RAP E3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:10 AM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
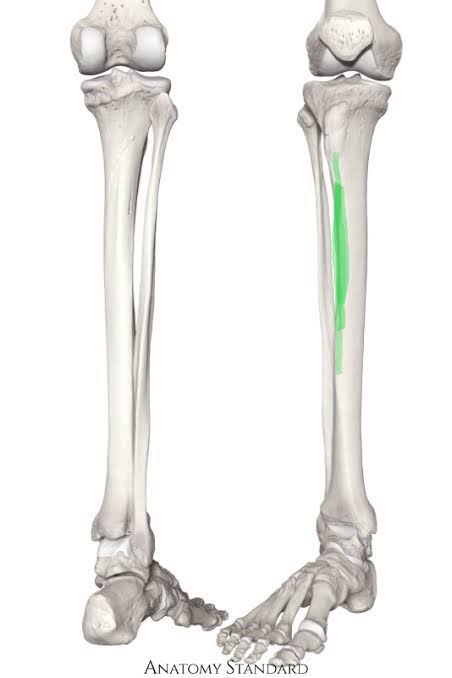
Anterior Crest of the Tibia
2
New cards
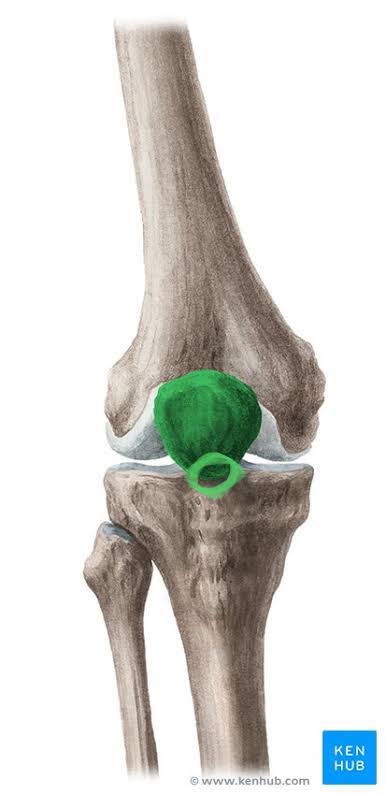
Apex of the Patella
3
New cards
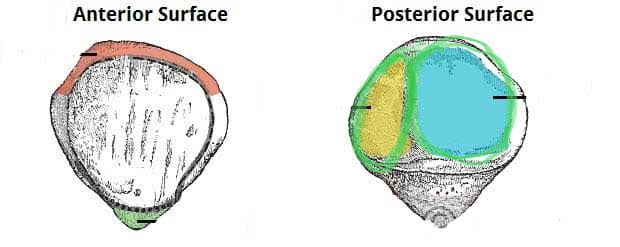
Articular Facets of the Patella (Blue = Lateral, Yellow = Medial)
4
New cards
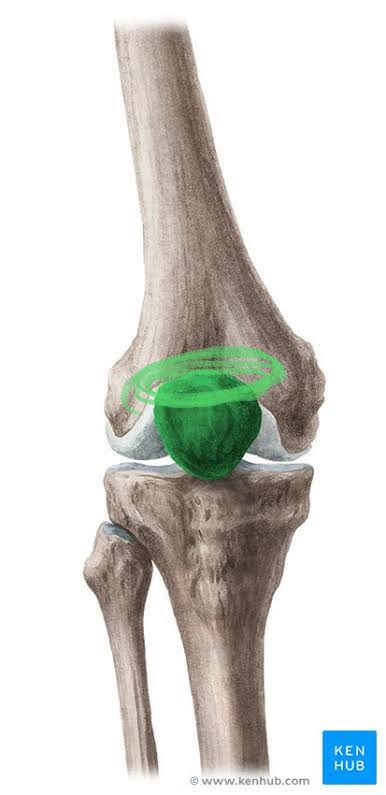
Base of Patella
5
New cards
Calcaneus Tarsal (Heel)
6
New cards
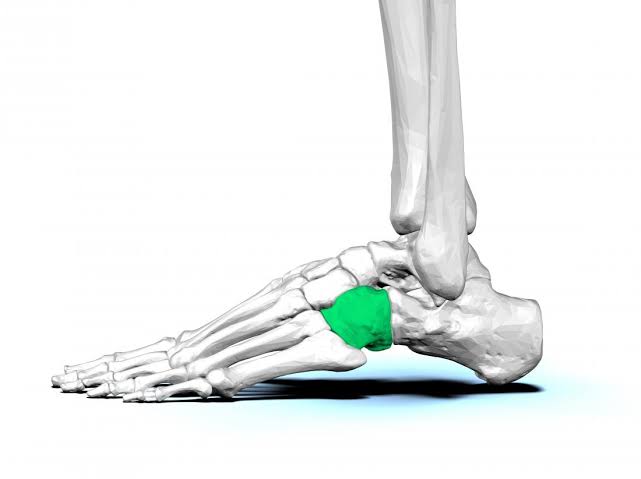
Cuboid Tarsal (Pinky side)
7
New cards
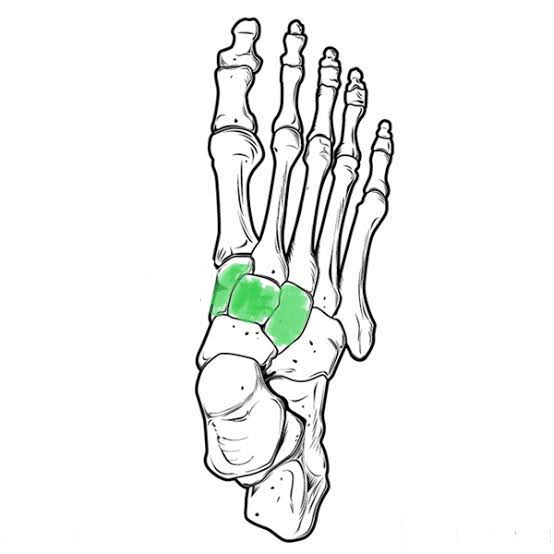
Cuneiform Tarsals (Three medial top)
8
New cards
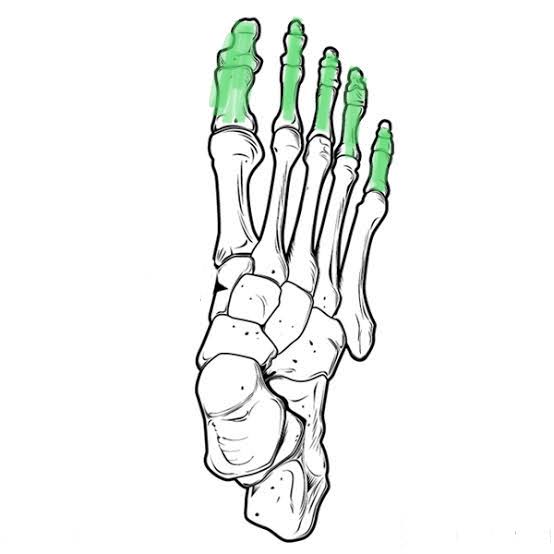
Phalanges of the Foot (Proximal, Medial and Distal)
9
New cards
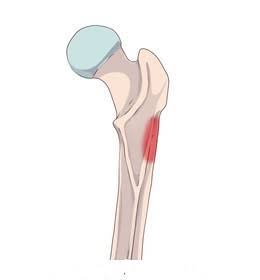
Gluteal Tuberosity (Where glutes attach) of Femur
10
New cards
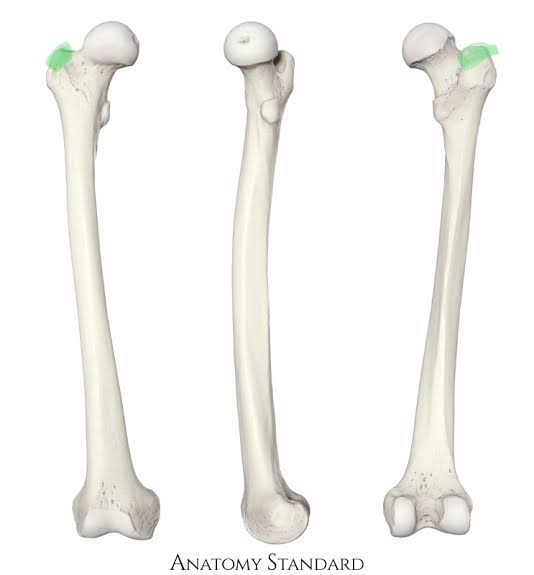
Greater Trochanter of Femur (Opposite to head)
11
New cards
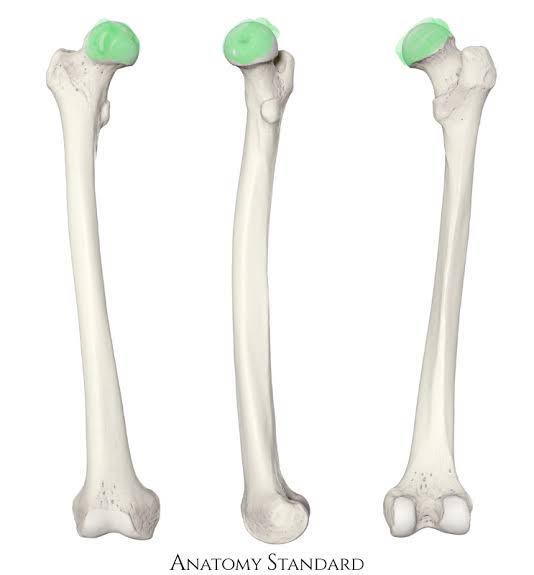
Head of the Femur
12
New cards
Lateral Condyle of the Femur
13
New cards
Lateral Epicondyle of the Femur
14
New cards
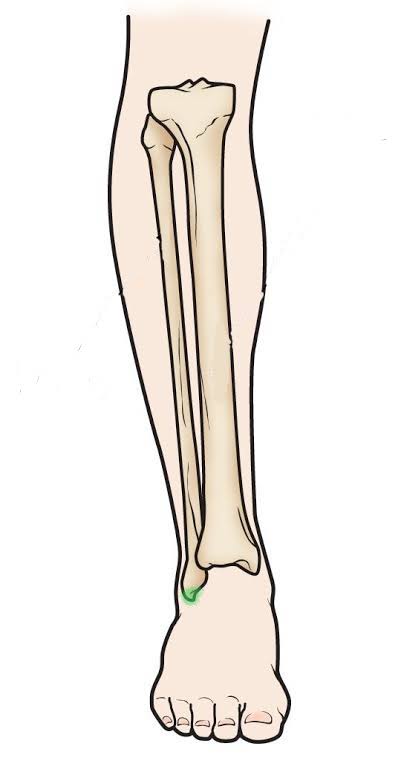
Lateral Malleolus of the Fibula
15
New cards
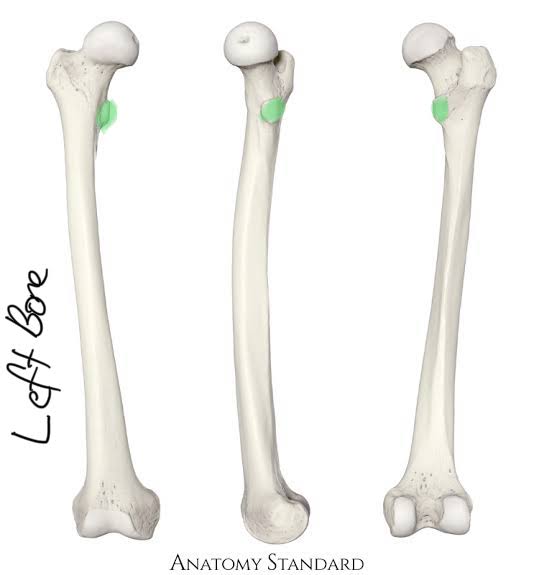
Lesser Trochanter of the Femur (Same side as head)
16
New cards
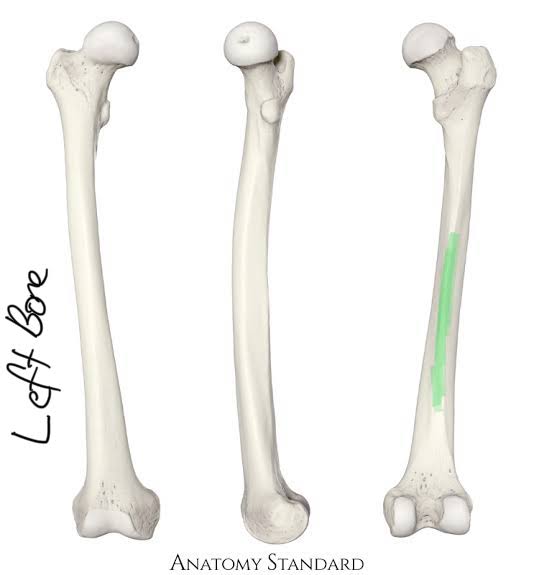
Linea Aspera of the Femur
17
New cards
