A-level Biology 2.1 Cell Structure
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Ultrastructure
the detailed structure of a biological entity.
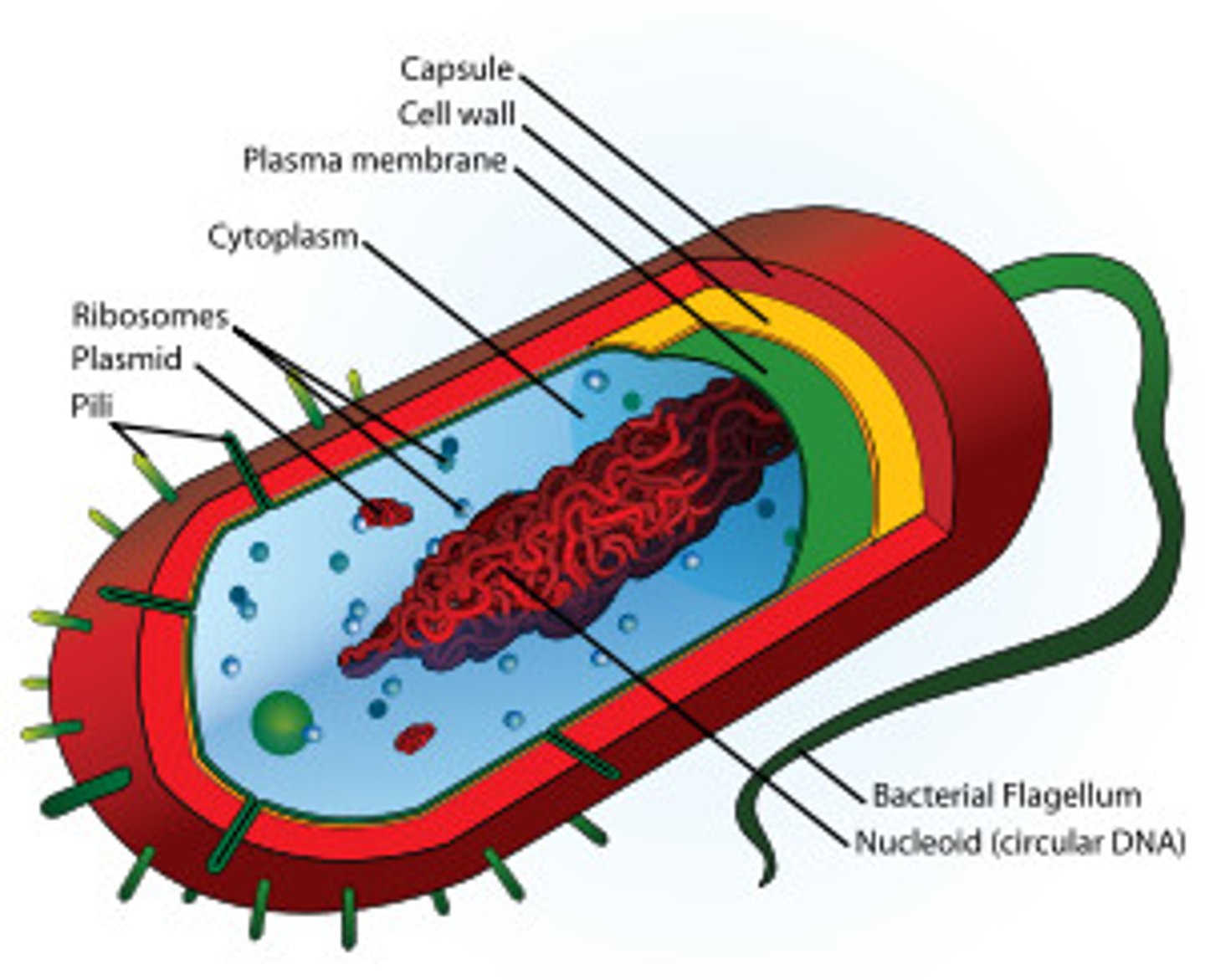
Prokaryotic
An organism whose cells do not have an enclosed organelles, such as bacteria.
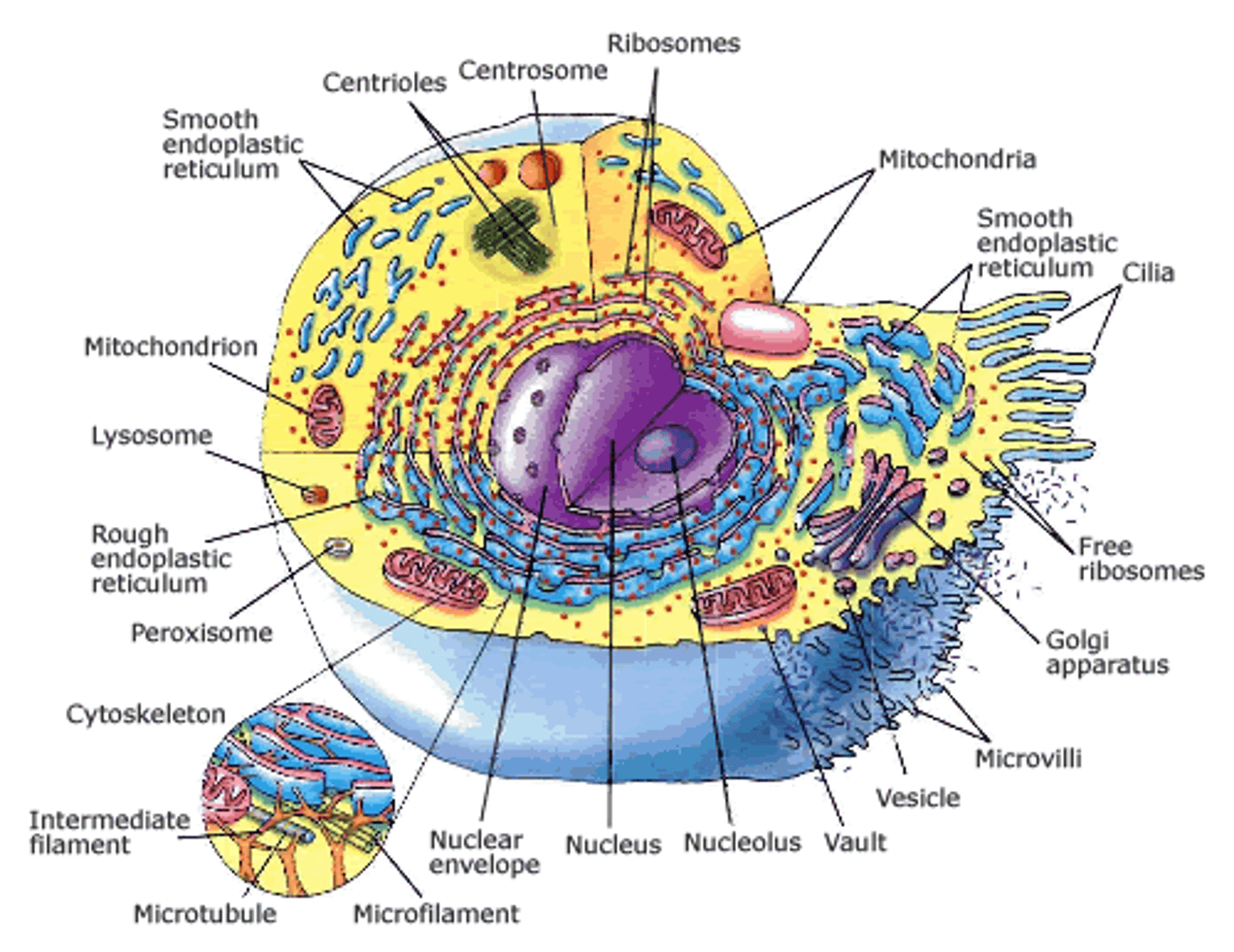
