Sex Determination/Development
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ASCI 442
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
chromosomal sex
genotype
mammals (XX, XY)
birds (ZW, ZZ)
some lizards and tortoises have no heteromorphic pair of chromosomes, sex is determined by temperature and steroids
in mammals one X is inactivated → barr body in female somatic cells
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
XXY
sterile
testicular hypoplasia
Turner’s Syndrome
XO
sterile
inactive “streak” ovaries
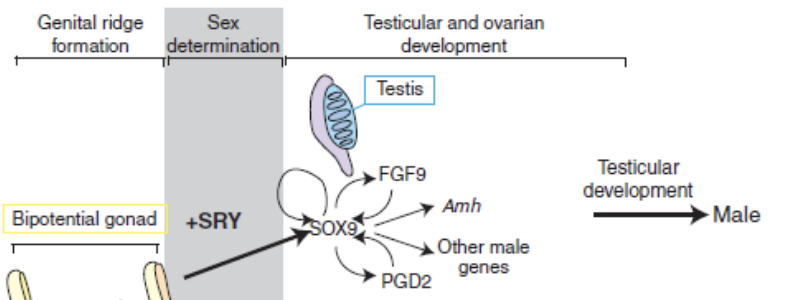
male gene expression allowing for bipotential gonad to differentiate
thermosensitive period
hot (30C) - female
28.5 C - ovotestis
cold (25C) - male
sertoli cells in differentiation
express SRY, SOX-9, AMH, seminiferous cords
female gene expression allowing for bipotential gonad to differentiate
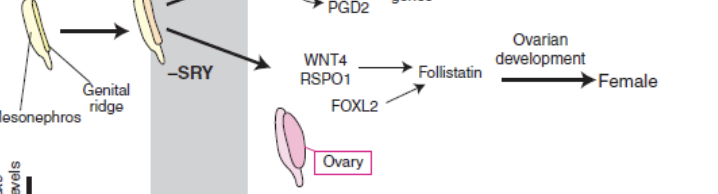
gonadal sex (differentiation of gonad)
undifferentiated gonad nezt to mesonephros
primordial germ cells migrate from yolk sac to mesonephros
chemostatic agent stimulates movement to the mesonephros and into indifferent gonad
primordial germ cell migration

morphological changes during gonadal differentiation
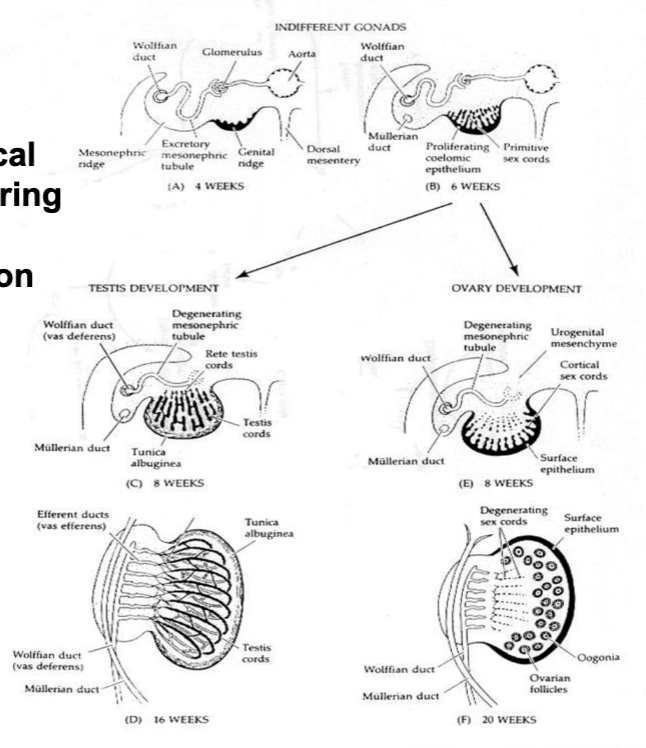