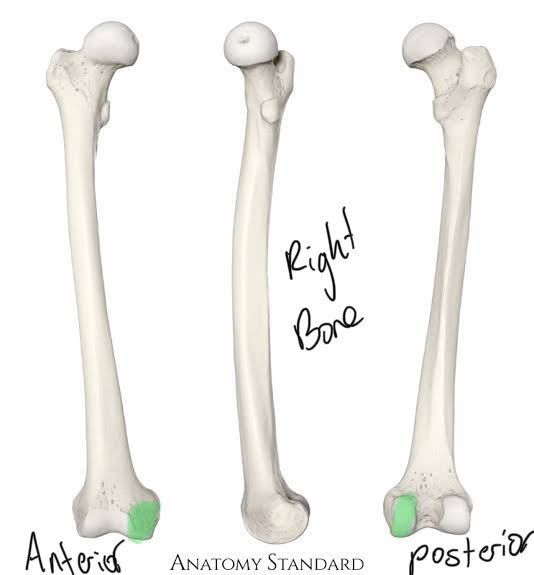
Medial Condyle of the Femur
18
New cards
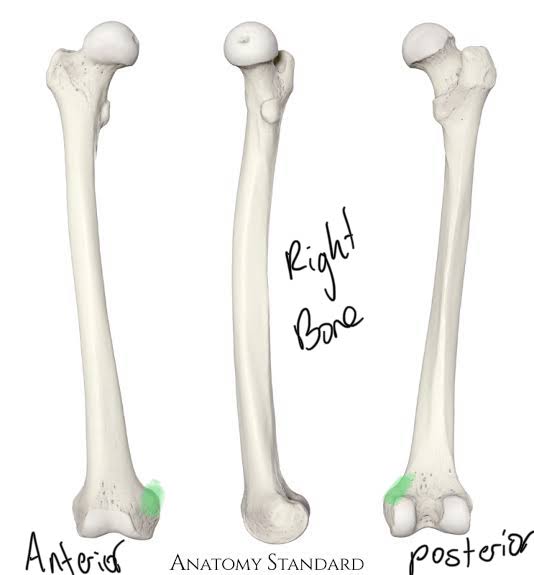
Medial Epicondyle of the Femur
19
New cards
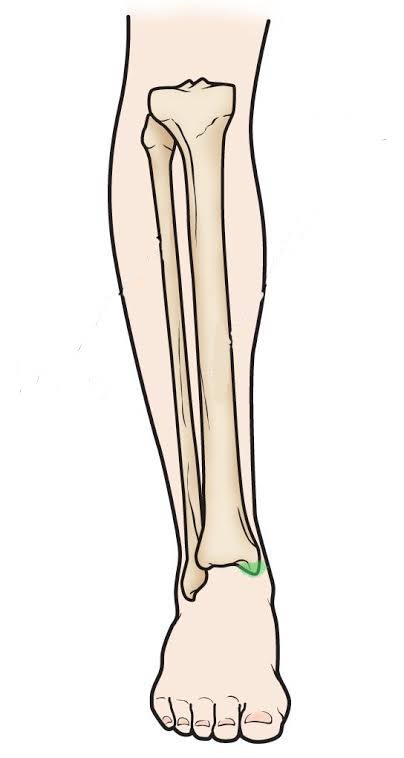
Medial Malleolus of the Tibia
20
New cards
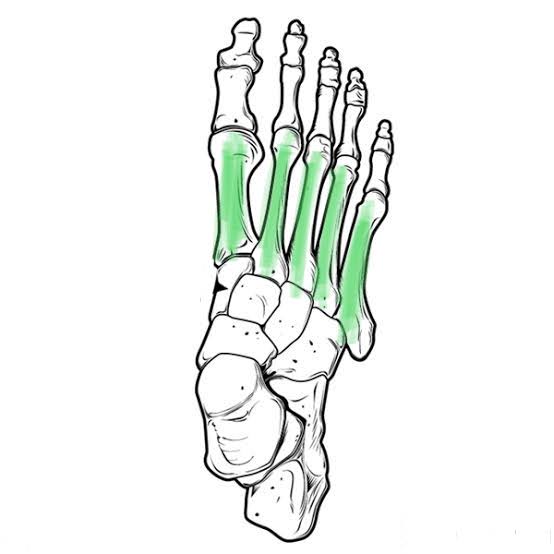
Metatarsals of the Foot
21
New cards
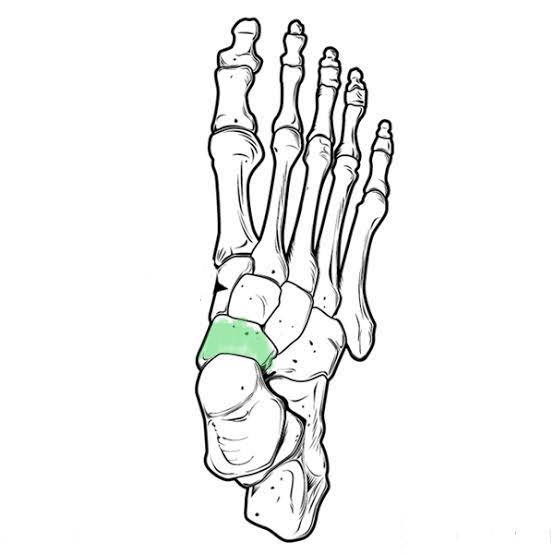
Navicular Tarsal (Under cuneiforms)
22
New cards
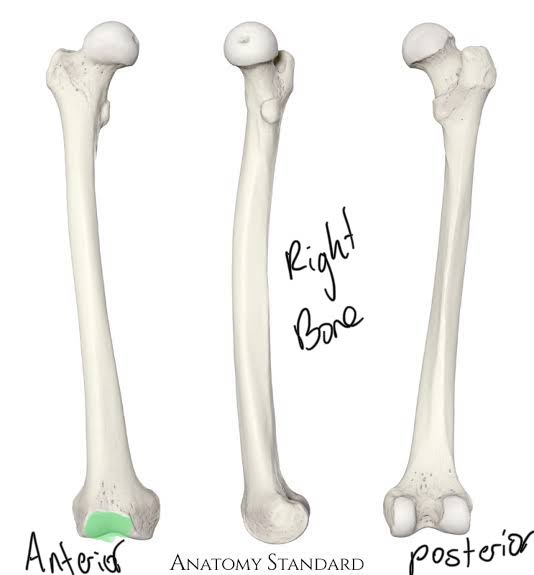
Patella Surface of the Femur
23
New cards
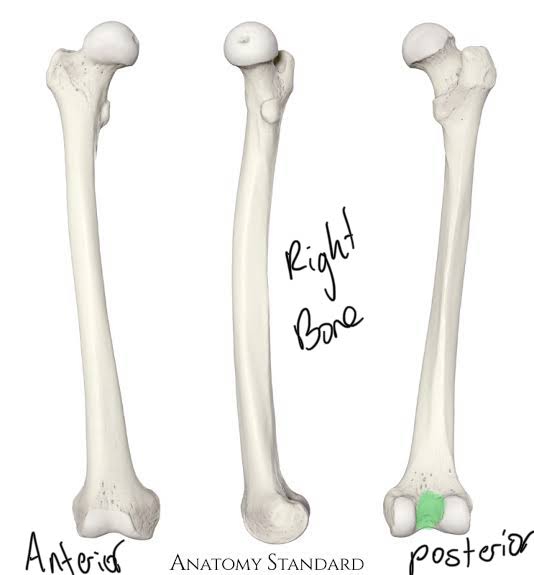
Popliteal Surface of the Femur
24
New cards
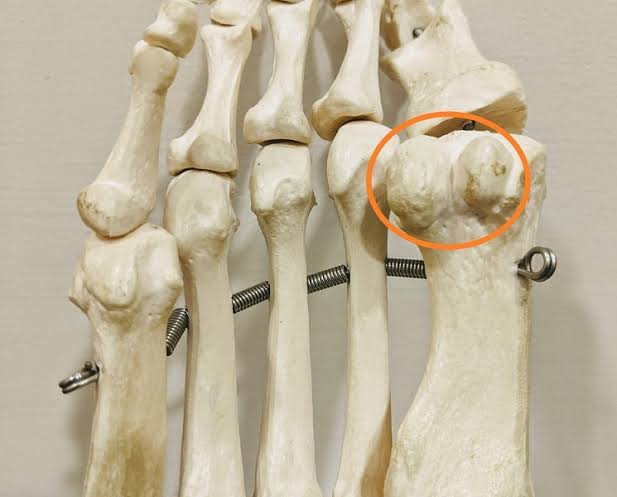
Sesamoid Bones of the Foot (Balls of big toe)
25
New cards
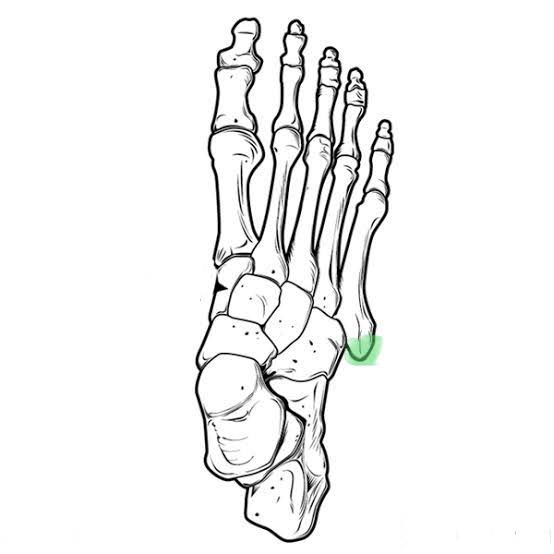
Styloid Process of the Foot
26
New cards
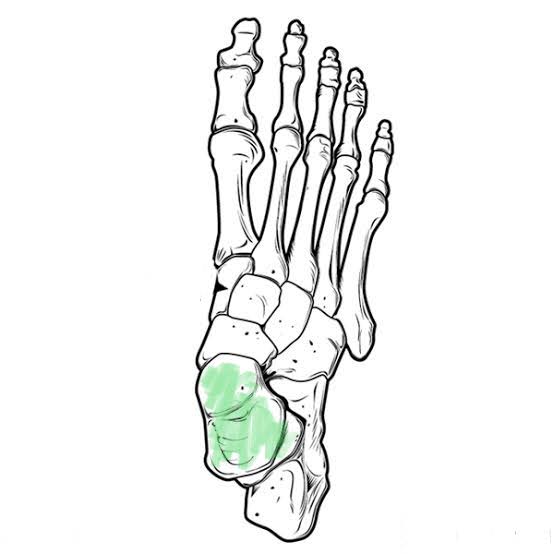
Talus Tarsal (Lower ankle bone)
27
New cards
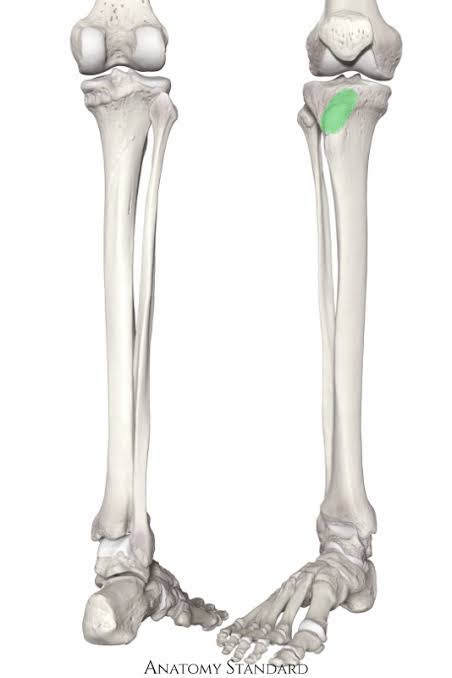
Tibial Tuberosity of the Tibula
28
New cards
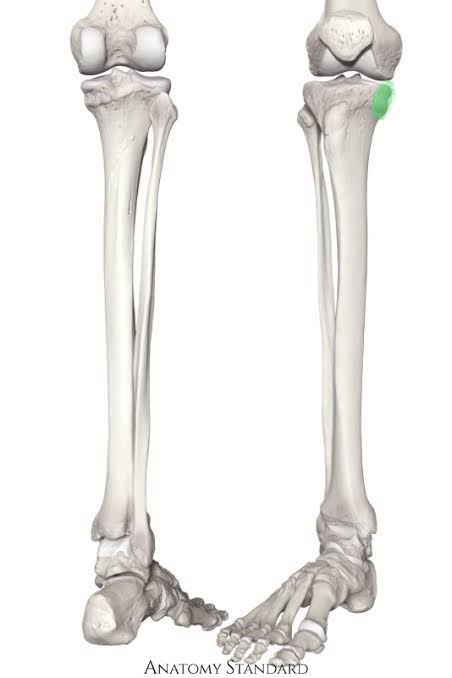
Medial Condyle of the Tibia
29
New cards
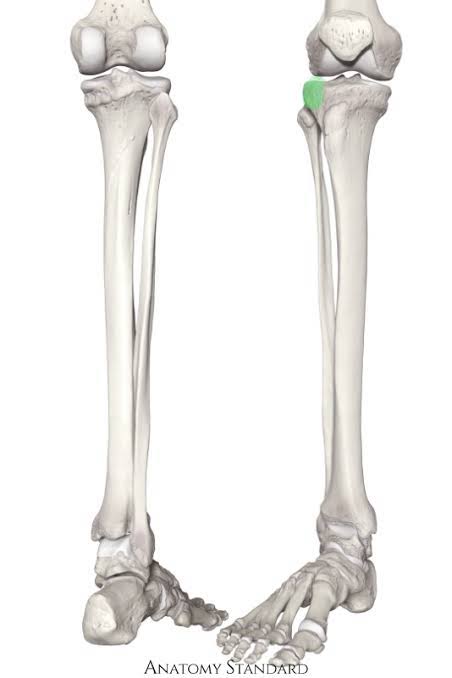
Lateral Condyle of the Tibia
30
New cards
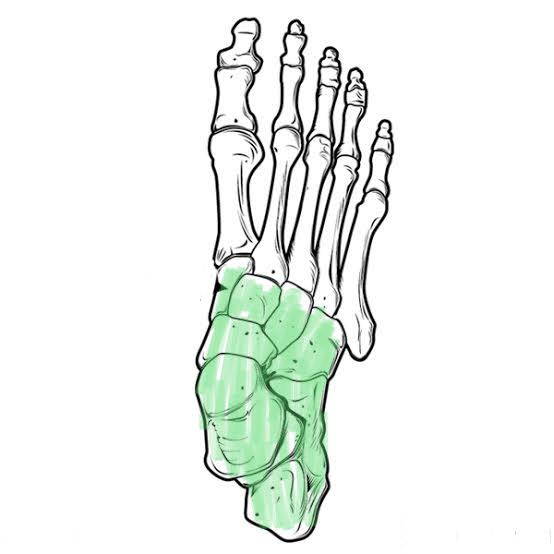
Tarsals of the Foot
31
New cards
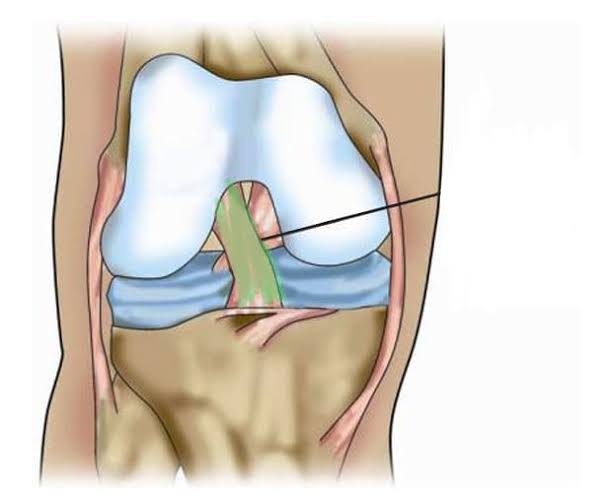
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (Inside knee)
32
New cards
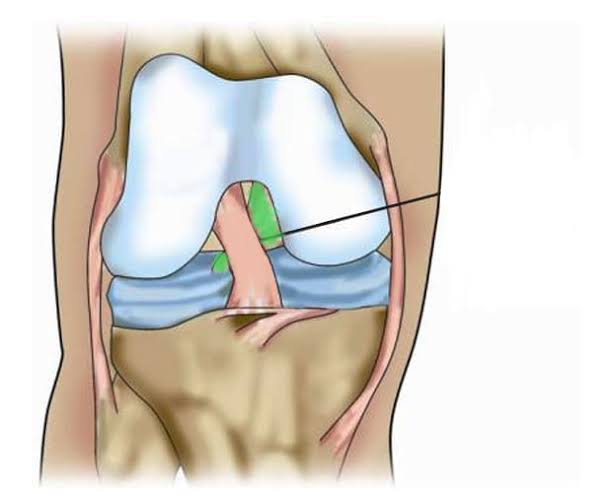
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (Inside knee)
33
New cards
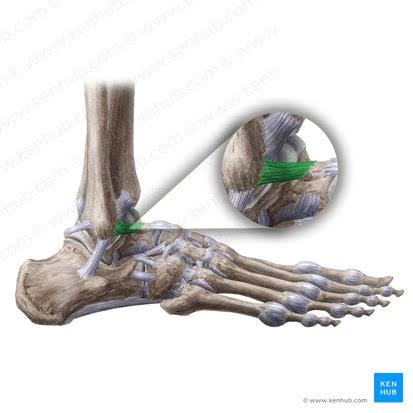
