senses
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
what are the 5 basic taste sensations on the tongue
sweet: organic compounds
salt: metal ions
sour: acids
bitter: alkaloids
umami: amino acid/meaty flavor
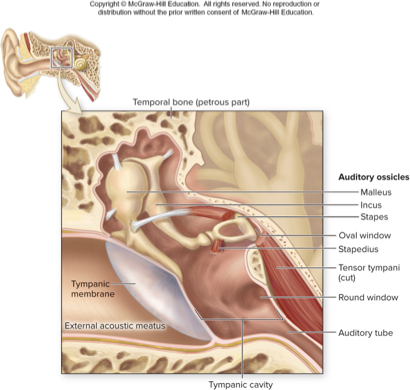
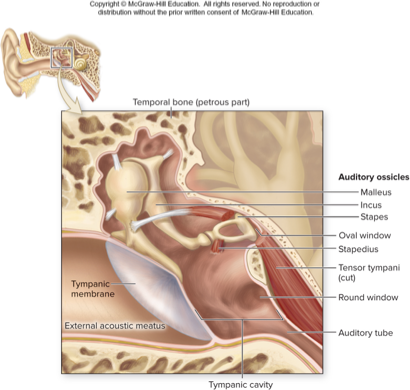
what part of the ear does this describe:
contains air-filled tympanic cavity
bony wall separates it from inner ear: oval and round window
contains auditory tube and auditory ossicles
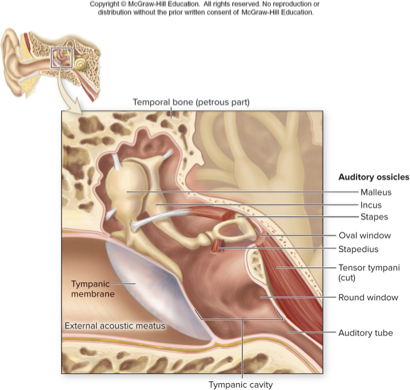
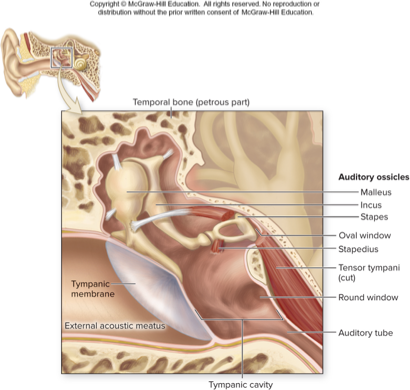
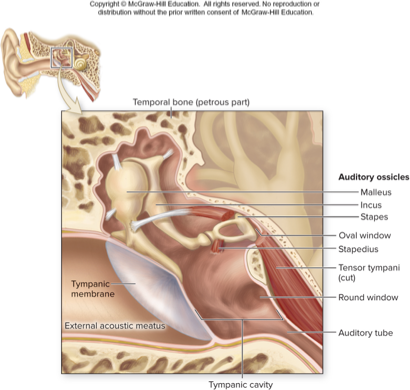
middle ear
what does this describe:
passage extending from middle ear to nasopharynx
middle ear infections often result from infections spreading from throat through auditory tube
usually closed but yawning allows air movement through the tube; equalizes pressure on either side of tympanic membrane
auditory tube or eustachian tube
what does this describe:
three tiny bones in middle ear
amplify sound waves and transmit them to oval window
vibrate along with eardrum, so stapes moves in and out of oval window initiating pressure waves in inner ear fluid
two small muscles restrict movement during loud sounds
auditory ossicles
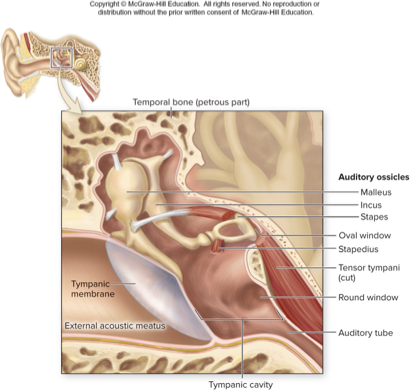
what does this describe:
attached to medial surface of tympanic membrane
resembles a hammer in shape
malleus
what does this describe:
middle ossicle resembling an anvil
incus
what does this describe:
resembles a stirrup of a saddle
has disclike footplate fitting into oval window
stapes
what two small muscles restrict ossicle movement during loud sounds and where do they attach
tensor tympany: attaches to malleus
stapedius: attaches to stapes
what does this describe:
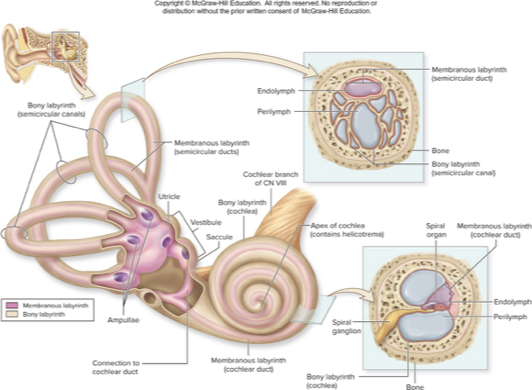
spaces with petrous part of temporal bone
bony labyrnith
membranous labyrnith
choclea
vestibule
semicircular canal
inner ear
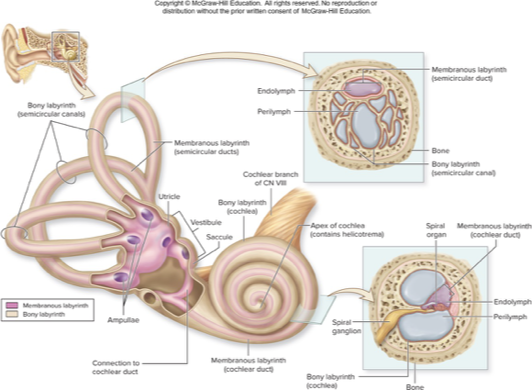
bony labyrinth
mazelike spaces in temporal bone
perilymph: interstitial fluid fills most of this space
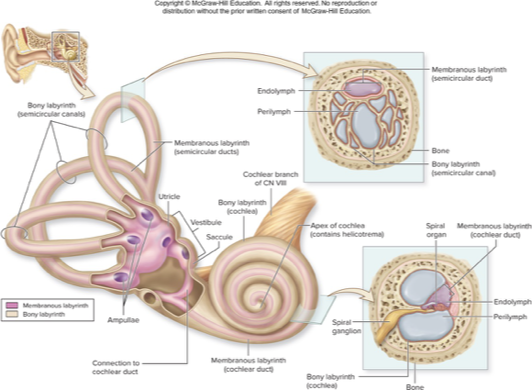
membranous labyrinth
membrane-lined fluid filled tubes within bony labyrinth
contains receptors for hearing and equilibrium
contains endolymph: similar to intracellular fluid and rich in K+
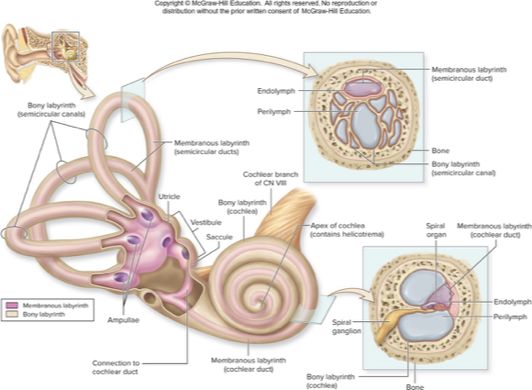
cochlea
houses membranous choclear duct
snail shaped chamber of inner ear
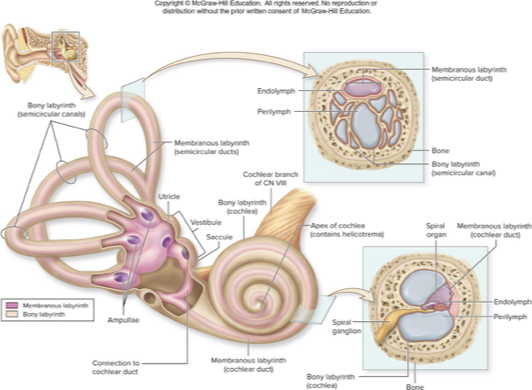
vestibule
contains 2 saclike, membranous parts: utricle and saccule, that are interconnected and positioned at right angles
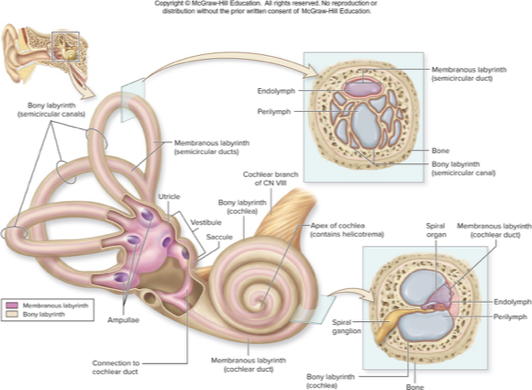
semicircular canal
contains membranous semicircular ducts
otitis media
infection of middle ear
young children
causitive agent from respiratory infection
fluid accumulation in ear
pressure, pain, reduced hearing, otoscope
may require myringotomy
