Pediatric Oncology
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 255 - Intro to Oncology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is the incidence rate of childhood cases of cancer per 1 000 000 children
153 cases per 1 million
what is the mortaltity rate of childhood cases of cancer per 1 000 000
26 cases per 1 million
in high income countries, ______ % of children are cured
80
in low income country, up to ____ x more likely to die from cancer
10 x
incidence of childhood cancer has ______ since 1992, but mortality has _____ due to improvements in cancer treatments
stayed the same; decreased
what is the childhood cancer ratio for male to female
1.2:1
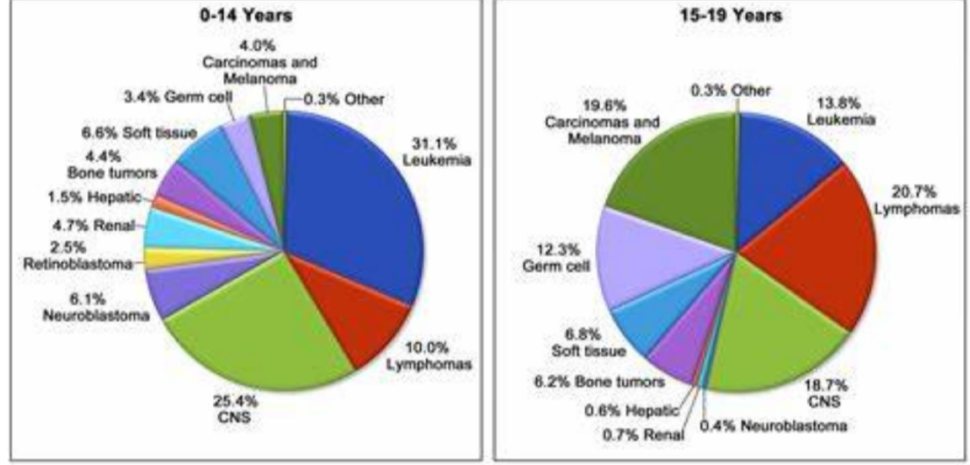
how does the type of cancer in children (0-14) differ from teenagers (15-19)
Children
most common cancer is leukemia (31%), Lymphoma and CNS cases
Teenagers
lymphoma numbers increase and huge increase in carcinomas and melanomas
3 risk factors for childhood cancers
Exposure to ionizing radiaiton
second hand smoke/alcohol during pregnancy
genetic disorders
3 examples of genetic disorders that incrase cancer predisposition
down syndrome
Li-Fraumeni
Von Hippel-Landau
Fanconi Anemia
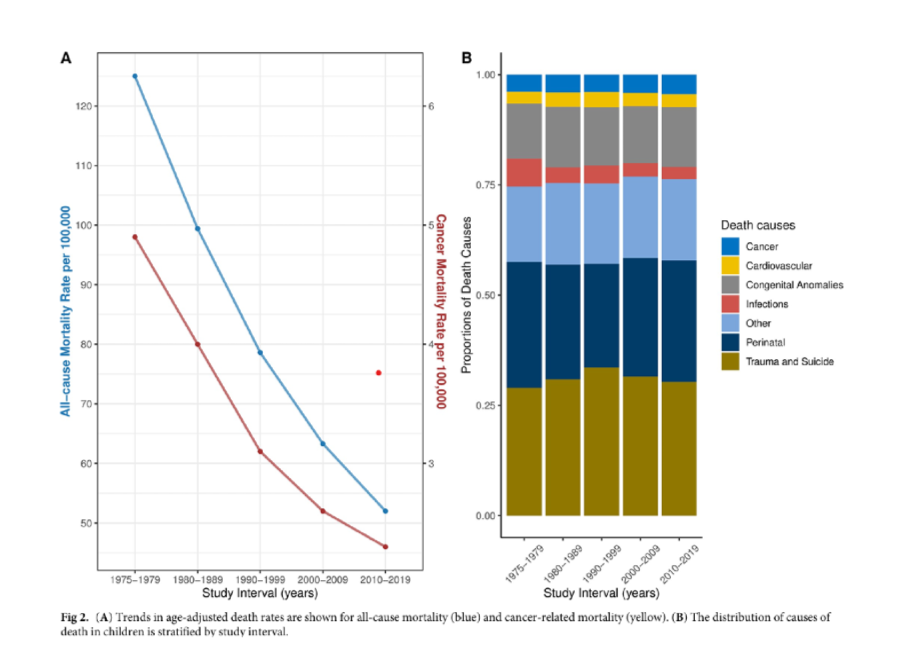
Is cancer the main cause of childhood mortality?