Anterior Talofibular Ligament
34
New cards
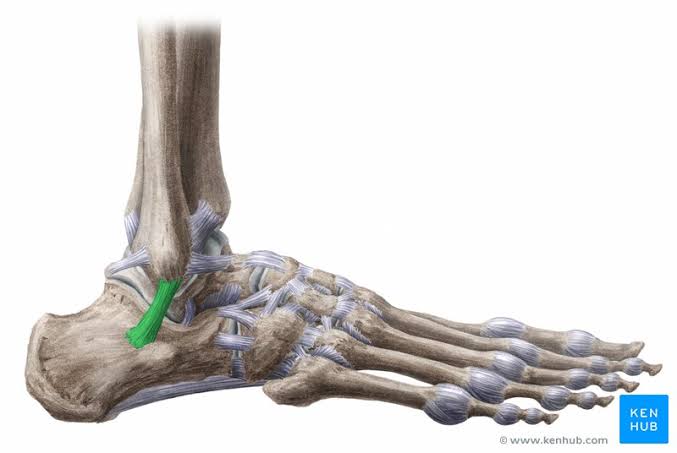
Calcaneofibular Ligament
35
New cards
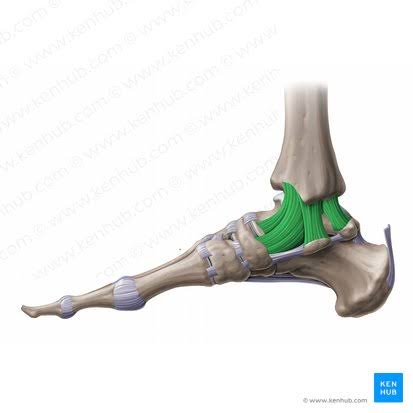
Deltoid Ligament (Multiple bands)
36
New cards
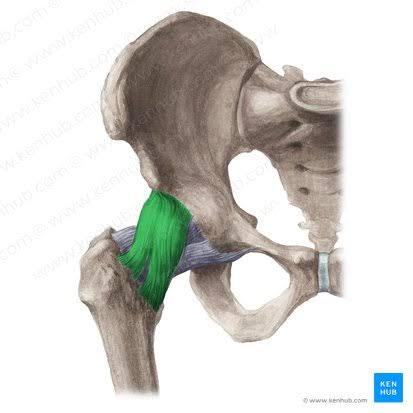
Iliofemoral Ligament (2 bands)
37
New cards
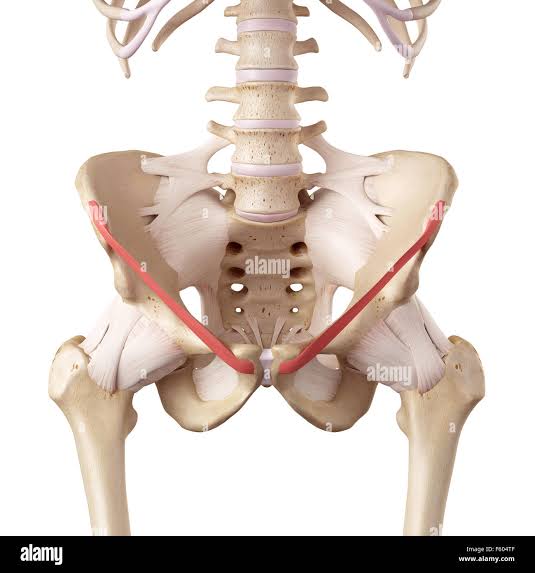
Inguinal Ligament
38
New cards
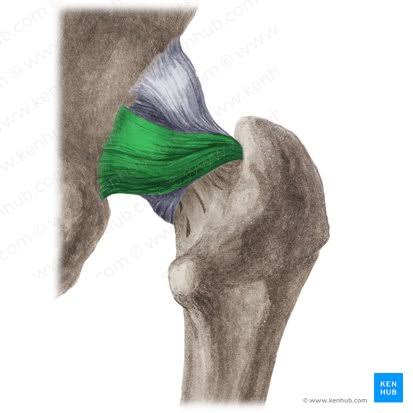
Ischiofemoral Ligament
39
New cards
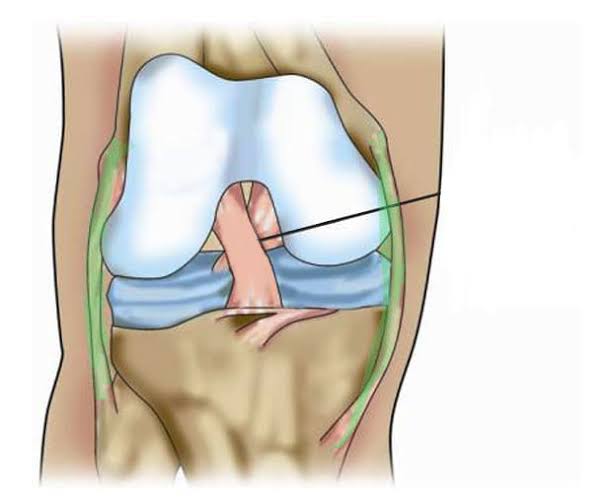
Medial and Lateral Collateral Ligaments of the Knee
40
New cards
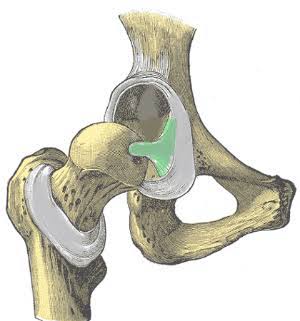
Ligamentum Teres Ligament (Cord inside acetabulum)
41
New cards
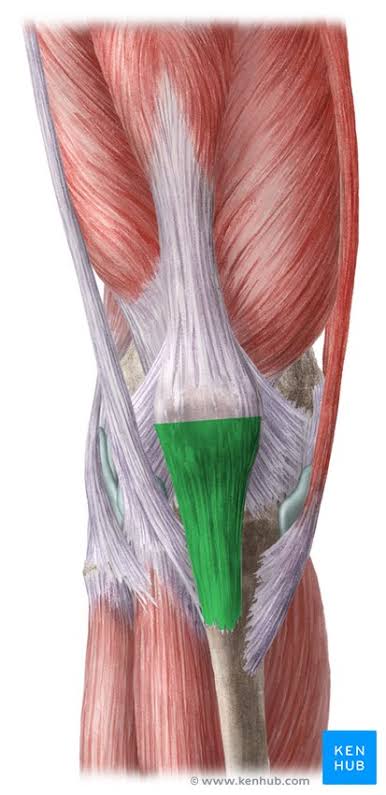
Patellar Ligament
42
New cards
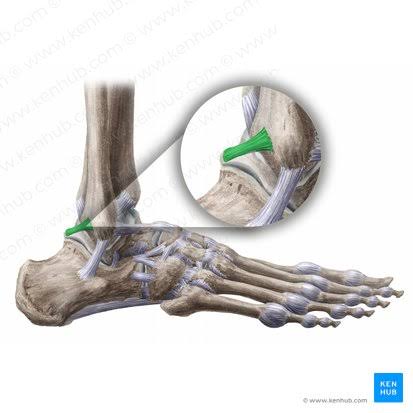
Posterior Talofibular
43
New cards
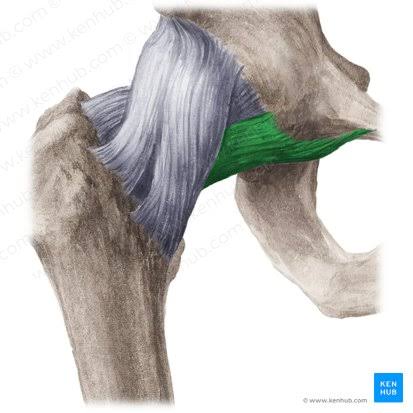
Pubofemoral Ligament
44
New cards
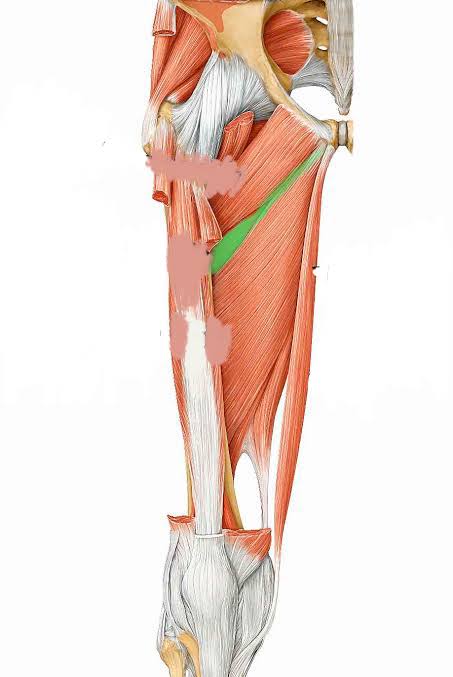
Adductor Brevis (Action: Adduction)
45
New cards
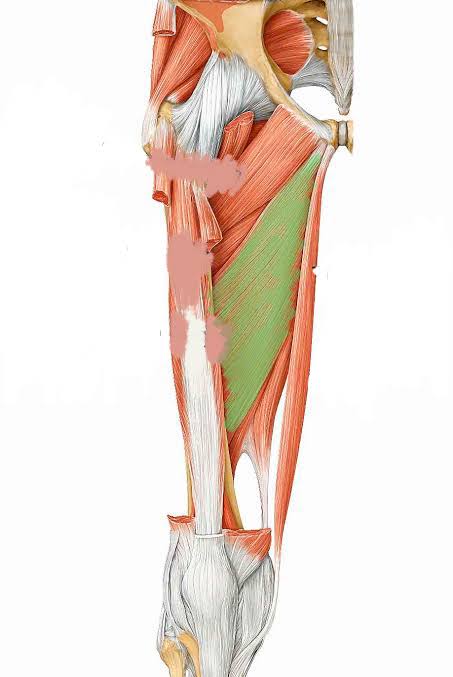
Adductor Longus (Action: Adduction)
46
New cards
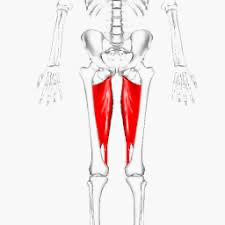
Adductor Magnus (Action: Adduction)
47
New cards
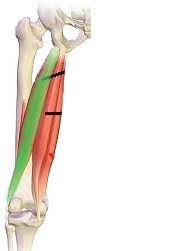
Biceps Femoris (Action: Flexion)
(Hamstring, inserts laterally)
(Hamstring, inserts laterally)
48
New cards
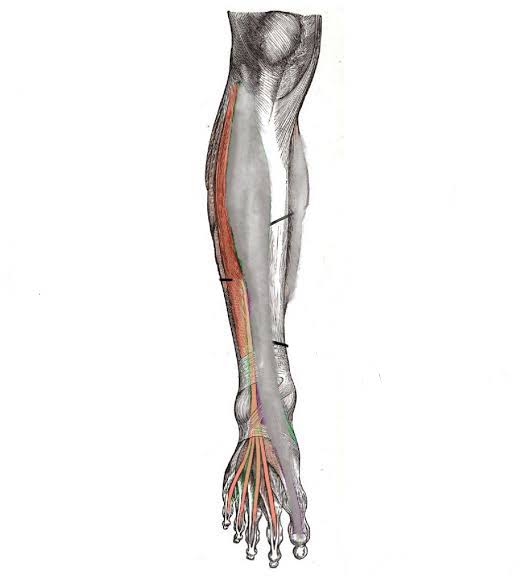
Extensor Digitorum Longus (Action: Toe Extension)
49
New cards
