Chapter 5 Beyond Mendel's Laws
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from chapter 5 e textbook
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
tay sachs disease is lethal by what age?
3-4
describe complete vs incomplete dominance,
complete - only one allele is expressed
incomplete, the heterozygous phenotype is expressed where its a mix.
a person with one disease causing allel has _____ the normal number of recepters
1/2
different alles that are both expressed in heterozygotes are _____-
codominant
what is an antigen
a molecule that elicits an immune response
define epistasis and give an example of it
one gene masking the expression of another gene, eye color is a good example, there are at least 10 genes in relation to eye color, unrelated as far as function, but offer a wide array of color
what is the bombay phenotype?
blood cells fail to present a antigens A & B on the top of red blood cells, so when tested they appear as type O blood, but in reality they are ABO
what is penetrance
the percentage of individuals with a genotype who have an associated phenotype
what is expressivity
severity or degree of a phenotype
what is pleiotropy?, give the best example of it
a single gene disease with several symptoms or that has more than one affect in different individuals.
EXAMPLE: Marfan Syndrome - a defect in an elastic connective tissue protein fibrillin,
Symptoms are lens dislocation, long libs, and caved in chest
what happens in alzheimer disease,
the amygdala and hippocampus, responsible for emotion and memory, become burried in 2 types of protein. Amyloid beta which form plaques outside brain cells because cells cannot remove the material fast enough. and Iron accumulates inside brain neurons,
define phenocopy, give an example
an environmentally caused trait that occurs in a familial pattern mimicking inheritance.
Example: Thalidomide exposure, Causing phocomelia
mitochondrial genes are ______ inherited because they pass only from the individuals mother.
maternally
how does mitochondrial DNA differ from regular DNA
mtdna doesnt cross over, it mutates faster, not wrapped in proteins,
a mutation in a mitochondrial gene that encodes a tRNA or rRNA can be devastating because?
it would impair the organelles general ability to manufacture proteins. Leading to many symptoms.
what is heteroplasmy?
mitochondria in the same cell that have different alleles of a gene
why is mitochondrial DNA more prone to mutation than DNA in the nucleus
mitochondrial DNA is not repaired
why is mitochondrial DNA useful in forensic investigations?
mitochondrial DNA is more likely to remain intact under forces that would degrade longer pieces of nuclear DNA, mtDNA is therefore useful in forensic analysis.
define linkage in relation to genetics
genes on the same chromosome
Define recombinant
a series of alleles on a chromosome that differs from the series of either parent
define linkage map
diagrams that show gene order on chromosomes, determined from crossover frequencies between pairs of genes
define centimorgan
a unit that indicates percent recombination between two loci linked on a chromosome, service as a measure of relative distance between them
what is linkage disequilbrium
a consequence of extremely tight linkage between DNA sequences in which two genes or DNA sequences are nearly always inherited together.
what is a haplotype
a series of genes linked on a chromosome that do not separate by crossing over
what is a LOD score and what does it mean?
a LOD score indicates the likelihood that crossover data indicate linkage rather than the inheritance of two alleles by chance
define genetic linkage?
genes that are linked are part of the same chromosome
what is a genetic markere
a DNA sequence, cut site, or repeat number inherited along with a gene of interest due to linkage
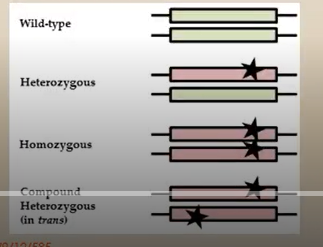
what is a compound heterozygote?
an individual who carries two different mutated alleles at the same gene locus
describe cystic fibrosis inheritance
multiple alleles can lead to cystic fibrosis,
give a situation in relation to incomplete dominance
FH - Familia hypercholesterolemia
Heterozygote - has half the number of receptors in their liver for low density lipoprotein cholesterol
Homozygous - for the mutant allele totally lacks the receptor so their serum cholesterol level is very high
codominance situation
blood types: ABO blood type - ABO gene can either be recessive, and have an A or B allele
What is a modifier gene of OCA 2
HERC 2, - a factor that regulates the amount of OCA 2 produced, loss of regulation results in BLUE EYES
What is Genetic heterogeneity
a situation where different genetic variations (mutations) can cause the same or similar disease or condition
what is recombination
chromosomes recombine during crossing over in prophase I of meiosis, new combinations of alleles are created,
What is LOD score,
indicates how close a marker is a gene of interest is on a chromosome indicating tightly linked