Eukaryotic
Cells with membrane-bound organelles
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
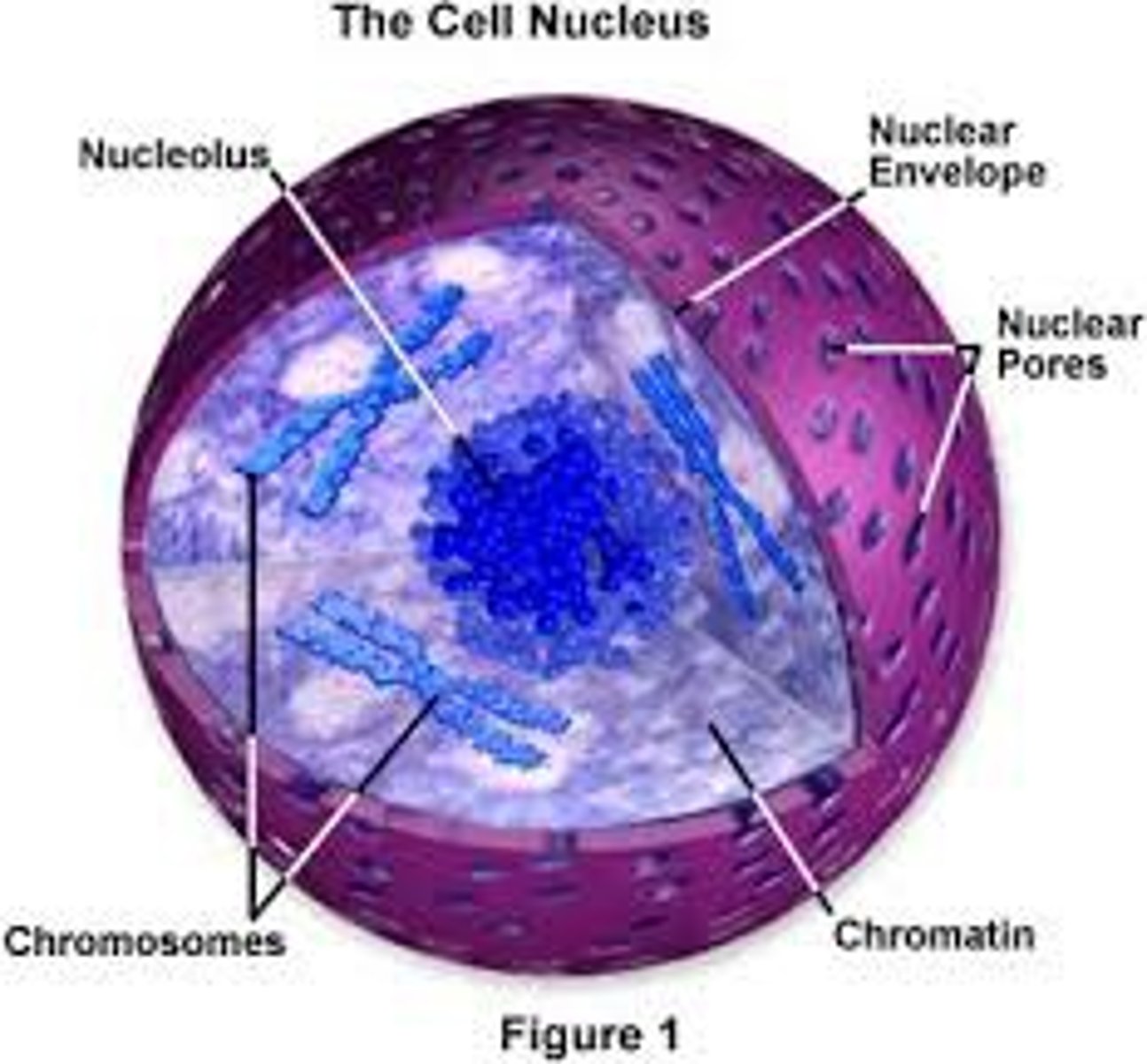
Nucleolus
The organelle where ribosomes are made, synthesized and partially assembled, located in the nucleus
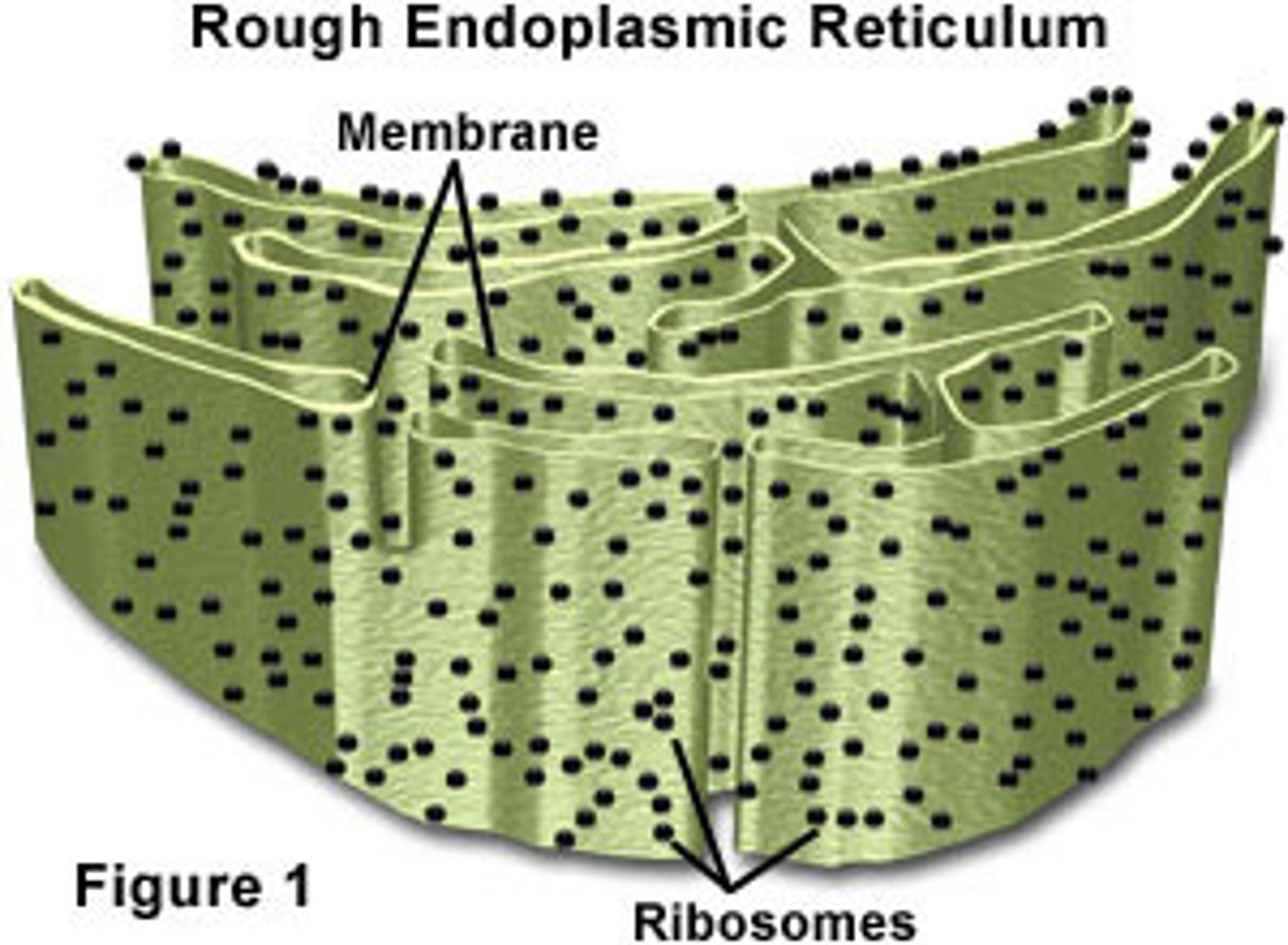
