Chapter 16: Therapy and Treatment
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Asylums - bloodletting, beatings, ice baths
Early Treatments: Where were mentally ill individuals held in the mid 1500s, what did treatment involve?
Philippe Pinel
Who was the first to recommend humane treatment of mentally ill individuals
Trephination
An early surgical procedure - in which an area of an individual’s skull was chipped through or cut through, leaving a hole through which the evil spirits could escape
– The oldest known surgical procedure
– Performed in Peru and Bolivia, Europe, North Africa
Prefrontal Lobotomy
Early surgical treatment - the connection of the prefrontal cortex to other brain areas is severed
Psychotherapy
Current Treatment - therapy for mental disorders in
which a person with a problem talks with a
psychological professional
Biomedical therapy
CurrentTreatment - herapy for mental
disorders in which a person with a problem is
treated with biological or medical methods to
relieve symptoms
Psychoanalysis
Insight therapy based on
the theory of Freud, emphasizing revealing
of unconscious conflicts
Free association
Dream interpretation
Resistance
Transference/countertransference
Psychodynamic therapy
a newer and more general term for therapies based on psychoanalysis, with an emphasis on transference, shorter treatment times, and a more direct therapeutic approach
– Pathogenic beliefs
In modern, therapists are more directive, focus is more on present, less time consuming.
Difference between psychodynamic therapy and psychoanalysis
Person-centered therapy
A non-directive insight therapy in which the client does all the talking and the therapist listens
– Focus is on subjective experience, sense of self,
immediate experiences, and potential to change
– Reflection: the therapist restates what the client
says rather than interpreting those statements
Behavioral Therapies
Types of therapies based on:
-- all normal and abnormal behaviors are learned
– action therapies based on the principles of
classical and operant conditioning
– aimed at changing disordered behavior without
concern for the original causes of such
behavior
Systematic Desensitization
A behavioral technique used to
treat phobias, in which a client is asked to make a list of ordered fears and taught to relax while concentrating on those fears
– Counterconditioning: replacing an old conditioned response with a
new one by changing the unconditioned stimulus
Aversion therapy
A type of behavioral therapy where the undesirable behavior is paired with an
aversive stimulus to reduce the frequency of the behavior
Exposure therapy
A type of behavioral techniques that introduce
client to controlled situations that are related to their anxieties or fears
Flooding
A behavioral technique in which person is rapidly and intensely
exposed to fear-provoking situation or object and prevented from
making usual avoidance or escape response
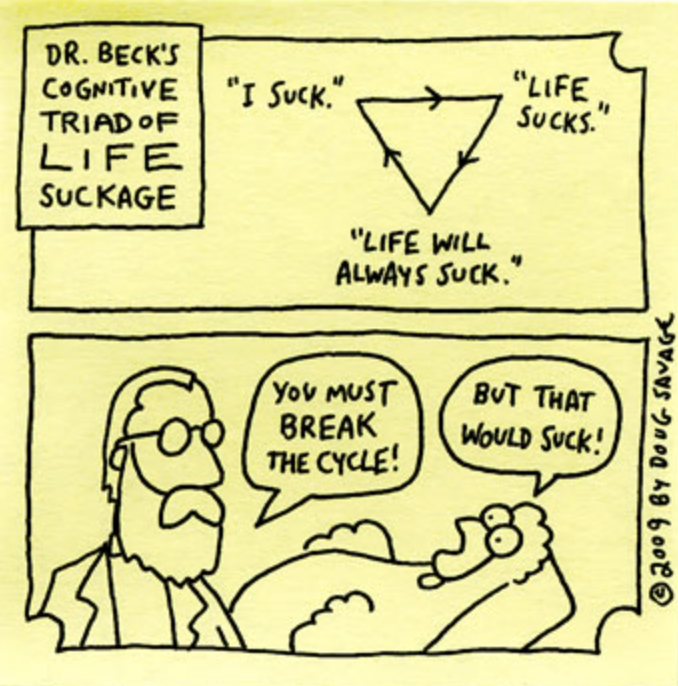
Aaron T. Beck
Who developed Congitive therapy
Cognitive therapy
A type of therapy in which the focus is on helping clients recognize distortions in
their thinking and replace distorted, unrealistic
beliefs with more realistic, helpful thoughts
Negatively biased errors in thinking that are purported to increase vulnerability to depression
What are cognitive distortions?
Relieve the symptoms and solve the problems.
Help develop strategies for solving future problems.
Help change irrational, maladaptive thinking.
Goals of CBT
“Depresogenic thinking“
faulty schemas about self (self-schemas), the world, and others give rise to and sustain faulty information processing
Self: “I am worthless“
Future: “Nothing will ever change“
World: “Everything is against me“
The negative Triad: Three main forms of negative thinking
Motivational Interviewing (MI)
A newer therapy: A type of therapy where therapist helps patient come up with their own reasons to commit to a change and include positive behavior changes.
initially developed for substance use disorders but also used in treatment of anxiety and mood disorders

