Aerodynamics Lesson 2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Physical Description of Lift
a wing produces lift by diverting air down
How do wings develop lift?
by diverting air down
Most of the lift is…
due to the action over the top of the wing

A wing that is creating no lift
Since no air was deflected downward, there is no net action on the air, which means there was no reaction on the wing

Downwash
The downward traveling air around the wing; the action that causes the reaction of lift

What is occurring since there has been a net change in the air passing over the wing?
There is a force acting on the air and a reaction force acting on the wing
How a wing generates lift in one sentence:
The wing produces lift by diverting air down.
Coanda Effect
A phenomenon that explains why fluids follow the shape of curved surfaces
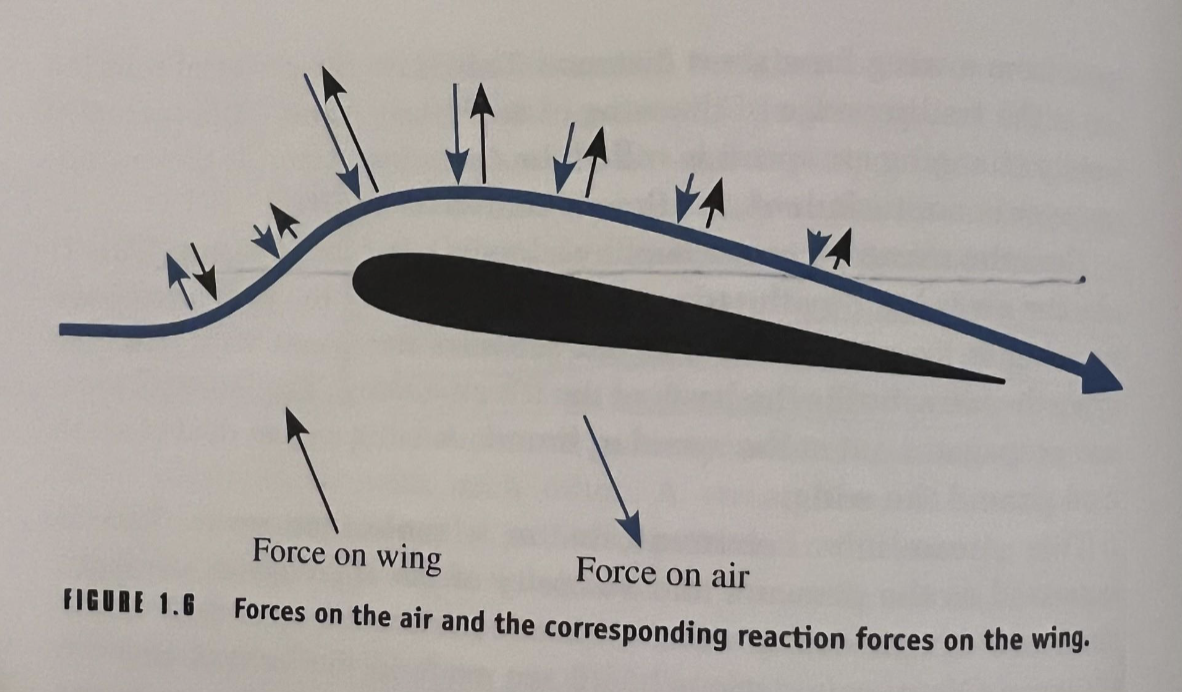
The direction of the force on the air is perpendicular to…
the bend and the magnitude (size) of the force is proportional to the tightness of the bend
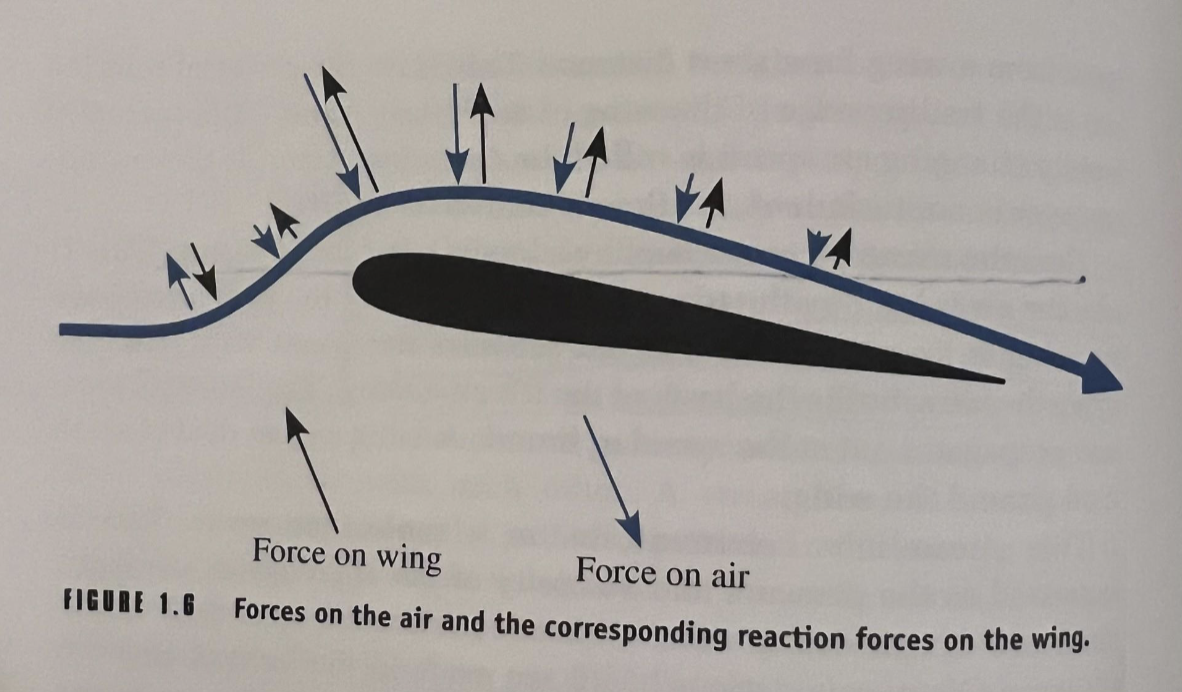
What do these forces, working through pressure, represent?
the mechanism in which the force is transferred to the wing
Forces on a Wing Applying to Newton:
How is downwash produced?
Air bends around the wing
Forces on a Wing Applying to Newton:
How does this apply to Newton’s first law?
bending the air requires a force on the air
Forces on a Wing Applying to Newton:
How does this apply to Newton’s third law?
There is an equal and opposite force on the wing
Forces on a Wing Applying to Newton:
The pressure difference across the wing is the mechanism…
by which lift is transferred to the wing owing to the bending of the air
Newton’s Second Law:
Lift is proportional to the
amount of air diverted per time multiplied by the vertical velocity of that air
How can the lift of a wing be increased?
by increasing the amount of air diverted, the vertical velocity of that air, or a combination of the two
What happens to lift when we double speed?
Vertical velocity will double, but also the amount of air diverted per unit of time will double.