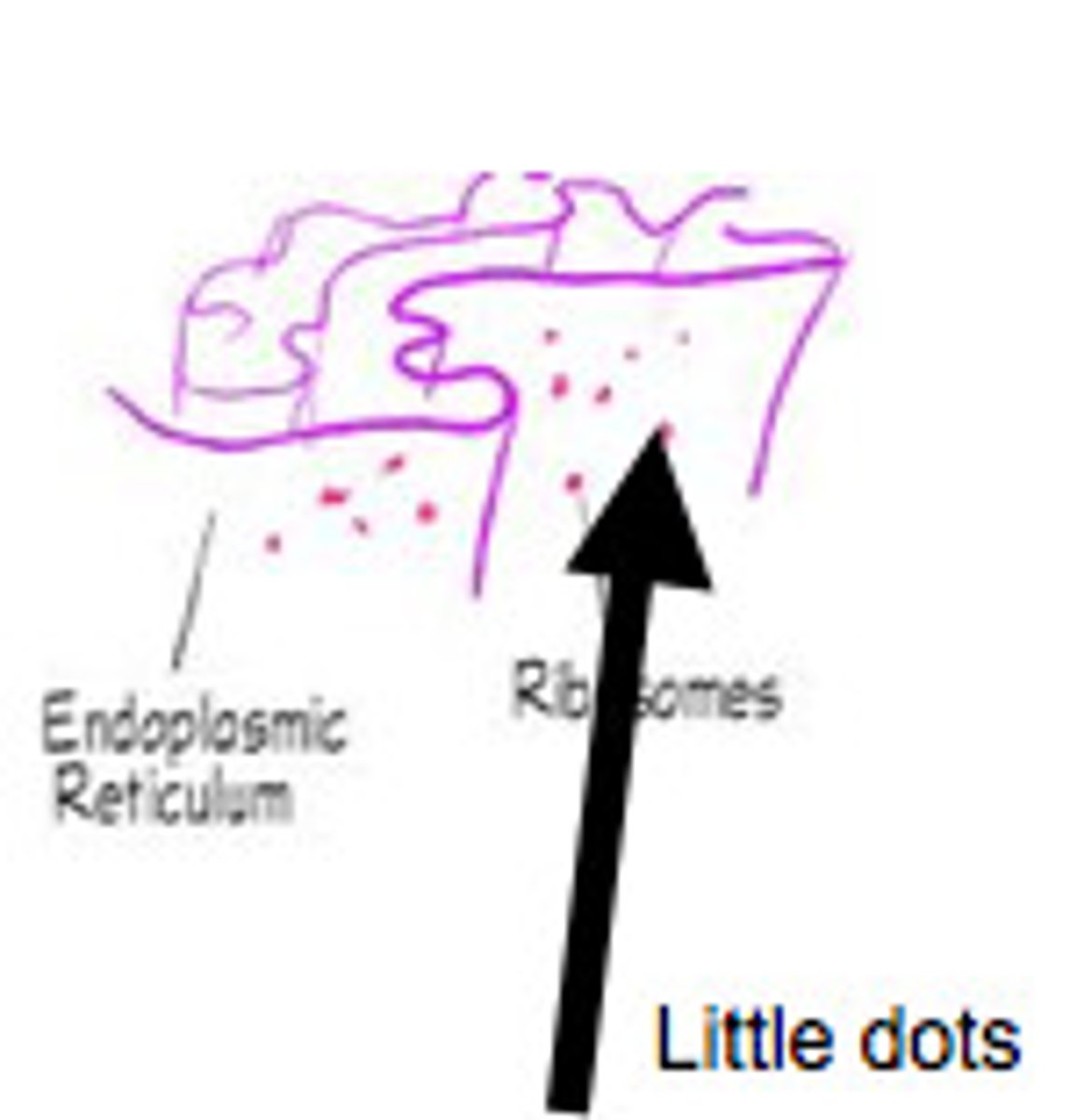
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
An endomembrane system covered with ribosomes where many proteins for transport are assembled.
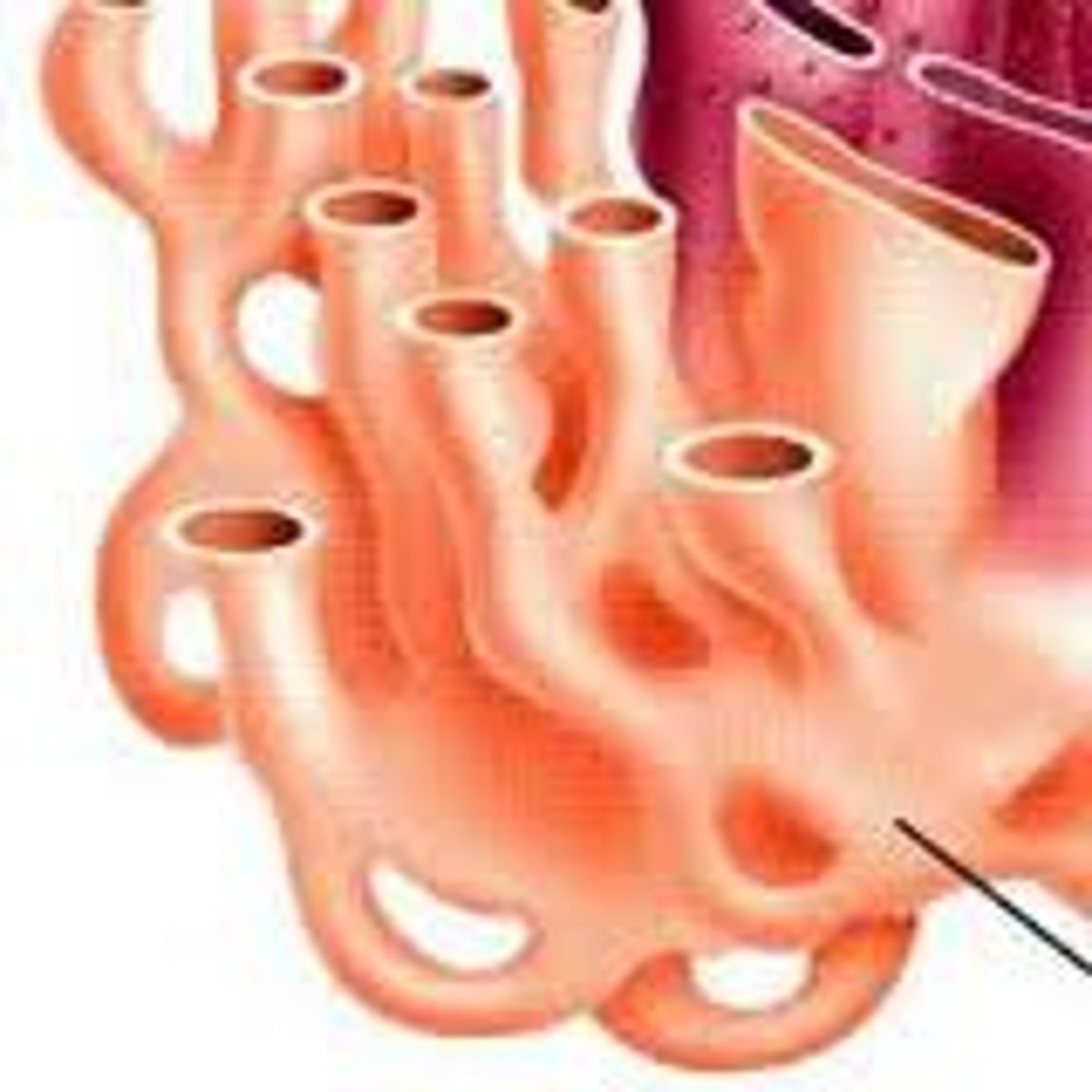
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Site of lipid synthesis.