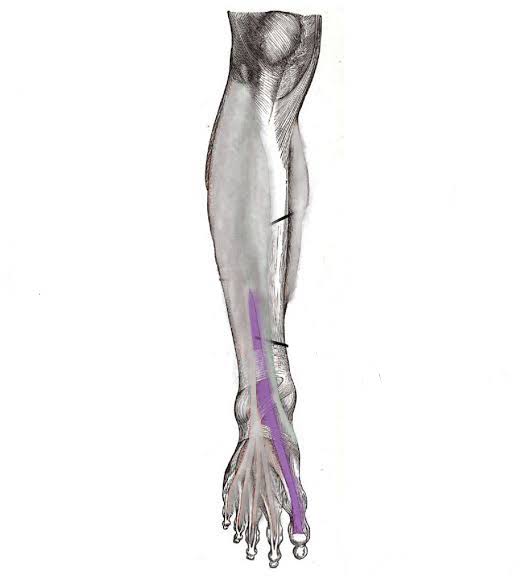
Extensor Hallucis Longus (Action: Dorsiflexion)
50
New cards
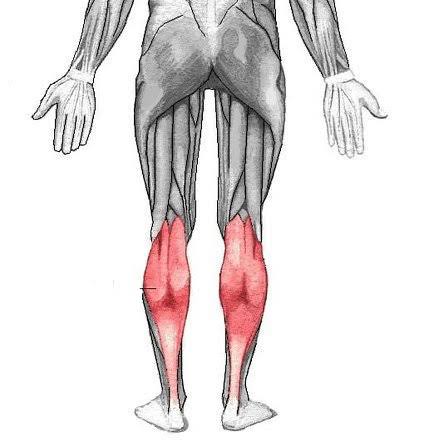
Gastrocnemius (Action: Knee Flexion)
51
New cards
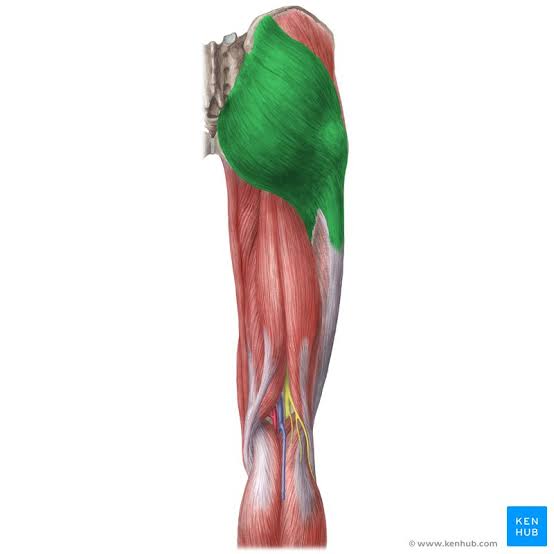
Gluteus Maximus (Action: Abduction)
52
New cards
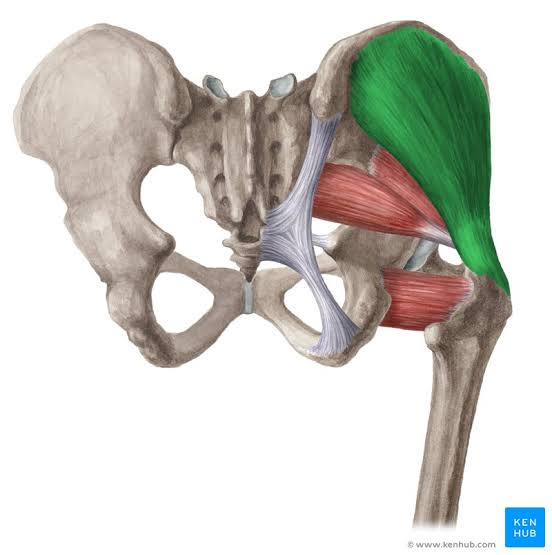
Gluteus Medius (Action: Abduction)
53
New cards
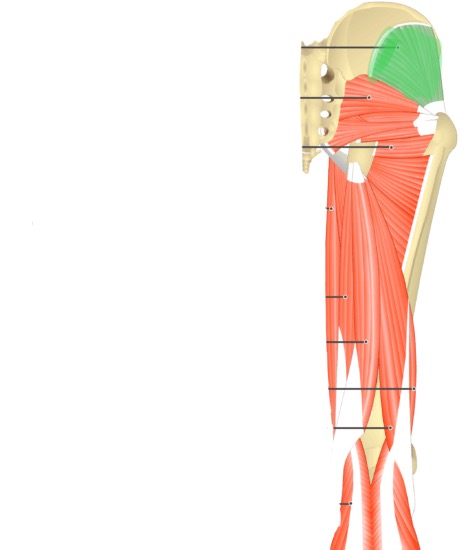
Gluteus Minimus (Action: Abduction)
54
New cards
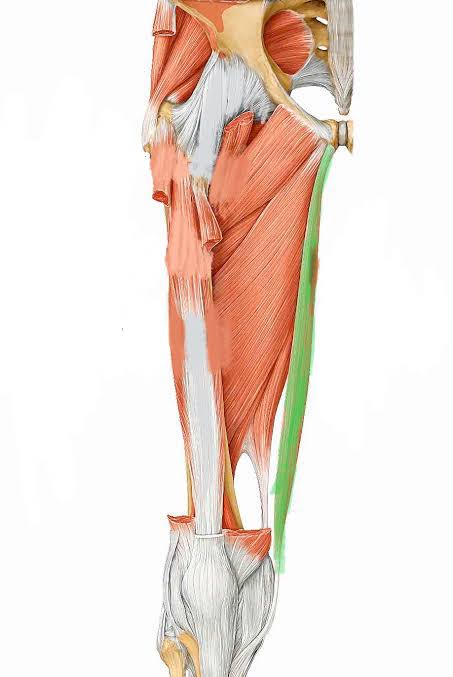
Gracilis (Action: Knee Flexion)
55
New cards
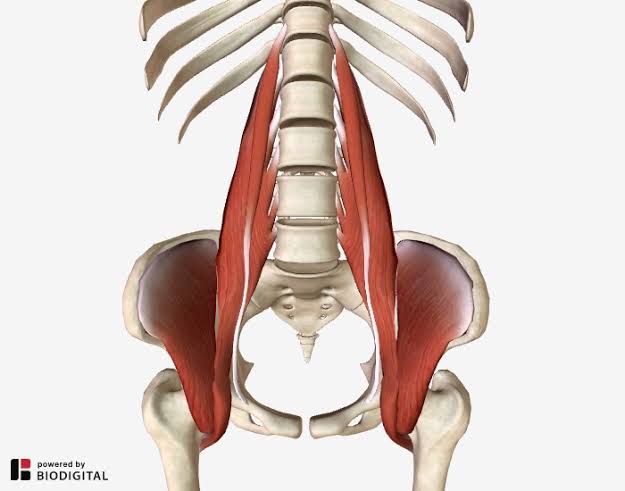
Iliopsoas (Action: External Rotation) (Made of major psoas, and iliacus \[on ilium\])
56
New cards
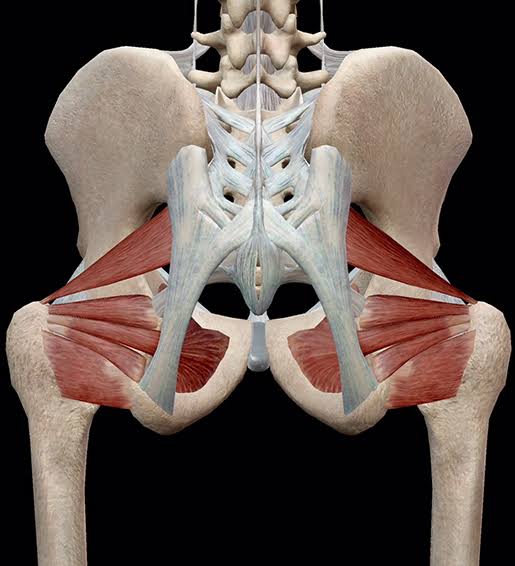
Lateral Rotators (Action: Lateral Rotation)
57
New cards
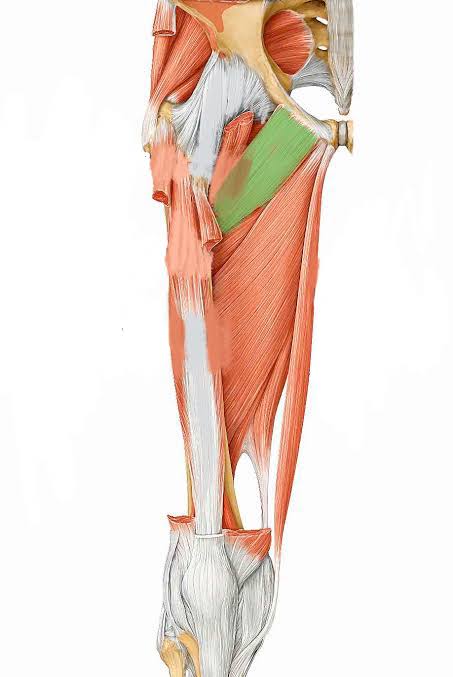
Pectineus (Action: Hip Flexion)
58
New cards
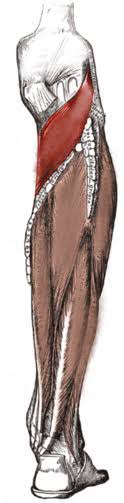
Popliteus (Action: External Rotation)
59
New cards
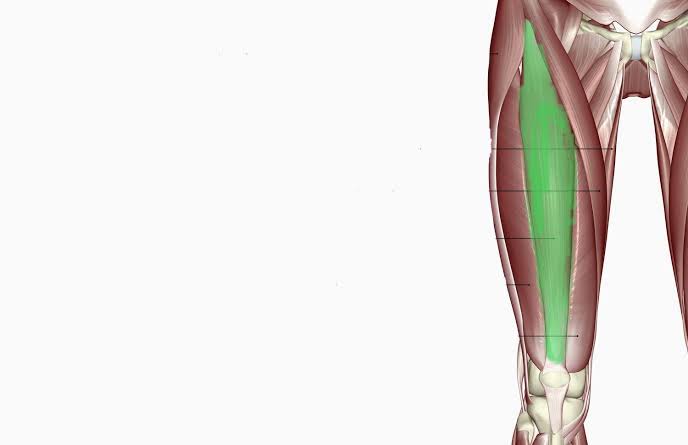
Rectus Femoris (Action: Knee Extension)
60
New cards
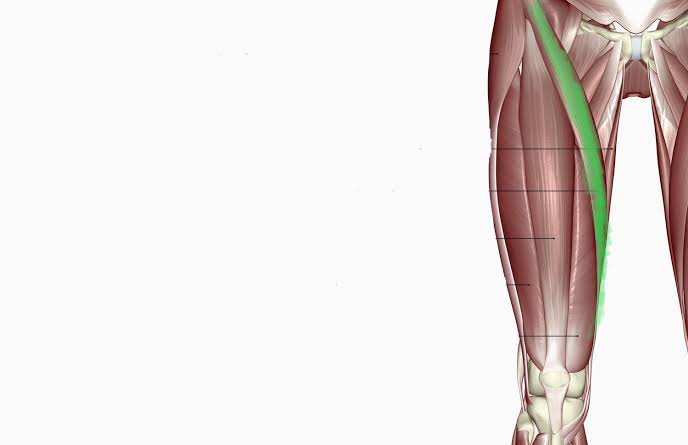
Sartorius (Action: Flexion)
61
New cards
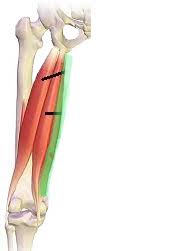
Semimembranosus (Action: Knee Flexion)
62
New cards
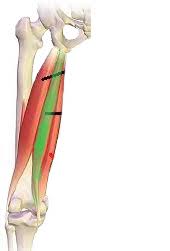
Semitendinosus (Action: Flexion)
63
New cards
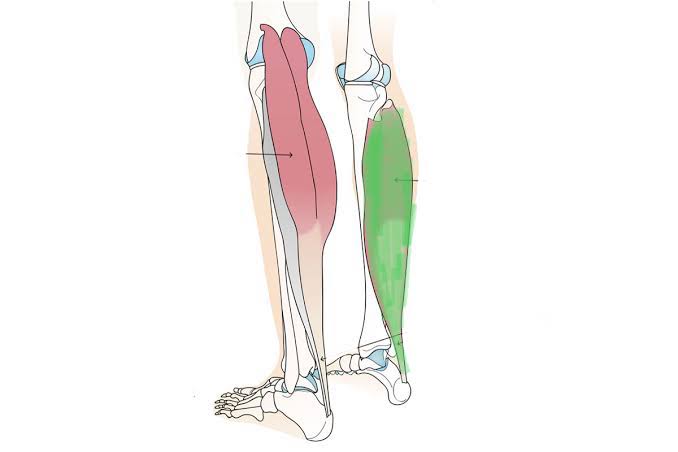
Soleus (Action: Knee Extension)
64
New cards
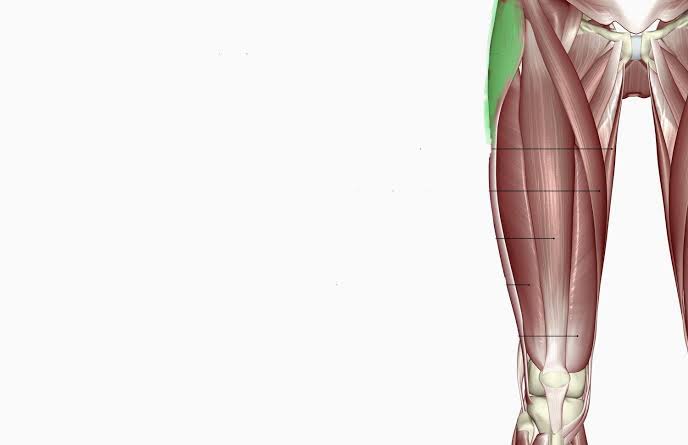
