for Weiner phenotypes (Table 7-5 pg. 155 in the text). What would be the most common Weiner type for the following races?
White: R1r
Black: R0r
Asian: R1R2
After you've done a panel, performed your ruling out process, and identified what antibody most likely present in a patient sample, what test should you generally do on the patient's RBC?
Phenotyping
Factors affecting HDFN
Host factors: genetic ability to produce antibodies
immunoglobulin class (IgG)
Antibody specificity
Out of the subclasses of IgG which are most potent
1 and 3
Outside the Rh (DCE) antibodies what other antibody is significant in HDFN
anti-K
When mom is ABO incompatible with fetus, why is detectable fetomaternal hemorrhage decreased?
Mom’s natural occurring antibodies could destroy RBCs from fetus
(ex. mom’s anti-A destroys A + RBCs)
Hydrops fetalis
edema, anemia and effusions in baby due to RBCs being destroyed so fast that spleen and liver have to help bone marrow
kernicterus
permanent brian damage due to build up of bilirubin
Monitoring HDFN
TITERS
ABID
ABSC
phenotype father
What phase are we most concerned with when performing ABSC on a mother?
AHG (IgG detection)
How to distinguish between passive and active anti-D

How to determine baby’s antigens (ABO Rh ) during pregnancy?
amniocentesis
chorionic villous
mom’s plasma in 2nd trimester
Baby Hgb in womb is less than 10g/dL, a ______ _____ is performed.
intrauterine transfusion
Requirments for intrauterine transfusion
Type O Neg
irradiated
CMV (-)
less than 7 days old
antigen neg for mom’s antibodies
wash to get hct of 80-85%
Diagnosis of HDFN via serology
perform front type and ABSC on baby
If (+) —→ ABSC on mom
If (+) and mom not around—→ DAT; (+) = Eluate
Fetal Bleed Screen
performed on Rh(-) mom with Rh(+) baby
(+)—> perform weak D on mom —(regardless of results)—> Kleihauer Betke——> give appropriate RhIg dose
Why do we perform a weak D test on mom even though we’re going to still request a Kleihauer Betke regardless of her results?
Weak D (+) = possible false (+) fetal bleed screen
Test performed post delivery

A Fetal Bleed Screen test is a _____test and if (+), it needs to be followed by a_____test such as Kleinhauer Betke or Fetal F flow to determine RhIG dosage
Qualitative; Quantitative
RhIg dosage calculation
*assume 5L