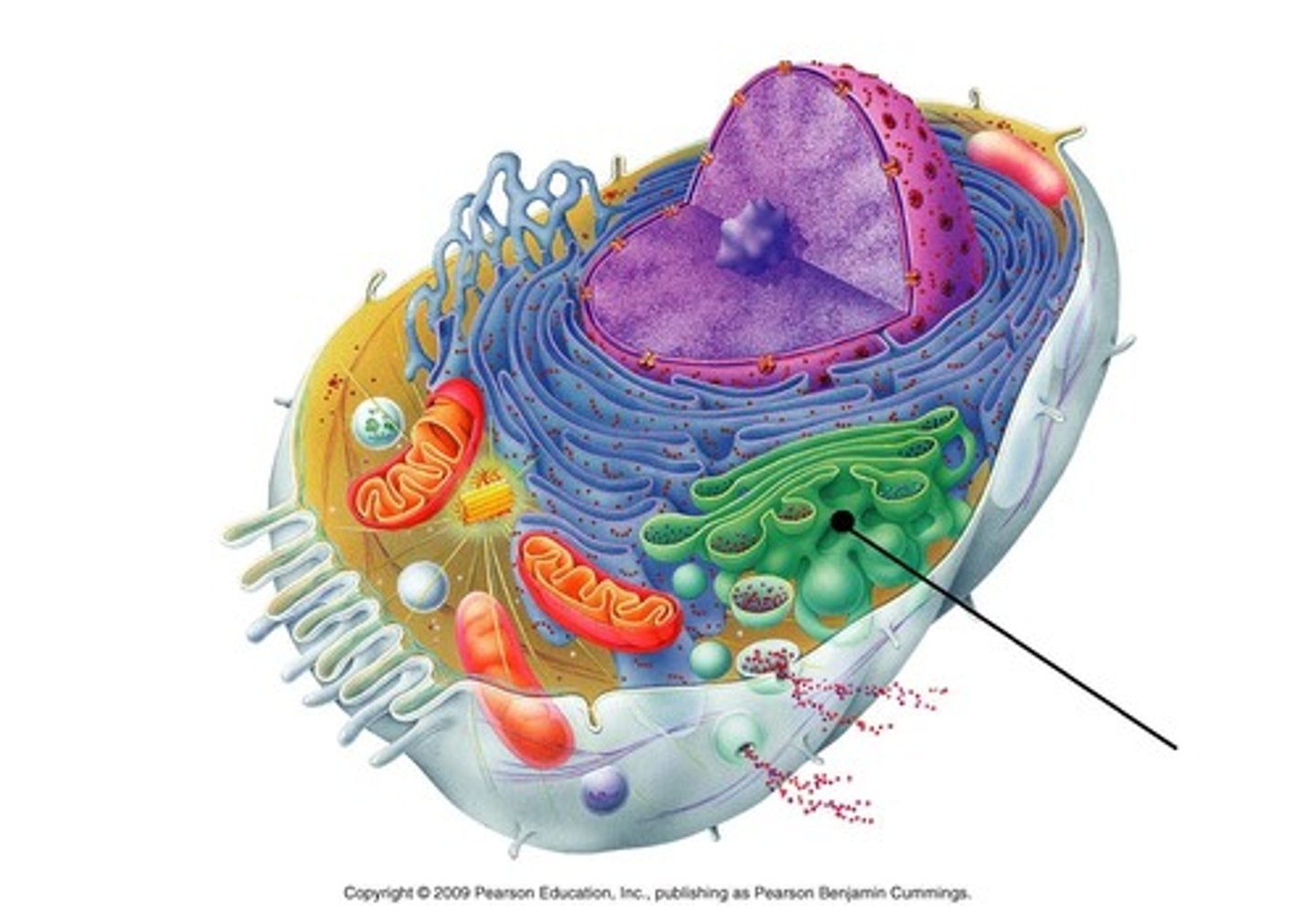
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
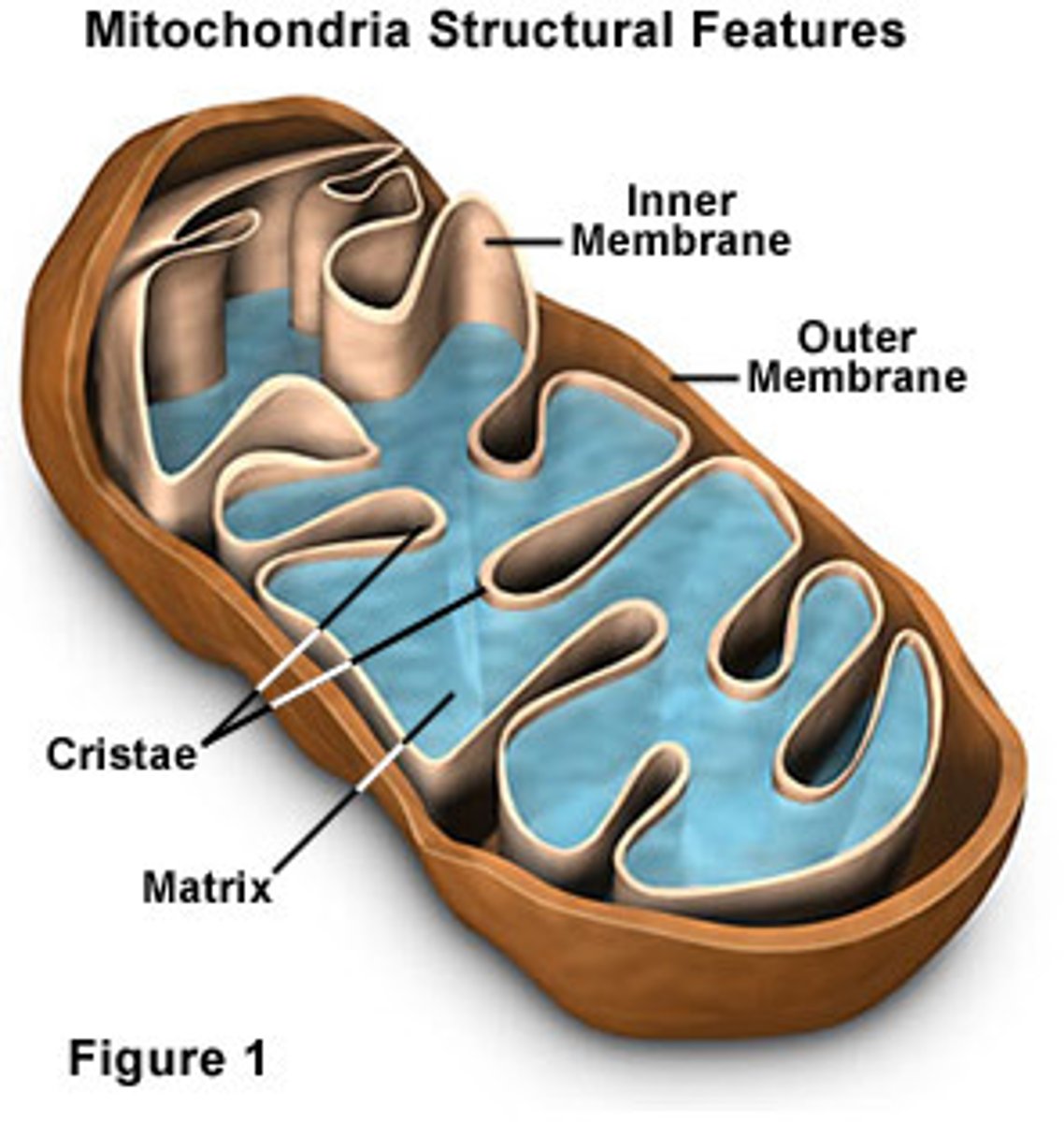
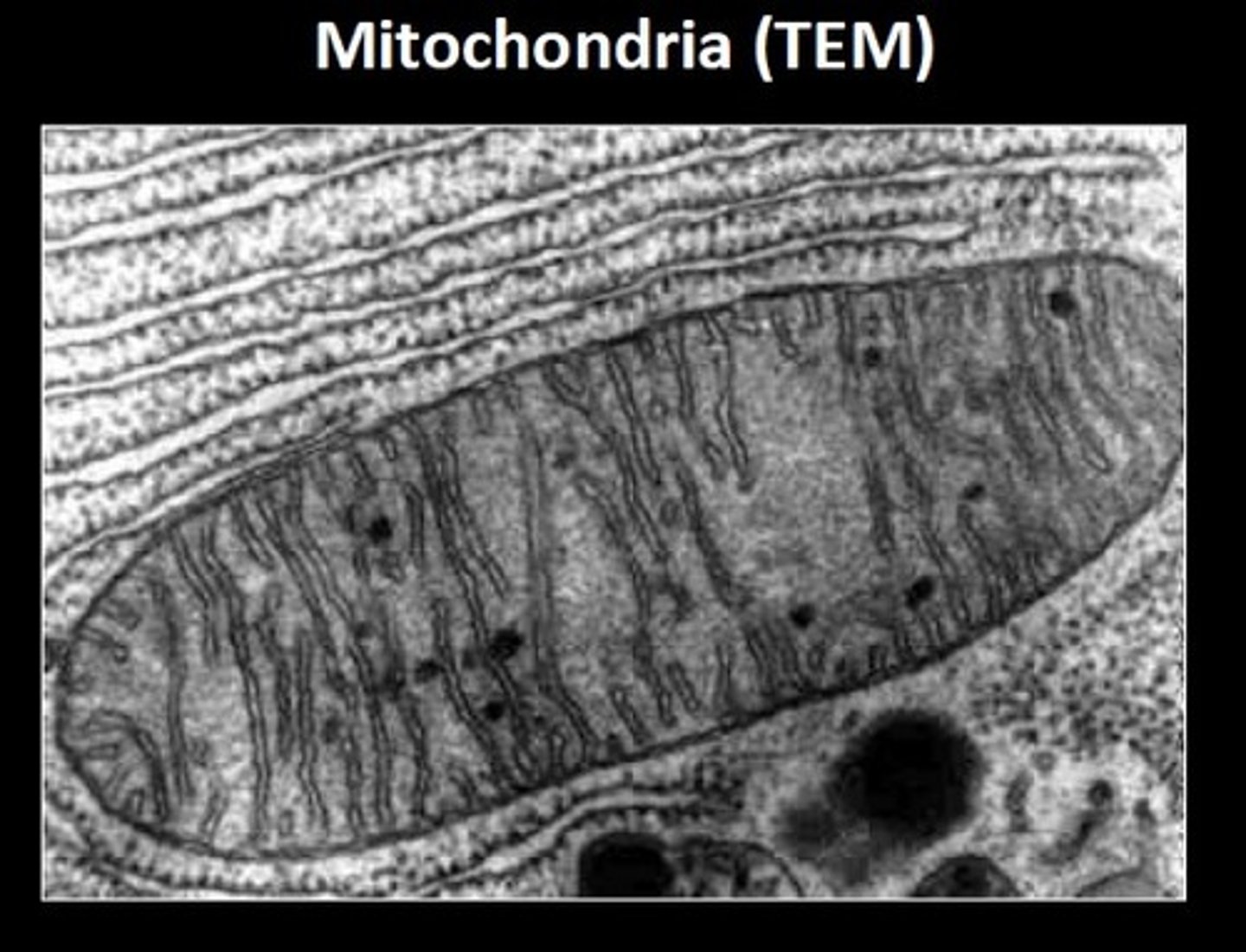
Mitochondria
Enclosed by two membranes with the inner membrane folded; contains its own DNA
