THEORY OF ARCHITECTURE AND PRINCIPLES OF PLANNING
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
In landscaping, ground cover is represented by grass and plants that provide a protective layer for soil, prevent erosion, and enhance the aesthetic appeal of outdoor spaces.
GRASS AND PLANTS
In the book called “The Neighborhood Unit” he discusses the idea of organized towns into cohesive neighborhoods which was applicable not only to new towns but to large city areas.
CLARENCE PERRY

In the Philippines, this type of land use planning emphasizes the proper management of land resources to ensure that the present generation can benefit from its continued use without compromising future generations.
SUSTAINABLE LAND USE PLANNING
In urban geography, a concept where urban settlement is confined to the area within the legal limits of the city and the congestion and virtually all of this area is occupied by urban residents.
TRUEBOUNDED CITY
Indicates a position in space; can be stable (centered) or aggressive (off-center) which creates visual tension.
POINT
Insulation materials are given R-value, which rates the materials resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the greater the insulating effect. R-values are additive.
R-VALUE
Invisible boundary surrounding the person’s body into which intruders may not come. It is a specific environment behavior concept.
PERSONAL SPACE
Is a commercial building with several small scale entrepreneurs who sell their commodities in a limited space or modules that provide them low rentals for the buyers to avail cheaper merchandize, both to retail and wholesale.
TIANGGE
Is a diagram, usually to scale, of the relationships between rooms, spaces, and other physical features at one level of a structure.
FLOOR PLAN
Is created, enclosed, molded, and organized by the spatial boundaries defined by elements of form.
SPACE
Is primary identifying characteristic of a volume. It is determined by the shapes and interrelationships of the planes that describe the boundaries of volume.