Tensor Fasciae Latae (Action: Hip Flexion)
65
New cards
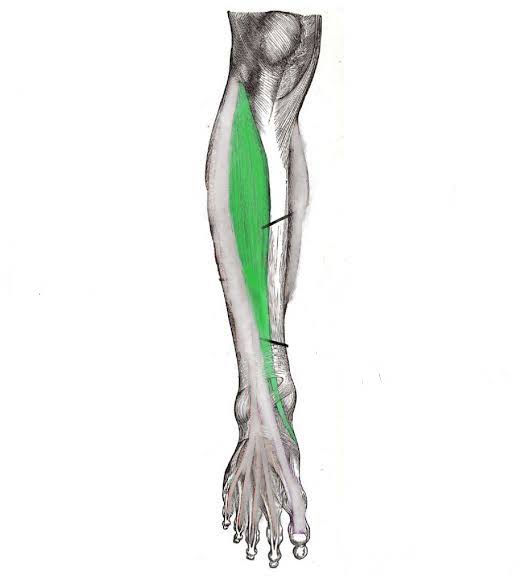
Tibialis Anterior (Action: Dorsiflexion)
66
New cards

Tibialis Posterior (Action: Plantar Flexion)
67
New cards
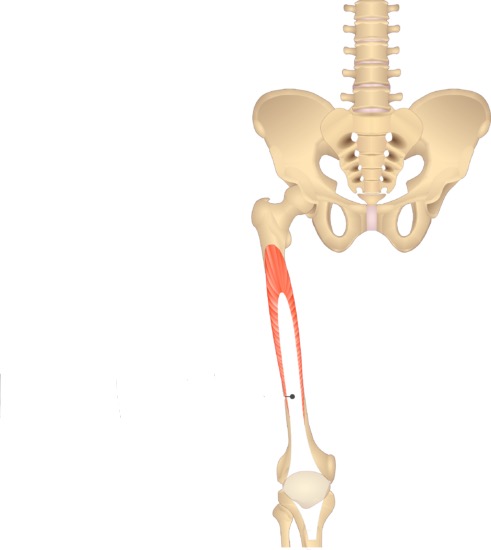
Vastus Intermedius (Action: Extension)
68
New cards
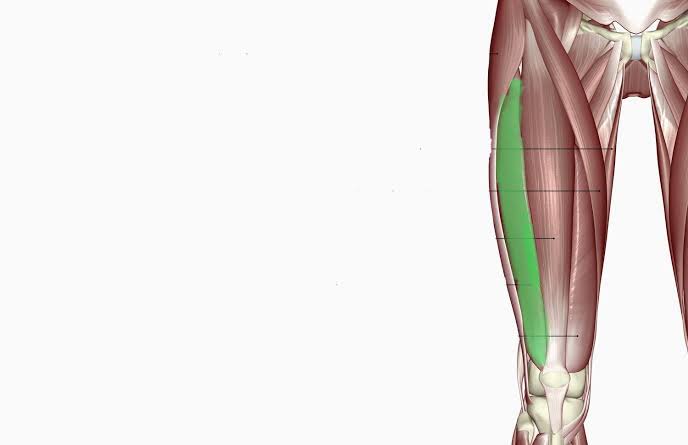
Vastus Lateralis (Action: Extension)
69
New cards
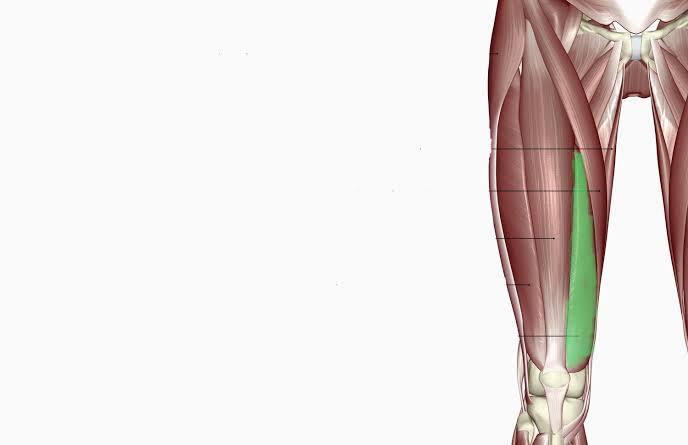
Vastus Medialis (Action: Extension)
70
New cards
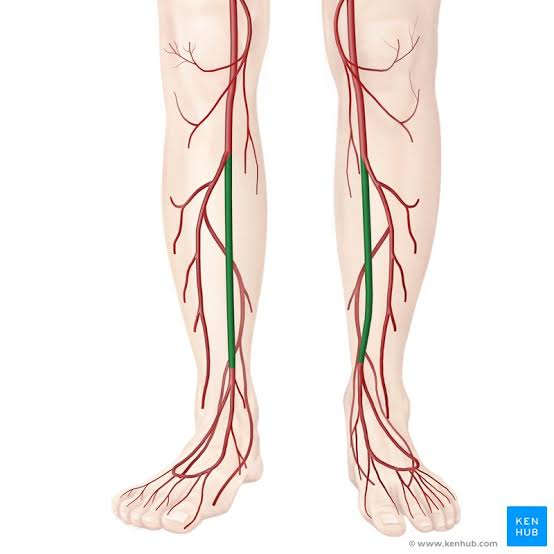
Anterior Tibial Arteries
71
New cards
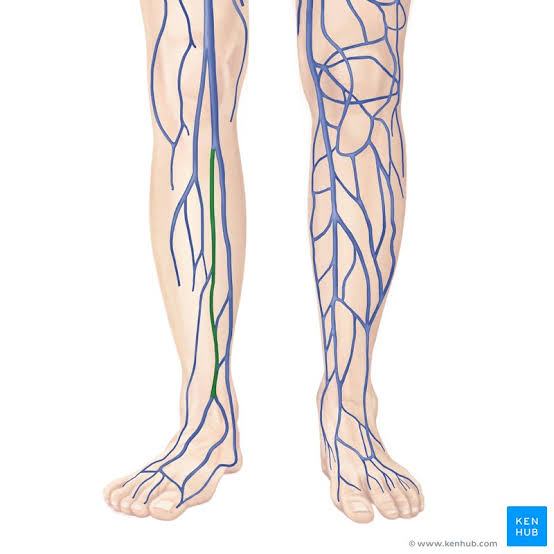
Anterior Tibial Veins
72
New cards
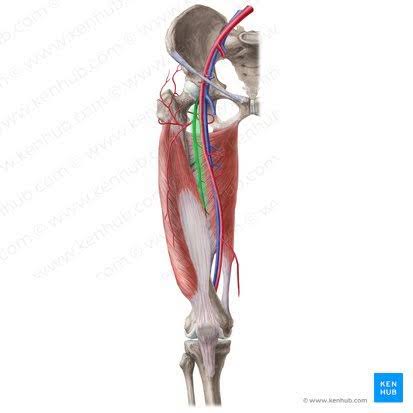
Deep Femoral Artery
73
New cards
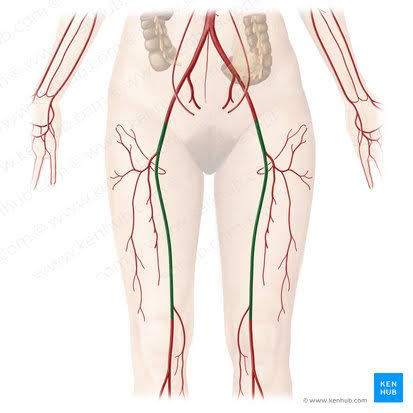
Femoral Arteries
74
New cards
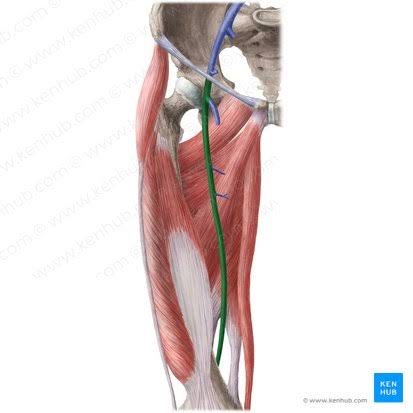
Femoral Veins
75
New cards
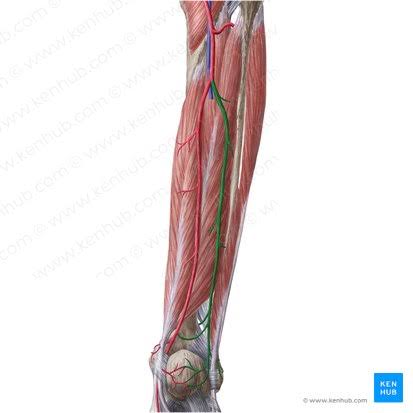
Fibular Artery
76
New cards
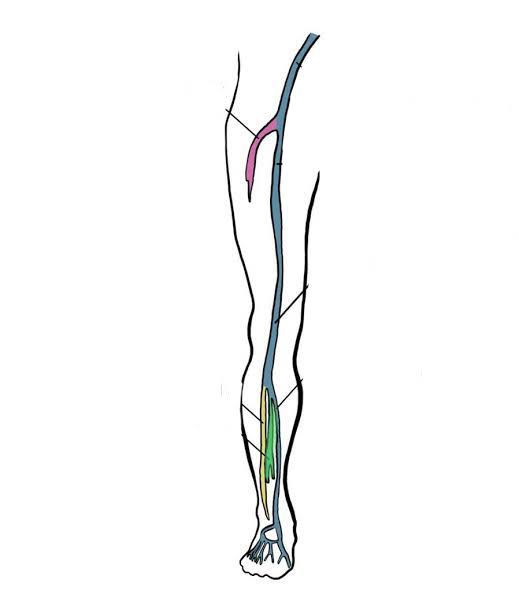
Fibular Vein
77
New cards
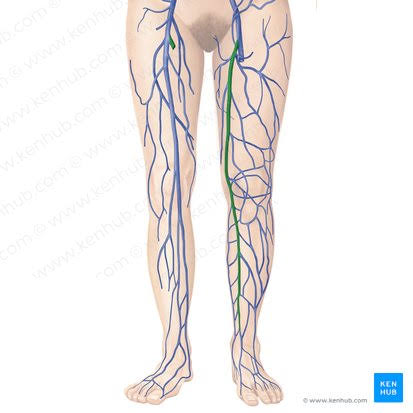
Great Saphenous Vein
78
New cards
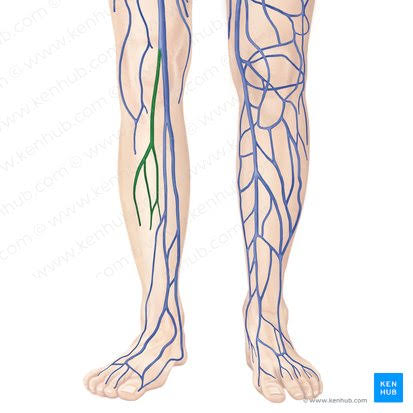
Lesser Saphenous Vein
79
New cards
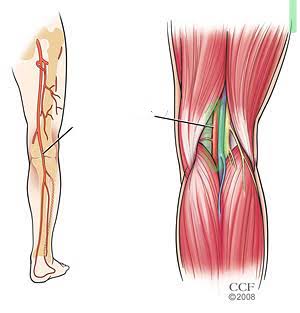
Popliteal Artery
80
New cards
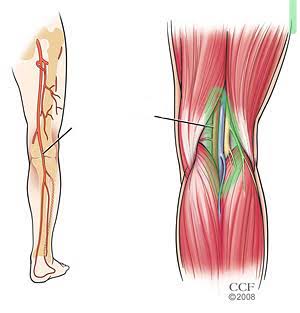
Popliteal Vein
81
New cards
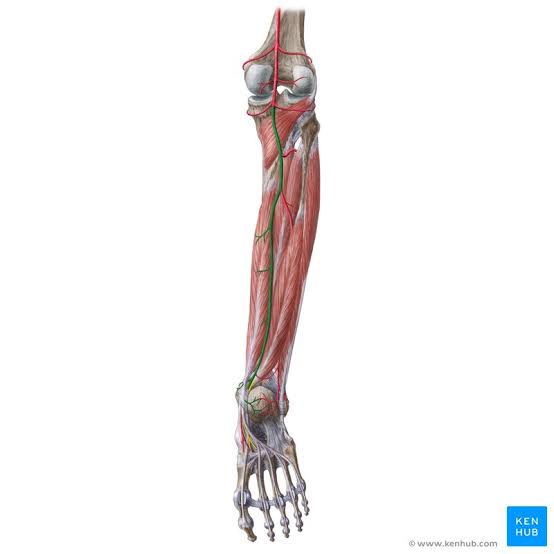
Posterior Tibial Artery
82
New cards
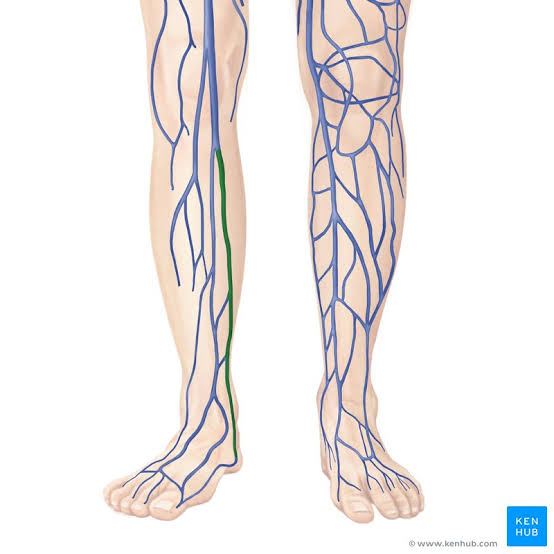
Posterior Tibial Veins