This means that the lift of the wing has gone up by a factor of 4
What if you double the angle of attack but speed stays the same?
The vertical velocity will double but the amount of air diverted is unaffected so lift on the wing doubles.
traditional definition of Geometric Angle of Attack
Angle between the chord line of the wing and the relative wind.
Effective Angle of Attack
Angle measured from the orientation where the wing has zero lift.
Critical Angle of Attack
The point where the angle of attack becomes so great that the airflow begins to separate from the trailing edge of the wing. This is where the stall begins.
Vertical velocity is proportional to?
the speed of the wing and the effective angle of attack of the wing
The amount of air being moved changes based on what?
air density and the speed of the aircraft
Where is more air diverted on a wing?
near the wing root rather than the wing tip
Drag
the retarding force that opposes an aircraft's motion through the air, requiring a certain amount of thrust to fly at a constant speed
Induced Drag
a byproduct of lift that increases as the angle of attack increases
What type of drag is always present as long as there is lift being generated?
Induced Drag
How does parasite drag increase?
It increases with the aircraft’s speed
The three types of Parasite Drag
Form Drag
Skin-Friction Drag
Interference Drag
Form Drag
created due to the shape of the aircraft and its protrusions
Skin-Friction Drag
A result of the aircraft’s surface being rough and can be viewed all the way to the microscopic level
Interference Drag
Occurs when two different airflows meet, mix, speed up, and become turbulent. This meeting of airflows increases energy loss.
_______ on the SR-20 help to reduce the effects of ________ _________
Fairings; Interference drag
Power
The rate at which work is done. In regard to an aircraft that has an engine, we can think of ______ as the rate fuel is consumed
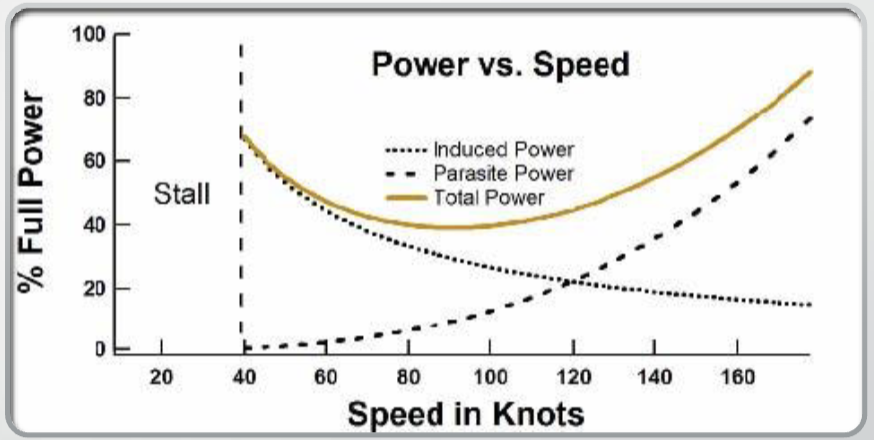
This graph shows the amount of power required to overcome drag and?