FORM
Is understood by organizing its elements into two opposing groups - positive groups - positive elements (figures) and negative elements (background).
VISUAL FIELD
It is a comparison showing differences, the opposite of similarity.
CONTRAST
It is a slope pattern for Elementary and High School campus where slopes are gentle to mild and have moderately difficult terrain.
10-15%
It is a type of point of reference where the observer does not enter within them, they are external. They are usually a rather simply defined physical object, buildings, sign, store or mountain.
LANDMARKS
It is evident by a comparison which the eye makes between the size, shape and tone of a various object or part of a competition.
PROPORTIONS
It is one of the school of thought who believed that the problems of the cities should be tackled one item at a time, beginning with the improvement of health and sanitary system.
SPECIALISTS
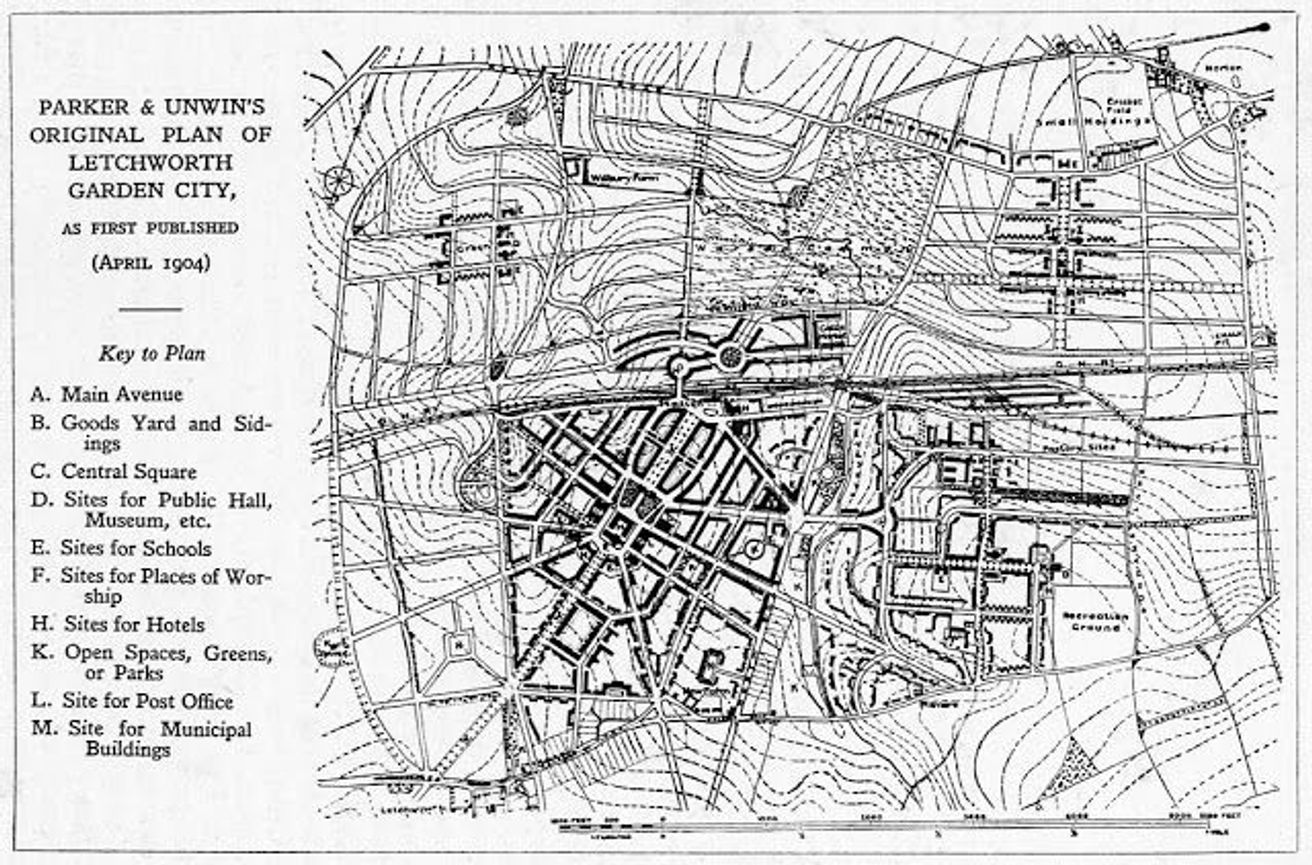
It is the “First Development Garden City” where it is a combination of landscaping, informal street layouts, and main axis focusing on town center.
LETCHWORTH
It is the rate at which water within the soil moves through a given volume of material (also measured in cm or inches per hour).
PERMEABILITY
Its use in the tropic results in a building that is comfortable, energy efficient and results in substantial savings in cooling and lighting.
PASSIVE COOLING
Kind of rhythm where equally spaced windows are introduced on the broken wall, then regular repetition is presented.
UNACCENTED RHYTHM
Land use plans and enact them through zoning ordinances. (Local Government Code of 1991)
RA 7160
Lands for well-being like parks, plazas, and of similar nature.
HEALTH AND GENERAL USE
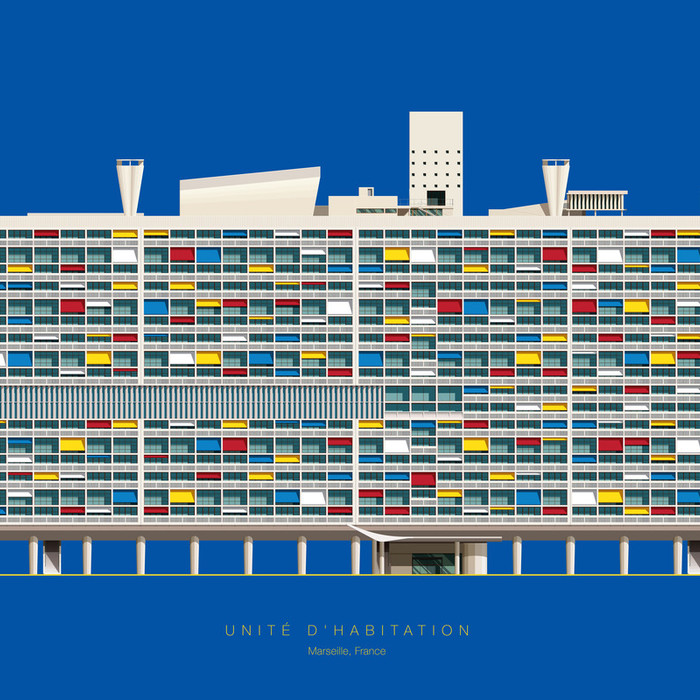

It is the structure that is supposed to be located at Marseilles. Le Corbusier planned a high density building that was a “super building” that contained 337 dwellings in only acres of land.