female vs male events
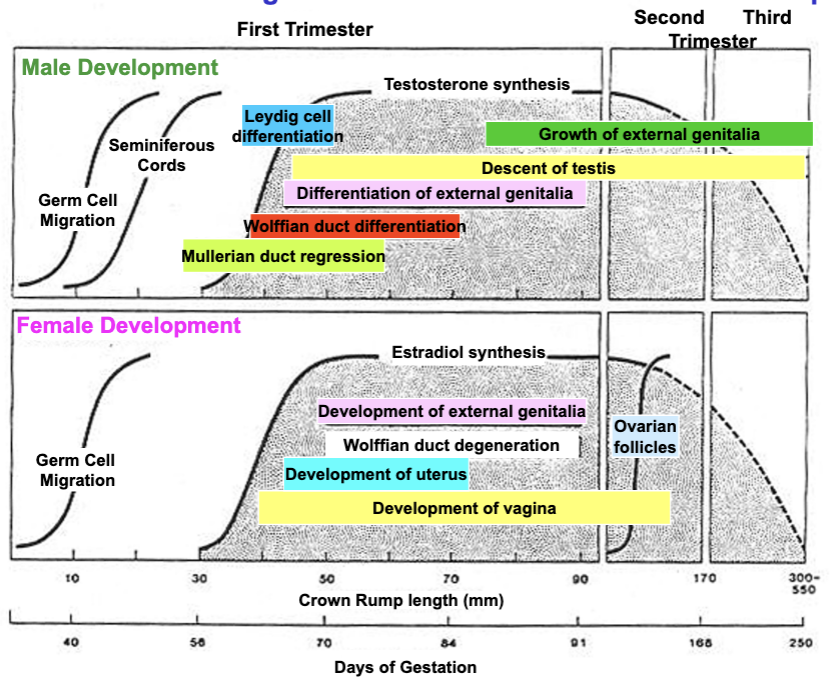
phenotypic sex
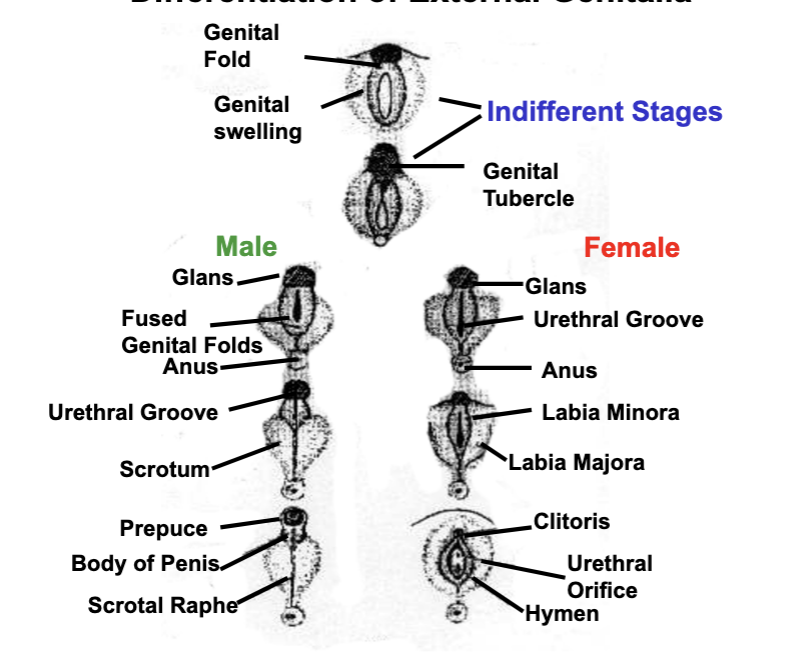
differentiation of reproductive tract and external genitalia
Mullerian duct → female tract → oviduct, uterus, cervix, vagina
Wolffian duct → male tract → epididymis, vas deferens, accesory sez glands
male gonade produces
AMH (Sertoli cells) blocks development of female tract
hormones: testosterone (maintain Wolffian ducts) and 5a-dihdrytestosterone (Leydig cells)
routes of testosterone metabolism in developing tissues

differentiation of external genitalia
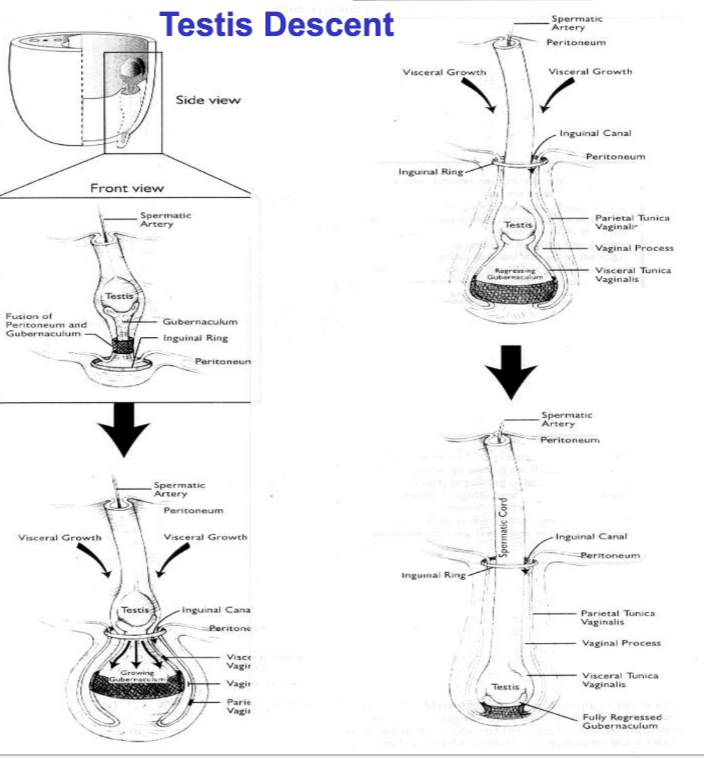
testis decent
caused by INSUL3 from the Leydig cells, tyrosine kinase receptor
hermaphrodite
congenital malformation in sexual development
true hermaphrodite
male and female structures
mosaic, ovotestis with XX AND XY
male psuedohermaphrodite
externally female, internally have testis
5a-reductase deficiency (Dominican Republic) prevents testosterone conversion to 5aDHT
can also be caused by lack of androgen receptor
testicular feminization
female psuedohermaphrodite
congenital adrenal hyperplasia
ACTH stimulates the adrenals to produce cortisol or aldosterone but lack of enzyme for the converson of P4 → cortisol increase enzyme for conversion of testosterone, causing masculinization
free martin
female born twin to a fale
fusion of placenta
female tract does not develop due to AMH/androgen exposure
sexual differentiation of the brain
testicular hormones: testosterone from testis of fetus results in male behavior. medial preoptic nucleus in brain is larger in males
rats castrated on day of birth have a female brian
give females testosterone at birth they develop a male brain
role of aromatization and a-fetaprotein
aromatization and a-fetoprotein
brain converts testosterone to estrogen (aromatization) estrogen causes changes in brain neurons
a-fetoprotein produced by fetal liver increase during late gestation, it binds to estrogen and inactivates its affect in females, does not bind testosterone (free in blood)
female has low levels of testosterone
animals that are exceptions to the rule
spotted hyenas
elephants
tammar wallabies