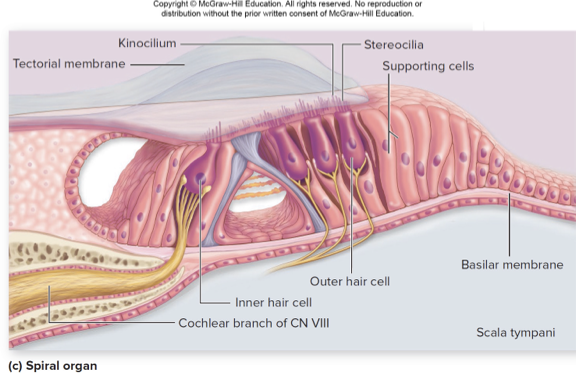
what does this describe:
sensory structure for hearing
within cochlear duct
thick sensory epithelium consisting of hair cells and supporting cells on basilar membrane
hair cells: receptors that release neurotransmitter to sensory neurons
single row of inner hair cells; three rows of outer hair cells
may have stereocillia, and kincilium at apex
base of hair cells synapse with sensory neurons
spiral organ
what is the pathway from sound wave to nerve signal
sound waves vibrate tympanic membrane
ossicle vibrates and transmits waves to oval window
fluid pressure waves in scala vestibuli pusch vestibular membrane causing pressure waves in endolymph of cochlear duct
specific regions of basilar membrane move
hair cells distored, causing changes in neurotransmitter release
sensory neurons with axons in CN VIII are stimulated to fire
pressure is transmitted to scala tympani and absorbed by round window
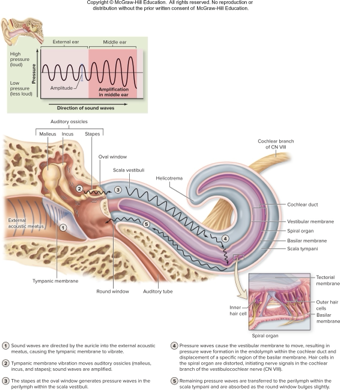
describe cochlear hair cell stimulation
hair cells are bathed in K+ edolymph that is far more positive than the fluid inside the cell
deafness
two types
conductive deafness: interference of wave transmission in external or middle ear
sensorineural deafness: malfunction in inner ear or cochlear nerve
equilibrium
coordination, balance, and orientation in 3-d space
vestibular apparatus
responsible for sensing equilibrium
3 semicircular ducts: angular acceleration
vestibule: macula saccule and macula utricle; static equilibrium and linear acceleration
what do these general functions describe:
provide information about external and internal environements
respond to a stimulus
each type of receptor responds best to a type of stimulus
sensory receptors
transducers
convert stimulus energy into electrical energy
receptors have resting membrane potential
receptor membrane have modality gates channels that respond to their type of stimulus
action potentials are conveyed to CNS for interpretation
receptors covey signals to CNA by ______
sensory neurons
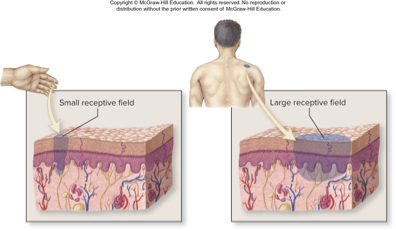
receptive field
the distribution area of the endings of a sensory neurons
smaller receptive fields allow more precise stimulus localization
sensation
a stimulus we are consciously aware of
to enter consciousness, signals must reach cerebral cortex
only a fraction of stimuli result in sensations
a lot of sensory input goes to other areas of the brain
receptors provide CNA information about stimulus ____,____,____, and _____
modality
location
intensity
duration
what does this describe:
receptor distribution
simple structures distributed throughout body
somatic sensory receptors
visceral sensory receptors
general sense receptor
somatic sensory receptors
tactile receptors of skin and mucous membranes; proprioceptors of joints, muscles, and tendons
visceral sensory receptors