UNITE D’ HABITATION
Leads directly to the entrance along a straight axia path.
FRONTAL
Linear forms extending outward from central form in a radial manner; basically combination of centrality and linearity; can create a network of centers linked by linear forms; form is best viewed from aerial view.
RADIAL FORM
Location of form relative to environment or the visual field.
POSITION
Maintains the continuity of the surface of a wall and can be deliberately obscured.
FLUSH
Maximize natural ventilation can reduce the need for air-conditioning air movement over the body, creates a cool feeling; Maximize breeze and remove hot air; Roof ventilation in cooler months, and energy-efficient aircon in hotter months).
PASSIVE VENTILATION
Measure the range of a color from dull to vivid; Brightness of dullness.
INTENSITY/ CHROMA/ SATURATION
Minimum road width in a neighborhood development to ease traffic flow.
6 METERS
Mixing the hue with grey.
TONES
Most effective for eastern or western exposures.
VERTICAL LOUVERS
Most effective when they have southern orientations.
HORIZONTAL OVERHANGS
Most elementary means of organizing forms and spaces in architecture.
BALANCE
Most typical and strongest type of spatia definition, natural introverted; appears in multiple scales from rooms to urban scales; examples are building skins, thin shells, diagrid which enclose building spaces.
FOUR PLANES (CLOSURE)
Naturally articulates the volume of space. The volume of space surrounding it and generates a field of influence or territory which it claims as its own. Horizontal and vertical elements of form generate different types of spaces.
THREE-DIMENSIONAL FORM
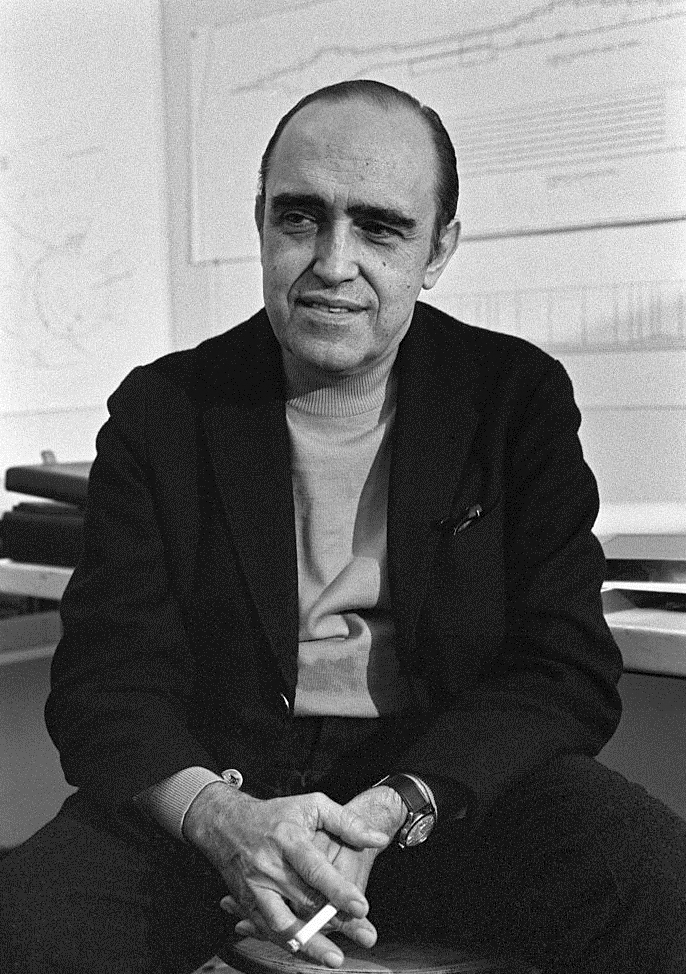

Oscar Niemeyer believed that relating large areas to each other is freedom as in the planned city of ________.
BRASILIA
Of land, a contiguous land area which is considered as a unit, which is a subject to a single ownership, and which is legally recorded as a single piece.