Dialectical -Behavioral therapy (DBT)
A newer therapy: Originally developed to treat BPD by Marsha Linehan
– “dialectical” means a synthesis or integration of
opposites
– focus on emotion regulation
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
A newer therapy: as originally designed to alleviate the distress associated
with traumatic memories
– very effective for patients diagnosed with PTSD
– utilizes eye movement to track a light or therapist’s
hand

Play therapy
A type of therapy used with children, can be nondirective or directive

Art therapy
Therapy involving use of art and creativity, used with both children and adults
Family therapy
Therapy in which family members meet together with a counselor or therapist to resolve problems that affect the entire family
Support groups/ Self-help groups
A type of group therapy:
people have similar problems
– meet together without a therapist or counselor
for the purpose of discussion, problem solving,
and social and emotional support
Therapy groups
A type of group therapy:Can focus on a specific problem or population
(e.g. DBT Group, Depression Group,
Mindfulness Group, Young Women Group)
Biomedical therapies
therapies that
directly affect the biological functioning of
the body and brain
■ Pharmacology
■ Electroconvulsive Therapy
■ Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Pharmacology
Drug Therapy
Psychoactive drugs
A chemical substance that affects brain function and alters perceptions, mood, cognition, consciousness, and/or behavior
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
A type of therapy in which electrodes are placed on either one or both sides of a person’s head and an electric current strong enough to cause a seizure or convulsion is passed through the electrodes
Severe, treatment-resistant depression, memory disruption
What is ECT used to treat? What are the side effects
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
-- uses a magnet to activate the brain
– used for depression, psychosis, anxiety
– targets a specific area of the brain
Clinical assessment, diagnosis, treatment plan
Three treatment steps
Dichotomous thinking, mind reading, emotional reasoning, personalization, overgeneralization, catastrophizing, “should“ statements, selective abstraction
Eight cognitive distortions
Dichotomous thinking
Example of which cognitive distortion: Things are black or white”; “You’re with me or against me.” This tendency toward “all-or-nothing” thinking is encountered in borderline personality and obsessive– compulsive disorders.
Mind reading
Example of which cognitive distortion: “They probably think that I’m incompetent”; “I just know that they will disapprove.” This processing style is common in avoidant and paranoid personality disorders.
Emotional reasoning
Example of which cognitive distortion: “I feel inadequate, so I must be inadequate”; “I’m feeling upset, so there must be something wrong.” This distortion is common among individuals suffering from anxiety disorders.
Personalization
Example of which cognitive distortion: “That comment wasn’t just random, I know it was directed toward me.” At the extreme, this is common in avoidant and paranoid personality
Overgeneralization
Example of which cognitive distortion: “Everything I do turns out wrong”; “It doesn’t matter what my choices are, they always fall flat.” At the extreme, this is common among depressed individuals
Catastrophizing
Example of which cognitive distortion: “If I go to the party, there will be terrible consequences”; “It would be devastating if I failed this exam”; “My heart’s beating faster, it’s got to be a heart attack.” This distortion is characteristic of anxiety disorders, especially social anxiety, social phobia, and panic.
panic
“Should statements“
Example of which cognitive distortion: “I should visit my family every time they want me to”; “They should do what I say because it is right.” This is common in obsessive– compulsive disorders and among individuals who feel excessive guilt.
Selective Abstraction
Example of which cognitive distortion “The rest of the information doesn’t matter. This is the salient point”; “I’ve got to focus on the negative details; the positive things that have happened don’t count.” At the extreme, this is common in depression.
Resistance
An individual's unconscious opposition to the exploration of painful thoughts, feelings, or memories
Transference
A client unconsciously projects feelings from past relationships onto their therapist
Countertransference
The therapist's emotional reaction to the client, stemming from their own past experiences
Free Association
Involves patients speaking whatever comes to mind without censorship to bypass conscious defenses and reveal unconscious thoughts, feelings, and repressed memories, helping uncover hidden conflicts and foster self-awareness in therapy
Sigmund Freud
Who founded psychoanalysis
The Unconscious Mind, Childhood Experiences, Conflict and Defense Mechanisms, Insight as Cure, Structure of Personality (Id, Ego, Superego)
What are the main assumptions guiding a psychoanalytic or psychodynamic approach to therapy?
Thoughts influence feelings & actions, Unproductive thinking, Change is possible
What are the assumptions underlying cognitive therapy?
Pharmacology, Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT), Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Three types of biomedical therapy:
Pathogenic Beliefs
Negative, maladaptive core beliefs that develop in response to childhood trauma and continue to cause emotional distress and hinder personal growth