Powerhouse of the cell
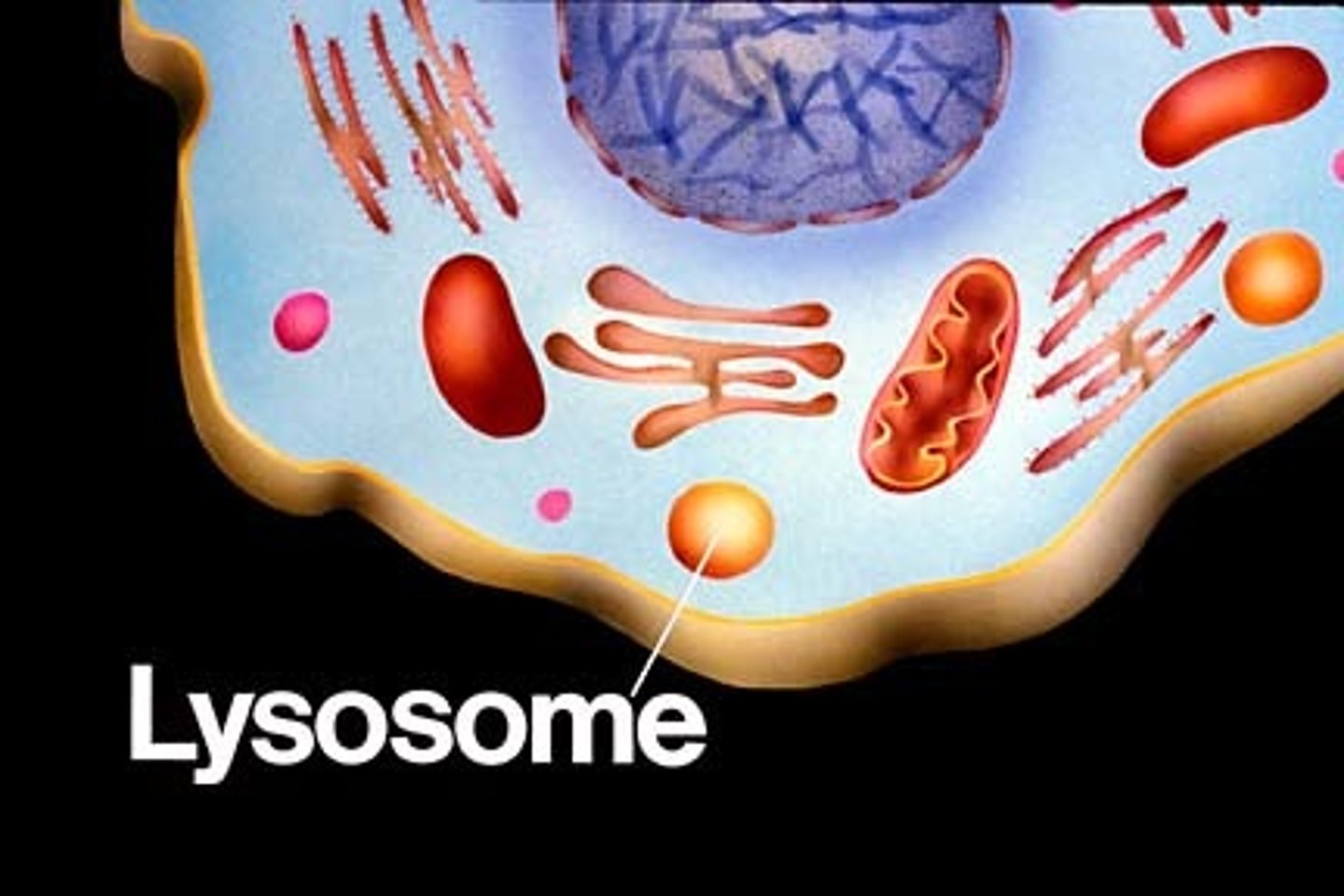
Lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
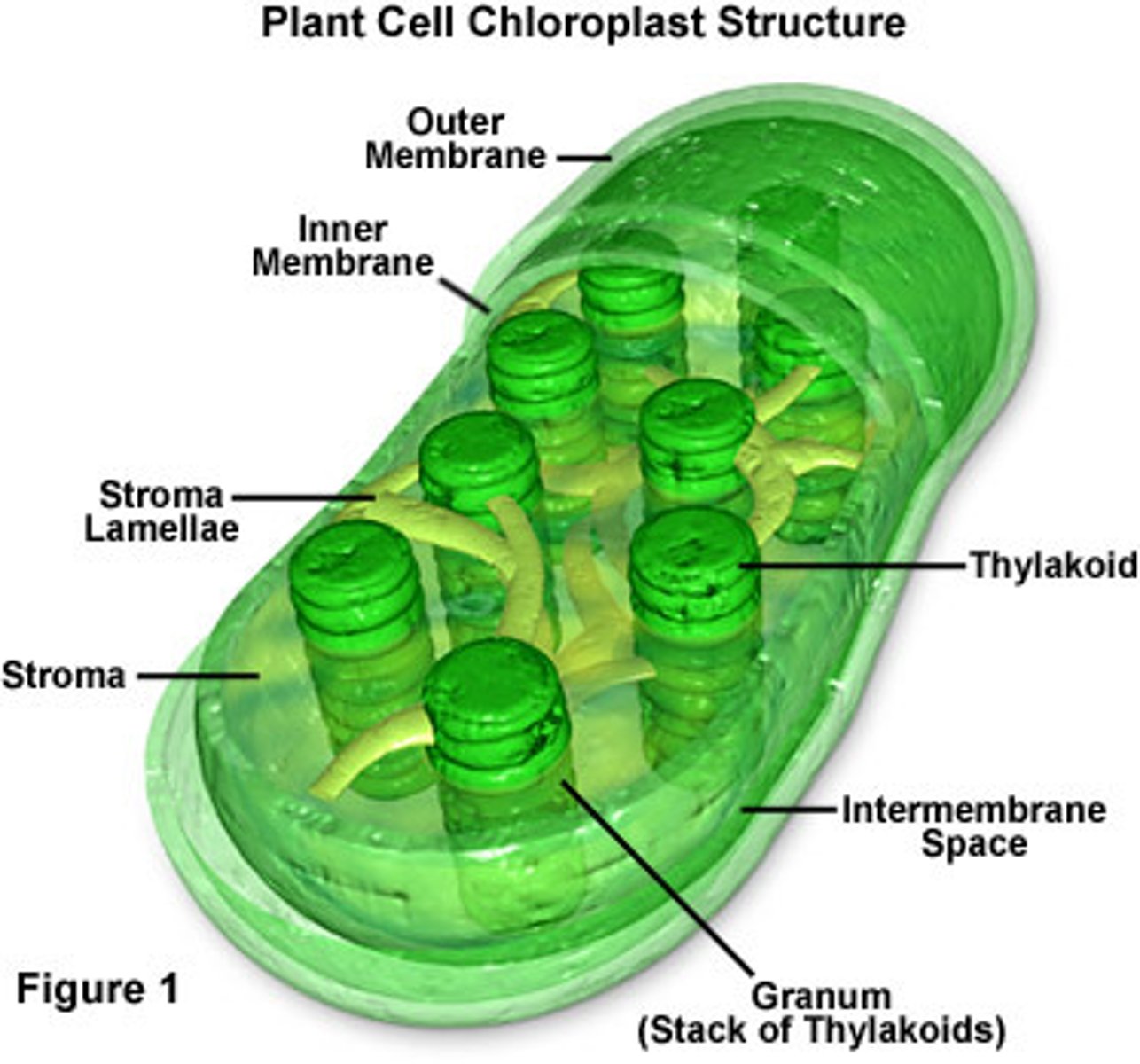
Chloroplasts
Where photosynthesis occurs; in plant cells only
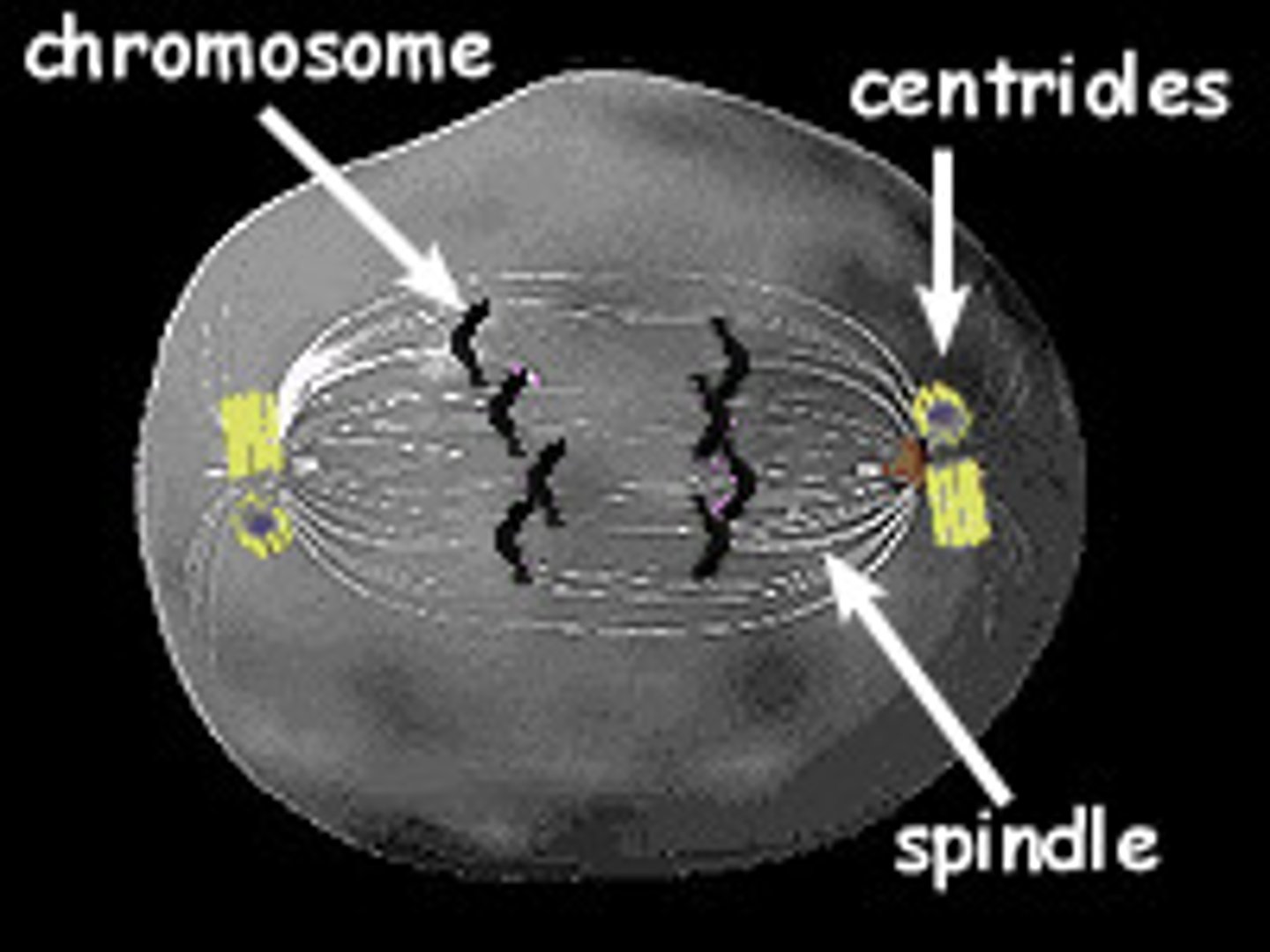
Centrioles