found in walls of internal organs, they monitor stretch, chemical environment, temperature, pain
what does this describe:
receptor distribution
specialized reecptors in complex sense organs of the head
5 special senses: olfactions, gustation, vision, audition, equilibrium
special sense receptors
what does this describe:
stimulus orgin
detect stimuli from external environment
skin and mucus membranes; special sense receptors
exteroceptors
what does this describe:
stimulus origin
detect stimuli from internal organs
visceral sensory receptors monitoring internal environment
interoceptors
what does this describe:
stimulus origin
detect body and limb movements
somatosensory receptors of muscles, tendons, and joints
proprioceptors
what does this describe:
modality of stimulus
detect chemicals dissolved in fluid
include receptors for external environment or internal environment
chemoreceptors
what does this describe:
modality of stimulus
detect changes in temperature
include receptors in skin, hypothalamus
thermoreceptors
what does this describe:
modality of stimulus
detect changes in light intensity, color, movement
in the retina of eye
photoreceptors
what does this describe:
modality of stimulus
detect distortion of cell membrane
include touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch receptors
function as baroreceptors, proprioceptors, tactile receptors, and specialized receptors in the inner ear
mechanoreceptors
what does this describe:
modality of stimulus
detect painful stimuli
somatic: detect chemical, heat or mechanical damage to body sruface or skeletal muslce
visceral: detect internal organ damage
nociceptors
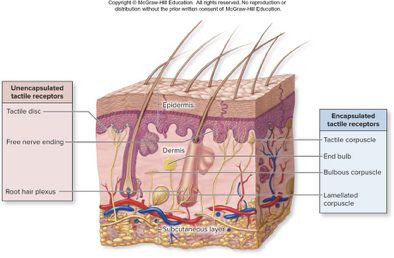
tactile receptors
abundant mechanoreceptors of skin and mucous membranes
endings can be encapsulated or unencapsulated
what does this describe:
dendritic ends of sensory neurons with NO protective cover
free nerve endings
root hair plexuses
tactile discs
unencapsulated tactile receptors
free nerve endings
terminal ends of sensory neuron dendrites
simplest tactile receptors
reside close to skin surface and in muscous membranes
mainly for pain and temperature but also light tough and pressure
may be phasic or tonic
root hair plexuses
wrap around hair follicle
located in deeper layer of dermis
detect hair displacement
phasic receptor
tactile discs
flattened endings of sensory neurons extending to tactile cells (merkel cells)
tactile cells are specialized epithelial cells in basal layer of epidermis
respond to light to
what does this describe:
neuron endings wrapped by connective tissue or covered by connective tissue and glial cells
end (krause bulbs)
lamellated (pasinnian corpuscles)
bulbous corpuscles
tactile corpuscles
encapsulated tactile recptors
end bulbs (krause)
ensheathed in connective tissue
located in dermis and mucus membranes