PARCEL
Often enclosed and secluded from the street, whose high density and variety of planning conveys a garden image. It sometimes included flower planters and a water feature and usually supplies a variety of seating possibilities.
GARDEN OASIS
On land, an encumbrance limiting its use, usually imposed for community or mutual protection.
RESTRICTION
One of four basic possibilities for two forms to group together. This requires that the two forms be relatively close to each other or share a common visual trait. Requires that the two forms have corresponding planar surfaces which are parallel to each other.
FACE TO FACE CONTACT
One of the most effective ways to reduce heat input to a building; can be installed in the roof, ceiling, & walls. Controls the rate a building loses or gains heat; keeps warmer air in during winter and excludes external heat in summer.
INSULATION

One of the most widely-used climate classification system; by Russian German climatologist WLADIMIR KOPPEN (1884). The concept that native vegetation is the best expression of climate. The Koppen climate classification scheme.
THE KOPPEN SYSTEM
One type of cues used in depth perception where in one object appears to cut off the view of another.
JUXTAPOSITION
Overlapping of two spatial fields and the emergence of a shared space.
INTERLOCKING SPACES
Path creates patterns of rest and movement within the penetrated space.
PASS THROUGH SPACE
Path of movement links the spaces since we move in time through a sequence of spaces. It affects our perceptions of the forms and spaces of the building.
CIRCULATION
Phenomenon of light and visual perception, most clearly distinguishes the form from its background and also affect the visual weight. It is the attribution that most clearly distinguishes a form from its environment.
COLOR
Phrase used to characterize development that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the needs of the future generation.
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT

Pioneered by Russian Engineer Vladimir Shukhov which also rely on double curved geometry but made of grid or lattice. It also relies on computer modelling programs for irregular curved surfaces.
GRIDSHELL STRUCTURE

Plane curves formed by the intersection of a right circular cone with a plane that cuts both halves of the cone.
HYPERBOLAS
Plane curves generated by a moving point that remains equidistant from a fixed line and a fixed point not on the line.