Structure in an animal cell that helps to organize cell division
Flagella
whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
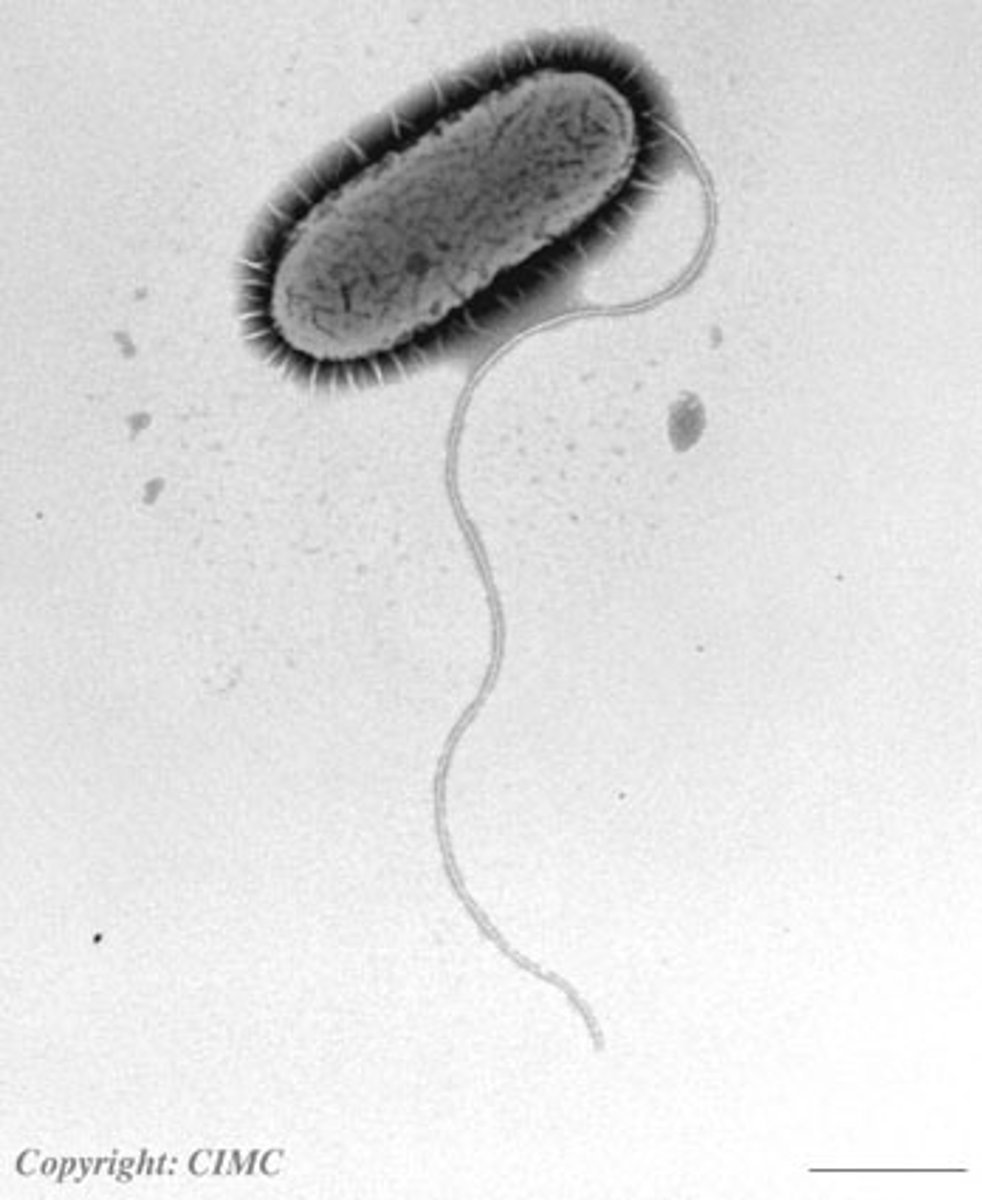
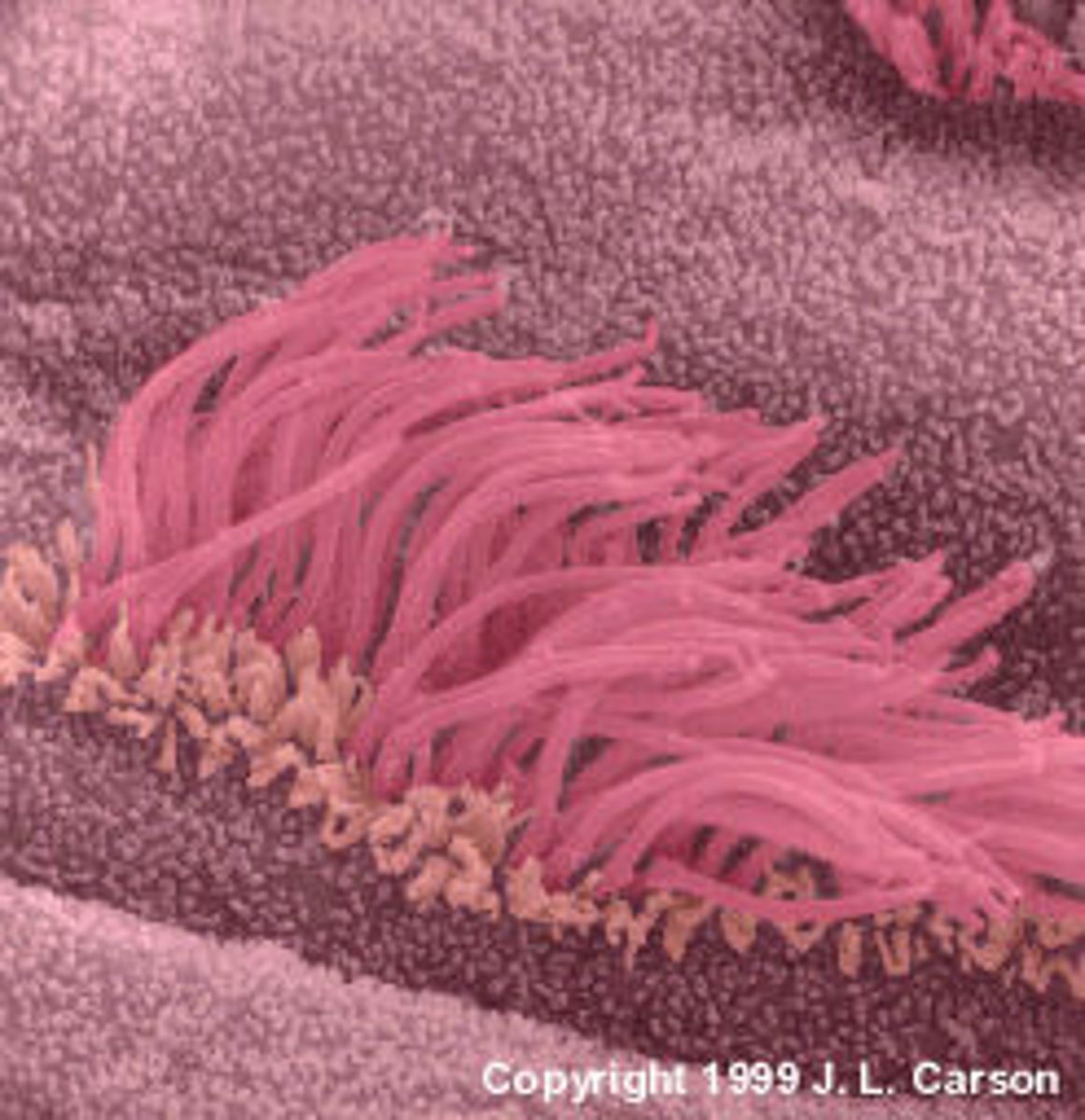
Cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion
Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
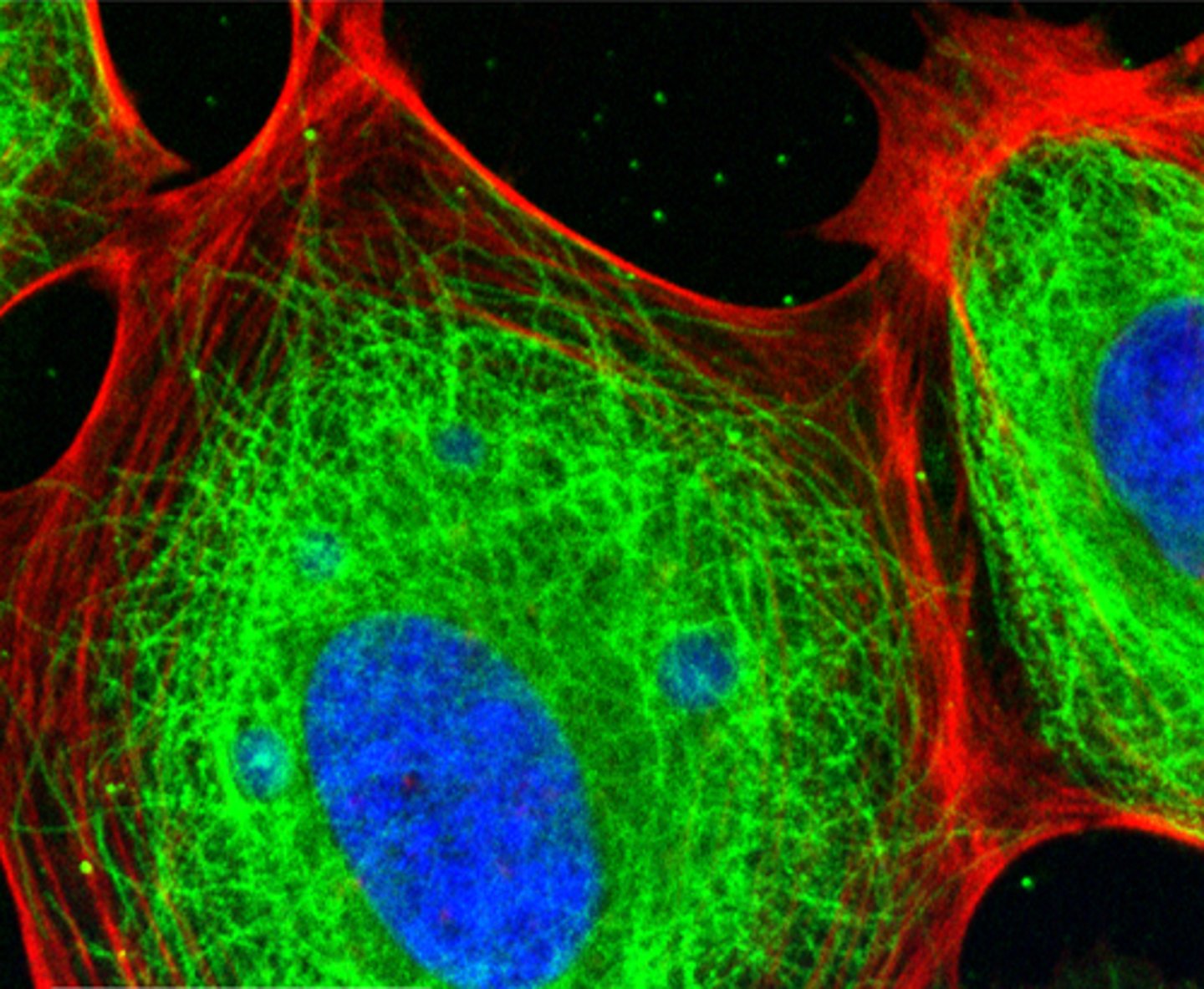
Cytoskeleton
A network of long protein strands in the cytosol that helps support the cell
Transmission electron microscope
an electron microscope that produces two-dimensional images.