detect pressure and low-frequency vibration
tonic recptors
lamellated corpuscles (pacinian)
wrapped in neurolemmocytes and concentric layers of connective tissue
located deep in dermis, hypodermis, some organ walls
detect deep pressure, coarse touch, high frequency vibration
phasic receptors
bulbous corpuscles (ruffini)
within dermis and subcutaneous layer
detect deep pressure and skin distortion
tonic receptors
tactile corpuscles (meissner)
are intertwined endings wrapped in modified neurolemmocytes, covered in connective tissue
in dermal papillae
discriminative light touch; allow. recognition of texture, shape
phasic receptors
reffered pain
inaccurate localization of sensory signals
signals from viscera perceived as originating from skin, muscle
many somatic and visceral sensory neurons send signals via the same ascending tracts within spinal cord
somatosensory cortex unale to determine true source
phantom pain
sensation associated with removed body part or limb
followed by amputation of limb
experience of pain from a removed part
stimulation of sensory neuron pathway on remaining portion
cell body of sensory neuron still alive
pain sometimes quite severe
olfaction
sense of smell
detect ordorants (chemcials in air)
adaptive
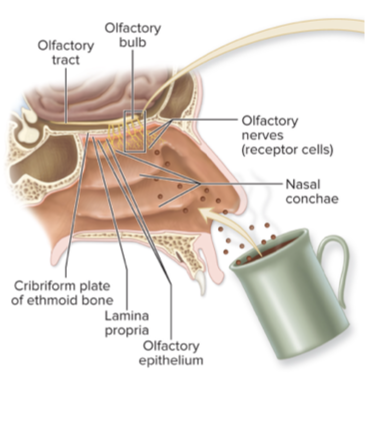
olfactory cells
receptor found in olfactory epithelium of nasal pasageways
neurons exposed to air
chemoreceptors
olfactory nerve goes directly to cerebral cortex
2000-4000 odors distinguished
gustation
sense of taste
detection of tastants
gustatory cells are cehmoreceptors within taste buds
what does this describe:
short and spiked
not taste buds/no role in gustation; help manipulate food
filiform papillae
what does this describe:
mushroom-shaped
each contains a few taste buds
located on tip and sides of tongue
fungiform papillae
what does this describe:
leaflike ridges
not well developed
house a few taste buds in early childhood
located on posterior lateral tongue
foliate papillae
what does this describe:
largest, least numerous
contain most of the taste buds
located in a row of 10-12 along posterior dorsal tongue surface
vallate (cirvumvallate) papillae
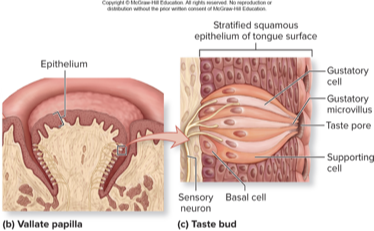
taste buds
onion shaped organs housing taste receptors
gustatory cells: receptor cells detect tastants (live 7-9 days)
supporting cells: sustain gustatory cells
basal cells: neural stem cells that replace gustatory cells
what 3 nerves have to do with taste
facial nerve (VII)
glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
vagus nerve (X)
describe the pathway of gustation
sensory neurons connect to multiple gustatory cells in the tongue and project to the medulla
in anterior parts of tongue, sensory neurons are part of the facial nerve
posterior part of tongue, sensory neurons are glossopharyngeal
secondary medullary neurons project to thalamus