PARABOLAS
Planning for roads, bridges, schools, public buildings, water supply, and waste disposal facilities.
CAPITAL FACILITIES PLANNING
Polyhedron having a polygonal base and triangular faces meeting at a common point or vertex; stable on any of its faces;basically hard and angular compared to the soft cone.
PYRAMID
Preparations of an accurate base map for urban planning starts with
ACCURATE AERIAL MOSAIC
Prescribes guidelines.
PRESCRIPTIVE
Primary shapes that can be extended or rotated to generate volume whose forms are distinct, regular, and easily recognizable.
PLATONIC SOLIDS
Prolongs the sequence of the approach and emphasizes the three-dimensional form of a building.
SPIRAL
Protect against low sun angles; Louvers may interfere with view.
LOUVERS HUNG FROM A SOLID OVERHANG
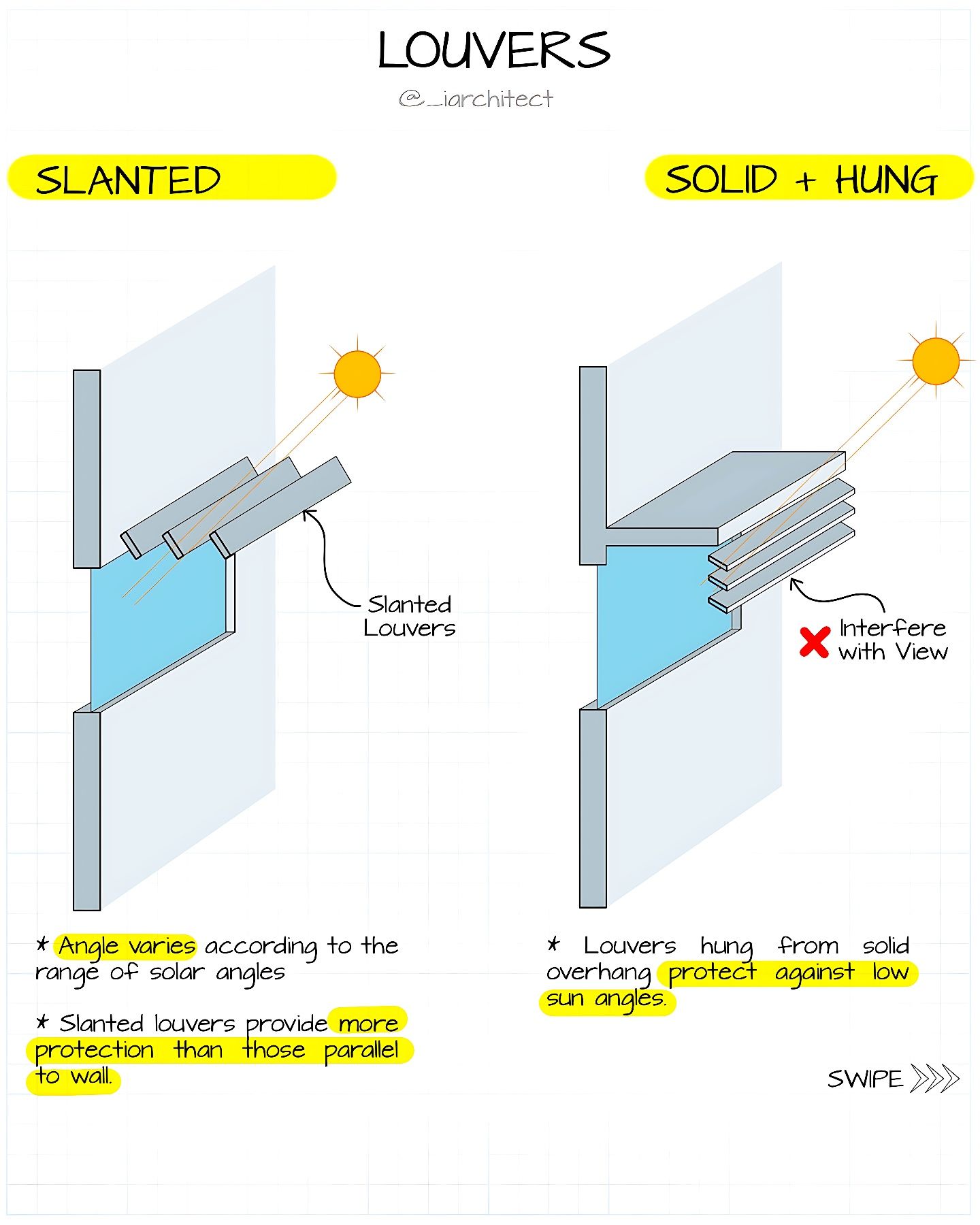
Provide more protection than those parallel to a wall; Angle varies according to the range of solar angles.
SLANTED LOUVERS
Provide spatial and visual continuity, establish visual relationships between adjacent spaces.
OPENINGS
Provides shelter and receives a portion of the exterior into the interior.
RECESSED
Published the book called, “Fields, Factories and Workshops; or Industry Combined with Agriculture with Manual Work”.
PETER KROPOTKIN

Reason for planning.
PROMOTE HUMAN GROWTH
Red-Violet, Blue-Violet, Yellow-Green, Blue-Green, Red-Orange, & Yellow-Orange
TERTIARY COLORS
Red, Blue, and Yellow
PRIMARY COLOR
Reducing the extent of paving and other hard surfaces with vegetation.
LANDSCAPING
Refers not to the actual dimensions but rather how small or large an object appears in relation to its normal size or the size of the other things in its context.
VISUAL SCALE
Refers to the program of the NHA of upgrading and improving blighted squatter areas within the cities and municipalities of Metro Manila pursuant to existing statutes and issuances. (RA 7279)
ZIP
Usually shiny aluminum foil laminated onto paper or plastic.
REFLECTIVE INSULATION
Relates to the feeling of warmth or coolness the color evokes.
TEMPERATURE
Relies of close proximity of the forms or sharing common trait such as shape, color, or material.
SPATIAL TENSION
Represented the proportioning of elements with perfect expression of beauty and harmony. The basic unit dimension was the diameter of the column from which other measurements are derived.