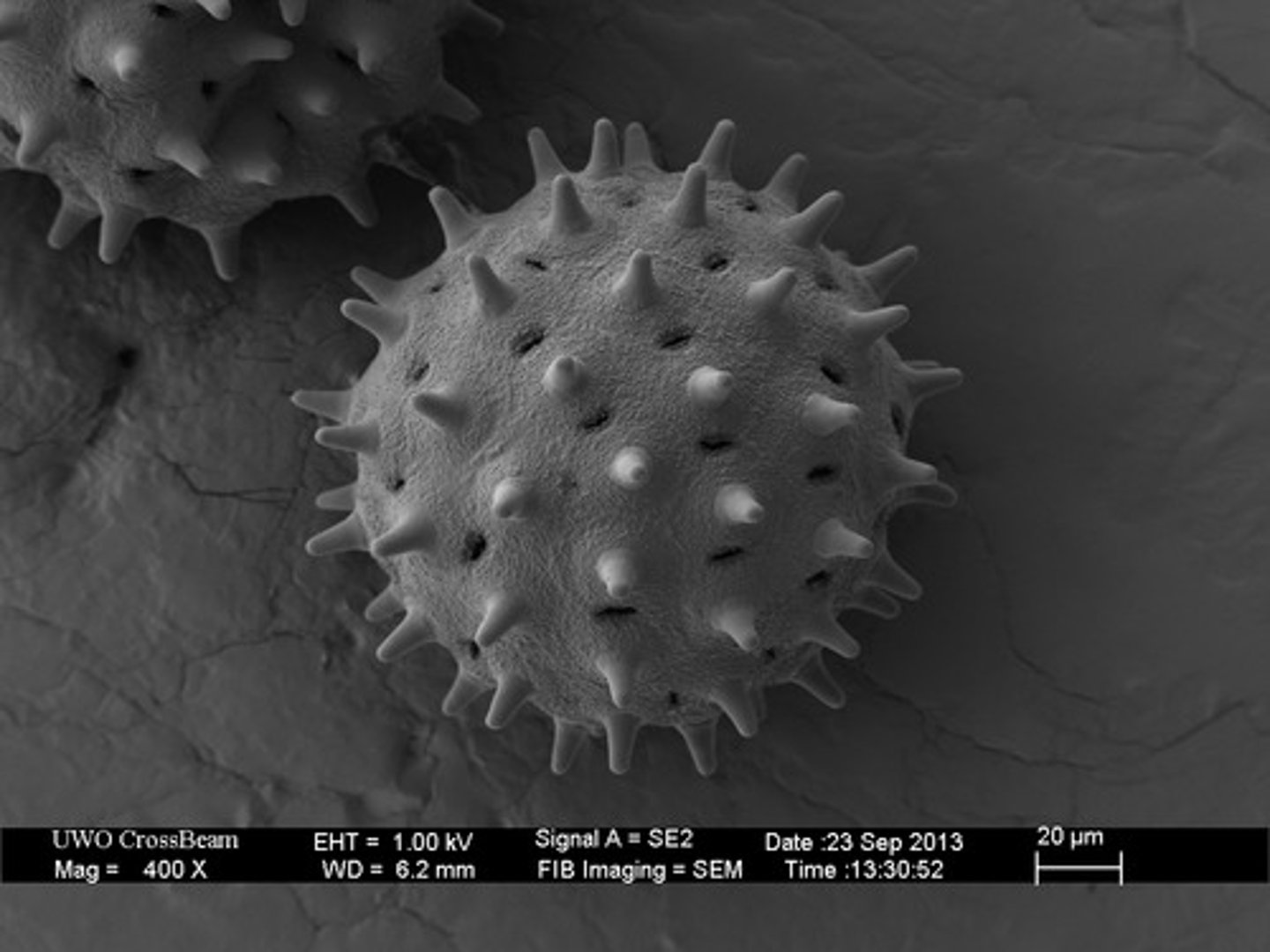
Scanning electron microscope
an electron microscope that generates a three-dimensional image.

Differential staining
Using specific stains to distinguish different types of cell
Magnification
The increase of an object's apparent size
Resolution
the shortest distance between two points on a specimen that can still be distinguished by the observer or camera system as separate entities
Eyepiece Graticule
a glass disc fitted into the eyepiece of the microscope. The disc is marked with a fine scale from 0 to 100.
Stage Micrometer
a microscope slide with a finely divided scale marked on the surface. The scale is of a known true length and is used for calibration of optical systems with eyepiece graticule patterns
Vesicles
small membrane sacs that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
Microfilaments
Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell
Microtubules
Thick hollow tubes that make up the cilia, flagella, and spindle fibers.
Intermediate Fibres
Provide mechanical strength and help maintain cell integrity.
Vacuoles
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
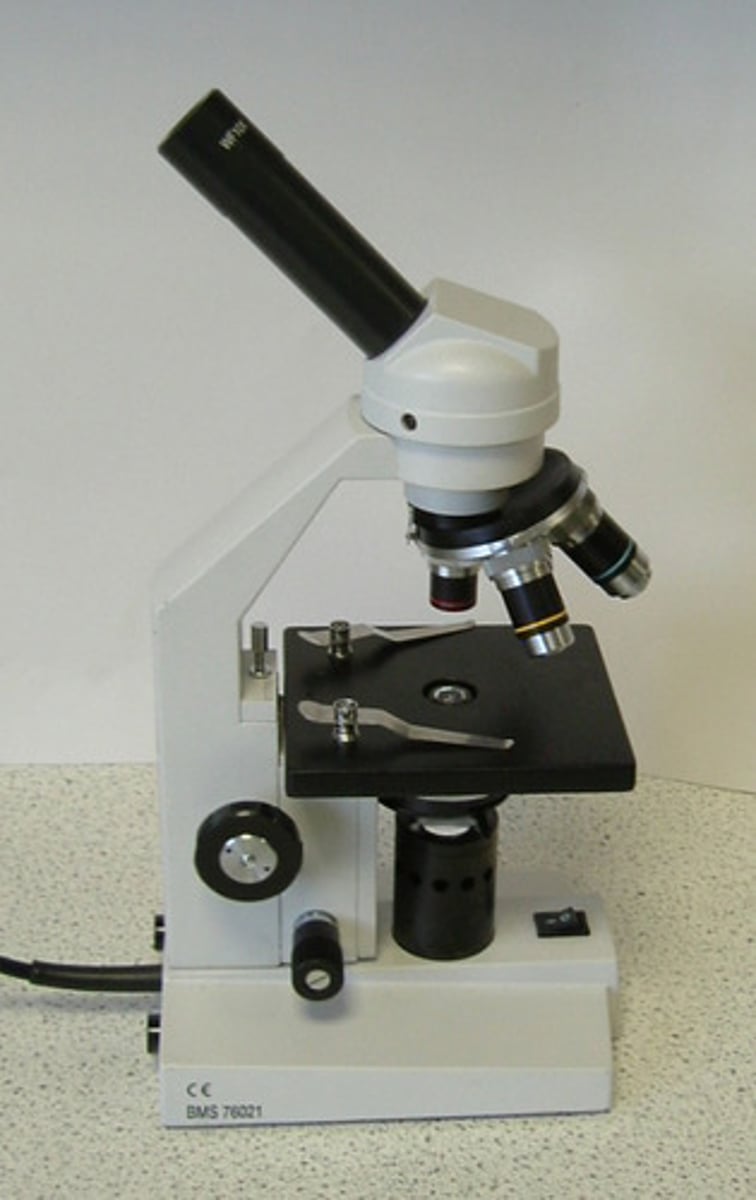
Light Microscope
Basic microscope that uses light and mirrors to magnify small objects.

Counterstain
A stain used to dye unstained cells a contrasting color in a differential stain
Safranin, Safranin, Methylene blue
Artefacts
Things you see down a microscope that isn't part of the cell eg. air bubbles, finger prints, dust
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
Chromatin
Clusters of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus of a cell
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
Cristae
series of inner membranes in mitochondria where cell respiration occurs

Matrix
Innermost compartment of the mitochondrion
Mitochondrial (mt)DNA
DNA located in mitochondria