no trauma and suicide is the leading cause
cancer is the smallest cause aside from cardiovascular
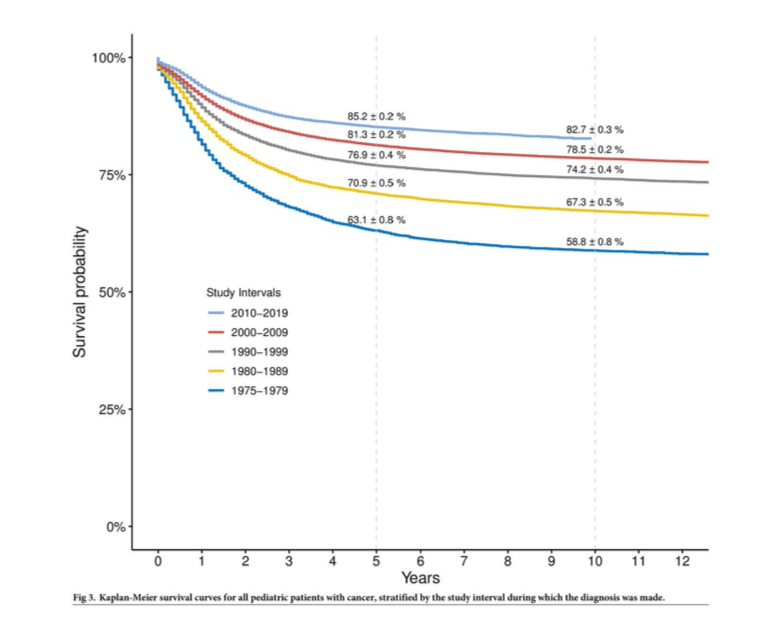
how has survival probability increased in the past 40 years
increased from 63% to 85%
increased by 20%
Two pros of work with children
more fun
healthy organs and few co-morbidities
Two cons of working with children
often uncooperative
need to gain trust of child and parent being able to treat them
need to factor in growth and development for treatment
Differences between childhood and adult cancer biology and origin
children
random non-inherited genetic mutations that occur in life
increase incidence in some genetic disorders
were not 100% sure what causes childhood cancers
Adults
many factors are due to environmental and lifestyle risk factors
more associated with chronic inflammation, prolonged exposure to carcinogens and age-related genetic mutations
Differences between children and adult cancers in term of characterization and behaviour
children
childhood tumors are characterized by histology
tend to spread more rapidly than adult cancers
biopsy is required
Adults
develop more slowly
categorized by anatomic site
Differences between children and adult cancer types of cell
children
childhood cancers tend to involve cells that are actively growing and developing
commonly affects blood cells, nervous systems, and bone or muscle cells
Adults
more likely originate from epithelial cells (carcinomas)
Differences between children and adult cancers treatment approaches
Children
treatment of childhood cancers often involves multimodal therapy
typically treated aggressive as the goal is to cure the pediatric cancers
Adult
cancer treatment focuses on managing the disease, particularly in older adults
treatment often involves a balance between extending life and maintaining QoL
Differences between children and adult cancers long term considerations
children
long-term survival and QoL are major concerns
survivors of childhood cancer require lifelong follow-up care to monitor and address late effects
Adults
in adults the focus is on managing comorbid conditions
the prescence of other chronic diseases can complicate cancer treatment
Differences between children and adult cancers long term considerations
Children
overall childhood cancers have a high survival rate, but can vary depending on type of cancer and resources
low and middle income countries, survival rates are often lower due to delayed diagnosis
Adult
prognosis differs on type of cancers and stage of diagnosis
survival rates are lower for advanced stage or for associated with lifestyle factors
Differences between children and adult cancer - long term effects
Children
survivors of childhood cancer are at risk for longer term health issues like secondary cancers, heart disease, infertility
Adult
long term effects of cancer treatmetn in adults can include chronic pain, fatigue, and emotional distress
Typical symptoms of childhood cancer
typicaly non-specific symptoms but relatively acute
fever
anorexia
pain
headaches
enlarged lymph nodes
obvious symptoms of childhood cancers
mass
enlarged lymph nodes
bruises (leukemia)
neurological signs (brain tumor)
the three Rs of children cancer management
review
refer
reassure

childhood malignanices move ____ than adult cancers
more rapidly and aggressively
Overall prognosis of childhood cancers
82% survival
what three diseases have an overall prognosis of 90-95%
Hodgkins lymphoma
Wilms Tumor
ALL
what diseases have prognosis below 50%
Stage 4 solid tumors
certain brain tumors
what novel type of therapy is helping change the treatment trajactory of child cancer
targeted therapies
impact of cancer diagnosis on child
developmental issues
loss of autonomy
hair loss
school re-entry
impact of cancer diagnosis on parent
more difficult than if they were ill themselves
guilt and anxiety
advocacy
marital issues
impact of cancer diagnosis on family
whole family illness
financial issues
geography issues