Unit 2.9 Nuclear Decay and Nuclear Energy
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is nuclear fission
The splitting of large, unstable nuclei to form smaller more stable nuclei (plus the emission of spare neutrons)
What usually needs to happen to induce fission
The unstable nuclei must absorb a neutron
What term is used to describe nuclei in which fission can be induced through the absorption of slow neutrons
Fissile nuclei
Alongside two smaller nuclei, what else is emitted in a fission reaction
Two or three neutrons
Gamma rays
Energy
What form of energy do all fission product has
Kinetic energy
Name a common fissile nuclei
Uranium-235
What are the 3 main component of the core a nuclear reactor
Fuel rod
Control rod
Moderator
What takes place during a chain reaction in a nuclear reactor
An unstable nucleus absorbs a neutron
The nucleus undergoes fission and release 2 or 3 further neutrons
These include more fission which results in a chain reaction
What is the consequence of an uncontrolled chain reaction in nuclear power station
The rate of fission events becomes to high and results in the production of too much energy. This can lead to a nuclear explosion
How is the chain reaction in a fission reactor kept under control
Control rod are positioned in between the fuel rods.
The rate of fission is controlled by moving these rods up and down
The lower the rods are inserted, the slower the rate of fission
What is the role of the moderator in a nuclear power reactor
To slow down the neutrons so they are travelling at speeds which allow the, to be absorbed by fissile nuclei and cause fission
What is nuclear fusion
The joining of two light nuclei to produce a heavier nucleus and release energy
Name two isotopes of hydrogen which are commonly used in a nuclear fusion
Deuterium and tritium
Which release more energy, nuclear fission or nuclear fusion
Fusion
Explain the difficult of generating energy through nuclear fusion
Requires very high temperatures which in itself requires large quantities of energy and also requires casing which can withstand them
Explain why nuclear fusion is currently not a viable way to produce energy on earth
With the current equipment and techniques, the energy required is greater than the energy produced, resulting in a net energy loss
What must the casing of a fission reactor do
Absorb any neutrons and gamma radiation that is released in the fission reactions, to prevent it from passing through to outside of the reactor
Why are fission produce particularly dangerous
They have very long half life Menai h they will remain radioactive for a very long time
What is the nuclear symbol for a neutron
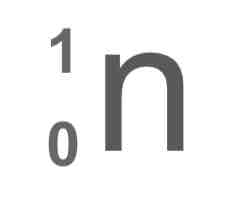
What are one way to store nuclear fusion
Magnetic field