tertiary thalamic neurons project to primary gustatory cortex
for sweet bitter and umami the tastants are _____
molecules
for salt and sour the tastants are _______
ions
conjunctiva
transparent lining of eye and lid surfaces
specialized stratified columnar epithelium
contains numerous goblet cells to moisten eye, blood vessels to nourish sclera, and abundant nerve endings
does not cover cornea
lacrimal apparatus
produces, collects, drains fluid
lacrimal fluid: water Na+, antibodies, lysozyme
lubricates, cleanses and moistens eye
lacrimal glands produces fluid and secretes it through ducts
blinks wash fluid over eye
fluid drains into lacrimal puncta
sac drains to nasolacrimal duct to nasal cavity
excess lacrimal fluid produces tears
posterior cavity (behind lens)
contains permanent vitreous humor
anterior cavity (in front of lens)
contains circulating aqueous humor
fibrous tunic
sclera & cornea
tough outer layer
vascular tunic
iris
ciliary body
choroid
middle layer with many vessels, lymph vessels, intrinsic muscles
retina tunic
pigmented layer
neural layer
internal or neural tunic
sclera
white of the eye
desne irregular CT
eye shape
protects internal components
attachment site for extrinsic eye muscles
cornea
anterior convex tansparent window
inner layer is simple squamous epithelium, middle layer collagen, outer layer stratified squamous eputhelium
no blood vessels
limubs: conreneal scleral junction
refracts light
choroid
extensive, posterior region
many capillaries nourish retina
many melanocytes make melanin to absorb extraneous light
ciliary body
ciliary muscles and processes
located just anterior to choroid
muscles and processes
iris
gives eye color; most anterior region of uvea
contains smooth muscle, melanocytes, vesseks, neural structures
divides anterior segment into anterior and posteior chambers
pupil is opening in center of iris
pigmented layer of retina
attached to choroid
provides vitamin A for photoreceptors
absorbs stray light to prevents light scatter
neural layer of retina
houses photoreceptors and asociated neurons
receives light and converts it to nerve signals
ora serrata
jagged edge
boudary between parts of retina
path of light through the eye
cornea
through aqueous anterior chamber
through pupil
through lens
through vitreous posterior chamber
retina
photoreceptor cell layer
outermost nueral layer
contains rods and cones
contain pigment that reacts to light
bipolar cell layer
their dendrites receive synaptic input from rods and cones
ganglion cell layer
innermost neural layer
their axons gather at optic disc and form optic nerve
horizontal cells
regulate signals between phtoreceptors and bipolar cells
amacrine cells
regulate signals between bipolar and ganglion cells
optic disc
contains no photoreceptors- blind spot
where ganglion axons exit toward brain
macula lutea