CLASSICAL ORDERS
Represents pure and the rational, bilaterally symmetrical figure with two equal and perpendicular axes.
SQUARE
Secondary forms clustered about a dominant central parent-form; requires the visual dominance of a geometrically regular and central form such as sphere, cone or cylinder; ideal as freestanding structures isolated within their context; can embody sacred or honorific places.
CENTRALIZED FORM
Series of forms arranged in a row or proportional change in the form’s dimensions; can be segmented or curvilinear; can front on or define an edge; can be oriented vertically as a tower element to establish or denote a point in space; can serve as organizing element with attached secondary forms. Examples are agora, three-lined canals, mile-high tower by FLW.
LINEAR FORM
Set of modular forms related and regulated by a three-dimensional grid which is a system of two or more intersections of the grid lines; most common grid is based on squares which is nonhierarchical and bidirectional and can be projected to create a spatial network of grid (3D).
GRID FORM
Shading devices shield windows and other glazed areas from direct sunlight. To reduce glare and excessive solar heat gain in warm weather.
SOLAR SHADING
Share common edge and can pivot about that edge.
EDGE-TO-EDGE CONTACT
Signifies stability; stable on its side,dynamic on its corners.
TRIANGLE
Similarly as the cost of the land, neighborhood character have this effect.
SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS
Simple figure contrasted from the background, with continuous flow around.
BASE PLANE
Louvers that are installed at a downward slope extending from the building’s facade over a glazed opening (like a window).
SLANTED LOUVERS
Simply explains events or phenomena; Neutral; Do not lean towards an ideology.
DESCRIPTIVE
Size and proportion of certain elements are directly related to their structural function (i.e depth of a beam is a critical dimension and the depth-to-span ratio is an indicator of its structural role).
STRUCTURAL PROPORTIONS
Size or proportion of something relative to an accepted standard of measurement.
MECHANICAL SCALE
Sometimes called “subscription money”, this is a deposit given to the seller to show that the potential buyer has serious intentions.
EARNEST MONEY
Spaces can be related to each other - as space within a space, interlocking spaces (abutting or sharing common border) and spaces linked by a common space (with intermediary space).
SPATIAL RELATIONSHIPS
Spaced grouped by proximity or the sharing of a common visual trait or relationship; with repetitive, cellular spaces that can be similar or dissimilar in terms of function, size, or orientation; flexible and does not have a rigid geometrical layout; important spaces are articulated to gain dominance; symmetry and axis can be used to strengthen and unify its portions.
CLUSTERED ORGANIZATION
Spaces organized within the field of a structural grid or other three-dimensional framework; the organizing power of grid results from regularity and continuity of its pattern which is a stable field of reference for organizing any type of spaces; one usual example is the structural grid of columns and beams. Transformation of the grid can also be possible by making irregular pattern in one or two, directions, by interruption, dislocation or rotation etc.
GRID ORGANIZATION
Spaces which tend to bring people together; Layouts where it is easy to maintain face-to-face contact.
SOCIOPETAL
Staking claims to places; Desire for control and expression of aesthetic tastes. Efforts to make an environment fit activity better; Done for psychological security.
PERSONALIZATION
Standard size and proportions due to manufacture process and mass production.
MANUFACTURED PROPORTIONS
Subtracting a portion of its volume, may or may not retain its initial identity; also known as mutilated forms; ambiguity of the original form results if the portion removed from its volume erode its edges and alters the profile.
SUBTRACTIVE TRANSFORMATION
System building is the complete integration of all _____.
SUBSYSTEMS
Tend to keep people apart and discourage conversations; Layouts where it is easy to avoid interaction.
SOCIOFUGAL
The ability of building materials to absorb, store, & release heat in tropical climates, materials with low thermal mass is preferable particularly on walls directly exposed to the sun. Lightweight construction such as timber respond quickly to cooling breezes; allows building to cooldown faster.
THERMAL MASS
The architects of the Renaissance, believing that their buildings had to belong to a higher order, returned to the Greek mathematical system of proportions.
RENAISSANCE THEORIES
The art and science of designing and constructing Buildings;
Greek: ARCHI = first or original; TECT = the ability to put things together.
ARCHITECTURE