83
New cards
What is a joint?
The point of contact between 2 bones, bone and cartilage, or bone and teeth. Also known as an articulation.
84
New cards
What are the 3 structural classifications of joints?
They are based on the presence or absence of a synovial cavity, and the type of connective tissue holding the joint together.
* Fibrous: No synovial cavity, held by dense, irregular CT
* Cartilaginous: No synovial cavity, held by (hyaline or fibro) cartilage CT
* Synovial: Has synovial cavity, held by dense, irregular CT in an articular capsule (articulating bones covered in articular cartilage to reduce friction and absorb shock)
SFCS
(Sargent, fairies can’t sing)
* Fibrous: No synovial cavity, held by dense, irregular CT
* Cartilaginous: No synovial cavity, held by (hyaline or fibro) cartilage CT
* Synovial: Has synovial cavity, held by dense, irregular CT in an articular capsule (articulating bones covered in articular cartilage to reduce friction and absorb shock)
SFCS
(Sargent, fairies can’t sing)
85
New cards
What is a synovial cavity?
Space between articulating bones
86
New cards
What are the 3 functional classifications of joints?
Based on the degree of movement permitted
* Synarthrosis: Immovable
* Amphiarthrosis: Slightly moveable
* Diarthrosis: Freely moveable
* Synarthrosis: Immovable
* Amphiarthrosis: Slightly moveable
* Diarthrosis: Freely moveable
87
New cards