maintain a constant speed and altitude
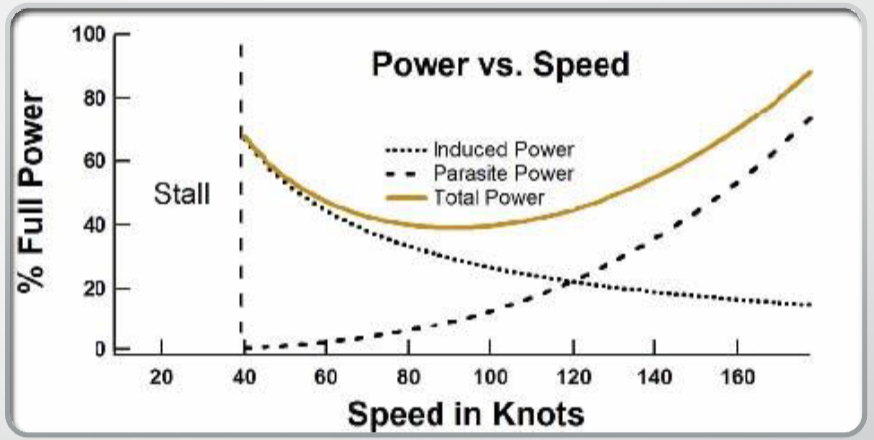
What is more prevalent at slower speeds?
Induced drag
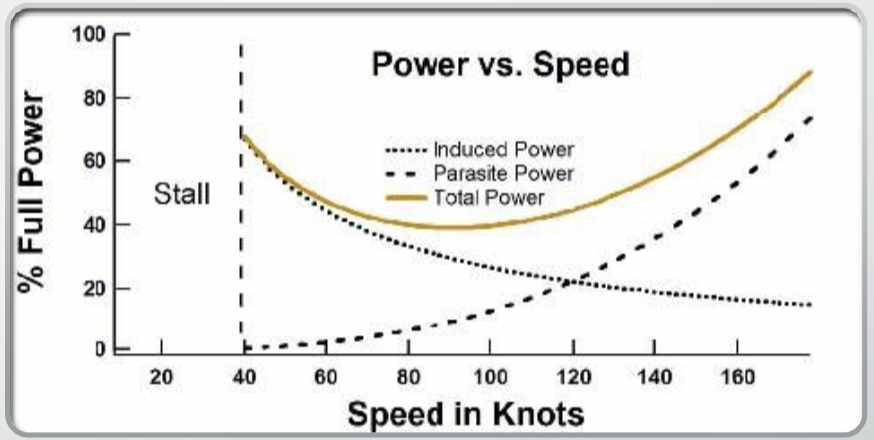
As speed increases, ______ _______ decreases and _________ _____ increases to where more power is required to overcome those effects
induced drag; parasitic drag
The point on the power curve where the effects of induced drag and parasitic drag (total drag) are minimized
L/D Max
Effects of Altitude on Power Required:
(This is why it is harder to breathe at high altitudes)
With an increase in altitude, there is a decrease in air density.
What must be increased as what is decreased to produce enough lift?
The angle of attack; air density
What happens to the downwash if you double the weight of an aircraft but want to maintain the same airspeed?
The vertical velocity of the downwash must double.
This is because the rate (mass) of air diverted stays the same, so to generate twice the lift (for double the weight), each unit of air must be deflected twice as fast downward.
Aspect ratio formula
wing span² / wing area
What happens to a wing’s efficiency when it flies close to the ground?
It experiences an increase in efficiency (reduced induced drag) when flying within about 1 wing’s length of the ground — this is known as ground effect.
Because of the additional lift under the wing created when in ground effect, what can be reduced, and how does this affect the angle of the downwash and induced drag?
Because of the additional lift under the wing, the angle of attack can be reduced, which reduces the angle of the downwash and decreases induced drag.
Problems with Bernoulli
Equilibrium means that no energy can be added to or removed from the airflow.
Problems With Bernoulli
In order to oppose the induced drag caused by lift, external work must be done by the
engine or else the wing will decelerate, which means it is not in equilibrium.