rounded yellowish region lateral to optic disc
contain fovea centralis
peripheral retina
contain primarily rods
functions most effectively in low light
detatched retina
occurs when outer pigmented and inner neural layers seperate
result of head trauma
increased risk in diabetics and nearsighted individuals
nutrient deprivation in inner layer
floaters
flashes of light
decreased vision
pneumatic retinopexy and scleral buckle are treatments
macular degeneration
physcial deterioration of macula lutea
leading cause of blidness
may be associated with diabetes, infection, hypertension, eye trauma
loss of visual acuity in center of visual field
diminished color perception and floaters
lens
changes shape to focus light on retina
cells within it have lost organleeles and are filled with crystallin protein
lens enclosed by dense fibrous elastic capsule
shape determines light refraction
shape determined by ciliary muscle and suspensory ligaments
cataracts
small opacities within the lens
usually as a result of aging
difficulty focusing on close objects
reduced visual clarity and reduced color intensity
needs to be removed when interferes with normal activities
phacoemulsification new surgery
vitreous humor
transparent gelatinous fluid in posteiror cavity
permanent fluid first produced in embryonic development
helps maintain eye shape
supports retina
aqueous humor
transparent watery fluis in anterior cavity
continuously produced by ciliary processes
nourishes and oxygenates lens and inner cornea
production circulation and drainage
plasma filtered aross capillary walls
circulates throug pupil
drain from chamber via scleral venous sinus then to nearby veins
glaucoma
increased intraocular pressure
may cause compression of choriod layer, constrict lbood vessels
reduced field of vision, dim vision, halos around light
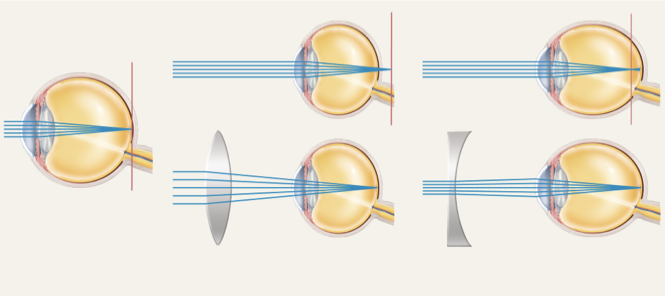
emmetropia
normal vision
parallel light rays focused on retina
hyperopia
far-sighted
trouble seeing up slose; eyeball too short
only convergent rays from distant points brought to focus
corrected with convex lens
myopia
near sighted
trouble seeing faraway objects; eyeball too long
only rays close to eye focus on retina
corrected with concave lens
astigmatism
unequal focusing
unequal curvatures in one or more refractive surfaces
presbyopia
are related change in vision
lens less able ot become spherical
reading close up is difficult
corrective convex lens
care be treated with surgery
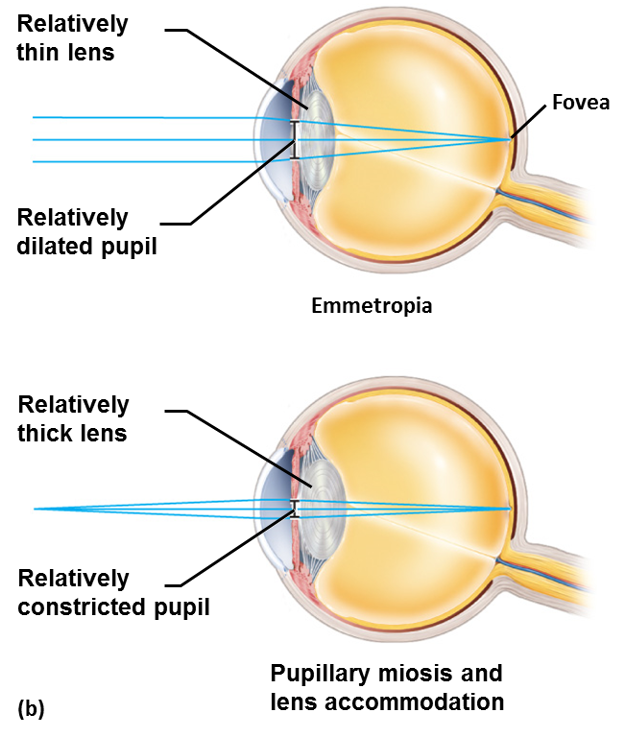
describe light transmission to retina
•Light is refracted (bent) as it passes through the cornea and lens
•Image upside down and reversed
•Light passing through the center of the cornea is not bent
•Cornea refracts light more than lens does
–Lens merely fine-tunes image
–Lens can change shape and become rounder to increase refraction for near vision (accommodation)