What is the structure and function of the 2 types of cartilaginous joints?
1. Synchondroses: Connected by hyaline cartilage, only found in kids (epiphyseal plate)
2. Symphyses: Ends of the articulating bones are covered in hyaline cartilage, but a disc of fibrocartilage joins them. Found in the midline of the body (pubic symphysis)
88
New cards
What is the structure and function of the 3 types of fibrous joints?
(All amphi or synarthrosis)
1. Sutures: Only between bones of the skull, interlocking irregular edges for strength. Amphiarthrosis as kids, develops into synarthrosis
2. Syndesmoses: Bigger distance between articulating bones, with a ligament surrounding the joint to limit movement, like anterior tibiofibular ligament, amphiarthrosis
3. Interosseous Membranes: A large sheet of CT joining a neighbouring long-bone, like between the raidus and ulna or between the tibia and fibula, amphiarthrosis
1. Sutures: Only between bones of the skull, interlocking irregular edges for strength. Amphiarthrosis as kids, develops into synarthrosis
2. Syndesmoses: Bigger distance between articulating bones, with a ligament surrounding the joint to limit movement, like anterior tibiofibular ligament, amphiarthrosis
3. Interosseous Membranes: A large sheet of CT joining a neighbouring long-bone, like between the raidus and ulna or between the tibia and fibula, amphiarthrosis
89
New cards
What are the 7 accessory structures of synovial joints?