Weeks of Gestation and RhIG dose
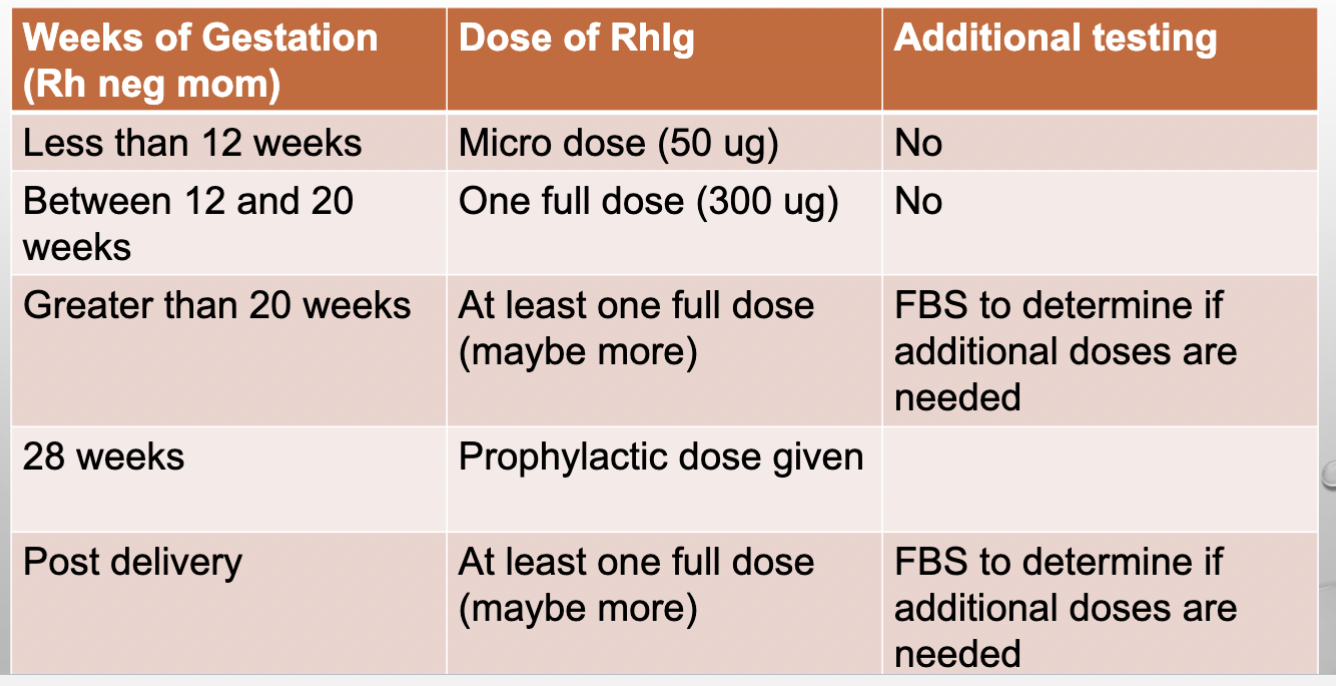
RhIG dosage flow chart
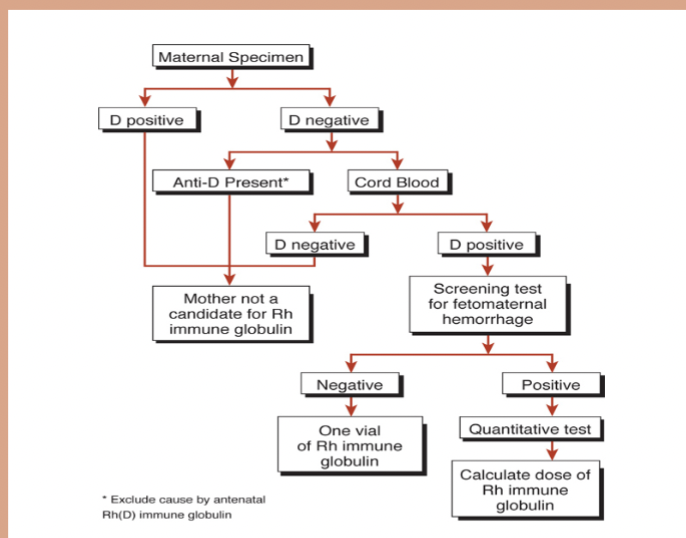
ABO HDFN
A/B baby and O mom
no serological test
phototherapy good enough (i.e. mild)
IgG antibodies
neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia (NAIT)
disorder in which fetal platelets contain antigen inherited from the father and lacks in mother
anti HPA-1
Most common ABO discrepancies occur in patients ____
plasma
First step if ABO discrepancy happpens
Repeat and pay extra attention
Guiding questions for ABO discrepancy
Age: old and young don’t produce anti-A/B
Diagnosis: ex hypogammaglobulinemia
Transfusion history
BM transplant
Medications: ex immunosuppressants
If mom is Rh (-) and her baby is weak D or undetermined Rh, what test is performed on mom ?
Kleinhauer Betke or Fetal F flow (FBS isn’t sensitive enough)
Sulfhydryl reagents like DTT, AET, EGA, 2-ME break _____bonds and destroy blood groups _____, _____, and ___.
disulfide;
destroy Kell, Lutheran, and LW
Enhancement medias LISS or LO-ION, PEG, and PEP enhance Ab-Ag by reducing ____ _____
zeta potential
Enzymes Papain, Trypsin, and Ficin destroy by reducing ____acid
sialic
Chloroquin removes bound IgG by breaking the ____bonds of the IgG molecules
disulfide
Most commonly performed elution method is with___
Acid
Heat (56C) and Lui Freeze Thaw are only utilized on _____
ABO
When making an eluate, why should we KEEP the last wash?
QC; to ensure that there is no unbound antibody
Cold Autoabsorption is done with _____cells or ____
autologous cells
OR
RESt (rabbit erythro stroma)
What is the Acquired B phenomenon
Type A with extra B in the front due to Bowel bacteria
When performing antibody titers for HDFN use cells _____for the corresponding antigen.
homozygous
except for anti-K since homo is hard to find
Elution techniques used for
separating multiple antibodies
clarification of “compound” antibodies
weak antigens (Del or A subgroups)
An eluate that is panreactive is most likely a ____
WAA (warm auto antibody)
When to use Autologous adsorption?
patient has not been transfused in the past 3 months AND there are enough cells
When to use Allogeneic adsorption?
patient has been transfused in the past 3 months (donor cells can potentially adsorb out the allo antibody you are looking for)
OR
not enough cells
pg 230
During a weak D test can you distinguish between weak D and partial D?
No, you need molecular testing.
(note: partial D can make anti-D)
When can a cold panel be used?
Discrepant backtype due to:
presence/ absence of allo- auto- antibodies
weak rxn due to low IgM
During adsorption, how many passes should be done?
strongest rxn + 1
( ex: DAT is 3+, do 4 passes)
For RhIg dosage, if the whole blood is given you divide by?
15ml instead of 30ml