1. Articular Capsule: Surrounds synovial joint to unite the bones, made up of 2 layers of membrane
2. Synovial Membrane:
1. Outer Fibrous Membrane, flexible for movement but with tensile strength to prevent dislocation
2. Inner Synovial Membrane, has lots of elastic fibres. Secretes synovial fluid into the joint, made up of hyaluronic acid from synovial cells and interstitial fluid from blood plasma. Fluid forms thin film to reduce friction and shock, supply oxygen and nutrients, and remove carbon dioxide and waste (via phagocytes in fluid) from chondrocytes in the cartilage.
3. Ligaments: Extra or intracapsular
4. Articular Discs: Made of fibrocartilage, and found between articulating surfaces of the bone. It binds to inside the fibrous membrane to allow shock absorption, weight distribution, and for the distribution of synovial fluid, also acting as an adaptable surface
5. Labrum: Fibrocartilage extending from the edge of the joint socket, to help deepen the socket and prevent dislocation
6. Bursa: Sac-like, filled with a small amount of fluid, places to reduce friction between skin, tendons, muscles or ligaments with bone
7. Tendon Sheath: Tube-shaped bursa wrapping around tendons with a lot of friction, to reduce it. Has 3 sections
1. Inner visceral later, attached to surface of tendons
2. Cavity, contains fluid, where tendons pass through
3. Outer parietal layer, attached to bone
\
AMLDLBT
\
90
New cards
What is the structure and function of the 6 types of synovial joints?
1. Plane joints: When articulating surfaces are flat or slightly curves, for a back and forth and side to side movement, sometimes rotation. (Intertarsals)
2. Hinge joints: When the convex surface of one bone fits in the concave surface of another. For flexion and extension. (Elbow)
3. Pivot joints: When the round or pointed surface of one bone articulates with a ring formed by bone and ligament. For rotation (axis on the atlas)
4. Condyloma joints: When the convex or oval projection of a bone fits in the depression of another. Allows for movement across 2 axis, flexion and extension one way and abduction and addiction the other way, together called circumduction. (Between metacarpals and phalanges)
5. Saddle joints: When the saddle-shaped articular surface allows another bone to fit into the space. For flexion and extension. (Trapezium carpal and metacarpal)
6. Ball-and-socket joint: When the ball-like surface of one bone fits in the cup-like surface of another. For flexion and extension, abduction and abduction, and rotation (hip joint)
\
PHPCSB
91
New cards
What is the function of the 5 accessory structures of the eye?
1. Eyelid: To shade eyes during sleep, protect eyes from light and foreign object, and assist in eye lubrication
2. Eyelashes: To protect from foreign objects, sweat, and light, and can initiate blinking
3. Eyebrow: “ but not for blinking
4. Lacrimal Caruncle: To protect the lacrimal tissue / tear ducts underneath
5. Conjunctiva: A thin mucus membrane for lubrication of the eye and inner eyelid, and protect from duct and debris (made of bulbar, vascular and palpebral)
92
New cards
Name the 3 structures of the superficial layer of the eye, and their function
Fibrous Tunic Layer
1. Cornea: A transparent window to let light in
2. Sclera: White continuation from cornea, for protection and as an anchor for extrinsic eye muscles
3. Canal of Schlemm: A sinus / tube that surrounds the cornea, and collects and reads robs aqueous humour
1. Cornea: A transparent window to let light in
2. Sclera: White continuation from cornea, for protection and as an anchor for extrinsic eye muscles
3. Canal of Schlemm: A sinus / tube that surrounds the cornea, and collects and reads robs aqueous humour
93
New cards
Name the 3 structures of the middle layer of the eye, and their function
Vascular Tunic Layer
1. Choroid: A network of capillaries supplied to the retina and sclera
2. Ciliary Body: Made up of ciliary muscle and processes that surround the lens and hold it in shape, allowing it to change and dilate when needed
3. Iris: Coloured part in front of the lens, made up of blood vessels, smooth muscle and pigment. Has an opening in the middle called the pupil that the smooth muscle changes the shape of
1. Choroid: A network of capillaries supplied to the retina and sclera
2. Ciliary Body: Made up of ciliary muscle and processes that surround the lens and hold it in shape, allowing it to change and dilate when needed
3. Iris: Coloured part in front of the lens, made up of blood vessels, smooth muscle and pigment. Has an opening in the middle called the pupil that the smooth muscle changes the shape of
94
New cards
Name the 3 structures of the inner layer of the eye, and their function
Retina Layer
1. Photoreceptors: Rods and cones, the specialised light receptors that take light into a neural signal
2. Macula Lutea: The small yellow region in the back of the eye, where upon focusing on an image, the centre of the macula lutea, the centre of the lens, and the centre of the image, are aligned
3. Fovea Centralis: A depression in the centre of the macula lutea, where only cones are located, for sharper, clear vision, as there are no blood vessels that cause blurring in the fovea centralis
1. Photoreceptors: Rods and cones, the specialised light receptors that take light into a neural signal
2. Macula Lutea: The small yellow region in the back of the eye, where upon focusing on an image, the centre of the macula lutea, the centre of the lens, and the centre of the image, are aligned
3. Fovea Centralis: A depression in the centre of the macula lutea, where only cones are located, for sharper, clear vision, as there are no blood vessels that cause blurring in the fovea centralis
95
New cards
Name the 3 internal structures of the eye and their function
1. Anterior cavity: Made up of an anterior and posterior chamber, contains aqueous humour for nourishment and to give shape
2. Posterior cavity: Filled with virtuous humour, to maintains round eye shape and hold the retina in place
3. Lens: Glass-like structure to transmit light from the environment, focusing it on the retina
96
New cards
Describe the pathway of light through the eye
1. Light passes through the cornea
2. Light moves through the anterior cavity and aqueous humour
3. Light moves through the pupil, onto the lens
4. Pathways of light can be altered slightly, before moving through the posterior cavity and vitreous humour
5. Pathway moves onto the retina, and moves past nerve cells to be absorbed by the retinal pigment epithelium at the back of the retina
6. Pigment in the retinal pigment epithelium absorbs and filters the light
7. Light is then absorbed by photoreceptors, turning the light into a neural signal via transduction
8. Neural signal moves to bipolar cells
9. Neural signal moves to ganglion cells, and the axons of these cells unite to form the optic nerve where the signal exits
97
New cards
What is accomodation and associated changes in the lens structure?
(Light bens due when moving through surfaces with different densities, and as a result the image at the retina is inverted. When the neural impulse reaches the brain, the brain will flip and correct the image. )
The lens allows for accomodation, which is changing its shape so that light reaches the fovea centralis for near and distant objects.
* The lens shape is changed using the ciliary body to be rounder, by contracting ciliary muscles and loosening ciliary processes, for when observing a short distance, as light refracts sharper, and reducing the focal length.
* For father distances, the lens is flatter and thinner via ciliary muscle relaxation and pulls the ciliary processes back, increasing focal length as light needs less bending to focus on fovea centralis.
The lens allows for accomodation, which is changing its shape so that light reaches the fovea centralis for near and distant objects.
* The lens shape is changed using the ciliary body to be rounder, by contracting ciliary muscles and loosening ciliary processes, for when observing a short distance, as light refracts sharper, and reducing the focal length.
* For father distances, the lens is flatter and thinner via ciliary muscle relaxation and pulls the ciliary processes back, increasing focal length as light needs less bending to focus on fovea centralis.
98
New cards
What are the differences between rods and cones?
Rods:
* More numerous
* Used in dim light
* Do not discriminate colour
* Multiple rods feed into one ganglion cell, several signals are mushed into one, less clear image
Cones:
* Less numerous
* Used in bright light
* Discriminates colours, with red, green and blue cones relating to different colours absorbed at different wavelengths of light
* One cone feeds one ganglion cell, for a more detailed, high resolution image
* More numerous
* Used in dim light
* Do not discriminate colour
* Multiple rods feed into one ganglion cell, several signals are mushed into one, less clear image
Cones:
* Less numerous
* Used in bright light
* Discriminates colours, with red, green and blue cones relating to different colours absorbed at different wavelengths of light
* One cone feeds one ganglion cell, for a more detailed, high resolution image
99
New cards
How is light absorbed in the retina? (light transduction)
Photoreceptors are the site of light transduction, which have photopigment integral proteins sticking out from them.
Photopigments have 2 parts, glycoprotein opsin and retinal, which absorbs the light
* In the dark retinal in photopigment is in cis-retinal (bent) form
* When light is absorbed, cis-retinal changes into trans-retinal (straight)
* Trans-retinal then separates from the opsin (bleaching)
* Isomerase enzyme then converts trans-retinal back into cis-retinal
* Cis-retinal binds with opsin again (regeneration), and the photopigment is functional
Photopigments have 2 parts, glycoprotein opsin and retinal, which absorbs the light
* In the dark retinal in photopigment is in cis-retinal (bent) form
* When light is absorbed, cis-retinal changes into trans-retinal (straight)
* Trans-retinal then separates from the opsin (bleaching)
* Isomerase enzyme then converts trans-retinal back into cis-retinal
* Cis-retinal binds with opsin again (regeneration), and the photopigment is functional
100
New cards
How does visual signal transduction occur in the dark? (Light transduction)
* Trans-retinal converts back into cis-retinal
* Na+ flows into the outer segment of the photoreceptor via ligand-gated Na+ channels, opened by cGMP
* The influx of Na+ in the photoreceptor causes partial depolarisation, opening voltage-gates Ca2+ channels
* The influx of Ca2+ in the photoreceptor causes the release of a neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft
* The NT released by rods is glutamate, which binds to bipolar cells and causes an inhibitory effect via hyper-polarisation
* Due to this, the ganglion cell is inactivated, no depolarisation occurs
* No AP travels along the optic nerve
* Na+ flows into the outer segment of the photoreceptor via ligand-gated Na+ channels, opened by cGMP
* The influx of Na+ in the photoreceptor causes partial depolarisation, opening voltage-gates Ca2+ channels
* The influx of Ca2+ in the photoreceptor causes the release of a neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft
* The NT released by rods is glutamate, which binds to bipolar cells and causes an inhibitory effect via hyper-polarisation
* Due to this, the ganglion cell is inactivated, no depolarisation occurs
* No AP travels along the optic nerve